1. Introduction
Esports refers to organized video game competitions that serve as a non-traditional model of sport that has established itself as a commercialized entertainment enterprise and produced hundreds of millions of dollars in revenue, especially over the past five years [1]. Today, this emerging industry has fostered a diverse and unique business model that is able to generate commercial value through multiple revenue streams, and has attracted a large number of investors as a result. In the existing literature, scholars' exploration of the eSports industry tends to focus on the competitive nature of the sport, thus ignoring the deeper value of the eSports industry under the commercialization model. However, with the gradual transformation of eSports from a marginalized entertainment activity to a global mainstream industry, the study of its business model is particularly important.
This study focuses on the complex business model of the eSports industry, exploring through literature research how today's eSports industry realizes multiple incomes in terms of commercial value and attracts diverse audiences and large investments through innovative business models. Secondly, this study also explores the challenges faced by the industry, such as policy regulation and restrictions, market saturation, and their impact on the future development of the industry. By examining these aspects, this study can make useful recommendations for policymakers and business decision-makers in the industry to optimize their business models and operational strategies.
In addition, this study provides some predictions for the future development of the eSports industry, which is not only part of the global digital economy, but also a key player with strong market potential and prospects for sustained growth.
2. Overview of the Esports Industry
2.1. Market Size and Growth
E-Sports is generally regarded as a kind of sport, which is an intellectual confrontation between people with the help of an electronic device platform. E-Sports is essentially an extension of sports, extending physical confrontation sports to virtual intellectual confrontation sports [2]. Driven by the Internet, the global reach of eSports competitions has reached unprecedented levels. Tournaments are broadcast live to millions of viewers worldwide, creating a shared experience. eSports represents a transformative development in the field of competitive activities, offering new opportunities for participation and commercialization. Its rise has challenged traditional notions of sport and competition, marking a shift towards a more inclusive and technologically integrated approach to sport. As the industry continues to evolve, it may play a key role in shaping the future of global entertainment and sports culture.
Over the past decade, the eSports industry has not only become a popular entertainment option, but has also shown considerable economic growth globally. Especially in China, eSports has seen a significant surge in market size and user base, becoming an important part of the digital economy. From Figure 1, it can be seen that the size of China's eSports market has grown rapidly, from 53.22 billion yuan in 2016 to 88.7 billion yuan in 2018, an increase of 66.7 percent.
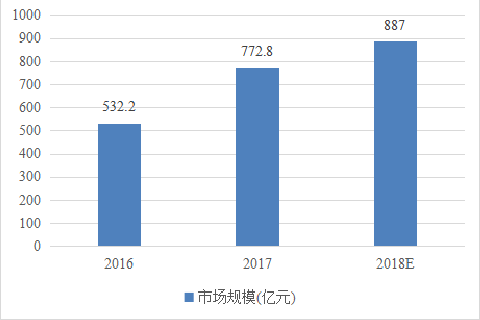
Figure 1: Chinese sports market size 2016 to 2018[2]
As shown in Figure 1, In 2019, China's eSports market size exceeded RMB 100 billion, a significant increase from the RMB 94 billion in 2018. Even in 2020, a year severely affected by the epidemic, the market size of the eSports industry reached 136.557 billion yuan. The user base of China's eSports reached 440 million people in 2019, growing to 490 million users by 2020. This shows the steady growth of the eSports market in terms of user size [3]. These figures illustrate not only the rapid popularity of eSports, but also its potential as a mainstream form of entertainment and a lucrative market segment.
The continued expansion of the eSports market can be attributed to several factors. Technological advancements and increasing popularity of digital platforms have enabled more viewers and gamers to participate from the comfort of their homes, further fueling the growth of the industry. Moreover, the inclusion of eSports in major cultural events such as the Asian Games has enhanced its legitimacy and visibility, attracting more participants and sponsors.
In addition, venture capital and corporate investment in eSports companies has enabled the scaling up of operations, the expansion of professional leagues, and the improvement of broadcasting and streaming facilities. These developments have not only improved the spectator experience, but also attracted a wider audience, thus further expanding the market.
In short, the eSports industry in China is in the process of experiencing significant growth in market size and user engagement. This trend is expected to continue as the industry becomes more integrated with the mainstream entertainment and sports industries, providing significant opportunities for investors and policymakers alike.
2.2. Key Market Players and Influence
2.2.1. Game Developers
The eSports industry is driven by a number of key market players, including game developers, live streaming platforms, professional teams and corporate sponsors. These players shape the current and future of the eSports market from their own perspectives.
Game developers are the cornerstone of the promotion of eSports, having released games suitable for competitive play and continuing to actively organize tournaments to promote their games in an official capacity, such as Riot Games' League of Legends and Valve's Dota 2 and CS:GO.The competitive nature of these games can better motivate the audience and players during the tournaments, attracting more people to play their games.
2.2.2. Streaming Platforms
Streaming platforms such as Twitch and YouTube provide viewing platforms for eSports, greatly expanding the audience base for eSports. These platforms make it easier to watch eSports events by streaming them live, and also provide professional players with opportunities to monetize through advertising and subscriptions[4].
2.2.3. Professional Teams and Players
Professional eSports teams and well-known players have an equally significant impact on the market. Professional teams such as FaZe Clan and Team Liquid not only have large fan bases around the world, but also enhance their market presence through sponsorships and brand partnerships.
2.2.4. Corporate Sponsors
The entry of corporate sponsors from non-eSports industries into eSports has brought a significant injection of capital into the industry. As mentioned in the study of Yuji Zhi, well-known brands such as Intel and Coca-Cola have not only increased the visibility of their own brands through sponsorship of eSports events but also promoted the commercialization of the eSports industry [5].
Overall, these market players in the eSports industry have contributed to the development of the eSports industry in their ways, and have gradually explored the market potential, making the eSports industry more professionalized and globalized. With the active participation and entry of these players, the future of the industry will see more opportunities and create more business value.
3. Analysis of E-Sports Business Model
3.1. Revenue Model
The increasing popularity and exponential growth of esports as a worldwide phenomenon has created a whole new industry with important implications for the different key players in the value chain [6]. For the sources of income of these participants, they can be categorized into direct and indirect income models.
3.1.1. Direct Revenue Model
First of all, direct income sources refer to those that are directly derived from the core activities of eSports. For example, when various large-scale eSports events are held, they can attract a large number of spectators, and the sale of on-site tickets is an important source of direct income. Tickets for these large-scale events are often sold out quickly after they go on sale [7], which demonstrates the high market demand and potential of the eSports industry.
Figure 2: WCG Global Reach [8]
As shown in Figure 2 is WCG, Word Cyber Games, a world e-sports competition. Founded in 2000 and organized by International Cyer Marketing (ICM) in Korea, the slogan of the WCG is "beyond the game". The WCG aims to promote human communication in the Internet age, and is also known as the eSports Olympics due to the wide range of countries and regions participating in the competition.
At the same time, during large tournaments, game companies often produce official team apparel, game-related peripherals, and so on, for each participating team. These items are usually sold at the tournament site or on the official website, and the excitement of the tournament attracts consumers to buy them, which in turn generates revenue for the organizers.
In addition, game developers will also sell all kinds of virtual goods directly in the game, such as game skins, special props to directly obtain income profits, this income method is extremely important for free-to-play games, because they can not be charged through the system of buyout, the direct sales of the game mall is often their main source of income.
3.1.2. Indirect Revenue Model
Indirect revenues from eSports activities can be categorized into brand sponsorship and advertising revenues. By sponsoring eSports teams or tournaments, companies can increase their brand exposure and attract fans of the teams to buy their products to show their support for the teams. Studies have shown that eSports provide a platform for brands to reach young consumers around the world, and sponsors can effectively increase their market reach in this way. [9]
The live broadcast of eSports matches on various streaming media platforms provides advertisers with the opportunity to display their product advertisements, which usually appear during the breaks of the live matches or in content related to the tournaments, and are able to attract the attention of millions of global viewers in a short period of several dozens of seconds, which greatly increases the exposure of their products. Zhanxin Wang's research points this out, and specifically emphasizes the high importance advertisers place on this type of advertising [10]. This type of advertisement placement can leave an impression on more viewers at a close cost.
3.2. Business Opportunities and Challenges
3.2.1. Business Opportunities
The global expansion of the eSports industry is one of the most notable features of its business model. With the popularization of the Internet and the advancement of digital media technology, eSports has successfully broken the geographical and physical constraints faced by traditional sports and achieved wide access to a global audience.
And such rapid globalization is mainly due to the following factors. First, the rapid development of the Internet has led to the development of streaming media platforms, which not only enable tournament organizers to broadcast live events globally in real time, but also make it possible for audiences around the world to watch the games at the same time through various devices and interact with each other regardless of geographic constraints. Second, in order to serve the global audience, many large-scale eSports events provide multilingual commentary and content services. This linguistic inclusiveness greatly increases the participation of viewers from non-native-speaking countries and generates different features brought by different languages and cultures. The inclusiveness and diversity of eSports as a cultural phenomenon attracts young people from all over the globe. Video games serve as a common interest and cultural bond that crosses national and cultural boundaries.
3.2.2. Risks and Challenges
According to He Pei Yi's research, it was found that the eSports industry is still facing certain challenges and changes [11]. First, the eSports industry remains in a grey area of policy and regulation in many countries. Although governments encourage the development of eSports on a macro level, there are a variety of restrictive issues in specific regulations and implementation, as well as unclear responsibilities and powers, all of which limit the development of the industry, and there is always uncertainty about policies and regulations.
Secondly, the market development ability of the e-sports industry needs to be further improved. At present, although the e-sports industry has diversified profit models, the actual profitability is still weak. More mature and perfect tournament organizers and more effective profit models are needed to support the healthy development of the industry. The market development ability of the eSports industry needs to be further improved. Currently, although the eSports industry has diversified profit models, the actual profitability is still weak. More mature and perfect tournament organizers and more effective profit models are needed to support the healthy development of the industry. Although eSports is extremely popular among young people, it still faces a low level of social acceptance at the broader social level. This not only limits its room for development, but also affects the introduction of potential investment and advertising revenue.
4. Future Developments and Recommendations
4.1. Future Trends
Nowadays, eSports has become a global phenomenon with evolving business models and markets. With the development of science and technology, the future eSports industry will also incorporate technological innovation and integration. For example, increasingly mature technologies such as VR and AR are expected to be more widely used in eSports to provide audiences with a more immersive viewing experience [12]. Meanwhile, eSports will continue to expand its international market, especially in emerging markets such as Asia and Africa, to attract more viewers and consumers to understand and join the field. With the formalization of eSports, related education and vocational training will become more systematic in order to cultivate more professionals.
4.2. Strategic Recommendations
Based on the current state of development and future trends of the eSports industry, the study has also come up with a number of constructive recommendations. First, more diversified business models need to be developed, and more kinds of profit channels can increase the stability of the industry's income. Improving social recognition and policy support are also important prerequisites to ensure the healthy development of the industry. By educating the public and promoting policy support, the social recognition of eSports can be improved, so that more people can accept eSports and participate in eSports. In addition, the establishment of a complete eSports industry chain, including vocational education, tournament organization, and player management, as well as the strengthening of market supervision, can also ensure the healthy development and sustainable growth of the industry.
In the face of future development, the eSports industry also needs to effectively manage potential risks. Enhance the health and psychological support for eSports players, including regular physical examinations and psychological counseling to prevent occupational diseases and psychological problems [13]. Also, bring better welfare policies for retired professional players to ensure their stable income after retirement.
5. Conclusion
The eSports industry is not only growing rapidly, but its mature business model has also created a rich source of income for market participants. Despite challenges such as unclear policies and regulations, the risk of market saturation and lack of social acceptance, eSports still demonstrates great market potential and the possibility of sustained growth.
This study mainly finds that the business model of the eSports industry is highly diversified, realizing commercial value through multiple revenue channels and attracting a wide range of viewers and investors. Its continuous global expansion also brings infinite possibilities for the industry's future development potential, while the uncertainty of policies and regulations, the intensification of market competition, and the enhancement of social acceptance are the key issues that need to be resolved in the process of eSports industry development.
Future research can continue to focus on the sustainable development strategies of the eSports industry and explore how to further expand the business model of eSports through technological innovation and market strategies. At the same time, researchers should also consider the impact of eSports on social culture and how to improve the positive social image and influence of eSports while promoting the development of the industry.
Through these conclusions and recommendations, this study hopes to provide practical see recommendations for business stakeholders in the eSports industry and support the continued growth and development of eSports as an emerging form of global entertainment.
References
[1]. Joey Gawrysiak, Rick Burton, Seth Jenny and Dylan Williams (2020). Using Esports Efficiently to Enhance and Extend Brand Perceptions – A Literature Review. Physical Culture and Sport. Studies and Research ,86(1),1 – 14. https://doi.org/10.2478/pcssr-2020-0008
[2]. Xu Tan. Business model and value assessment of e-sports companies[D]. Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2020.DOI:10.27307/d.cnki.gsjtu.2019.000820.
[3]. Wang zhanxin,Xie ruile. Research on the commercial value brought by e-sports industry--Taking the development of e-sports in China in 2020 as an example[J]. Marketing World,2021(30):17-18.
[4]. Lei Xi,Xia Siyong. Current Situation and Countermeasures on the Development of E-Sports Industry in China[J]. Journal of Beijing Sport University,2005(08):1033-1035.DOI:10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2005.08.009.
[5]. You Jizhi,Bute. Research on the development status and prospect of e-sports industry chain in China[J]. Journal of Jilin Sports Institute,2018,34(03):56-62.DOI:10.13720/j.cnki.22-1286.2018.03.011.
[6]. José Manuel Saiz-Alvarez (2021). Knowledge Management in the Esports Industry: Sustainability, Continuity, and Achievement of Competitive Results. Sustainability 2021, 13(19), 10890.https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910890
[7]. Chen X. Analysis of the relationship between e-sports business development and capital ecological operation[J]. Journal of Jiamusi Vocational College,2024,40(01):97-99.
[8]. Wu Yi. Research on the Current Situation and Countermeasures of the Development of China's E-Sports Industry [D]. Xi'an Sports Institute,2017.
[9]. Yang Yue. Research on e-sports and e-sports industry in the new era[J]. Sports Science,2018,38(04):8-21.DOI:10.16469/j.css.201804002.
[10]. Wang zhanxin,Xie ruile. Research on the commercial value brought by e-sports industry--Taking the development of e-sports in China in 2020 as an example[J]. Marketing World,2021(30):17-18.
[11]. He Peiyi. Research on the current situation and development of China's e-sports industry [D]. Shanghai International Studies University,2013.
[12]. Wang Feng. Reflections on the business model of e-sports in China[J]. Sports Culture Guide,2014(12):90-93.
[13]. LIU Yifei,TANG Xinghua. Research on the development of e-sports in China and its countermeasures[J]. Martial Arts Research,2020,5(12):150-153.DOI:10.13293/j.cnki.wskx.008746.
Cite this article
Sun,J. (2024). An Overview of Esports Business Model Research. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,105,7-13.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Joey Gawrysiak, Rick Burton, Seth Jenny and Dylan Williams (2020). Using Esports Efficiently to Enhance and Extend Brand Perceptions – A Literature Review. Physical Culture and Sport. Studies and Research ,86(1),1 – 14. https://doi.org/10.2478/pcssr-2020-0008
[2]. Xu Tan. Business model and value assessment of e-sports companies[D]. Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2020.DOI:10.27307/d.cnki.gsjtu.2019.000820.
[3]. Wang zhanxin,Xie ruile. Research on the commercial value brought by e-sports industry--Taking the development of e-sports in China in 2020 as an example[J]. Marketing World,2021(30):17-18.
[4]. Lei Xi,Xia Siyong. Current Situation and Countermeasures on the Development of E-Sports Industry in China[J]. Journal of Beijing Sport University,2005(08):1033-1035.DOI:10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2005.08.009.
[5]. You Jizhi,Bute. Research on the development status and prospect of e-sports industry chain in China[J]. Journal of Jilin Sports Institute,2018,34(03):56-62.DOI:10.13720/j.cnki.22-1286.2018.03.011.
[6]. José Manuel Saiz-Alvarez (2021). Knowledge Management in the Esports Industry: Sustainability, Continuity, and Achievement of Competitive Results. Sustainability 2021, 13(19), 10890.https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910890
[7]. Chen X. Analysis of the relationship between e-sports business development and capital ecological operation[J]. Journal of Jiamusi Vocational College,2024,40(01):97-99.
[8]. Wu Yi. Research on the Current Situation and Countermeasures of the Development of China's E-Sports Industry [D]. Xi'an Sports Institute,2017.
[9]. Yang Yue. Research on e-sports and e-sports industry in the new era[J]. Sports Science,2018,38(04):8-21.DOI:10.16469/j.css.201804002.
[10]. Wang zhanxin,Xie ruile. Research on the commercial value brought by e-sports industry--Taking the development of e-sports in China in 2020 as an example[J]. Marketing World,2021(30):17-18.
[11]. He Peiyi. Research on the current situation and development of China's e-sports industry [D]. Shanghai International Studies University,2013.
[12]. Wang Feng. Reflections on the business model of e-sports in China[J]. Sports Culture Guide,2014(12):90-93.
[13]. LIU Yifei,TANG Xinghua. Research on the development of e-sports in China and its countermeasures[J]. Martial Arts Research,2020,5(12):150-153.DOI:10.13293/j.cnki.wskx.008746.









