1. Introduction
The original generation robots are a kind of remote control operator, while the second generation robots can achieve the purpose of automatically completing certain operations according to the program prepared in advance. The current generation robots are more intelligent. They can use various sensors to capture information and then analyze it through intelligent technology to achieve the expected autonomous action. A current robot is generally composed of hardware and software. The hardware of the robot is an integration of machinery and electronics, including the body of the robot, as well as the components of the control system. Software refers to the operating system of the robot and various application packages. With the continuous updating and iteration of software types and functions, requirements for hardware are becoming stricter and stricter. Nowadays, robots become more and more intelligent, especially medical surgical robots. This paper mainly studies the effective solutions to the limitations of surgical robots, including the application of current artificial intelligence technology in some specific medical fields. This paper can help understand how artificial intelligence technology can solve the limitations of surgical robots from both hardware and software aspects, the problems that still exist today, as well as the future development and ethical issues that people are concerned about.
2. Hardware: the development of surgical robots
Since the 1960s and 1970s, the design and control of general-purpose robotic arms were studied, and in the following two decades, robotics was developed to perform simple tasks on upper production lines. As robotics continued to evolve, more applications in new areas appeared in the 1990s, particularly in the health care and service sectors as well as in defense [1]. Robotics development is analyzed through the range of hardware and software applications of robots. Firstly, hardware makes up the body of the robot. For example, most robotic vehicles and robotic dogs are now relatively mature in technology, but humanoid machines are not yet flexible enough. They have rigid movements and a high failure rate when performing their assigned tasks. However, robots like those developed by Boston Company have developed better and better body size, stiffness, flexibility, and perception. Moreover, they can already do many difficult actions. Different types of robots are now used in specific fields, such as search and rescue missions, service robots, and the health care industry.
2.1. Strengths of surgical robots
The surgical robot is a medical device mainly used for minimally invasive surgeries. Figure 1 shows researchers using a surgical robot, which can be seen as the surgeon driving the surgical robot through a computer console at a certain distance from the patient to perform the surgery. Laparoscopic surgery is an important transition from traditional open surgery to minimally invasive surgery, usually using traditional surgical instruments such as endoscopes, small tubes, and miniature cameras [2]. However, the freedom to use traditional surgical instruments is limited because most actuators are rigidly connected to axial handheld instruments, which makes some procedures difficult to perform, especially in narrow surgical areas and complex surgical settings [3,4]. Surgical robots can effectively help solve these difficulties. One of the most popular teleoperated robots, the da Vinci system, has four robotic arms, each consisting of an active part and a passive part, and only the active part can move during the operation. Out of the four robotic arms, three of them operate surgical instruments and the other is a kind of camera with two lenses, which can provide the surgeon with a clearer, three-dimensional vision and facilitate surgeons to observe the surgical area [3,5]. In addition, surgical robots can eliminate physiological tremors, thus reducing the probability of accidents and making surgery safer and more reliable [6].
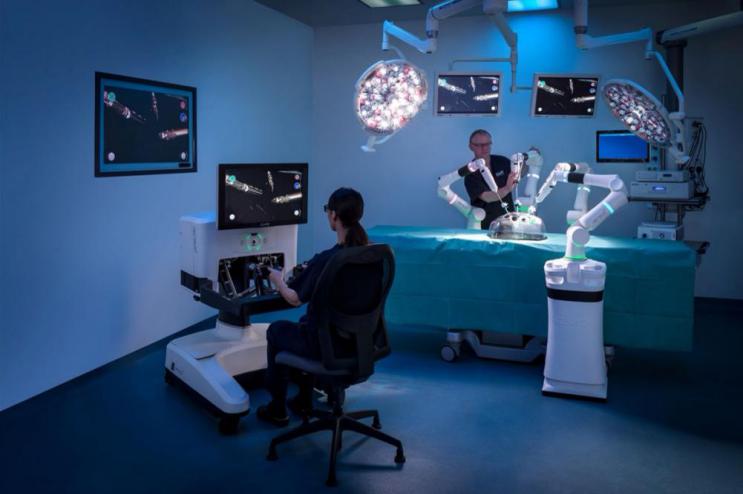
Figure 1. Robotic arms and the surgeon’s console [6].
2.2. Limitations of surgical robots
However, surgeons cannot perceive the magnitude of the force while performing surgery due to the difficulty of installing any electronic sensors on the robotic arm, which means that even small errors in operation can cause large damage to human tissue [7]. The surgical robot can also calculate the best target position by automatic positioning through system calculations, but there are still some problems that have failed to be taken into account [5]. Moreover, when the robot performs adaptive scene analysis, the operation time may be prolonged in order to avoid singularities, and the failure rate of the operation and the cost of the associated optical tracking system may increase as a result [8]. Although the surgical robot offers a great degree of convenience and efficiency, more research is needed to improve and increase its safety and reliability in order to get the most appropriate position for the surgical operation, which requires higher demands on the software.
3. Software: the development of intelligent medical robots
If hardware is the body of a robot, then the software is the robot's brain, controlling its behaviour. Many robots are autonomous or semi-autonomous. They simply perform actions according to a program and act according to the program design. They can perform repetitive movements but are not intelligent. It can be said that artificial intelligence gives robots the ability to think about problems, and robots are the outward expression of artificial intelligence. Intelligent robots are advanced robots that are capable of achieving predetermined goals independently and autonomously, using various sensors to obtain information about the environment. The expert system interprets the data from the sensors and enables inference, prediction, diagnosis, design, and control, increasing not only its safety but also its reliability. Its research areas include language learning and processing, knowledge representation, reasoning, machine learning, etc. It has been applied to intelligent control, expert systems, machine translation, aerospace applications and many other fields [9].
3.1. Strengths of intelligent medical robots
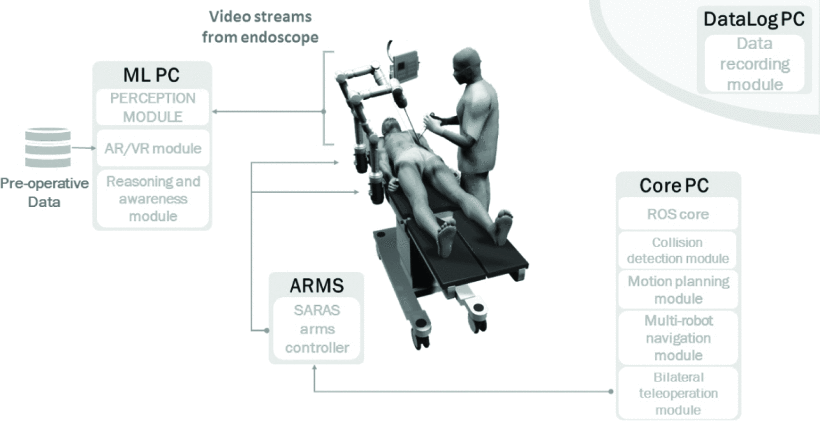
Since its introduction at the Conference on Machine Simulation Intelligence in 1956 and its rapid development, artificial intelligence has gradually been applied to the field of medicine, and in recent years it has played an increasingly important role in medical robotics, drug development, medical imaging, clinical assistance and treatment selection [10]. For minimally invasive surgery, as medical technology continues to advance, in addition to the da Vinci system, there are now robots that can be targeted to perform specific tasks, such as intelligent tissue-autonomous robots that are designed for soft tissue suturing. There are also autonomous robotic systems capable of achieving direct collaboration with surgeons. For instance, the Smart Autonomous Robotic Assistant Surgeon Project (SARAS) is capable of performing surgical operations that are normally performed by assistant surgeons [11]. It is able to process real-time data and compare it with actual surgical data through embedded specific surgical knowledge. By recognising and interpreting the surgeon's movements, it can predict the development of the operation. Figure 2 illustrates the SARAS Solar-Surgery platform architecture, which can be clearly seen with two autonomous robotic arms holding laparoscopic surgical instruments that can collaborate with the attending surgeon through voice commands, etc. The SARAS AI is able to receive, understand, and execute explicit requests, making decisions like humans and cooperating with the attending surgeon when necessary. The artificial intelligence integrates a perception module, a cognitive module, and a planning module, which allow it to reconstruct the surgical environment with sensor markers, identify possible anomalies, predict the development and needs of the surgeon's operation, and plan the appropriate trajectory for the decisions made by the surgical instruments through the cognitive module. The minimally invasive surgical system SARAS Solo-Surgery is able to autonomously understand current and future surgical situations and perform predefined operations at the right time and place.
Figure 2. Solo-Surgery platform architecture [11].
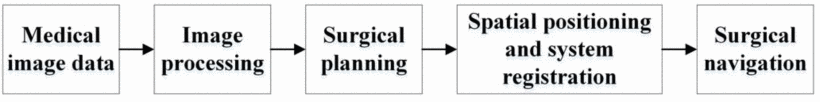
As mentioned earlier, the surgical robot can calculate the best position through the system, but this does not guarantee that this is the most appropriate position for the operation, and AI-guided surgery can better solve this problem. Surgeons usually need a long period of training and years of experience to be able to perform precise surgical operations. An AI-assisted surgical navigation system can build a dataset by collecting a large number of videos of experienced surgeons performing surgery and then converting the information about the surgical incisions in the scene into digital data. Figure 3 illustrates the general surgical navigation process, where, depending on the surgical situation before the surgeon performs the operation, the AI model presents the appropriate incision line as a reference, which can be safer than before and reduce the probability of accidents [12]. The integration of artificial intelligence technologies into health care continues to deepen, and the shortcomings and limitations of surgical robots are slowly being solved.
Figure 3. The procedure of general surgical navigation [10].
In addition to its evolving and significant role in minimally invasive surgery, artificial intelligence systems can be used to reduce common complications in balloon angioplasty applications [13]. Based on AI deep learning capabilities, researchers have attempted to investigate AI neurotechnology to decode the motor intent of an amputee's peripheral nerves through an AI agent, and have obtained satisfactory performance and high success rates through a series of tests [14]. With all these examples of applications and ongoing process research, it is easy to see that AI is not only being used more and more widely, but is also becoming more and more targeted, applying AI techniques and robotics to specific scenarios and practical needs.
3.2. Limitations of intelligent medical robots
However, this does not mean that the development of AI is smooth sailing. Along with its rapid development, AI is also facing many engineering ethical issues, particularly in the areas of privacy and surveillance, such as the opacity of AI systems and bias in decision-making systems and human-computer interaction [15]. In addition to ethical issues, the responsibilities and obligations of AI and robotics are also a concern, including the moral responsibility of AI, and the practical responsibility, which requires better laws to regulate and constrain its development [16].
In addition to this, AI technology continues to have limitations. Currently, the results of AI technology play an important role in many specific areas, including speech recognition, image recognition, etc., but functioning in the so-called individual zone is only part of the various areas of the human brain that perform intelligent work; it does not perform the full range of functions similar to the human brain. It has speech recognition and image recognition, but artificial intelligence cannot yet work in concert with functions such as self-control, self-awareness, and self-understanding. Currently, there are also a number of researchers who have proposed a number of ways to address the limitations of AI, for example, through the extension of AI models and the development of a super-intelligent model of brain function, by combining artificial life technologies and AI technologies with memory functions to build a brain intelligence model to extend current AI [8]. In the future, robotics and AI technology will continue to evolve and improve, becoming not only more efficient and intelligent, but also more safe and reliable.
4. Conclusion
Artificial intelligence technology and robots have been developed for many years, playing an increasingly important role in the medical and health field. With the continuous improvement of technology, more and more problems have been improved and solved. With the help of medical intelligent robots, doctors can make more accurate judgments. By providing doctors with clearer stereo vision and eliminating physiological tremors, surgical robots improve the safety and reliability of surgery, which not only reduce the burden of doctors, but also help patients recover faster. In particular, the emergence of artificial intelligence surgical navigation technology can help doctors find the most appropriate operation position more quickly by processing a large amount of collected data, videos and other information, and further improve the efficiency of surgery. In the future, artificial intelligence technology will continue to be used to assist doctors in disease diagnosis and surgery, with more expansion, becoming more intelligent, safe and effective. In addition, service robots and robots working in dangerous and harsh environments will also get greater development. The combination of artificial intelligence technology and robot technology will become more efficient and intelligent, realizing machines with both robot limbs and human intelligence, and creating a more intelligent world. At the same time, the issue of engineering ethics should also be paid attention to. When robots obtain corresponding rights, they should also have corresponding obligations and assume corresponding responsibilities.
References
[1]. Westervelt, E.R. Robot modeling and control. scholar.google.co.uk. Available: https://scholar.archive.org/work/55knin3xf5czvle3uis2qmemni/access/wayback/http://konku k.ac.kr/~cgkang/courses/robotics/courseMaterials/SpongBookReview.pdf.
[2]. Bergeles, C. and Yang, G. From Passive Tool Holders to Microsurgeons: Safer, Smaller, Smarter Surgical Robots. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 61(5), 1565-1576 (2014). doi:10.1109/TBME.2013.2293815. Available: https://From Passive Tool Holders to Microsurgeons: Safer, Smaller, Smarter Surgical Robots | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore.
[3]. Zahraee, A. H., Szewczyk, J. and Morel, G. Simulation for Optimal Design of Hand-Held Surgical Robots, presented at the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, MN. USA, Sept. 3-6, 2009.
[4]. Liu, Y., Zhao, Z., Chang, F. and Hu, S. An Anchor-Free Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Surgical Tool Detection in Robot-Assisted Surgery. IEEE Access 8, 78193-78201 (2020). doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989807. Available: https://An Anchor-Free Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Surgical Tool Detection in Robot-Assisted Surgery | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore.
[5]. Adhami, L. and Coste-Maniere, E. Positioning tele-operated surgical robots for collision-free optimal operation, presented at the proceedings 2002 IEEE International Conference on RA, DRD-WO, USA, Aug. 11-15, 2002.
[6]. Puntambekar, S.P. et al. Colorectal cancer surgery: by Cambridge Medical Robotics Versius Surgical Robot System—a single-institution study. Our experience. Journal of Robotic Surgery (2021). doi:10.1007/s11701-021-01282-9. Available: https://search-ebscohost-com.ez.xjtlu.edu.cn/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edssjs&AN=edssjs. AE09D220&site=eds-live&scope=site.
[7]. Lee, T. K., Kim, C. Y. and Lee, M. C. Modeling of torque transmission characteristics in surgical robot, presented at the 2009 ICCAS-SICE, Fukuoka, Japan, Aug. 18-21, 2009.
[8]. Dong, X., Li, J., Jiang, G., Zhou, Y., Zhang, H. and Liu, H. Scene Adaptivity Analysis for the Image-Guided Surgical Robots, presented at 2019 IEEE 7th ICCSNT , Dalian, CHN, Oct. 19-20, 2019, pp. 525-529.
[9]. Lu, H. Li, Y., Chen, M., Kim, H. and Serikawa, S. Brain Intelligence: Go beyond Artificial Intelligence. Mobile Networks and Appications, 368-375 (2018). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0932-8. Available: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11036-017-0932-8#citeas.
[10]. Liu, Y. and Tang, P. The Prospect for the Application of the Surgical Navigation System Based on Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Reality. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality (AIVR), 244-246 (2018). doi:10.1109/AIVR.2018.00056.
[11]. Oleari, E. et al. Enhancing Surgical Process Modeling for Artificial Intelligence development in robotics: the SARAS case study for Minimally Invasive Procedures. 2019 13th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT), 1-6 (2019). doi:10.1109/ISMICT.2019.8743931.
[12]. Igarashi, M. Artificial Intelligence-assisted system development in gastrointestinal endoscopy and surgery. 2020 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC), 1-3 (2020). doi:10.1109/OECC48412.2020.9273702.
[13]. Uğurlutan, R. and Ayaz, M. An Artificial Intelligence Solution For Reduce Complications at Tissue Expansion. 2019 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), 1-4 (2019). doi:10.1109/TIPTEKNO.2019.8894998.
[14]. Luu, D. K. et al. Artificial Intelligence Enables Real-Time and Intuitive Control of Prostheses via Nerve Interface, in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 69(10), 3051-3063 (2022). doi:10.1109/TBME.2022.3160618.
[15]. Müller, V. C. Ethics of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, in The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Summer 2021., E. N. Zalta, Ed. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University (2021). Accessed: Dec. 01, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2021/entries/ethics-ai/.
[16]. Ashrafian, H. Artificial Intelligence and Robot Responsibilities: Innovating Beyond Rights. Sci Eng Ethics 21(2), 317–326 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11948-014-9541-0.
Cite this article
Guo,J. (2023). The Development of Medical Robotics in the Context of Artificial Intelligence. Applied and Computational Engineering,8,1-6.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Westervelt, E.R. Robot modeling and control. scholar.google.co.uk. Available: https://scholar.archive.org/work/55knin3xf5czvle3uis2qmemni/access/wayback/http://konku k.ac.kr/~cgkang/courses/robotics/courseMaterials/SpongBookReview.pdf.
[2]. Bergeles, C. and Yang, G. From Passive Tool Holders to Microsurgeons: Safer, Smaller, Smarter Surgical Robots. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 61(5), 1565-1576 (2014). doi:10.1109/TBME.2013.2293815. Available: https://From Passive Tool Holders to Microsurgeons: Safer, Smaller, Smarter Surgical Robots | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore.
[3]. Zahraee, A. H., Szewczyk, J. and Morel, G. Simulation for Optimal Design of Hand-Held Surgical Robots, presented at the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, MN. USA, Sept. 3-6, 2009.
[4]. Liu, Y., Zhao, Z., Chang, F. and Hu, S. An Anchor-Free Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Surgical Tool Detection in Robot-Assisted Surgery. IEEE Access 8, 78193-78201 (2020). doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989807. Available: https://An Anchor-Free Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Surgical Tool Detection in Robot-Assisted Surgery | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore.
[5]. Adhami, L. and Coste-Maniere, E. Positioning tele-operated surgical robots for collision-free optimal operation, presented at the proceedings 2002 IEEE International Conference on RA, DRD-WO, USA, Aug. 11-15, 2002.
[6]. Puntambekar, S.P. et al. Colorectal cancer surgery: by Cambridge Medical Robotics Versius Surgical Robot System—a single-institution study. Our experience. Journal of Robotic Surgery (2021). doi:10.1007/s11701-021-01282-9. Available: https://search-ebscohost-com.ez.xjtlu.edu.cn/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edssjs&AN=edssjs. AE09D220&site=eds-live&scope=site.
[7]. Lee, T. K., Kim, C. Y. and Lee, M. C. Modeling of torque transmission characteristics in surgical robot, presented at the 2009 ICCAS-SICE, Fukuoka, Japan, Aug. 18-21, 2009.
[8]. Dong, X., Li, J., Jiang, G., Zhou, Y., Zhang, H. and Liu, H. Scene Adaptivity Analysis for the Image-Guided Surgical Robots, presented at 2019 IEEE 7th ICCSNT , Dalian, CHN, Oct. 19-20, 2019, pp. 525-529.
[9]. Lu, H. Li, Y., Chen, M., Kim, H. and Serikawa, S. Brain Intelligence: Go beyond Artificial Intelligence. Mobile Networks and Appications, 368-375 (2018). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-017-0932-8. Available: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11036-017-0932-8#citeas.
[10]. Liu, Y. and Tang, P. The Prospect for the Application of the Surgical Navigation System Based on Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Reality. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality (AIVR), 244-246 (2018). doi:10.1109/AIVR.2018.00056.
[11]. Oleari, E. et al. Enhancing Surgical Process Modeling for Artificial Intelligence development in robotics: the SARAS case study for Minimally Invasive Procedures. 2019 13th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT), 1-6 (2019). doi:10.1109/ISMICT.2019.8743931.
[12]. Igarashi, M. Artificial Intelligence-assisted system development in gastrointestinal endoscopy and surgery. 2020 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC), 1-3 (2020). doi:10.1109/OECC48412.2020.9273702.
[13]. Uğurlutan, R. and Ayaz, M. An Artificial Intelligence Solution For Reduce Complications at Tissue Expansion. 2019 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), 1-4 (2019). doi:10.1109/TIPTEKNO.2019.8894998.
[14]. Luu, D. K. et al. Artificial Intelligence Enables Real-Time and Intuitive Control of Prostheses via Nerve Interface, in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 69(10), 3051-3063 (2022). doi:10.1109/TBME.2022.3160618.
[15]. Müller, V. C. Ethics of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, in The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Summer 2021., E. N. Zalta, Ed. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University (2021). Accessed: Dec. 01, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2021/entries/ethics-ai/.
[16]. Ashrafian, H. Artificial Intelligence and Robot Responsibilities: Innovating Beyond Rights. Sci Eng Ethics 21(2), 317–326 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11948-014-9541-0.