1. Introduction
Apple was founded in 1976 and quickly became one of the largest companies in the world. Over the years, Apple has been an integral part of the technology market. As a leading global technology company, Apple not only excels in technological innovation, but also attributes its success to clever marketing strategies. Since its founding in 1976, Apple has firmly established its leadership in the global technology industry with a series of innovative products such as Mac, iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. This article will first use Porter's Five Forces Model to analyze Apple's business status; then focus on the 4P marketing model (product, price, channel, promotion) framework to explore how Apple can maintain its market competitiveness and analyze the effectiveness of its specific strategic implementation; finally, suggestions are put forward for Apple to cope with future changes in the market environment and the rapid development of the technology industry.
2. Analysis of Apple's Business Status Based on Porter's Five Forces
Before discussing Apple's marketing strategy, it is necessary to analyze the market competition pressure faced by Apple through Porter's Five Forces Model. Porter's Five Forces Model includes competition within the industry, threat of potential entrants, threat of substitutes, bargaining power of suppliers and bargaining power of buyers. Through this analysis, we can better understand why Apple implements its specific marketing strategy.
2.1. Competition Within the Industry
In terms of competition within the industry, Apple faces pressure from multiple powerful competitors, such as technology giants such as Samsung, Huawei, and Xiaomi. These companies have seized market share by launching products with advanced technology but more competitive prices. Figure 1 below shows the market share of leading smartphone brands in Taiwan as of August 2023.
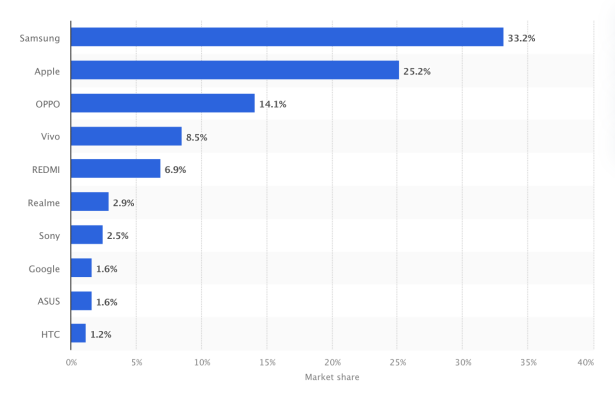
Figure 1: Market share of leading smartphone brands in Taiwan 2023 [1].
2.2. Threat of Potential Entrants
Although the entry barriers to the smartphone and consumer electronics markets are high, the threat of potential entrants still exists. With the reduction of technology costs and the market's thirst for innovation, emerging companies may enter the market through other strategies, bringing new competitive pressure.
2.3. Threat of Substitutes
For Apple, the threat of substitutes is mainly reflected in the rise of other technology products and services, such as wearable devices, smart home systems, and software services. These substitutes may weaken consumer demand for Apple's core products.
2.4. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Bargaining power of suppliers is another major challenge facing Apple. Although Apple has strong bargaining power over the supply chain due to its large scale, some key components still rely on a small number of suppliers, such as suppliers of semiconductor chips and high-end display screens. (Extended) If these suppliers raise prices or fail to deliver on time, Apple's production and cost control will be at risk.
2.5. Buyer Bargaining Power
As market competition intensifies, buyer bargaining power is also rising. Consumers pay more and more attention to cost-effectiveness when purchasing smartphones, tablets and other technology products, and have more choices between multiple brands.
Through the analysis of Porter's Five Forces Model, it can be seen that when facing multiple market pressures, Apple must maintain its competitive advantage through innovative product strategies, flexible pricing strategies, perfect channel management and efficient promotion methods. It is based on these pressures that Apple has formulated and implemented its sophisticated 4P marketing strategy to meet market challenges and consolidate its leadership in the global technology market.
3. Apple's Marketing Strategy Based on the 4Ps Model
3.1. Product Strategy: Innovation Driven and Ecosystem Construction
Since its establishment, Apple has always regarded product innovation as its core competitiveness. Not only is it unique in hardware innovation, but Apple also provides a unique user experience through product design optimization and ecosystem integration. Its product strategy is reflected in a diversified product portfolio and high-end market positioning, as well as a closed software and hardware ecosystem.
3.1.1. Product Innovation and Diversification
Apple takes technological innovation as its core and creates unique value for users through leading technology. The release of the M1 chip marks a breakthrough in Apple's hardware design. For example, the M1 chip integrates CPU, GPU and neural network engine, greatly improving the performance and energy efficiency of the Mac series and redefining the standard of high-end computers. Apple's product diversification strategy is also worthy of attention. Taking the iPhone as an example, Apple covers the mid-to-high-end market through a variety of products such as basic models and Pro models. The iPhone SE shows Apple's successful attempt in the price-sensitive market. The model has attracted a large number of consumers with its core technology and lower prices. Gupta and Singhe states that Apple iPhone's unique advantages in innovation and ecosystem make it still highly competitive in the fierce market competition [2].
3.1.2. High-End Positioning
Apple's high-end positioning runs through its product design and marketing strategy. According to table 1, comparing prices with other well-known brands like Samsung and Huawei shows that Apple is targeting the upper/middle class, not the middle class.
Table 1: Compare Apple iPhone X VS Huawei P20 Pro VS Samsung Galaxy S9 [3].
Brand/Phone | Apple iphone X | Huawei P20 Pro | Samsung Galaxy S9 |
Storage | 64 GB | 128 GB | 64 GB |
Ram | 3 GB | 6 GB | 4 GB |
Display size | 5.8 In (14.73cm) | 6.1 In (15.49cm) | 5.8 In (14.73cm) |
PCAD | Approx. $1560 | Approx. $1140 | Approx. $1015 |
Through premium pricing, Apple has successfully positioned itself as a symbol of high-end consumer goods. Although the high price of iPhone X exceeds the market average, its global sales have proved the effectiveness of this strategy. While launching high-end products, Apple also provides products at different prices through a price stratification strategy to meet the needs of different consumers. The success of the iPhone SE once again verifies the effectiveness of this strategy, attracting consumers with limited budgets with its powerful functions and reasonable prices.
3.1.3. Ecosystem and User Stickiness
Apple's ecosystem strategy is the core of its product strategy. By building a closed and highly integrated ecosystem, Apple not only improves user experience, but also enhances user brand loyalty. Survey data shows that Apple user loyalty is as high as over 90%, significantly higher than its competitors. This achievement is attributed to Apple's long-term investment in the combination of software and hardware and user experience optimization.
3.2. Pricing Strategy
3.2.1. Market Impact of Premium Pricing Strategy
Apple's premium pricing strategy aims to highlight its brand's high-end positioning through high-priced products and maximize the profit per unit of product. Take the iPhone X as an example. Its $999 price was widely regarded as a challenge to the market price ceiling when it was released. However, it turned out that the market's acceptance of this pricing strategy was much higher than expected. In the first quarter after its release, the iPhone X contributed 35% of Apple's global smartphone market profits. This data shows the success and market influence of the premium pricing strategy.
3.2.2. Price Tiering Strategy (Price Differentiation/Segemented)
In addition to premium pricing, Apple also responds to different market demands through price tiering strategies. The success of the iPhone SE is a typical case of price tiering strategy. While maintaining its high-end product line, Apple has entered the mid-range market by launching more affordable products, satisfying people with different demand elasticity and thus expanding its market coverage. This strategy not only helps Apple attract more users in the global market (as shown in the figure, Apple has the largest loyal fixed user group), but also alleviates the market's dependence on high-end product sales to a certain extent, reducing market risks.
Price discrimination can be seen in Apple’s pricing strategy. According to Cheng, D., Lack of competition encourages price discrimination, so, according to the survey, iPhones are usually more expensive in countries with less wealth inequality [4].
In addition, Apple also adopts differentiated pricing strategies in different product lines. For example, when Apple launches a new product, it usually retains the previous generation of products and lowers their prices, thus forming a product price system of "new and old alternation". This strategy not only extends the market life of old products, but also further meets the needs of different consumers through a multi-level price layout.
3.2.3. Psychological Pricing Strategy
Apple's pricing strategy also includes a deep understanding of consumer psychology. For example, when Apple sets prices, it often uses psychological price points such as US$99 or US$999, using people's psychological characteristics of price sensitivity to induce consumers to think that these prices are much lower than integer prices, making them easier to accept. In addition, Apple also uses the "bait pricing" strategy to launch multiple models with different configurations and prices at the same time when the product is released, using the highest configuration and high-priced products as "bait" to highlight the cost-effectiveness of the middle configuration products, thereby promoting the sales of the middle models.
In addition, Apple also uses skimming pricing, product differentiation, trade-in and other strategies. The success of these pricing strategies is not only reflected in sales, but also in consumers' brand loyalty and willingness to buy. According to market research data, Apple's pricing strategy has greatly improved consumers' purchase decision-making speed and reduced the purchase resistance caused by price sensitivity to a certain extent.
3.3. Channel Strategy
Apple's channel strategy not only involves the sales channels of products, but also covers supply chain management, inventory control and the construction of brand experience. Through refined channel management, Apple ensures that every link of the product from production to the hands of consumers is efficient and stable.
3.3.1. Supply Chain Management and Global Layout
Apple's supply chain management strategy is one of the cores of its channel strategy. Through the global supply chain layout, Apple ensures that its products can be supplied to the global market at the fastest speed and with high quality. Apple's supply chain partners are spread all over the world. Through strict quality control and meticulous production management, Apple can effectively reduce production costs while ensuring the high quality of its products.
Apple's success in supply chain management is not only reflected in the scale of its supply chain, but also in its flexible management of the supply chain. For example, when different market demands fluctuate, Apple can quickly adjust its production plan to ensure the timely supply of products and the balance of market demand. This flexibility management is particularly important during the global epidemic. Apple has ensured that the supply chain of its products is not interrupted and maintained a stable supply in the market by quickly adjusting its supply chain structure.
3.3.2. Brand Experience and Retail Network
Apple has established a unique retail network around the world, which is not only a channel for its product sales, but also an important part of the brand experience. The design and layout of the Apple Store not only provides the ultimate customer experience, but also enhances consumers' recognition and loyalty to the Apple brand through the display of brand culture.
The success of the Apple Store is largely due to its high attention to customer service and brand experience. Ashby, David, Khasawneh and Rami states that Apple, Sony, and Dell have the best customer service [5]. According to J.D. Power's customer satisfaction survey, Apple's retail stores have been among the best for many years. Apple has successfully made each Apple Store an important window for brand promotion by providing excellent customer service and unique brand experience. The design style of Apple's retail stores not only emphasizes product display, but also focuses on creating an atmosphere that integrates technology and art, so that consumers can feel the core values of the Apple brand when entering the Apple Store.
Apple also actively uses online channels to expand its market coverage. Apple's online store provides a seamless shopping experience, and users can easily purchase products and services through the website or App Store. Online channels not only expand Apple's market coverage, but also provide users with more convenience and choices. In addition, Apple also uses digital marketing methods to accurately convey product information to potential customers, further improving the conversion rate of online sales.
Apple's channel strategy is not only reflected in the reach of end consumers, but also through strict supply chain management to ensure efficient production of products and timely delivery worldwide. Apple's global distribution network covers almost all major markets, and its supply chain management system enables Apple to respond quickly to market demand worldwide through sophisticated inventory control and efficient logistics arrangements. This efficient supply chain management not only improves Apple's market competitiveness, but also reduces the risks caused by inventory backlogs or supply shortages.
3.4. Promotion Strategy
3.4.1. Integration of Advertising and Promotion Strategies
Apple's promotion strategy occupies an important position in the entire marketing strategy. Apple's investment in advertising and brand promotion is not only reflected in advertising in traditional media, but also in achieving wider brand communication through digital platforms and social media. Apple's advertising style is usually concise and impactful and conveys the brand's sense of technology and foresight through high-quality visual and music design. For example, Apple's advertisements during major sporting events such as the Super Bowl often attract widespread attention. These advertisements show the innovation of Apple products and strengthen the brand's high-end image in the minds of consumers through unique narrative methods. Apple has also further enhanced the brand's market influence through social media and digital marketing methods. For another example, Apple's "Shot on iPhone" marketing campaign successfully stimulated users' creative enthusiasm by displaying photos and videos taken by users through social media platforms and achieved widespread brand communication through user-generated content (UGC). This marketing campaign not only demonstrated the powerful shooting function of the iPhone, but also enhanced the brand's interactivity and user loyalty through user participation.
3.4.2. Maintenance of Public Relations and Word-of-Mouth
Apple attaches great importance to maintaining and enhancing its brand image through public relations strategies and word-of-mouth effects. Apple's product launch is not only a display of new products, but also a global brand promotion event. These launches attract the attention of global media and consumers through carefully planned demonstrations and communication strategies.
In addition to product launches, Apple also actively maintains developer communities and user groups. Apple holds the Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) every year to showcase the latest software and technologies and has established close ties with global developers. This interaction not only promotes the innovative development of the Apple ecosystem, but also enhances developers' dependence on the Apple platform, thereby consolidating Apple's leadership in the global technology ecosystem. In addition, Apple has cultivated a large number of loyal users and developer groups by supporting education and training programs. Apple's developer community provides rich resources and support for developers around the world, making more developers willing to develop applications for the Apple platform.
4. Competitor Analysis and Strategy Comparison
Apple's marketing strategy is significantly different from that of its main competitors, such as Samsung and Google. Lopez points out that although Samsung and Google have technological advantages in some areas, Apple still maintains a clear lead in overall market performance and user loyalty [6].
4.1. Comparison with Samsung
Samsung's competitive advantage is mainly reflected in its extensive product line and technological innovation. Samsung has attracted consumers with different demand elasticity by covering the smartphone market from low-end to high-end. At the same time, Samsung's innovations in display technology and camera technology have increased its competitiveness. However, Samsung still lacks in brand loyalty and consistency of user experience compared to Apple. Apple has successfully built a highly loyal user group through its closed ecosystem and high-quality user experience, which has enabled it to maintain a strong market influence in the global smartphone market.
4.2. Comparison with Google
Google has strong competitiveness in artificial intelligence and cloud computing technology, and its Android operating system occupies most of the global smartphone market. However, Google is relatively limited in the expansion of its hardware product line. Although its Pixel series of mobile phones are technologically advanced, their market share is low. In contrast, Apple has created a closed and efficient ecosystem by integrating hardware, software and services. This all-round integration advantage has enabled Apple to maintain significant competitiveness in user experience and brand loyalty.
5. Future Development Suggestions and Strategic Adjustments
With the changes in the market environment and the rapid development of the technology industry, Apple needs to continue to adjust its strategy to meet future challenges. The following are some suggestions for Apple's future development:
1) Consolidate the mid-range market: Although Apple dominates the high-end market, the mid-range market still has great potential. Apple can further enhance market coverage and increase the profit margin of mid-range products by expanding its mid-range product line; 2) Strengthen information technology and digital transformation: Apple can further increase its investment in artificial intelligence and big data analysis, deeply understand consumer needs, and provide more personalized products and services. At the same time, explore the application of AR and VR technologies in online shopping platforms to enhance user interactivity and online sales attractiveness; 3) Flexible pricing strategies to cope with economic fluctuations: The uncertainty of the global economy requires companies to have stronger adaptability. Apple can maintain its market competitiveness by launching products at different price points and regular promotions, especially in times of economic fluctuations, to attract price-sensitive consumers; 4) Increase investment in emerging markets: Emerging markets have huge growth potential. Apple can increase its investment in these markets, launch products that meet local needs, and strengthen targeted marketing to enhance brand influence.
6. Conclusion
Apple's success stems from its careful layout in product design, pricing strategy, channel expansion and promotional means. Through the flexible application of the 4P marketing model, Apple has not only established a strong brand image in the global market, but also maintained its leading position in the global technology industry through technological innovation and excellent user experience.
This article is narrow in scope and is limited to Apple. Therefore, the research on other competing companies is shallow, and the arguments used may be outdated. Future research can further explore how other companies that compete with Apple use the 4P model to formulate marketing strategies, and through horizontal comparison of strategies, link market share and development prospects, and study the dynamic effects. The research limited to one company introduced in this article hopes to inspire further research on this topic.
References
[1]. Slotta, D. (2023) Market share of leading smartphone brands in Taiwan 2023. https://www.statista.com/statistics/883219/taiwan-leading-smartphone-brands-market-share/
[2]. Gupta, H., & Singhe, A. (2023). Prediction and Analysis of Smartphone Among Customers. In Proceedings of the New Frontiers in Science and Technology Conference. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/NFST.2023.10525754.
[3]. Gadgets Now (2021) Compare Apple iPhone X VS Huawei P20 Pro VS Samsung Galaxy S9. https://www.gadgetsnow.com/compare-mobile-phones/Apple-iPhone-X-vs-Huawei-P20-Pro-vs-Samsung-Galaxy-S9
[4]. Cheng, D. (2022) Identification of Direct Socio-Geographical Price Discrimination: An Empirical Study on iPhones. https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07903
[5]. David, Khasawneh and Rami (2008) An Analysis of Home Computer Customer Service Hotlines. Marietta Vol. 4, Iss. 2, (2008): 48-58, 78
[6]. Hernandez Lopez, Y. (2024). Effect of brand value on customer loyalty: The Apple case. Retrieved from Universidad Rey Juan Carlos Digital Repository: https://burjcdigital.urjc.es/bitstream/handle/10115/32888/2023-24-FCEE-J-2110-2110038-y.hernandez.2020-MEMORIA.pdf?sequence=-1&isAllowed=y
Cite this article
Wang,J. (2025). Apple's Marketing Strategy: Comprehensive Application and Strategic Analysis of the 4P Model. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,148,118-125.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2024 Workshop: Human Capital Management in a Post-Covid World: Emerging Trends and Workplace Strategies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Slotta, D. (2023) Market share of leading smartphone brands in Taiwan 2023. https://www.statista.com/statistics/883219/taiwan-leading-smartphone-brands-market-share/
[2]. Gupta, H., & Singhe, A. (2023). Prediction and Analysis of Smartphone Among Customers. In Proceedings of the New Frontiers in Science and Technology Conference. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/NFST.2023.10525754.
[3]. Gadgets Now (2021) Compare Apple iPhone X VS Huawei P20 Pro VS Samsung Galaxy S9. https://www.gadgetsnow.com/compare-mobile-phones/Apple-iPhone-X-vs-Huawei-P20-Pro-vs-Samsung-Galaxy-S9
[4]. Cheng, D. (2022) Identification of Direct Socio-Geographical Price Discrimination: An Empirical Study on iPhones. https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07903
[5]. David, Khasawneh and Rami (2008) An Analysis of Home Computer Customer Service Hotlines. Marietta Vol. 4, Iss. 2, (2008): 48-58, 78
[6]. Hernandez Lopez, Y. (2024). Effect of brand value on customer loyalty: The Apple case. Retrieved from Universidad Rey Juan Carlos Digital Repository: https://burjcdigital.urjc.es/bitstream/handle/10115/32888/2023-24-FCEE-J-2110-2110038-y.hernandez.2020-MEMORIA.pdf?sequence=-1&isAllowed=y









