1. Introduction
In recent decades, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Virtual Reality (VR) have seen rapid development and are revolutionizing various fields, including entertainment, training, manufacturing, and education [1, 2]. The amalgamation of AI and VR holds great potential to revolutionize the field of education through the provision of personalized and immersive learning experiences to students. Existing research has demonstrated the positive impact of VR technology on education and learning processes [3, 4], by enabling users to interact with virtual objects in real-time and engendering a first-person experience [5, 6]. This approach offers numerous benefits over traditional learning environments [7, 8], including enhanced motivation and engagement as well as the improved performance on learning activities [9-11]. Nevertheless, a significant obstacle to the creation of meaningful VR experiences is the need for extensive manual labor and the technical challenges involved in developing virtual environments.
To overcome this issue, the integration of Machine Learning (ML) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms into their Procedural Content Generation (PCG) methods for automatically generating new content that is tailored to educational applications has been studied. In the textual educational content area, previous research has explored the use of ML algorithms for generating educational content such as vocabulary contexts and quiz questions [12-14], as well as using crowdsourced rating method to identify nutritious content [15]. These studies demonstrate the potential of ML algorithms to automate the generation of nutritious educational content, which can be time-consuming and challenging for humans to undertake.
Researchers have begun exploring the amalgamation of ML algorithms and PCG techniques to create non-textual content, such as VR learning applications that offer interactive user experiences [16, 17]. RL-based methods have been found to be particularly effective, as they leverage simulation to train generative models without requiring prior collection of training data. The proposed approach involves the training of an RL agent on a simulation platform to generate new VR environments, thereby circumventing the issue of diminishing novelty effects over time [18, 19]. The resulting VR learning applications offer user experience (UX)-driven environments, which maintain user engagement and promote enhanced learning outcomes [20].
Despite the potential of ML algorithms, significant advancements are yet to be made in developing and refining these algorithms to produce high-quality and effective educational content and VR environments. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research in reinforcement AI learning content generation for VR applications in education, with each section focusing on a specific aspect of content generation for VR educational applications. The article investigates the procedure and effectiveness of these models through different evaluation metrics and further analyzes the outcomes. Finally, the paper concludes with an examination of the potential applications of these models in real-world education and highlights future research directions in this field.
2. Method
2.1. Overview of the PCG model
This paper will demonstrate a systematic review of previous research on automatic content generation for educational purposes, while explaining the complete ML pipeline step-by-step where to collect, label, and train data during the automatic generation and identification phases, and finally generate nutritious content using the trained data by running the trained model on a platform. The overview of the PCG model procedure can be found in Figure 1.
Collect dataset: obtain data for training, which can either download datasets available publicly or create a custom dataset for a specific purpose.
Dataset pre-processing: a consolidated format consumed by the data loader during model training which is key workflow for an efficient recommendation. The chosen dataset is pre-processed to obtain a subset of the features input for the model engineered by the project.
Model construction: collect data to implement models which can improve the content generating, teaching, and learning process during instruction for educational purpose, as well as keep constantly updated.
Educational data mining: a paradigm geared at creating models, tasks, procedures, and algorithms for examining data from educational contexts. The data that is analyzed is obtained from computer information systems such as nature language, information, and performance dataset. EDM looks for patterns, associations, and predictions to draw conclusions about performance and behavior, such as characterizing learners’ behaviors and achievements [8].
Content generation: computer-generated contents can furnish a methodical and comprehensive approach of creating qualitied contents that is tailored to specific learning objectives.
Model testing: testing approaches varies from different project goals, which include a set of constraints on good contexts, filters to operationalize contents, etc.
Embedded experiments: the aim is to test the effectiveness in helping students learn contents. Data collected from the tests and outcome measures will be analyzed using descriptive statistics.
Evaluation metrics: the model is analyzed and rated based on the criteria of reaching evaluation metrics of training performance results, such as human-authored examples or human ratings crowdsourced. The method includes control experiment, questionnaires, quizzes, etc.
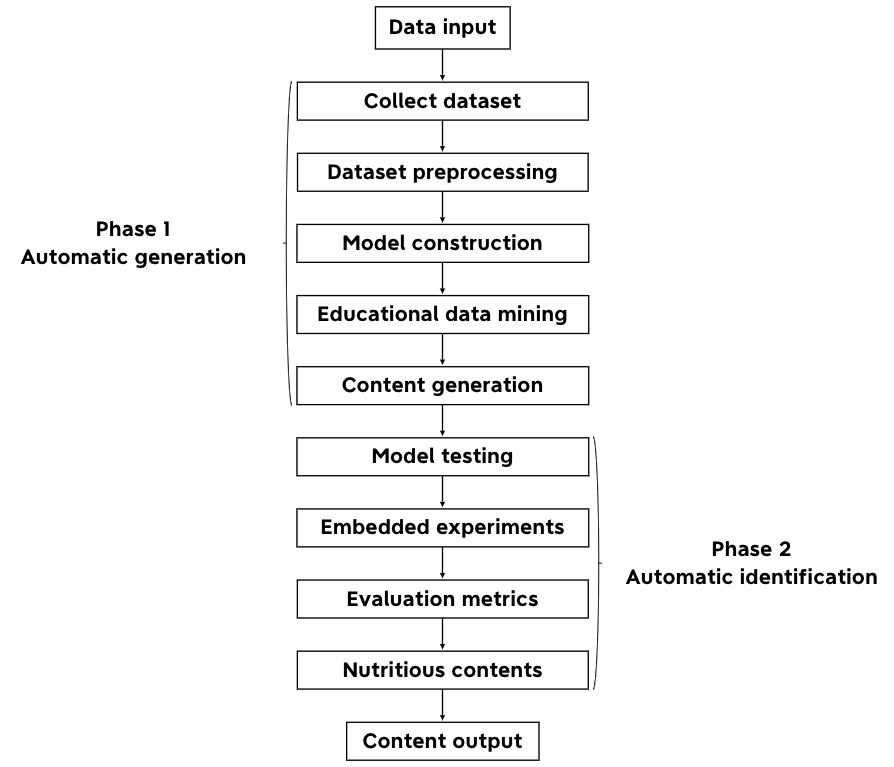
Figure 1. Overview of the PCG model procedure.
2.2. Datasets
This study examines various datasets used to train models, including publicly available datasets such as Google N-gram and Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) and custom datasets tailored for specific projects. The use of certain algorithms like reinforcement learning in creating 3D VR environments does not necessarily require initial datasets, as they can generate efficient representations of complex situations and tasks through high-dimensional sensory input and simulation [21].
There are three main datasets that requires to be maintained, namely natural language dataset, student information dataset, and student performance dataset [22]. The natural language dataset will be collected in advance, while students will be required to submit personal information and undergo a pretest to assess their learning level and cognitive ability before using the app. Their performance will be continually recorded during app usage to enable the automatic adjustment of the learning plan.
The explored datasets used in different studies includes the Google N-gram dataset, SQuAD, and custom dataset for the reading tutor project. For example, Liu et al. utilized the Google N-gram dataset to create contexts, while QG-Net was trained on the SQuAD dataset. Another study used a dataset consisting of a vocabulary word and a context that exemplifies its usage, rated by amateur raters based on its usefulness in reinforcing the word's meaning and comprehensibility to high school students.
2.3. Models
2.3.1. Student model. Student models employ data and mathematical modeling techniques to reflect students' learning abilities, preferences, and knowledge acquisition during the learning process. Such models can track the students' progress and predict their future learning performance, which can provide personalized feedback and more targeted assistance. The data collection process involves various means such as presenting a series of questions to the users, identifying words that the users frequently make mistakes or ask for help with, and monitoring changes in users' study levels and learning conditions over time [23]. The application of the student model can thus aid the software to adjust to changes in the learning difficulty and content.
One example of such applications is Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) technology used in intelligent tutoring systems. ASR technology allows users to operate the software using their voice, simplifying the learning process. Additionally, ASR plays a vital role in continuous learning and learning assessment by allowing users to practice pronunciation and conversation, providing immediate feedback on accuracy, and creating student models to evaluate learning proficiency and performance. Mostow et al. identified three areas of knowledge necessary to support the ASR engine: the acoustic model, the pronunciation lexicon, and the language model [24].
2.3.2. Pedagogical model. Pedagogical models refer to mechanisms that facilitate teaching and learning by adjusting the method of instruction based on students' proficiency and content difficulty. One such model is the Automatic Vocabulary Example Rater (AVER), which utilizes machine learning algorithms to score unfamiliar contexts for unknown words. AVER employs training and test data in the form of target vocabulary words, example contexts, and human ratings of their usefulness. AVER uses linear regression and logistic regression to rate contexts automatically for a given target word, enabling the selection of effective learning contexts. Another model is the Diagnostic Question Generator (DQGen), which generates cloze questions for diagnostic assessments of a child's comprehension of a given text. DQGen generates distractors that test different aspects of comprehension, including syntax, semantics, and inter-sentential processing. Wei et al. utilized natural language processing tools and question templates to generate questions, which were subsequently utilized to model and score children's self-questioning responses. The language model outperformed the trigram model in distinguishing complete and incomplete questions from irrelevant speech and silence.
2.3.3. RL-based PCG model for VR application. Lopez et al. have recently presented a novel approach towards the creation of immersive virtual reality (VR) learning environments utilizing deep reinforcement learning (RL) techniques. Their proposed method holds significant implications for the development of personalized and adaptive systems in VR learning applications. Reinforcement Learning is defined as a Markov Decision Process where an RL agent interacts with a simulation environment through sensory inputs to determine actions that maximize long-term rewards. Unlike supervised machine learning algorithms, RL methods do not require a training dataset and can handle complex scenarios and tasks via simulation environments [25, 26]. The suggested approach has the potential to facilitate experiential learning and maintain user engagement in VR learning applications. The resulting 3D virtual environments are customized to individual preferences and can be utilized across various interfaces, including VR headsets, smartphones, and computers, to augment user interactions with virtual environments.
3. Application and discussion
3.1. PCG based on RL
The integration of PCG and ML techniques is investigated by researchers for the automated creation of educational VR content. This approach shows great potential for producing personalized and adaptive educational environments in various domains including education. Given the importance of engagement and experiential learning in contemporary human-computer interaction (HCI) design, PCG can play a crucial role in generating effective and meaningful content. RL has been employed to personalize narrative-centered applications using affective and cognitive modeling, while also generating new VR educational environments that can be adjusted in real-time [27]. Additionally, the use of computational formalism based on multi-armed bandits and Long-Short Term Memory Networks approaches have been proposed to generate new training scenarios for the Army [28].
Cunningham et al. proposed a Deep RL approach towards procedural PCG to automatically generate multiple interconnected VR environments for personalized learning [29]. RL approaches to PCG offer advantages over supervised learning methods, as they do not require training data. This work significantly contributes to the advancement of RL-based PCG by showcasing the capability to produce diverse contexts for teaching the same fundamental concept. A case study is presented to demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed RL-based PCG approach using probability distributions within virtual environments. The proposed method holds potential in enabling the automatic creation of a series of virtual environments linked by a shared concept or theme.
3.2. PCG in intelligent tutoring system
The field of AI has seen increasing interest in developing applications that enhance the skills of users through engaging them in real-world learning environments by leveraging ML and AI to tailor training based on the learning needs, goals, and preferences of learners. One example of this is a firefighting training application that uses PCG to generate scenarios that reflect different levels of skill required [30]. Another application is a PCG-based learning tool for teaching fractional arithmetic, which creates multiple levels within the application to improve engagement and learning outcomes [31]. Similarly, a PCG approach with gamification was used to enhance students' engagement in math learning [32].
Recent studies have proposed PCG frameworks based on genetic algorithms and Support Vector Machines, which generate educational game content based on desired learning objectives and individual preferences [33, 34]. Furthermore, the planning of tutorials constitutes a critical element of adaptive training systems that employ reinforcement learning techniques to provide dynamically customized learning experiences based on the Interactive, Constructive, Active, Passive framework for cognitive engagement [35]. The policies that performed the best were those that maximized learning gains by utilizing an adaptive fading technique. As learners progressed through the training course, they were provided with less remedial instruction, which was less cognitively demanding. This data-driven approach to tutorial planning offers the potential for deeply adaptive training experiences by continually refining policies based on learners' individual needs and responses.
3.3. Future directions on VR educational content creation
This article presents a discussion on the potential of utilizing AI-based learning to enhance the efficacy of virtual reality (VR) content creation and suggests directions for further research. Acknowledging the nascent stage of the current work, the article highlights the need for testing in educational settings. Firstly, the prior work concentrating on generating multiple virtual environments for a simulated manufacturing system to impart fundamental pedagogical concepts needs to be extended. Subsequently, future research should focus on generating various immersive VR learning environments for both manufacturing and service systems, incorporating a diverse array of variables and constraints to facilitate personalized and adaptive learning applications and maintain students’ engagement and motivation over time [36, 37]. Secondly, the article notes that creating content in Unity3D for VR entails a time-consuming and steep learning curve. Thus, future work should seek an approach for content creation that can be easily and rapidly implemented without requiring programming expertise, making it affordable for educators to adopt and implement in their curriculum. Additionally, the study would have been improved by a larger sample size, and future research should evaluate the effect of RL-based instructional policies within a run-time virtual learning environment. Furthermore, extending RL-based policies to support remedial coaching interventions that target human-performance dimensions is an important next step.
Figure 2 shows the software architecture and user flow for implementing the proposed Deep RL approach to PCG for creating VR learning environments with multiple contexts linked by an overarching theme. The approach utilizes the Unity real-time creation engine in combination with ML-Agents SDK to implement the RL algorithm policy that maximizes the expected reward for generating optimal policies. The user interacts with the VR learning environment through an application hosted in Unity, which communicates defined data, including language, image, video, 3D scene, etc. to the ML-Agents platform to determine the appropriate environment to be generated and pass this information back to Unity to realize. The action and state correspond to content generation decisions and the provided parameters in the PCG context.
The proposed approach can dynamically accept state and reward from the user and system that dictates certain environments with different contexts and constraints the agent should generate and build. It addresses the complexity of visual, physical, and cognitive factors in VR learning environments and provides a foundation for future technology roadmap that may enable PCG in educational settings to achieve more personalized and automatic systems capable of exploration, prediction, decision-making, and self-evolution. The proposed approach has been validated through simulations to meet the required parameters for building safe, robust, and comprehensible AI platforms beyond the generative AI phase.
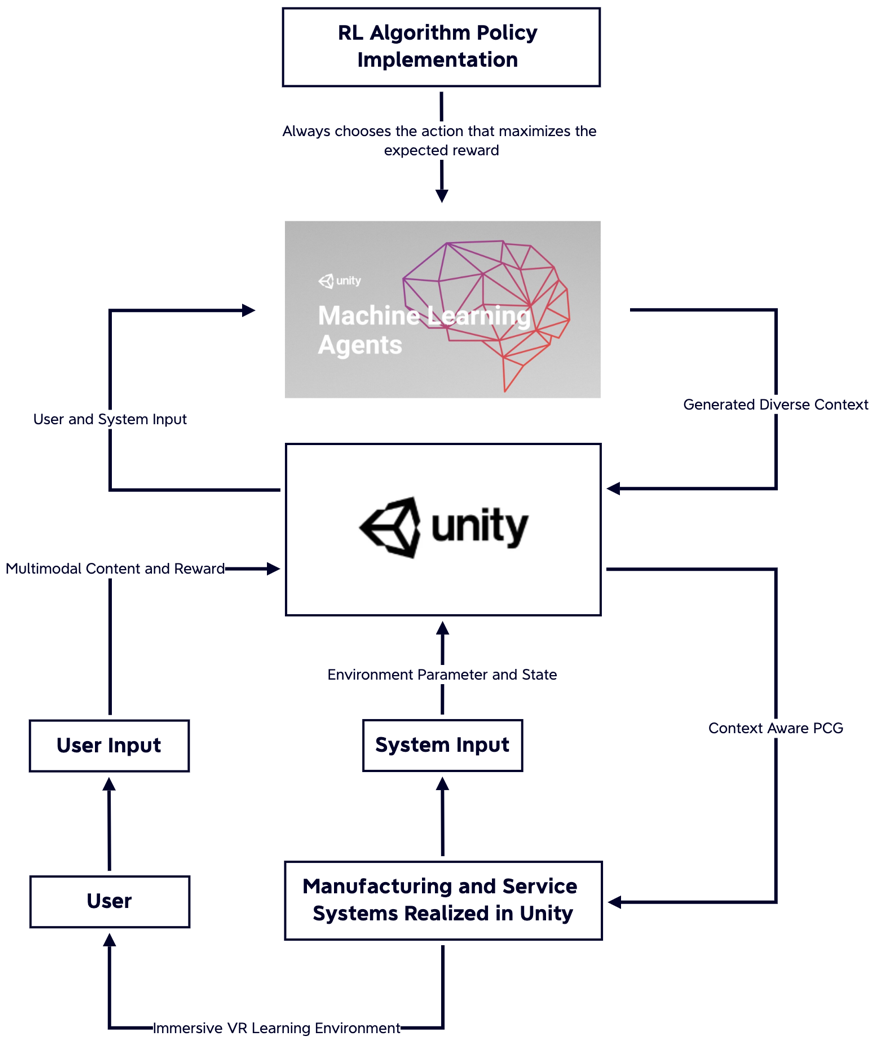
Figure 2. Software architecture and user flow for proposed PCG RL approach.
4. Conclusion
This systematic review aims to comprehensively evaluate the state of research on RL-based PCG for VR educational applications. The review identifies the potential of PCG methods to reduce resource requirements for VR content generation and provide personalized content using ML. RL-based approaches can learn to generate virtual environments in multiple personalized contexts connected by a common theme without requiring a dataset for training compared to PCG approaches. However, the review highlights the need for future studies to demonstrate the capability of the proposed deep RL-based PCG method in generating a diverse range of high-quality contexts to teach the underlying pedagogical concept by using less parameterized representations to enhance generalizability for VR applications.
The review suggests that future work should seek to develop easy, rapid, and affordable approaches for educational content creation that can be implemented into curriculum without usability issues. Additionally, the impact of this approach on personalization should be studied in run-time virtual learning environments to evaluate its impact on motivation and learning outcomes of learners.
References
[1]. Guttentag D A 2010 Virtual reality: Applications and implications for tourism Tourism management 31(5) 637-651
[2]. Choi S Jung K & Noh S D 2015 Virtual reality applications in manufacturing industries: Past research, present findings, and future directions. Concurrent Engineering 23(1) 40-63
[3]. Jensen L Konradsen F 2018 A review of the use of virtual reality head-mounted displays in education and training Education and Information Technologies 23 1515-1529
[4]. Kavanagh S Luxton-Reilly A Wuensche B Plimmer B 2017 A systematic review of virtual reality in education Themes in Science and Technology Education 10(2) 85-119
[5]. Dickey M D 2005 Brave new (interactive) worlds: A review of the design affordances and constraints of two 3D virtual worlds as interactive learning environments Interactive learning environments 13(1-2) 121-137
[6]. Dawley L Dede C 2014 Situated learning in virtual worlds and immersive simulations Handbook of research on educational communications and technology 723-734
[7]. Çaliskan O 2011 Virtual field trips in education of earth and environmental sciences Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 15 3239-3243
[8]. Barata P N A et al 2015 Consolidating learning in power systems: Virtual reality applied to the study of the operation of electric power transformers IEEE Transactions on Education 58(4) 255-261
[9]. Witmer B G Singer M J 1998 Measuring presence in virtual environments: A presence questionnaire Presence 7(3) 225-240
[10]. Winn W et al 2002 When does immersion in a virtual environment help students construct understanding In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Learning Sciences, ICLS Vol. 206 pp. 497-503
[11]. Alhalabi W 2016 Virtual reality systems enhance students’ achievements in engineering education Behaviour & Information Technology,35(11) 919-925
[12]. Liu L et al 2009 Automated Generation of Example Contexts for Helping Children Learn Vocabulary In International Workshop on Speech and Language Technology in Education
[13]. Chen W Mostow J 2011 Using Automatic Question Generation to Evaluate Questions Generated by Children In 2011 AAAI Fall Symposium Series
[14]. Mostow J et al 2017 Developing, evaluating, and refining an automatic generator of diagnostic multiple choice cloze questions to assess children's comprehension while reading. Natural Language Engineering 23(2) 245-294
[15]. Mostow J et al 2015 Automatic Identification of Nutritious Contexts for Learning Vocabulary Words. International Educational Data Mining Society
[16]. Lopez C E et al 2019 Reinforcement learning content generation for virtual reality applications. In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference Vol. 59179 p V001T02A009 American Society of Mechanical Engineers
[17]. López C E et al 2020 Deep reinforcement learning for procedural content generation of 3d virtual environments Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 20(5)
[18]. Tsaramirsis G et al 2016 Towards simulation of the classroom learning experience: Virtual reality approach In 2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom) pp 1343-1346 IEEE
[19]. Akçayır M et al 2017 Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature Educational research review 20 1-11
[20]. Mikropoulos T A et al 2011 Educational virtual environments: A ten-year review of empirical research (1999–2009) Computers & education 56(3) 769-780
[21]. Arulkumaran K et al 2017 Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 34(6) 26-38
[22]. Mostow J Beck J 2006 Some useful tactics to modify, map and mine data from intelligent tutors. Natural Language Engineering 12(2) 195-208
[23]. Beck J E et al 2008 Does help help? Introducing the Bayesian Evaluation and Assessment methodology. In Intelligent Tutoring Systems: 9th International Conference, ITS 2008, Montreal Canada June 23-27 2008 Proceedings 9 pp. 383-394 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
[24]. Mostow J et al 1999 Giving help and praise in a reading tutor with imperfect listening—because automated speech recognition means never being able to say you're certain CALICO journal, 407-424
[25]. Kaelbling L P et al 1996 Reinforcement learning: A survey. Journal of artificial intelligence research 4 237-285
[26]. Xu X et al 2014 Reinforcement learning algorithms with function approximation: Recent advances and applications. Information sciences 261 1-31
[27]. Wang, P et al 2017 Interactive Narrative Personalization with Deep Reinforcement Learning In IJCAI pp 3852-3858
[28]. Rowe J et al 2018 Toward automated scenario generation with deep reinforcement learning in gift In Proceedings of the Sixth Annual GIFT User Symposium pp 65-74
[29]. Cunningham J et al 2020 Multi-context generation in virtual reality environments using deep reinforcement learning In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference Vol 83983 p V009T09A072 American Society of Mechanical Engineers
[30]. Hullett K Mateas M 2009 Scenario generation for emergency rescue training games. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Foundations of Digital Games pp 99-106
[31]. Smith A M et al 2012 A case study of expressively constrainable level design automation tools for a puzzle game. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games pp 156-163
[32]. Rodrigues L et al 201 A math educacional computer game using procedural content generation In Brazilian Symposium on Computers in Education (Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação-SBIE) Vol 28 No 1 p 756
[33]. Hooshyar D et al 2018 A procedural content generation-based framework for educational games: Toward a tailored data-driven game for developing early English reading skills Journal of Educational Computing Research 56(2) 293-310
[34]. Hooshyar D et al 2018 A data‐driven procedural‐content‐generation approach for educational games Journal of Computer Assisted Learning 34(6) 731-739
[35]. Spain R et al 2022 A reinforcement learning approach to adaptive remediation in online training The Journal of Defense Modeling and Simulation 19(2) 173-193
[36]. Corno L Mandinach E B 1983 The role of cognitive engagement in classroom learning and motivation. Educational psychologist 18(2) 88-108
[37]. Chao T et al 2016 Using digital resources for motivation and engagement in learning mathematics: Reflections from teachers and students Digital Experiences in Mathematics Education 2 253-277
Cite this article
Wang,Y. (2023). Procedural content generation for VR educational applications: The investigation of AI-based approaches for improving learning experience. Applied and Computational Engineering,17,23-31.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Guttentag D A 2010 Virtual reality: Applications and implications for tourism Tourism management 31(5) 637-651
[2]. Choi S Jung K & Noh S D 2015 Virtual reality applications in manufacturing industries: Past research, present findings, and future directions. Concurrent Engineering 23(1) 40-63
[3]. Jensen L Konradsen F 2018 A review of the use of virtual reality head-mounted displays in education and training Education and Information Technologies 23 1515-1529
[4]. Kavanagh S Luxton-Reilly A Wuensche B Plimmer B 2017 A systematic review of virtual reality in education Themes in Science and Technology Education 10(2) 85-119
[5]. Dickey M D 2005 Brave new (interactive) worlds: A review of the design affordances and constraints of two 3D virtual worlds as interactive learning environments Interactive learning environments 13(1-2) 121-137
[6]. Dawley L Dede C 2014 Situated learning in virtual worlds and immersive simulations Handbook of research on educational communications and technology 723-734
[7]. Çaliskan O 2011 Virtual field trips in education of earth and environmental sciences Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 15 3239-3243
[8]. Barata P N A et al 2015 Consolidating learning in power systems: Virtual reality applied to the study of the operation of electric power transformers IEEE Transactions on Education 58(4) 255-261
[9]. Witmer B G Singer M J 1998 Measuring presence in virtual environments: A presence questionnaire Presence 7(3) 225-240
[10]. Winn W et al 2002 When does immersion in a virtual environment help students construct understanding In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Learning Sciences, ICLS Vol. 206 pp. 497-503
[11]. Alhalabi W 2016 Virtual reality systems enhance students’ achievements in engineering education Behaviour & Information Technology,35(11) 919-925
[12]. Liu L et al 2009 Automated Generation of Example Contexts for Helping Children Learn Vocabulary In International Workshop on Speech and Language Technology in Education
[13]. Chen W Mostow J 2011 Using Automatic Question Generation to Evaluate Questions Generated by Children In 2011 AAAI Fall Symposium Series
[14]. Mostow J et al 2017 Developing, evaluating, and refining an automatic generator of diagnostic multiple choice cloze questions to assess children's comprehension while reading. Natural Language Engineering 23(2) 245-294
[15]. Mostow J et al 2015 Automatic Identification of Nutritious Contexts for Learning Vocabulary Words. International Educational Data Mining Society
[16]. Lopez C E et al 2019 Reinforcement learning content generation for virtual reality applications. In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference Vol. 59179 p V001T02A009 American Society of Mechanical Engineers
[17]. López C E et al 2020 Deep reinforcement learning for procedural content generation of 3d virtual environments Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 20(5)
[18]. Tsaramirsis G et al 2016 Towards simulation of the classroom learning experience: Virtual reality approach In 2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom) pp 1343-1346 IEEE
[19]. Akçayır M et al 2017 Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature Educational research review 20 1-11
[20]. Mikropoulos T A et al 2011 Educational virtual environments: A ten-year review of empirical research (1999–2009) Computers & education 56(3) 769-780
[21]. Arulkumaran K et al 2017 Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 34(6) 26-38
[22]. Mostow J Beck J 2006 Some useful tactics to modify, map and mine data from intelligent tutors. Natural Language Engineering 12(2) 195-208
[23]. Beck J E et al 2008 Does help help? Introducing the Bayesian Evaluation and Assessment methodology. In Intelligent Tutoring Systems: 9th International Conference, ITS 2008, Montreal Canada June 23-27 2008 Proceedings 9 pp. 383-394 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
[24]. Mostow J et al 1999 Giving help and praise in a reading tutor with imperfect listening—because automated speech recognition means never being able to say you're certain CALICO journal, 407-424
[25]. Kaelbling L P et al 1996 Reinforcement learning: A survey. Journal of artificial intelligence research 4 237-285
[26]. Xu X et al 2014 Reinforcement learning algorithms with function approximation: Recent advances and applications. Information sciences 261 1-31
[27]. Wang, P et al 2017 Interactive Narrative Personalization with Deep Reinforcement Learning In IJCAI pp 3852-3858
[28]. Rowe J et al 2018 Toward automated scenario generation with deep reinforcement learning in gift In Proceedings of the Sixth Annual GIFT User Symposium pp 65-74
[29]. Cunningham J et al 2020 Multi-context generation in virtual reality environments using deep reinforcement learning In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference Vol 83983 p V009T09A072 American Society of Mechanical Engineers
[30]. Hullett K Mateas M 2009 Scenario generation for emergency rescue training games. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Foundations of Digital Games pp 99-106
[31]. Smith A M et al 2012 A case study of expressively constrainable level design automation tools for a puzzle game. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games pp 156-163
[32]. Rodrigues L et al 201 A math educacional computer game using procedural content generation In Brazilian Symposium on Computers in Education (Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação-SBIE) Vol 28 No 1 p 756
[33]. Hooshyar D et al 2018 A procedural content generation-based framework for educational games: Toward a tailored data-driven game for developing early English reading skills Journal of Educational Computing Research 56(2) 293-310
[34]. Hooshyar D et al 2018 A data‐driven procedural‐content‐generation approach for educational games Journal of Computer Assisted Learning 34(6) 731-739
[35]. Spain R et al 2022 A reinforcement learning approach to adaptive remediation in online training The Journal of Defense Modeling and Simulation 19(2) 173-193
[36]. Corno L Mandinach E B 1983 The role of cognitive engagement in classroom learning and motivation. Educational psychologist 18(2) 88-108
[37]. Chao T et al 2016 Using digital resources for motivation and engagement in learning mathematics: Reflections from teachers and students Digital Experiences in Mathematics Education 2 253-277









