1. Introduction
Mobile payments are now the mainstay of payment methods, and the increasing level of consumption has become the norm in an economically mobile society. With the development of the internet, mobile payments have a complete and precise definition in economic circulation.
Mobile payments are a payment service executed via mobile devices, many mobile systems are available on ios and Android devices and require a bank account to be tied to the relevant mobile payment platform. Mobile payments can be made in several ways, in addition to traditional payment methods such as cash, cheques, and credit and debit cards, and can also be made on a mobile device [1]. And the rise of online shopping has been shaped by the rise of mobile payments, often operating in the form of Apple Pay, Alipay, WeChat, etc. Consumers can easily make cashless and cardless payments through their mobile devices, and this porFigure payment method has dramatically increased the spending power of the masses, driving economic development and circulation. This article would like to explore mobile payments’ impact on online shopping. The paving of the way for the development of online shopping is evident in the adoption of mobile payments, which has had a positive spending impact on online household shopping, suggesting that there are synergies between mobile payments and e-commerce platforms that are attractive for the interface of different related platforms [2]. However, regarding the positive effects, there is also a negative side, with security being the primary issue for mobile payment systems. Data breaches are common in online shopping and payments. When they occur, payment card information such as username, credit card number, expiry date, cardholder verification value, and purchase service code is at risk of being compromised, which can result in financial loss to the user and even exposure to fraud and identity theft [3]. This makes online shopping much less safe and secure.
This article is divided into three sections, mobile payments, online shopping, and the relationship between the two. Through a specific analysis of mobile payments and online shopping, the definitions and roles of the two are clarified, and the relationship between the two is compared in depth jointly so that the interplay between mobile payments and online shopping can be drawn.
2. Literature Review
To explore the relationship between mobile payments and online shopping in China, this literature review focuses on the popularity of mobile payments in China in the last decade and whether it has contributed to the development of the online shopping industry.
2.1. Mobile Payments
Mobile payments are indispensable in everyday life in China, making online and offline transactions more convenient [2]. Mobile payments can also be made in various ways, such as Alipay, WeChat payments, or even earlier SMS payments. According to Ariadne, mobile remote payments entered a period of rapid growth in 2013, accounting for 97.4% (51.7% of mobile internet payments and 45.7% of SMS payments). The growth rate of mobile payments in China is phenomenal, Y Huang, X Wang, X Wang [3] state that total mobile payment transactions in China jumped from RMB 14.5 trillion in 2013 to RMB 277.4 trillion in 2018, an annual growth rate of 80%. In terms of both transaction volume and penetration, China's mobile payments have been firmly established as the world's number one [3]. According to Ipsos, China's mobile payment penetration rate was much higher than that of many developed countries, such as the UK and the US in 2016. Mobile payments have risen to prominence in China for their convenience and efficiency. The security of mobile payments has been analysed by many scholars, such as Y Wang, C Hahn, and K Sutrave [1]. Mobile payment is essentially a payment service based on "trust" [4] Alipay, WeChat, and other platforms use face recognition, fingerprint payments, and random payment passwords to gain the trust of users while ensuring the security of their money.
2.2. Online Shopping
With the development of technology, online shopping plays as important a role in people's lives as mobile payments. Back in 2015, according to a study by Paypal, 33% of online shopping in China was done through smartphones. W Yang, P Vatsa, W Ma, H Zheng [2] argue that the growth of mobile payments is tied to the growth of e-commerce and that with the popularity of online shopping, online mobile payments have become the primary payment method for online purchases. After the COVID-19 outbreak, people were afraid to shop offline or even unable to shop offline out of fear of the virus, which also forced more and more people to use online shopping channels [5-9]. One of the advantages of online shopping is the ease of transaction, which relies on cooperation with mobile payments. In a study by [10], the determinants of Chinese consumers' satisfaction with online shopping were shown to include website design, security, quality of information, payment methods, quality of e-services, product quality, product range, and delivery services. Most of these consumers choose payment methods based on convenience and, more importantly, on security [11]. From the literature mentioned above, many scholars have studied the topic of mobile payments and online shopping within the last 25 years. But most of the research on mobile payments has been on the historical development of mobile payments and the outlook for the future. Most of the studies on online shopping have analysed the popularity and advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce and user satisfaction. Only W Yang, P Vatsa, W Ma, and H Zheng [2] analysed the relationship between online shopping and mobile payments but with a focus on gender differences. In summary, no scholar has attempted to examine the popularity of mobile payments in China in the last decade and whether it has contributed to the development of the online shopping industry. The subject matter of this paper is innovative and will be examined in detail in the following papers.
2.3. The Relationship Between Mobile Payments and Online Shopping
Mobile payments have been integrated into people's daily lives, and online shopping has become the norm. Yet there is an inextricable relationship between the two, with mobile payments having a positive spending impact on online shopping, suggesting a synergy between mobile payments and e-commerce platforms [2]. According to the study, the two prominent examples of mobile payments in China are Alipay and WeChat Pay, through which Alibaba and Tencent are rapidly going live with all kinds of life application scenarios (shopping, travel, dining, etc.) to build a core online shopping industry chain [4]. This shows that mobile payment is a prerequisite and foundation for online shopping. According to the survey, with the increase in Internet penetration and the number of Chinese Internet users, the mobile payment market has exceeded 4 billion yuan in one year [12]. Internet users and the intensity of their purchases have significantly increased the use of mobile payments. This shows that the two are influencing each other and developing together. However, despite the positive effects of both, there are some drawbacks to the close relationship. While mobile payments and online shopping have brought great convenience to the general public, there are also security issues, as consumers face several risks, such as online fraud and credit card fraud. This significantly threatens the security of consumers' and users' property and information. The convenience and speed of mobile payments have led to unscrupulous elements on the internet taking advantage of online shopping and committing criminal acts. Mobile payment technology risks include data transmission security and user information security, which is a primary concern for mobile payment users [13]. However, this is also the result of the mutual result of mobile payment and online shopping, through which these accidents lead to less loyalty of consumers towards mobile payment and online shopping, thus yielding more negative effects. Regardless of the positive or negative effects, the relationship between mobile payments and online shopping has been close and co-evolved from the beginning to the end, with the premise that the two interactions have a sFigure network security base.
3. Method
This essay will take a survey method to study and analyse the relationship between mobile payments and online shopping in China today. Using today's Chinese market as a starting point, information is collected and categorised by reviewing relevant data through the online data research website Statista. The available data is analysed so that theory and practice are combined to conduct a comprehensive study, for example, the number of mobile payment users in China, the primary motivations for mobile payments in China, the main types of payment for electronic payments in China, the penetration rate of online shopping in China, and the change in the usage rate of online shopping in China before and after the epidemic. Concrete and exact conclusions are drawn, and in-depth research is conducted to analyse the future development trends of these two industries.
4. Results
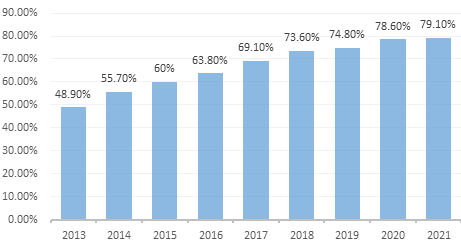
Figure 1: Penetration rate of online shopping in China from 2013 to June 2022.
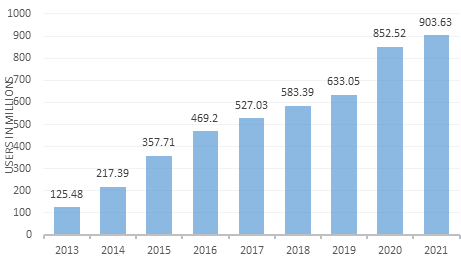
Figure 2: Number of mobile payment users in China from 2013 to 2021(in millions).
4.1. Online Shopping and Mobile Payment Penetration in China
Figure 1 shows that the penetration rate of online shopping in China continues to increase from 2012 to 2022 (from 42.9% in 2012 to 80% in 2022). These two graphs demonstrate that the number of users using online shopping and mobile payments will grow in tandem from 2013 to 2021, that the market for mobile payments is gradually expanding, and that online shopping has a strong and growing mass base. However, this Figure is insufficient to prove that the two affect each other.
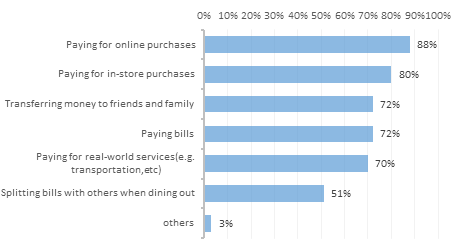
Figure 3: Main purchase types using e-payments among respondents in China in October 2022.
Figure 3 shows that in October 2022, 88% of Chinese respondents indicated that online shopping was the main reason for using mobile payments, with convenience and speed indirectly reflected. Combined with Figure 1 and Figure 2 above, it can be seen that the popularity of mobile payments has positively impacted the development of online shopping, and the trend is positive. Mobile payment is a prerequisite for online shopping, reflecting the importance of mobile payment for online shopping.
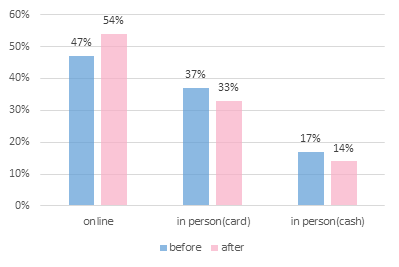
Figure 4: Preference for payment methods before and after COVID-19 in China as of August 2020.
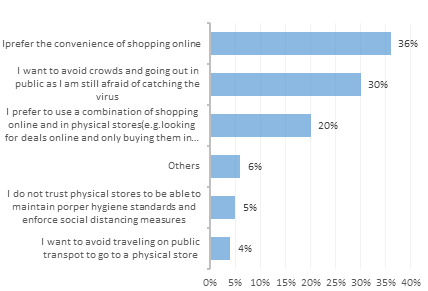
Figure 5: Reasons for shopping less frequently in physical stores as before post-COVID-19 restrictions among consumers in China as of June 2021.
4.2. Impact of the Epidemic on Online Shopping and Mobile Payments
Figure 4 shows that the number of online payment users showed a significant upward trend of 7% after the new crown outbreak in 2020 compared to the number of online payment users before the outbreak, while the proportion of people choosing the offline payment method (cash or credit card) decreased significantly. This is because 36% of people found it easier and faster to shop online during the outbreak, while 30% chose to shop online for fear of contracting the virus. The reasons in Figure 5 are sufficient to demonstrate the benefits of online shopping. Online shopping is an offshoot of mobile payments, dramatically improving people's standard and quality of life. Combined with the internet age has taken consumption and technology to a new level. This leads to the conclusion that online shopping has a positive, catalytic impact on mobile payments.
To sum up, online shopping and mobile payment are mutually influential, mutually beneficial, and develop together.
5. Discussion
From the above study, it is possible to obtain the impact and link between mobile payment and online shopping. The impact of mobile payment on online shopping is significant. Mobile payment is one of the keys to online shopping as it allows consumers to pay for goods conveniently and quickly without having to pay at a physical shop or use other less secure or less convenient payment methods. This provides consumers with a more flexible and convenient way to pay for their purchases, catering to the needs of different consumers. At the same time, the encryption technology and security mechanisms of mobile payments allow consumers to use them with confidence, protecting their payment information and personal privacy. And the emergence of mobile payments has accelerated the development of online shopping, promoting competition and innovation. Because consumers can conveniently pay for goods, they are more likely to choose and compare between different online shopping platforms, thus improving the competitiveness and quality of service between platforms. At the same time, mobile payment online shopping has had a profound impact on online payments. The rise of online shopping has promoted the development of mobile payments, which have provided a more convenient, fast, and secure way to pay for online shopping.
And the development of online shopping has contributed to the popularity of mobile payments. Whereas in the past, consumers had to go to a physical shop and pay in cash or by cheque, traditional payment methods, online shopping can be done through the internet, and consumers only need to use credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, and other mobile payment methods to complete their purchases. And online shopping places higher demands on the technology and security of mobile payments. Because online shopping involves sensitive information such as payment information and personal privacy, mobile payments must provide higher security and technical support. Mobile payment institutions also continue to enhance the security and stability of their payment systems to meet consumers’ needs and improve the efficiency and quality of payments.
Overall, the two interact for the benefit of each other.
6. Conclusions
This article focuses on the impact of mobile payment and online shopping, combining the definition and role of mobile payment and online shopping for research and analysis. Mobile payment is a new industry that combines the advantages of speed and convenience with Internet technology. Mobile payment is leading a new payment concept and trend [4].
The impact of mobile payment on online shopping is very positive; it promotes the development and innovation of online shopping, provides more convenient and flexible payment methods, and brings a better shopping experience to consumers. Online shopping is based on big data in different online platforms to provide purchase channels for the masses, combined with specific personal preferences and convenient consumption methods. Online shopping has had a positive impact on mobile payments. It promotes the popularity and development of mobile payments, improves the efficiency and security of payments, and provides more opportunities for innovation and development. Online shopping is, therefore, inseparable from mobile payments and must be developed on the premise of mobile payment outputs; the development of mobile payments must be driven by online shopping, and it follows that one cannot be without the other. However, some risks and negative outputs (property, information leakage, etc.) are also caused by mobile payments and online shopping, and the solution still requires a combination of both. Whether the impact is positive or negative, the mutual influence of the two on each other is evident. It can be developed more closely in the future, focusing on cyber security issues, protecting users' privacy and property security while expanding the market scale and achieving a win-win situation for mobile payments and online shopping. However, this article still has some inadequate points, such as fewer investigation cases of negativity in mobile payment and online shopping. Specific data on the close relationship between the two has not been shown, which will be further analysed and explored in future studies.
References
[1]. Wang, Y., Hahn, C. and Sutrave, K. (2016). Mobile payment security, threats, and challenges. 2016 Second International Conference on Mobile and Secure Services (MobiSecServ). [online] Available at:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7440226/citations#citations.
[2]. Yang, W., Vatsa, P., Ma, W. and Zheng, H. (2023). Does mobile payment adoption really increase online shopping expenditure in China: A gender-differential analysis. Economic Analysis and Policy, 77, pp.99–110.
[3]. Huang, Y., Wang, X. and Wang, X. (2020). Mobile Payment in China: Practice and Its Effects. Asian Economic Papers, 19(3), pp.1–18.
[4]. Huang, J. (2017). How Mobile Payment Is Changing The World How Mobile Payment Is Changing The World.
[5]. Alhaimer, R. (2022). Fluctuating Attitudes and Behaviors of Customers toward Online Shopping in Times of Emergency: The Case of Kuwait during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Internet Commerce, 21(1), pp.26–50.
[6]. Chang, H. and Meyerhoefer, C.D. (2021). COVID‐19 and the Demand for Online Food Shopping Services: Empirical Evidence from Taiwan. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 103(2), pp.448–465.
[7]. Gao, X., Shi, X., Guo, H., and Liu, Y. (2020). To buy or not buy food online: The impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on the adoption of e-commerce in China. PLOS ONE, 15(8), p.e0237900.
[8]. Hao, N., Wang, H.H., and Zhou, Q. (2020). The impact of online grocery shopping on stockpile behavior in Covid-19. China Agricultural Economic Review, 12(3), pp.459–470.
[9]. Zheng, H. and Ma, W. (2021). Click it and buy happiness: does online shopping improve the subjective well-being of rural residents in China? Applied Economics, 53(36), pp.4192–4206.
[10]. Guo, X., Ling, K.C. and Liu, M. (2012). Evaluating Factors Influencing Consumer Satisfaction towards Online Shopping in China. Asian Social Science, 8(13), p.40.
[11]. Franzak, F., Pitta, D. and Fritsche, S. (2001). Online relationships and the consumer’s right to privacy. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 18(7), pp.631–642.
[12]. Li, J., Wang, J., Wangh, S. and Zhou, Y. (2019). Mobile Payment With Alipay: An Application of Extended Technology Acceptance Model. IEEE Access, 7, pp.50380–50387.
[13]. Chen, H. and Li, W. (2017). Mobile device users’ privacy security assurance behavior. Information and Computer Security.
Cite this article
Zhang,K. (2023). The Impact Between Mobile Payments and Online Shopping in China. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,24,35-42.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang, Y., Hahn, C. and Sutrave, K. (2016). Mobile payment security, threats, and challenges. 2016 Second International Conference on Mobile and Secure Services (MobiSecServ). [online] Available at:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7440226/citations#citations.
[2]. Yang, W., Vatsa, P., Ma, W. and Zheng, H. (2023). Does mobile payment adoption really increase online shopping expenditure in China: A gender-differential analysis. Economic Analysis and Policy, 77, pp.99–110.
[3]. Huang, Y., Wang, X. and Wang, X. (2020). Mobile Payment in China: Practice and Its Effects. Asian Economic Papers, 19(3), pp.1–18.
[4]. Huang, J. (2017). How Mobile Payment Is Changing The World How Mobile Payment Is Changing The World.
[5]. Alhaimer, R. (2022). Fluctuating Attitudes and Behaviors of Customers toward Online Shopping in Times of Emergency: The Case of Kuwait during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Internet Commerce, 21(1), pp.26–50.
[6]. Chang, H. and Meyerhoefer, C.D. (2021). COVID‐19 and the Demand for Online Food Shopping Services: Empirical Evidence from Taiwan. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 103(2), pp.448–465.
[7]. Gao, X., Shi, X., Guo, H., and Liu, Y. (2020). To buy or not buy food online: The impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on the adoption of e-commerce in China. PLOS ONE, 15(8), p.e0237900.
[8]. Hao, N., Wang, H.H., and Zhou, Q. (2020). The impact of online grocery shopping on stockpile behavior in Covid-19. China Agricultural Economic Review, 12(3), pp.459–470.
[9]. Zheng, H. and Ma, W. (2021). Click it and buy happiness: does online shopping improve the subjective well-being of rural residents in China? Applied Economics, 53(36), pp.4192–4206.
[10]. Guo, X., Ling, K.C. and Liu, M. (2012). Evaluating Factors Influencing Consumer Satisfaction towards Online Shopping in China. Asian Social Science, 8(13), p.40.
[11]. Franzak, F., Pitta, D. and Fritsche, S. (2001). Online relationships and the consumer’s right to privacy. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 18(7), pp.631–642.
[12]. Li, J., Wang, J., Wangh, S. and Zhou, Y. (2019). Mobile Payment With Alipay: An Application of Extended Technology Acceptance Model. IEEE Access, 7, pp.50380–50387.
[13]. Chen, H. and Li, W. (2017). Mobile device users’ privacy security assurance behavior. Information and Computer Security.









