1. Introduction
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, it has made significant breakthroughs in key fields such as emotional computing, natural language processing and voice recognition, and gradually established a deeply established emotional bond with human beings, promoting the expansion of artificial intelligence to a wider range of fields. Among them, AI voice cloning technology, as an important symbol of technological change, relies on deep learning model to realize accurate recognition and extraction of voice features, and then generate "new sound" highly similar or almost consistent with the original sound. The technology shows excellent performance in nature, fluency and emotional synchronous transcription, and has a high level of humanity and authenticity characteristics.
Continuous human-machine emotional interaction is the core element of AI voice cloning technology in the era of intelligence [1]. It has become an indispensable and valuable tool for content creators and service platforms [2], not only creating new characters for artistsand bringing immersive experiences to gamers [3] [4], but also revolutionizing the problems of interaction and cross-language communication among groups with language barriers [5]. At the same time, the technology also relies on the user data for model upgrade and iteration, and the man-machine forms a close shared relationship in the closed loop [6].
Through literature review, a large number of studies mainly focus on machine system design [7] and human emotional response [8], especially in the research of attachment emotion [9] [10], shared behavior [11] [12]. For example, some studies show that the internal model of attachment is mainly composed of the beliefs of self and others, which guides the behavioral response of users by regulating and influencing emotional intensity [13]; other studies, emphasizing the importance of cooperation and sharing between human and machine, and compare the relationship between shared behavior and human and machine to the relationship between sharp spearhead and blunt spear rod [14]. However, the existing literature considers less about the actual behavioral responses of users after attachment to new technologies, indicating that future research needs to focus more on the intrinsic connection between attachment and shared behavior, and in-depth explore the actual behavioral responses of users after technology adoption to more fully understand the emotional and behavioral dynamics in human-machine relationships.
In conclusion, this study innovative attachment concept as an organizational structure, and try to in the stimulus-body-response (SOR) framework, into the AI voice cloning technology of human nature, authenticity characteristics, and attachment emotion and trust attitude four key variables as independent variables, while the voice sharing behavior as the dependent variable, to build a comprehensive man-machine attachment voice sharing model. This paper conducts empirical test through large sample data and structural equation model (SEM), and aims to provide a new theoretical perspective and practical guidance for voice creation and technology promotion, and help the man-machine relationship achieve the goal of more intimate and harmonious coexistence in the era of intelligence.
2. Literature review and model construction
2.1. Theoretical basis: the S-O-R model
The S-O-R model, developed from Mehrabian and Russell based on consumer behavior theory, believes that stimulation (S) in the environment will affect an individual's emotion and cognition (O), and then affect the change of individual behavior (R) [15]. This model has been widely used in many fields, including smartphone [16], online shopping [17], disease prevention [18], etc.
In the S-O-R model, the stimulus, as the leading variable, similar to the "trigger", can trigger the emotional or cognitive response of users [19]. In this study, the stimulus factors specifically refer to the emotional response characteristics formed between human-computer interactions. The intermediary variable of the model is organism, which represents the intermediate state between stimulus and response [20], mainly represented by affective state and cognitive state [21]. The mediation variable in this study mainly refers to the user's emotional experience after the use of AI cloned voice technology. The outcome variable of the model is reaction, also known as behavior [22], which represents the individual's response to stimuli, which can be approach or avoidance behavior [23]. This study focuses on the user's approach to the technology, such as stay, sharing, purchase, etc. These behavioral responses may become the final form after human-computer interaction [24].
Although researchers of the S-O-R model usually use survey methods to measure user response to post-stimulus effects [25], studies in specific contexts such as human-computer attachment, and human-computer attachment as a stimulus to test user response behavior are relatively scarce [26]. Therefore, this study applies the S-O-R model to the mechanism of user shared behavior under human-machine attachment, trying to explain the relationship between environmental stimuli (humanlike and authenticity), the internal state of the user as an organism (attachment emotion and trust degree), and behavioral responses (shared willingness). To this end, this study used a dynamic research model to reproduce the psychological contrast and behavioral changes before and after user use and sharing [27], aiming to fill the shortcomings in the existing literature on user behavioral response in human-computer attachment situations and provide new theoretical support for understanding user behavior in human-computer interaction.
2.2. Research hypothesis
2.2.1. Humanoid — Stimulus level
"Humanoid" is embodied in the appearance design of artificial intelligence, facial expressions, social applications, and interaction and communication with human beings, which makes artificial intelligence quite similar to human beings in different aspects [28]. For a long time, artificial intelligence has been discussed under the framework of "individualism" in the methodology, especially on how to adapt to the non-social environment, the academic circle has launched an in-depth discussion [29]. The "human-like" characteristics of artificial intelligence provide new ideas to solve this contradiction, and greatly promote the social interaction between man and machine [30]. Interaction promotion Thanks to the AI voice cloning technology system, it can feedback a specific language in real time [31], and can simulate real social interaction scenes in only 3-4 seconds [32]. In fact, the voice model forms a closed-loop interaction with the cognitive model, which significantly improves the quality of social dialogue based on the emotional intelligent interaction model [33].
Moreover, human beings will also project human-like qualities such as autonomy and dependence to artificial intelligence to meet their basic needs of belonging and security, so as to establish a long-term attachment relationship with AI[34]. At present, advanced AI voice technology is also designed as "social agent", and is widely used in related fields [35] with distinct "people-oriented" characteristics, such as healthcare and personal assistant [36][37], which further promotes the formation of closer attachment relationship between man and machine [38]. Many studies have shown that the human-like characteristics of technology are crucial to the establishment of human-machine trust relationship [39]. When the human-like characteristics are weakened, it will have a greater negative impact on the construction of human-machine trust relationship [40]. Based on the above analysis, this study includes the theoretical model and proposed the following hypotheses:
H1a: The humanoid of AI voice cloning technology has a positive correlation effect on authenticity.
H1b: The humanoid of AI voice cloning technology has a negative impact on user trust.
H1c: The humanoid of AI voice cloning technology has a positive correlation effect on user attachment.
2.2.2. Authenticity — Stimulus level
Authenticity, derived from the Latin word "authenticus" and the Greek word "authentikos", represents a trustworthy, authoritative, and acceptable trait [41]. Research shows that the "perceived authenticity" of human beings is continuously regulated by "perceived quality" and "vitality" [42], which can interfere in users' consumption behavior [43], and has a positive correlation with brand "loyalty". Specifically, when users have trust and friendly attitude towards a brand with real characteristics [44][45], their purchase intention and behavior trendswill significantly increase [46][47] .
In the field of artificial intelligence, considering authenticity is equally important [48]. On the one hand, the customized services of artificial intelligence can significantly deepen the authenticity of human perception [49] and gradually develop into new human-machine consumption emotions [50]; On the other hand, users impressed by the "real" scenes shaped by artificial intelligence may even regard artificial intelligence as potential emotional partners [51]. However, it has also raised users' questions about the ethics of "trusted" digital partners. Despite similar digital partners, users do not necessarily perceive their authenticity [52]. This is the "authenticity" presented by artificial intelligence, which is mostly "colonized" by the consciousness of designers, full of data doctrine and monitoring capitalism [53][54], and there is invisibility [55]. At present, there is still a lack of systematic empirical tests of the "authenticity" measurement in the field of artificial intelligence [56]. Therefore, this study included authenticity in the theoretical model to innovate relevant quantitative research and propose the following research hypotheses:
H2a: The authenticity of AI voice cloning technology has a negative impact on user trust.
H2b: The authenticity of AI voice cloning technology has a positive correlation on user attachment.
2.2.3. Attachment — Organism level
Attachment theory, first developed by Bowlby [57] and Ainsworth et al [58], describes the intimate relationship between infants and caregivers, and was later applied to explain patterns of relationships between adults, covering the dual attachment to the psychological (emotional) and body. Nowadays, attachment theory has been widely used in the study of human-computer interaction. Human beings instinctively desire to accompany and expect belonging [59], prompting the two sides to gradually form a certain relationship or emotional bond [60].
In the past, humans met this instinctive need by interacting with life bodies (e. g., family members, friends, colleagues, pets) and now interacting with inanimate bodies such as robots or artificial intelligence [61]. Human beings in the high-pressure environment are more eager for the company of AI partners [62], and this human-machine closeness mode is similar to the behavior trajectory of human approaching attachment characters. When the target user interacts with AI and feels "preference", it will stimulate their attachment to AI [63], that is, the higher the secure human attachment to AI, the higher the trust [64]. If artificial intelligence shows the willingness to promise and loyalty to users, it will stabilize and enhance the construction of emotional bond between man and machine [65]. It can be seen that attachment emotions not only improve the quality of perceptual experience and information exchange in human-computer dialogue, but also enhance their higher degree of self-disclosure [66]. Therefore, this study incorporated emotional attachment into the relationship between users and AI voice cloning technology [67] and makes the following assumptions:
H3a: Users' attachment to AI voice cloning technology has a positive correlation effect on trust.
H3b: The user's attachment to AI voice cloning technology has a positive correlated effect on voice sharing behavior.
2.2.4. Trust — Organism level
Trust is a particularly important issue in the field of artificial intelligence. Some researchers define trust as a kind attitude towards others, and a confidence in the behavior of the trusted person [68]. In general, users tend to rely on algorithms [69] when performing objective tasks, and under the support of trust [70], gradually improve the perception and willingness of artificial intelligence [71], so as to form a specific and solid human-machine attachment style. Obviously, trust is one of the key reasons why people use and rely on a certain technology [72].
Interestingly, trust is vulnerable to the influence of various factors, including past experience [73], communication [74] , behavior, especially for involving medical [75], hotel service [76] and other related areas of users is very obvious, such users often do not believe in artificial intelligence, partly because the artificial intelligence model of human basic moral prediction and judgment is not complete, lead to man-machine perception of unequal, thus hindered the trust in the field of moral related building [77]. At the same time, the positive motivation of users will also significantly affect the trust relationship between man and machine [78]. In terms of this study, relatively few studies explore the relationship between human-computer attachment and trust [79]. Therefore, we included trust in the research model to expand the theoretical research and propose the following assumptions:
H4: Users' trust in AI voice cloning technology has a negative correlation effect on voice sharing behavior.
2.2.5. Voice sharing — Response level
"Sharing" is a complex system involving multiple elements including sender and receiver, knowledge and information, information transmission channel and external environment [80]. Users with high demand for a sense of belonging and involvement are susceptible to their own attachment emotions and will take shared behavior as a response [81]. Such activities that rely on human-computer interaction not only promote the creation of information, but also strengthen the sharing of knowledge [82][83]. Some researchers have found that users with high frequency of an AI platform can make a good prediction of the interpersonal relationship and social atmosphere [84]. However, although users' voice sharing behavior in AI voice cloning technology provides a new way for the operation mode [85], they still need relevant voice data management standards and safe and effective data sharing facilities to support [86], so as to ensure the security and effectiveness of voice sharing behavior. Specifically, when more people participate in sharing information with AI, some users may feel a sense of exploitation, thus reducing their trust in the technology [87]. It can be seen that trust also affects users' intention to share information [88].
Through real-time interaction with users, the AI sharing platform constantly "learns" and corrects data. With its unique personalized and ultra-personalized performance, it can meet the needs of different users [89]. Therefore, the present study summarized the response part into voice-shared behavior.
In conclusion, this paper systematically combs the factors that may affect the attachment and sharing behavior of users to AI voice cloning technology, and provides a corresponding theoretical basis for the promotion of new technologies and enabling human auditory society. To achieve this goal, this study constructed a voice sharing model under human-machine attachment under the SOR framework (see Figure 1).
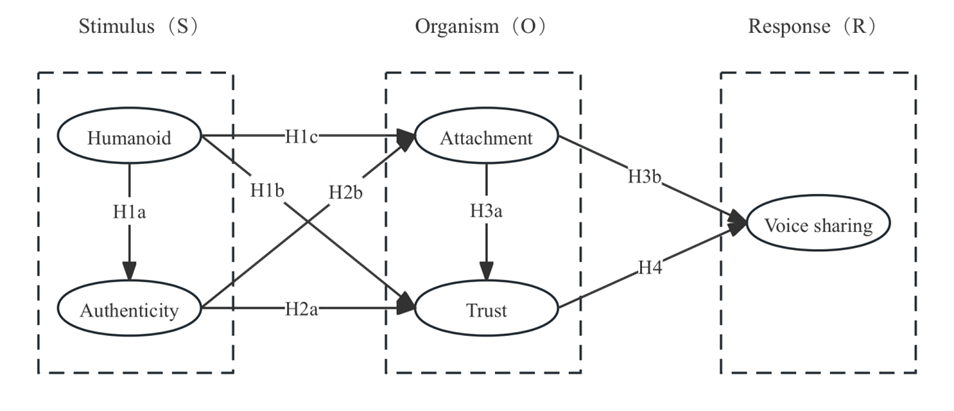
Figure 1: Behavioral mechanism model of voice sharing under human-machine attachment
3. Research method and design
The theoretical model proposed in this paper covers five key variables: humanoid, authenticity, attachment, trust, and voice sharing. In view of the strong subjectivity of these variables and difficult to quantify directly, this paper chooses to use structural equation model (SEM) to analyze the complex influence relationship between them in order to verify the research hypothesis. In the specific implementation process, this paper verifies the above hypothesis about the influencing factors of IBM SPSS 28.0 and AMOS 28.0.
Considering that the five variables in the research model have relatively mature scales as references, the authors made an innovative design of the questionnaire in combination with the unique theme of AI voice cloning technology. The questionnaire underwent two rounds of strict review by experts, which not only included the basic demographic data of the tested subjects, but also included multiple scales. Among them, the humanoid scale is adapted from the research results of Park et al. [90], the authenticity scale refers to Kim et al. [91], the attachment scale is adapted from Han et al. [92], the trust scale is modified according to Chang et al. [93], and the voice sharing scale is adapted from Bock et al. [94]. Each variable in the model included three carefully designed measurement items, plus basic information from manual statistics, and a total of 22 question items were presented in the questionnaire. In order to ensure the validity of the questionnaire, all variables were strictly measured in this paper, especially with the words requiring each respondent to fill in according to the actual situation, and answered using the seven-level Likert scale, from "1 = strongly disagree" to "7 = strongly agree". Before the official release of the questionnaire, 30 users of AI voice cloning technology were first pre-tested, and the defects and feedback in the expression of the items were modified and adjusted, and finally the final version of the questionnaire was formed.
Before the official release of the questionnaire, in order to more accurately locate the target user groups, the questionnaire was widely released to the groups in professional fields such as news communication, broadcasting and hosting, artificial intelligence, as well as the people in related fields such as web celebrity bloggers. In addition, given that AI voice cloning technology is a newly developed technology that is not widely used and understood by the public, a special screening question is set up in the questionnaire: " Have you ever used AI voice cloning technology?”. If you choose "Yes", you can continue to fill in the main part of the questionnaire; if "No", skip the main items to ensure the authenticity and validity of the data collected.
4. Data analysis and model testing
4.1. Descriptive statistical analysis
A total of 600 questionnaires were collected in this round of survey. After excluding 298 invalid questionnaires (i. e., users who chose "not used" the technology), a total of 302 valid samples were obtained, which meant that the users of AI voice cloning technology accounted for 50.33% of the total sample size.
According to the demographic data of the study sample (N=302), there were 160 men, accounting for 52.98%, and 142 women, accounting for 47.02%. The male-female ratio is basically the same, so the sample is somewhat representative. In terms of age distribution, 21-30 years were dominated, accounting for 29.8%, followed by the ages under 20 and 31-40 years. The age distribution is basically in line with the characteristics of the current AI voice cloning technology users, that is, young people are the main users of the technology. In terms of academic qualifications, the undergraduate and junior college respondents dominated, accounting for 35.76% and 37.76%, respectively. From the professional point of view, the use of students is the most prominent, accounting for 42.05%. In addition, when investigating the frequency of AI voice cloning technology, it was found that more respondents chose to "sometimes use", accounting for 47.35%. In terms of the daily use time, the user group of about 2-3 hours is the largest, accounting for 35.43%. The details are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of the demographic characteristics of the survey sample (N=302)
Variable | Option | Frequency | Percentage |
Sex | Man | 160 | 52.98% |
Woman | 142 | 47.02% | |
Age | Under 20 | 79 | 26.16% |
21-30 Years old | 90 | 29.8% | |
31-40 Years old | 70 | 23.18% | |
41-50 Years old | 32 | 10.6% | |
51-60 Years old | 15 | 4.97% | |
61 Years old | 16 | 5.3% | |
Record of formal Schooling | High school and below | 39 | 12.91% |
Specialty (technical secondary school / junior college) | 108 | 35.76% | |
undergraduate course | 113 | 37.42% | |
Graduate student or above | 42 | 13.91% | |
Occupation | student | 127 | 42.05% |
Enterprise staff | 79 | 26.16% | |
professional | 52 | 17.22% | |
Government / public institutions | 26 | 8.61% | |
other | 18 | 5.96% | |
Frequency of use of AI voice cloning technology | Almost not (less than twice a week) | 55 | 18.21% |
Few (2-4 times a week) | 49 | 16.23% | |
Sometimes (5-7 times a week) | 143 | 47.35% | |
Often (once a day) | 32 | 10.6% | |
Always (many times a day) | 23 | 7.62% | |
Each time using the AI voice cloning technology length | Less than 1 hour | 26 | 8.61% |
2-3 Hours | 107 | 35.43% | |
3-4 Hours | 56 | 18.54% | |
5-6 Hours | 92 | 30.46% | |
More than 6 hours | 21 | 6.95% |
4.2. Testing of validity and reliability
To ensure the reliability of the data of this study, the study conducted a rigorous reliability and validity test. Firstly, through reliability analysis, the Cronbach's α coefficient of the obtained samples was between 0.745 and 0.999, both greater than 0.7, indicating the overall design reliability of the questionnaire and high reliability. Second, the KMO value of 0.896 and the p-value of the Bartlett spherical test approached 0.000 were all statistically significant, further demonstrating the reliability of the data. In addition to the reliability analysis, the study also estimated and tested the combined reliability (CR) input. According to the data in Table 2, the CR values are greater than 0.6, and the AVE values are greater than the recommended minimum value of 0.36, which proves that the high reliability of the overall internal quality of the questionnaire is ideal, and that the convergent validity of the structure is acceptable.
Table 2: Model confirmatory factor analysis
Variable | Question item | Factor load | Cronbach’s α | AVE | CR |
Humanoid(H) | H1 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
H2 | 0.999 | ||||
H3 | 1.000 | ||||
Authenticity (R) | R1 | 0.762 | 0.762 | 0.520 | 0.764 |
R2 | 0.680 | ||||
R3 | 0.717 | ||||
Attachment(A) | A1 | 0.841 | 0.800 | 0.586 | 0.805 |
A2 | 0.858 | ||||
A3 | 0.561 | ||||
Trust (T) | T1 | 0.828 | 0.909 | 0.620 | 0.859 |
T2 | 0.907 | ||||
T3 | 0.892 | ||||
Voice Sharing (S) | S1 | 0.700 | 0.745 | 0.520 | 0.684 |
S2 | 0.742 | ||||
S3 | 0.417 |
Differentiation validity is an important measure of the degree of difference between different constructs (or variables). It focuses on whether the correlation between each construct and its corresponding measure items is significantly higher than that between them and the other constructs. According to Table 3, the diagonal is the square root of AVE, and the values (minimum value is 0.721) are greater than the correlation coefficient on the off-diagonal (maximum value is 0.681), indicating that the model has good discriminatory validity.
Table 3: Measures the discriminatory validity of the model
H | AU | A | T | S | |
H | 0.999 | ||||
AU | 0.458 | 0.721 | |||
A | 0.470 | 0.520 | 0.766 | ||
T | 0.422 | 0.544 | 0.681 | 0.787 | |
S | 0.506 | 0.658 | 0.491 | 0.437 | 0.721 |
4.3. Model goodness-of-fit and hypothesis testing
In the structural equation model (SEM), the fit degree index of the model is the key factor in determining the acceptance degree of the research model. In this study, the hypothesis theoretical model is modified according to the modified value and the corresponding model is established, and also makes the parameter estimation by using the maximum likelihood estimation method. According to the data in Table 4, the fitting of the measurement model and the data is shown: χ2/df=2.391<3, RMSEA=0.068<0.08,GFI=0.918>0.9,TLI=0.974>0.9,CFI=0.980>0.9,NFI=0.966>0.9. It shows that the measurement model and data in this study have a good fit index, and have a high data and model fit, which can meet the requirements of subsequent analysis.
Table 4: Overall fit coefficient
Coefficient | Reference value | Fitted value |
x2/df | ≤3.0 | 2.391 |
RMSMA | <0.08 | 0.068 |
GFI | ≥0.9 | 0.918 |
TLI | ≥0.9 | 0.974 |
CFI | ≥0.9 | 0.980 |
NFI | ≥0.9 | 0.966 |
4.4. Pathway analysis of the structural equation model
Structural equation model (SEM) path analysis is a powerful statistical method for exploring the causal relationships between variables. Table 5 shows the results of the model path analysis, and β represents the path coefficient; S. E represents the normalization error; C. R represents the critical proportional value (if CR is greater than ± 1.96, the path coefficient has reached the 0.05 significance level); P represents the likelihood to determine the significance of the path coefficient (* p <0.05, * * p <0.01, * * * p <0.001).
Table 5: Results of the model pathway analysis
Hypothesis | Way | β | SE | CR | P | Assume verification results | ||
H1a | Humanoid | → | Authenticity | 0.519 | 0.046 | 8.344 | *** | support |
H1b | Humanoid | → | Trust | 0.217 | 0.029 | 3.650 | *** | support |
H1c | Humanoid | → | Attachment | -0.152 | 0.045 | -3.129 | ** | support |
H2a | Authenticity | → | Trust | 0.698 | 0.069 | 6.725 | *** | support |
H2b | Authenticity | → | Attachment | -0.577 | 0.169 | -4.299 | *** | support |
H3a | Attachment | → | Trust | 1.469 | 0.394 | 7.030 | *** | support |
H3b | Attachment | → | Voice sharing | 1.881 | 0.407 | 6.044 | *** | support |
H4 | Trust | → | Voice sharing | -1.199 | 0.164 | -5.062 | *** | support |
Under the framework of SOR (Stimulus-organism-response) theory, this study explores how humanity and authenticity as stimulus factors affect individuals' trust and attachment emotions, and eventually form phonological sharing behavior. Based on the pathway analysis in Table 5, the following variable relationships were obtained. First, at the stimulus level, human-like nature was significantly positively correlated with authenticity (β =0.519, p <0.001), attachment (β =0.217, p <0.001), and negatively associated with trust (β = -0.152, p <0.01), assuming Hla, H1b, and H1c were supported. Authenticity was significantly positively associated with attachment (β =0.698, p <0.001), and significantly negatively associated with trust (β = -0.577, p <0.001), indicating that the assumptions H2a and H2b hold. Secondly, at the level of organism and response, attachment and trust (β =1.469, p <0.001), and voice sharing (β =1.881, p <0.001) were significantly positively related. Trust and voice sharing were significantly negatively related (β = -1.199, p <0.001), assuming that H3a, H3b and H4 were true. The path coefficient is shown in Figure 2.
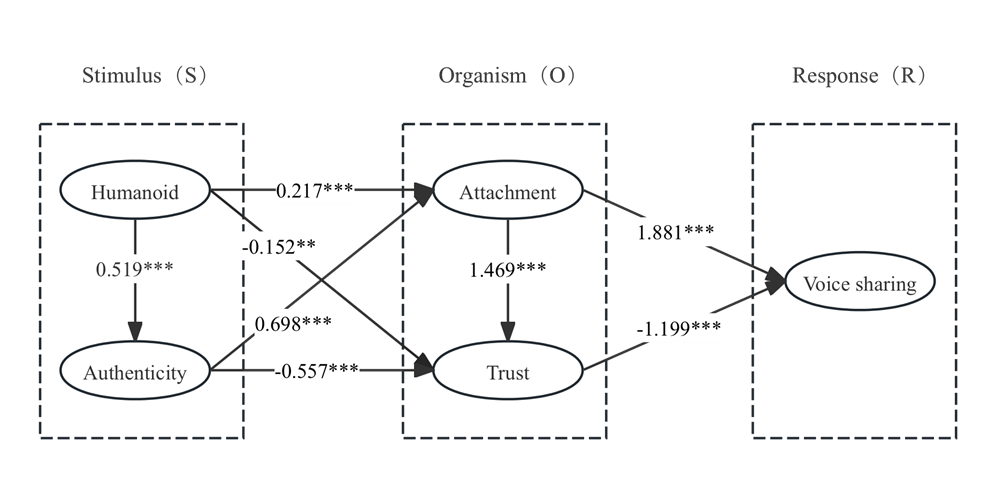
Figure 2: Path analysis diagram of voice sharing behavior mechanism model under man-machine attachment
4.5. Mediation effect detection
The study used structural equation model (SEM) and Bootstrap method for mediation effect analysis, repeated sampling 5000 times with 95% confidence interval, and explored the complex relationships between variables, including direct effects, indirect effects and relationships between latent variables. The results in Table 6 show that the confidence intervals for all effects contain no 0, proving that the mediation effect exists in this paper, namely, humanity (Effect = 0.7454, p <0.001) and authenticity (Effect=0.6874, p <0.001) have a significant mediation effect on voice sharing.
Table 6: Bootstrap Results of mediation effect test (N=302)
Intermediary path | Direct effect | Indirect effect path | Indigo effect | The 95% confidence interval | Gross effect | |
LLCI | ULCI | |||||
Humanoid→Voice sharing | 0.2655 | Humanoid→Attachment→Voice sharing | 0.1149 | 0.0608 | 0.1730 | 0.7454 |
0.2570 | Humanoid→Attachment→Trust→Voice sharing | 0.1234 | 0.0645 | 0.1852 | ||
0.3004 | Humanoid→Trust→Voice sharing | 0.0800 | 0.0357 | 0.1319 | ||
0.1511 | Humanoid→Authenticity→Attachment→Voice sharing | 0.2293 | 0.1477 | 0.3107 | ||
0.1588 | Humanoid→Authenticity→Trust→Voice sharing | 0.2216 | 0.1379 | 0.3054 | ||
0.1491 | Humanoid→Authenticity→Attachment→Trust→Voice sharing | 0.2313 | 0.1457 | 0.3160 | ||
Authenticity →voice sharing | 0.5995 | Authenticity→Attachment→Voice sharing | 0.0879 | 0.0383 | 0.1463 | 0.6874 |
0.5892 | Authenticity→Attachment→Trust→Voice sharing | 0.0982 | 0.0453 | 0.1565 | ||
0.6228 | Authenticity→Trust→Voice sharing | 0.0646 | 0.0224 | 0.1130 | ||
5. Conclusion analysis
Based on the SOR (stimulus-organism-response) theoretical model framework, this study deeply explores the influence of AI voice cloning technology on the user's psychological behavior transition, thus proposing a dual-action model. This model, starting from the unique perspective of user attachment emotion, provides an important theoretical reference for understanding voice sharing behavior in the context of human-computer attachment. By the structural equation model, this study concludes the following conclusions:
5.1. Results analysis
5.1.1. Stimulus level relationship
The results show that there is a significant positive correlation between the human-like characteristics of AI voice cloning technology and attachment emotions, which is consistent with the study by Rosenthal-von der Putten et al., who believe that people are easy to form emotional attachment to artificial organisms [95]. Similarly, the authenticity characteristics is also positively associated with the presentation of attachment emotions, which is consistent with the study of Fu that authenticity is a prerequisite for loyalty [96]. AI voice cloning technology can accurately imitate and copy the sound characteristics of specific individuals, so that users can feel familiar and bound in the process of human-computer interaction, and then develop attachment to the technology. Attachment has become an important driving force to stimulate users' voice sharing behavior.
The results showed that there was a significant negative relationship between humanity, authenticity and trust. The conclusion seems contrary to common sense, often suggesting that more "human" or "real" technologies should be easier to gain the trust of their users. However, users still express deep concerns about the privacy, security and information control of the technology of highly humanoid and real AI technologies. As Osorio pointed out, he believes that the brand management of technology should be more cautious when deciding when to cultivate authenticity and when to choose creativity [97], which means that relying on humanity and authenticity alone is not enough to guarantee users' attachment and trust in technology. Future technologies should fully consider user needs and concerns to develop effective strategies to promote the generation of shared behaviors among users.
5.1.2. Organism and response level relationship
Attachment is positively correlated with trust and voice sharing. When users establish a deep attachment relationship with AI, they expect to meet their own psychological needs through communication and cooperation with them, and even build a romantic lover relationship between man and machine. This view is supported by Singh empirical research, the study points out that the user of virtual intelligent assistant (VAI) trust is an important predictor of their emotional attachment with VAI, and consumer self-disclosure behavior plays a regulatory role [98], shows that when the user is willing to disclose their own more information to AI, man-machine emotional attachment has been further sublimation. At the same time, in the deep interweaving of human-machine emotion, users will not only take the initiative to take voice sharing behavior, but also actively promote the expansion and popularization of the technology.
Trust and voice sharing present a negative correlation. Voice sharing often requires users to expose their personal information and communication content to third-party platforms, which naturally raises concerns about privacy and security. When users perceive that their information is controlled by the platform, they may have resistance and avoidance, leading to a continuous reduction in the willingness to share voice. This finding echoes studies by Wirtz et al [99] and Lu et al [100], who reveal the importance of users distinguishing different sources of credibility in virtual interactions. However, with the evolution of human-computer interaction and the convergence of rich media elements, the relevant negative impact is expected to gradually weaken. Technological progress can not only provide better privacy protection measures for users, but also is expected to promote the gradual improvement of users' voice sharing behavior.
5.1.3. Mediation effect analysis
The results show that humanity and authenticity not only directly have a significant impact on voice sharing behavior, but also affect users' voice sharing behavior indirectly by affecting their attachment and trust. The findings highlight the central role of humanoid nature in influencing voice-sharing behavior. At the same time, users' attachment and trust are interrelated and coupled to each other, and they constitute an important driving force for the development of voice sharing behavior. Attachment creates a close emotional link between users and technology, and also provides strong support for the formation of human-machine trust; which stimulates the willingness of users to participate in voice sharing behavior. The conclusion also coincides with the study of Tsai et al., who emphasized that the interpersonal factors of supersocial interaction and perceptual dialogue play a mediating role in enhancing consumer participation in human-computer interaction [101], indicating that technology not only attracts users through function and performance, but also its social attributes and interpersonal interaction ability. In the future, in the design and development of human-computer interaction technology, more attention should be paid to the human-like technology, authenticity characteristics and the establishment of the emotional bond and trust relationship between man and machine.
5.2. Path discussion
5.2.1. Eliminate estrangement, beware of "human-machine lovelorn" phenomenon
With the vigorous rise of digital communication mode, the emotional gap between people is undoubtedly further deepened. In the face of emotional setbacks and social fears in life, people are increasingly inclined to seek emotional talk to AI voice functions. This phenomenon has brought dual impact: on the one hand, the sense of reality, presence and romance created by AI voice cloning technology may induce human beings to rely too much on the communication with them, thus gradually weakening the emotional connection with real human; on the other hand, as the emerging and unpopularized technology, the technical complexity and human adaptability still differ different, the panic caused by technological change may further widen the gap between man and machine, this paper is vividly called "man-machine lovelorn".
In the era of intelligence, we should accelerate the education popularization and practical application of new technologies, improve users' rational and critical thinking ability of AI voice cloning technology, avoid the psychological gap due to over-dependence, and clarify the relationship between self and AI, especially whether as a substitute for real lovers. At the same time, system designers should establish a perfect feedback and insight mechanism to make it more suitable with human voice habits and thinking mode. In addition, we should actively maintain and expand the social relationship with real human beings, because good interpersonal relationship is the source of health and happiness, and deep communication with external people can make people feel rich and full of their own life, which cannot be replaced by any technology.
5.2.2. Build trust and walk out of the dilemma of "man-machine sadomasochism"
When building the trust relationship between man and machine, there will always be multiple challenges such as data risk, technical ethics, and algorithm black box. So far, trust still cannot be established completely by relying on artificial intelligence itself, and the unilateral efforts of human beings is easy to lead to the imbalance of human-machine relationship. Once the "sunk cost" intensifies, it may cause a series of problems such as cyber sadistic love and social withdrawal, casting a shadow over the seemingly dreamy love between man and machine.
In order to deal with such problems, the optimization and upgrading of the internal algorithm and model of AI voice cloning technology should be enhanced to ensure the stability and accuracy of the technology and avoid voice errors and decoding. At the same time, the system should have adaptive ability, timely response to user language, page interactive feedback, not only to determine the listening experience and voice quality, also want to the user's expression, customized degree and adapt to the scene, to reduce the user in voice sharing by receiving negative feedback of "loneliness". On this basis, gradually enhance the reliability of the system and dependence, whether for professional voice users get auditory enjoyment, or make voice disorder perception emotional flow, are technology should achieve the goal, meet the expectations and needs of different users, and in the value trust, man-machine gradually into intimate community.
5.2.3. Return to the main body and restart the human-machine attachment relationship
With the development and popularization of artificial intelligence, the relationship between man-machine is changing quietly. Man, once seen as the master of AI, has gradually turned into a partner and a partner with AI. However, this technological change is not without challenges. The ethical issues it brings, such as data hegemony and algorithmic dictatorship, are like an undercurrent hidden under a calm sea, which can cause unpredictable "disasters" at any time. This makes us deeply aware that the automatic decision-making of AI voice function cannot exist in isolation from human ethical guidance.
Return to subject consciousness, does not mean that promoting personal centralism, but to seek the perfect integration between "subjectivity" and AI "intelligence", realize a new value beyond the two alone, this concept and our country in the global artificial intelligence governance initiative advocated by the "people-oriented" thought is closely linked. In the new era of human-machine collaboration, human beings need to re-examine and emphasize their own subject value, keep a clear mind and a firm position, and enhance their ethical awareness and intelligent literacy. At this time, the true and false discrimination of the love between man and machine will become no longer important, but more important is the self-awareness and growth of human beings born from love. It is believed that this will be a profound "two-way rush" between human beings and AI voice cloning technology, working together to create a better future of the voice society.
6. Prospect and limitation
From the unique perspective of human-machine attachment, this study gives new insights to the sharing behavior of AI voice cloning technology, and also provides valuable reference for the promotion and marketing strategy of new technologies. Compared with the traditional technology sharing mode, the sharing behavior of AI voice cloning technology from the perspective of human-machine attachment is more driven by emotion. This driving force comes not only from the realism and flexibility of the "sound" given by technology, but deeper, from the deep and unique attachment links established between man and machine.
Looking ahead, the communication between people and AI is expected to be an important complement to interpersonal communication, but that does not mean that "we expect less from each other". Instead, we should look at technology in a more sober and prudent manner, and to shape and apply it in a way that respects ourselves and values humanity. When we talk to AI voice cloning technology, we should make sure that the technology is truly "for our use" and becomes an "extension of ourselves", " rather than replacing or weakening our real existence. At the same time, we are also full of expectations, hoping that this "rose" of emotion between man and machine can blossom more gorgeous and benefit a wider audience.
In fact, the phenomenon of "voice sharing" in this study is not only a sharing of technology, but also a reflection of "spiritual resonance" and "soul resonance", which is similar to the process of choosing our future "partner" in real life, which involves deep emotional connection and resonance. Therefore, we have reason to believe that in the future of technological development, the attachment between man and machine will play an increasingly important role, bringing more warmth and color to life.
This study also has some limitations. First, based on the S-O-R perspective, without considering the effects of non-cognitive factors such as personal habits and ethics, future research can focus on this to refine the model. Secondly, the questionnaire survey may not be able to comprehensively summarize the phenomenon. The future research can supplement the qualitative research methods, such as in-depth interview or observation methods, to improve the objectivity and scientificity of the research. Finally, the data of this study are cross-sectional, which cannot demonstrate the dynamic process of variables, and future studies need to add longitudinal design to reveal the dynamic evolution of behavior.
References
[1]. Kozielski, R., Mazurek, G., Miotk, A., & Maciorowski, A.(2017).E-commerce and social media indicators.In Mastering market analytics: Business metrics–Practice and application (pp.313-406).Emerald Publishing Limited.
[2]. Gupta, R., Kumar, P., Swain, P.K., Kumar, D., & Garg, N.(2024, April).Neural Voice Replication: Multispeaker Text-to-voice Synthesizer.In 2024 International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computer Science for Interdisciplinary Applications (ICETCS) (pp.1-6).IEEE.
[3]. Karle, R.(2017).Leveraging Sound, Space and Visual Art in an Installation.
[4]. Teng, C.I.(2010).Customization, immersion satisfaction, and online gamer loyalty.Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1547-1554.
[5]. Khan, N.F., Hemanth, N., Goyal, N., Pranav, K.R., & Agarwal, P.(2024, April).Call Translator with Voice Cloning Using Transformers.In 2024 IEEE 9th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT) (pp.1-6).IEEE.
[6]. Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., & Palaniswami, M.(2013, September).Internet of things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions.Future Generation Computer Systems, 29(7), 1645–1660.
[7]. Rouse, W.B., & Cody, W.J.(1987).On the design of man-machine systems: Principles, practices, and prospects.IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 20(5), 281-288.
[8]. Kostov, V., & Fukuda, S.(2001, September).Development of man-machine interfaces based on user preferences.In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications (CCA'01)(Cat.No.01CH37204) (pp.1124-1128).IEEE.
[9]. Gillath, O., Ai, T., Branicky, M.S., Keshmiri, S., Davison, R.B., & Spaulding, R.(2021).Attachment and trust in artificial intelligence.Computers in Human Behavior, 115, 106607.
[10]. Guerreiro, J., & Loureiro, S.M.C.(2023).I am attracted to my cool smart assistant!analyzing attachment-aversion in AI-human relationships.Journal of Business Research, 161, 113863.
[11]. Razak, N.A., Pangil, F., Zin, M.L.M., Yunus, N.A.M., & Asnawi, N.H.(2016).Theories of knowledge sharing behavior in business strategy.Procedia Economics and Finance, 37, 545-553.
[12]. Yu, T.K., Lu, L.C., & Liu, T.F.(2010).Exploring factors that influence knowledge sharing behavior via weblogs.Computers in human behavior, 26(1), 32-41.
[13]. Slade, A.(1999).Attachment theory and research: Implications for the theory and practice of individual psychotherapy with adults.
[14]. Flemisch, F., Abbink, D.A., Itoh, M., Pacaux-Lemoine, M.P., & Weßel, G.(2019).Joining the blunt and the pointy end of the spear: towards a common framework of joint action, human–machine cooperation, cooperative guidance and control, shared, traded and supervisory control.Cognition, Technology & Work, 21, 555-568.
[15]. Mehrabian, A., & Russell, J.A.(1974).An approach to environmental psychology Cambridge.MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 8.
[16]. Chen, S.C., Chung, K.C., & Tsai, M.Y.(2019).How to achieve sustainable development of mobile payment through customer satisfaction—the SOR model.Sustainability, 11(22), 6314.
[17]. Peng, C., & Kim, Y.G.(2014).Application of the stimuli-organism-response (SOR) framework to online shop** behavior.Journal of Internet Commerce, 13(3-4), 159-176.
[18]. Pandita, S., Mishra, H.G., & Chib, S.(2021).Psychological impact of covid-19 crises on students through the lens of Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) model.Children and Youth Services Review, 120, 105783.
[19]. Chan, T.K., Cheung, C.M., & Lee, Z.W.(2017).The state of online impulse-buying research: A literature analysis.Information & Management, 54(2), 204-217.
[20]. Zheng, X., Men, J., Yang, F., & Gong, X.(2019).Understanding impulse buying in mobile commerce: An investigation into hedonic and utilitarian browsing.International journal of information management, 48, 151-160.
[21]. Basha, N.K., Aw, E.C.X., & Chuah, S.H.W.(2022).Are we so over smartwatches?Or can technology, fashion, and psychographic attributes sustain smartwatch usage?.Technology in Society, 69, 101952.
[22]. Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y.(2018).Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of Stimulus-Organism-Response.International Journal of Information Management, 39, 169-185.
[23]. Robert, D., & John, R.(1982).Store atmosphere: an environmental psychology approach.Journal of retailing, 58(1), 34-57.
[24]. Bitner, M.J.(1992).Servicescapes: The impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees.Journal of marketing, 56(2), 57-71.
[25]. Jeong, J., Kim, D., Li, X., Li, Q., Choi, I., & Kim, J.(2022).An empirical investigation of personalized recommendation and reward effect on customer behavior: a stimulus–organism–response (SOR) model perspective.Sustainability, 14(22), 15369.
[26]. Cheng, W., Tsai, H., Chuang, H., Lin, P., & Ho, T.(2020).How can emerging event sustainably develop in the tourism industry?From the perspective of the SOR model on a two-year empirical study.Sustainability, 12(23), 10075.
[27]. Chen, Z., King, B., & Suntikul, W.(2019).Festivalscapes and the visitor experience: An application of the stimulus organism response approach.International Journal of Tourism Research, 21(6), 758-771.
[28]. Fink, J.(2012).Anthropomorphism and human likeness in the design of robots and human-robot interaction.In Social Robotics: 4th International Conference, ICSR 2012, Chengdu, China, October 29-31, 2012. Proceedings 4 (pp.199-208).Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
[29]. Dafoe, A., Bachrach, Y., Hadfield, G., Horvitz, E., Larson, K., & Graepel, T.(2021).Cooperative AI: machines must learn to find common ground.
[30]. Duffy, B.R.(2002).Anthropomorphism and robotics.The society for the study of artificial intelligence and the simulation of behaviour, 20.
[31]. Sarker, M.K., **e, N., Doran, D., Raymer, M., & Hitzler, P.(2017).Explaining trained neural networks with semantic web technologies: First steps.arxiv preprint arxiv:1710.04324.
[32]. Lowry, M., Bajwa, A.R., Pressburger, T., Sweet, A., Dalal, M., Fry, C., ...& Mahadevan, N.(2018).Design Considerations for a Variable Autonomy Exeuctive for UAS in the NAS.In 2018 AIAA Information Systems-AIAA Infotech@ Aerospace (p.1633).
[33]. Goodman, P.H., Zou, Q., & Dascalu, S.M.(2008).Framework and implications of virtual neurorobotics.Frontiers in neuroscience, 2, 255.
[34]. Darling, K.(2016).Extending legal protection to social robots: The effects of anthropomorphism, empathy, and violent behavior towards robotic objects.In Robot law (pp.213-232).Edward Elgar Publishing.
[35]. Robins, B., Dautenhahn, K., Te Boekhorst, R., and Billard, A.(2005).Robotic assistants in therapy and education of children with autism: can a small humanoid robot help encourage social interaction skills?Univ Access Inf.Soc.4, 105–120.
[36]. Romero, O.J., Zhao, R., & Cassell, J.(2017, August).Cognitive-Inspired Conversational-Strategy Reasoner for Socially-Aware Agents.In IJCAI (pp.3807-3813).
[37]. Tulk Jesso, S., Kennedy, W.G., & Wiese, E.(2020).Behavioral Cues of Humanness in Complex Environments: How People Engage With Human and Artificially Intelligent Agents in a Multiplayer Videogame.Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 7, 531805.
[38]. Sugiyama, S., & Vincent, J.(2013).Social robots and emotion: Transcending the boundary between humans and ICTs.Intervalla, 1(1), 1-6.
[39]. Califf, C.B., Brooks, S., & Longstreet, P.(2020).Human-like and system-like trust in the sharing economy: The role of context and humanness.Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 154, 119968.
[40]. Tripp, J., McKnight, H., & Lankton, N.K.(2011).Degrees of humanness in technology: what type of trust matters?.
[41]. Cappannelli, G., & Cappannelli, S.C.(2004).Authenticity: Simple strategies for greater meaning and purpose at work and at home.Emmis Books.
[42]. Pandey, P., & Rai, A.K.(2024).Analytical modeling of perceived authenticity in AI assistants: application of PLS-predict algorithm and importance-performance map analysis.South Asian Journal of Business Studies.
[43]. Beattie, J., & Fernley, L.(2014).The Age of Authenticity: An Executive Summary.Cohn & Wolfe: New York, NY, USA.
[44]. Moulard, J.G., Raggio, R.D., & Folse, J.A.G.(2016).Brand authenticity: Testing the antecedents and outcomes of brand management's passion for its products.Psychology & marketing, 33(6), 421-436.
[45]. Morhart, F., Malär, L., Guèvremont, A., Girardin, F., & Grohmann, B.(2015).Brand authenticity: An integrative framework and measurement scale.Journal of consumer psychology, 25(2), 200-218.
[46]. Park, J., Hong, E., & Park, Y.N.(2023).Toward a new business model of retail industry: The role of brand experience and brand authenticity.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 74, 103426.
[47]. Kumar, V., & Kaushal, V.(2021).Perceived brand authenticity and social exclusion as drivers of psychological brand ownership.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 61, 102579.
[48]. Peterson, C.(2004).Character strengths and virtues: A handbook and classification.American Psychological Association, 25.
[49]. Lee, G., & Kim, H.Y.(2024).Human vs.AI: The battle for authenticity in fashion design and consumer response.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 77, 103690.
[50]. Gutkind, L.(Ed.).(2008).Keep it real: Everything you need to know about researching and writing creative nonfiction.WW Norton & Company.
[51]. Nader, K., Toprac, P., Scott, S., & Baker, S.(2024).Public understanding of artificial intelligence through entertainment media.AI & society, 39(2), 713-726.
[52]. Turkle, S.(2007).Authenticity in the age of digital companions.Interaction studies, 8(3), 501-517.
[53]. Van Dijck, J.(2014).Datafication, dataism and dataveillance: Big Data between scientific paradigm and ideology.Surveillance & society, 12(2), 197-208.
[54]. Haggart, B.(2019).The age of surveillance capitalism: The fight for a human future at the new frontier of power, S.Zuboff (2018).journal of digital media & policy, 10(2), 229-243.
[55]. Beerends, S., & Aydin, C.(2024).Negotiating the authenticity of AI: how the discourse on AI rejects human indeterminacy.AI & SOCIETY, 1-14.
[56]. Lopez, F.G., & Rice, K.G.(2006).Preliminary development and validation of a measure of relationship authenticity.Journal of Counseling Psychology, 53(3), 362.
[57]. Bowlby, J.(1982).Attachment and loss: retrospect and prospect.American journal of Orthopsychiatry, 52(4), 664.
[58]. Ainsworth, M.D.S., Bell, S.M., & Stayton, D.J.(2013).Infant–Mother Attachment and Social Development:‘Socialisation'as a Product of Reciprocal Responsiveness to Signals.In Becoming a person (pp.30-55).Routledge.
[59]. Baumeister, R.F., & Leary, M.R.(2017).The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation.Interpersonal development, 57-89.
[60]. Ryan, R.M., & Deci, E.L.(2000).Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new directions.Contemporary educational psychology, 25(1), 54-67.
[61]. Birnbaum, G.E., Mizrahi, M., Hoffman, G., Reis, H.T., Finkel, E.J., & Sass, O.(2016).What robots can teach us about intimacy: The reassuring effects of robot responsiveness to human disclosure.Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 416-423.
[62]. Rever, G.W.(1972).Attachment and Loss.Vol.1. Attachment.
[63]. Hiolle, A., Canamero, L., Davila-Ross, M., & Bard, K.A.(2012).Eliciting caregiving behavior in dyadic human-robot attachment-like interactions.ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems (TiiS), 2(1), 1-24.
[64]. ikulincer, M.(1998).Attachment working models and the sense of trust: An exploration of interaction goals and affect regulation.Journal of personality and social psychology, 74(5), 1209.
[65]. You, S.& Robert, L.P.(2018).Emotional Attachment, Performance, and Viability in Teams Collaborating with Embodied Physical Action (EPA) Robots, Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 19(5), pp.377-407.
[66]. Pelau, C., Volkmann, C., Barbul, M., & Bojescu, I.(2023).The Role of Attachment in Improving Consumer-AI Interactions.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence (Vol.17, No.1, pp.1075-1084).
[67]. Guerreiro, J., & Loureiro, S.M.C.(2023).I am attracted to my cool smart assistant!analyzing attachment-aversion in AI-human relationships.Journal of Business Research, 161, 113863.
[68]. Valsesia, F., Nunes, J.C., & Ordanini, A.(2016).What wins awards is not always what I buy: How creative control affects authenticity and thus recognition (but not liking).Journal of Consumer Research, 42(6), 897-914.
[69]. Castelo, N., Bos, M.W., & Lehmann, D.R.(2019).Task-dependent algorithm aversion.Journal of Marketing Research, 56(5), 809-825.
[70]. Hoff, K.A., & Bashir, M.(2015).Trust in automation: Integrating empirical evidence on factors that influence trust.Human factors, 57(3), 407-434.
[71]. Oldmeadow, J.A., Quinn, S., & Kowert, R.(2013).Attachment style, social skills, and Facebook use amongst adults.Computers in human behavior, 29(3), 1142-1149.
[72]. Söllner, M., & Leimeister, J.M.(2013).What we really know about antecedents of trust: A critical review of the empirical information systems literature on trust.Psychology of Trust: New Research, D.Gefen, Verlag/Publisher: Nova Science Publishers.
[73]. Chen, Y.H., Chien, S.H., Wu, J.J., & Tsai, P.Y.(2010).Impact of signals and experience on trust and trusting behavior.Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 13(5), 539-546.
[74]. Prieto, A.G.(2009).From conceptual to perceptual reality: trust in digital repositories.Library Review, 58(8), 593-606.
[75]. Esmaeilzadeh, P., Mirzaei, T., & Dharanikota, S.(2021).Patients’perceptions toward human–artificial intelligence interaction in health care: experimental study.Journal of medical Internet research, 23(11), e25856.
[76]. Chao, P., Fu, H.P., & Lu, I.Y.(2007).Strengthening the quality–loyalty linkage: The role of customer orientation and interpersonal relationship.The Service Industries Journal, 27(4), 471-494.
[77]. Hu, P., & Lu, Y.(2021).Dual humanness and trust in conversational AI: A person-centered approach.Computers in Human Behavior, 119, 106727.
[78]. Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y.(2018).Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of Stimulus-Organism-Response.International Journal of Information Management, 39, 169-185.
[79]. Deriu, V., Pozharliev, R., & De Angelis, M.(2024).How trust and attachment styles jointly shape job candidates’ AI receptivity.Journal of Business Research, 179, 114717.
[80]. Buckley, S.B., & Jakovljevic, M.(2012).Knowledge Management Innovations for Interdisciplinary Education: Organizational Applications.Pennsylvania: IGI Global, 207-232.
[81]. Ma, W.W., & Chan, A.(2014).Knowledge sharing and social media: Altruism, perceived online attachment motivation, and perceived online relationship commitment.Computers in human behavior, 39, 51-58.
[82]. Olan, F., Suklan, J., Arakpogun, E.O., & Robson, A.(2021).Advancing consumer behavior: The role of artificial intelligence technologies and knowledge sharing.IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management.
[83]. Cohen, W.M., & Levinthal, D.A.(1990).Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation.Administrative science quarterly, 35(1), 128-152.
[84]. Bommer, W.H., Miles, E.W., & Grover, S.L.(2003).Does one good turn deserve another?Coworker influences on employee citizenship.Journal of Organizational Behavior, 24(2), 181–196.
[85]. Cabrera, A., & Cabrera, E.F.(2002).Knowledge-sharing dilemmas.Organization Studies, 23(5), 687–1710.
[86]. Evangelista, E., Kale, R., McCutcheon, D., Rameau, A., Gelbard, A., Powell, M., ...& Bensoussan, Y.(2024).Current practices in voice data collection and limitations to voice AI research: a national survey.The Laryngoscope, 134(3), 1333-1339.
[87]. Lefkeli, D., Karataş, M., & Gürhan-Canli, Z.(2024).Sharing information with AI (versus a human) impairs brand trust: The role of audience size inferences and sense of exploitation.International Journal of Research in Marketing, 41(1), 138-155.
[88]. Zierau, N., Flock, K., Janson, A., Söllner, M., & Leimeister, J.M.(2021).The influence of AI-based chatbots and their design on users’ trust and information sharing in online loan applications.In Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS).-Koloa (Hawaii), USA.
[89]. Malik, A., De Silva, M.T., Budhwar, P., & Srikanth, N.R.(2021).Elevating talents' experience through innovative artificial intelligence-mediated knowledge sharing: Evidence from an IT-multinational enterprise.Journal of International Management, 27(4), 100871.
[90]. Park, J., Woo, S.E., & Kim, J.(2024).Attitudes towards artificial intelligence at work: Scale development and validation.Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology.
[91]. Kim, M.J., Lee, C.K., & Jung, T.(2020).Exploring consumer behavior in virtual reality tourism using an extended stimulus-organism-response model.Journal of travel research, 59(1), 69-89.
[92]. Han, S., Kim, K.J., & Kim, J.H.(2017).Understanding nomophobia: Structural equation modeling and semantic network analysis of smartphone separation anxiety.Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 20(7), 419-427.
[93]. Chang, H.H., & Chen, S.W.(2008).The impact of online store environment cues on purchase intention: Trust and perceived risk as a mediator.Online information review, 32(6), 818-841.
[94]. Bock, G.W., Zmud, R.W., Kim, Y.G., & Lee, J.N.(2005).Behavioral intention formation in knowledge sharing: Examining the roles of extrinsic motivators, social-psychological forces, and organizational climate.MIS quarterly, 29(1), 87-111.
[95]. Rosenthal-von der Pütten, A.M., Krämer, N.C., Hoffmann, L., Sobieraj, S., & Eimler, S.C.(2013).An experimental study on emotional reactions towards a robot.International Journal of Social Robotics, 5, 17-34.
[96]. Fu, X.(2019).Existential authenticity and destination loyalty: Evidence from heritage tourists.Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 12, 84-94.
[97]. Osorio, M.L., Centeno, E., & Cambra-Fierro, J.(2023).An empirical examination of human brand authenticity as a driver of brand love.Journal of Business Research, 165, 114059.
[98]. Singh, R.(2022).“Hey Alexa–order groceries for me”–the effect of consumer–VAI emotional attachment on satisfaction and repurchase intention.European Journal of Marketing, 56(6), 1684-1720.
[99]. Wirtz, J., Patterson, P.G., Kunz, W.H., Gruber, T., Lu, V.N., Paluch, S., & Martins, A.(2018).Brave new world: Service robots in the frontline.Journal of Service Management, 29(5), 907–931.
[100]. Lu, V.N., Wirtz, J., Kunz, W.H., Paluch, S., Gruber, T., Martins, A., & Patterson, P.G.(2020).Service robots, customers and service employees: What can we learn from the academic literature and where are the gaps?Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 30, 361–391.
[101]. Tsai, W.H.S., Liu, Y., & Chuan, C.H.(2021).How chatbots' social presence communication enhances consumer engagement: the mediating role of parasocial interaction and dialogue.Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 15(3), 460-482.
Cite this article
Meng,K. (2024). AI Voice Cloning Technology under Human-machine Attachment Shared Mechanism Behavior Research. Communications in Humanities Research,36,150-167.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICADSS 2024 Workshop: International Forum on Intelligent Communication and Media Transformation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Kozielski, R., Mazurek, G., Miotk, A., & Maciorowski, A.(2017).E-commerce and social media indicators.In Mastering market analytics: Business metrics–Practice and application (pp.313-406).Emerald Publishing Limited.
[2]. Gupta, R., Kumar, P., Swain, P.K., Kumar, D., & Garg, N.(2024, April).Neural Voice Replication: Multispeaker Text-to-voice Synthesizer.In 2024 International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computer Science for Interdisciplinary Applications (ICETCS) (pp.1-6).IEEE.
[3]. Karle, R.(2017).Leveraging Sound, Space and Visual Art in an Installation.
[4]. Teng, C.I.(2010).Customization, immersion satisfaction, and online gamer loyalty.Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1547-1554.
[5]. Khan, N.F., Hemanth, N., Goyal, N., Pranav, K.R., & Agarwal, P.(2024, April).Call Translator with Voice Cloning Using Transformers.In 2024 IEEE 9th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT) (pp.1-6).IEEE.
[6]. Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., & Palaniswami, M.(2013, September).Internet of things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions.Future Generation Computer Systems, 29(7), 1645–1660.
[7]. Rouse, W.B., & Cody, W.J.(1987).On the design of man-machine systems: Principles, practices, and prospects.IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 20(5), 281-288.
[8]. Kostov, V., & Fukuda, S.(2001, September).Development of man-machine interfaces based on user preferences.In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications (CCA'01)(Cat.No.01CH37204) (pp.1124-1128).IEEE.
[9]. Gillath, O., Ai, T., Branicky, M.S., Keshmiri, S., Davison, R.B., & Spaulding, R.(2021).Attachment and trust in artificial intelligence.Computers in Human Behavior, 115, 106607.
[10]. Guerreiro, J., & Loureiro, S.M.C.(2023).I am attracted to my cool smart assistant!analyzing attachment-aversion in AI-human relationships.Journal of Business Research, 161, 113863.
[11]. Razak, N.A., Pangil, F., Zin, M.L.M., Yunus, N.A.M., & Asnawi, N.H.(2016).Theories of knowledge sharing behavior in business strategy.Procedia Economics and Finance, 37, 545-553.
[12]. Yu, T.K., Lu, L.C., & Liu, T.F.(2010).Exploring factors that influence knowledge sharing behavior via weblogs.Computers in human behavior, 26(1), 32-41.
[13]. Slade, A.(1999).Attachment theory and research: Implications for the theory and practice of individual psychotherapy with adults.
[14]. Flemisch, F., Abbink, D.A., Itoh, M., Pacaux-Lemoine, M.P., & Weßel, G.(2019).Joining the blunt and the pointy end of the spear: towards a common framework of joint action, human–machine cooperation, cooperative guidance and control, shared, traded and supervisory control.Cognition, Technology & Work, 21, 555-568.
[15]. Mehrabian, A., & Russell, J.A.(1974).An approach to environmental psychology Cambridge.MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 8.
[16]. Chen, S.C., Chung, K.C., & Tsai, M.Y.(2019).How to achieve sustainable development of mobile payment through customer satisfaction—the SOR model.Sustainability, 11(22), 6314.
[17]. Peng, C., & Kim, Y.G.(2014).Application of the stimuli-organism-response (SOR) framework to online shop** behavior.Journal of Internet Commerce, 13(3-4), 159-176.
[18]. Pandita, S., Mishra, H.G., & Chib, S.(2021).Psychological impact of covid-19 crises on students through the lens of Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) model.Children and Youth Services Review, 120, 105783.
[19]. Chan, T.K., Cheung, C.M., & Lee, Z.W.(2017).The state of online impulse-buying research: A literature analysis.Information & Management, 54(2), 204-217.
[20]. Zheng, X., Men, J., Yang, F., & Gong, X.(2019).Understanding impulse buying in mobile commerce: An investigation into hedonic and utilitarian browsing.International journal of information management, 48, 151-160.
[21]. Basha, N.K., Aw, E.C.X., & Chuah, S.H.W.(2022).Are we so over smartwatches?Or can technology, fashion, and psychographic attributes sustain smartwatch usage?.Technology in Society, 69, 101952.
[22]. Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y.(2018).Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of Stimulus-Organism-Response.International Journal of Information Management, 39, 169-185.
[23]. Robert, D., & John, R.(1982).Store atmosphere: an environmental psychology approach.Journal of retailing, 58(1), 34-57.
[24]. Bitner, M.J.(1992).Servicescapes: The impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees.Journal of marketing, 56(2), 57-71.
[25]. Jeong, J., Kim, D., Li, X., Li, Q., Choi, I., & Kim, J.(2022).An empirical investigation of personalized recommendation and reward effect on customer behavior: a stimulus–organism–response (SOR) model perspective.Sustainability, 14(22), 15369.
[26]. Cheng, W., Tsai, H., Chuang, H., Lin, P., & Ho, T.(2020).How can emerging event sustainably develop in the tourism industry?From the perspective of the SOR model on a two-year empirical study.Sustainability, 12(23), 10075.
[27]. Chen, Z., King, B., & Suntikul, W.(2019).Festivalscapes and the visitor experience: An application of the stimulus organism response approach.International Journal of Tourism Research, 21(6), 758-771.
[28]. Fink, J.(2012).Anthropomorphism and human likeness in the design of robots and human-robot interaction.In Social Robotics: 4th International Conference, ICSR 2012, Chengdu, China, October 29-31, 2012. Proceedings 4 (pp.199-208).Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
[29]. Dafoe, A., Bachrach, Y., Hadfield, G., Horvitz, E., Larson, K., & Graepel, T.(2021).Cooperative AI: machines must learn to find common ground.
[30]. Duffy, B.R.(2002).Anthropomorphism and robotics.The society for the study of artificial intelligence and the simulation of behaviour, 20.
[31]. Sarker, M.K., **e, N., Doran, D., Raymer, M., & Hitzler, P.(2017).Explaining trained neural networks with semantic web technologies: First steps.arxiv preprint arxiv:1710.04324.
[32]. Lowry, M., Bajwa, A.R., Pressburger, T., Sweet, A., Dalal, M., Fry, C., ...& Mahadevan, N.(2018).Design Considerations for a Variable Autonomy Exeuctive for UAS in the NAS.In 2018 AIAA Information Systems-AIAA Infotech@ Aerospace (p.1633).
[33]. Goodman, P.H., Zou, Q., & Dascalu, S.M.(2008).Framework and implications of virtual neurorobotics.Frontiers in neuroscience, 2, 255.
[34]. Darling, K.(2016).Extending legal protection to social robots: The effects of anthropomorphism, empathy, and violent behavior towards robotic objects.In Robot law (pp.213-232).Edward Elgar Publishing.
[35]. Robins, B., Dautenhahn, K., Te Boekhorst, R., and Billard, A.(2005).Robotic assistants in therapy and education of children with autism: can a small humanoid robot help encourage social interaction skills?Univ Access Inf.Soc.4, 105–120.
[36]. Romero, O.J., Zhao, R., & Cassell, J.(2017, August).Cognitive-Inspired Conversational-Strategy Reasoner for Socially-Aware Agents.In IJCAI (pp.3807-3813).
[37]. Tulk Jesso, S., Kennedy, W.G., & Wiese, E.(2020).Behavioral Cues of Humanness in Complex Environments: How People Engage With Human and Artificially Intelligent Agents in a Multiplayer Videogame.Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 7, 531805.
[38]. Sugiyama, S., & Vincent, J.(2013).Social robots and emotion: Transcending the boundary between humans and ICTs.Intervalla, 1(1), 1-6.
[39]. Califf, C.B., Brooks, S., & Longstreet, P.(2020).Human-like and system-like trust in the sharing economy: The role of context and humanness.Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 154, 119968.
[40]. Tripp, J., McKnight, H., & Lankton, N.K.(2011).Degrees of humanness in technology: what type of trust matters?.
[41]. Cappannelli, G., & Cappannelli, S.C.(2004).Authenticity: Simple strategies for greater meaning and purpose at work and at home.Emmis Books.
[42]. Pandey, P., & Rai, A.K.(2024).Analytical modeling of perceived authenticity in AI assistants: application of PLS-predict algorithm and importance-performance map analysis.South Asian Journal of Business Studies.
[43]. Beattie, J., & Fernley, L.(2014).The Age of Authenticity: An Executive Summary.Cohn & Wolfe: New York, NY, USA.
[44]. Moulard, J.G., Raggio, R.D., & Folse, J.A.G.(2016).Brand authenticity: Testing the antecedents and outcomes of brand management's passion for its products.Psychology & marketing, 33(6), 421-436.
[45]. Morhart, F., Malär, L., Guèvremont, A., Girardin, F., & Grohmann, B.(2015).Brand authenticity: An integrative framework and measurement scale.Journal of consumer psychology, 25(2), 200-218.
[46]. Park, J., Hong, E., & Park, Y.N.(2023).Toward a new business model of retail industry: The role of brand experience and brand authenticity.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 74, 103426.
[47]. Kumar, V., & Kaushal, V.(2021).Perceived brand authenticity and social exclusion as drivers of psychological brand ownership.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 61, 102579.
[48]. Peterson, C.(2004).Character strengths and virtues: A handbook and classification.American Psychological Association, 25.
[49]. Lee, G., & Kim, H.Y.(2024).Human vs.AI: The battle for authenticity in fashion design and consumer response.Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 77, 103690.
[50]. Gutkind, L.(Ed.).(2008).Keep it real: Everything you need to know about researching and writing creative nonfiction.WW Norton & Company.
[51]. Nader, K., Toprac, P., Scott, S., & Baker, S.(2024).Public understanding of artificial intelligence through entertainment media.AI & society, 39(2), 713-726.
[52]. Turkle, S.(2007).Authenticity in the age of digital companions.Interaction studies, 8(3), 501-517.
[53]. Van Dijck, J.(2014).Datafication, dataism and dataveillance: Big Data between scientific paradigm and ideology.Surveillance & society, 12(2), 197-208.
[54]. Haggart, B.(2019).The age of surveillance capitalism: The fight for a human future at the new frontier of power, S.Zuboff (2018).journal of digital media & policy, 10(2), 229-243.
[55]. Beerends, S., & Aydin, C.(2024).Negotiating the authenticity of AI: how the discourse on AI rejects human indeterminacy.AI & SOCIETY, 1-14.
[56]. Lopez, F.G., & Rice, K.G.(2006).Preliminary development and validation of a measure of relationship authenticity.Journal of Counseling Psychology, 53(3), 362.
[57]. Bowlby, J.(1982).Attachment and loss: retrospect and prospect.American journal of Orthopsychiatry, 52(4), 664.
[58]. Ainsworth, M.D.S., Bell, S.M., & Stayton, D.J.(2013).Infant–Mother Attachment and Social Development:‘Socialisation'as a Product of Reciprocal Responsiveness to Signals.In Becoming a person (pp.30-55).Routledge.
[59]. Baumeister, R.F., & Leary, M.R.(2017).The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation.Interpersonal development, 57-89.
[60]. Ryan, R.M., & Deci, E.L.(2000).Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new directions.Contemporary educational psychology, 25(1), 54-67.
[61]. Birnbaum, G.E., Mizrahi, M., Hoffman, G., Reis, H.T., Finkel, E.J., & Sass, O.(2016).What robots can teach us about intimacy: The reassuring effects of robot responsiveness to human disclosure.Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 416-423.
[62]. Rever, G.W.(1972).Attachment and Loss.Vol.1. Attachment.
[63]. Hiolle, A., Canamero, L., Davila-Ross, M., & Bard, K.A.(2012).Eliciting caregiving behavior in dyadic human-robot attachment-like interactions.ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems (TiiS), 2(1), 1-24.
[64]. ikulincer, M.(1998).Attachment working models and the sense of trust: An exploration of interaction goals and affect regulation.Journal of personality and social psychology, 74(5), 1209.
[65]. You, S.& Robert, L.P.(2018).Emotional Attachment, Performance, and Viability in Teams Collaborating with Embodied Physical Action (EPA) Robots, Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 19(5), pp.377-407.
[66]. Pelau, C., Volkmann, C., Barbul, M., & Bojescu, I.(2023).The Role of Attachment in Improving Consumer-AI Interactions.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence (Vol.17, No.1, pp.1075-1084).
[67]. Guerreiro, J., & Loureiro, S.M.C.(2023).I am attracted to my cool smart assistant!analyzing attachment-aversion in AI-human relationships.Journal of Business Research, 161, 113863.
[68]. Valsesia, F., Nunes, J.C., & Ordanini, A.(2016).What wins awards is not always what I buy: How creative control affects authenticity and thus recognition (but not liking).Journal of Consumer Research, 42(6), 897-914.
[69]. Castelo, N., Bos, M.W., & Lehmann, D.R.(2019).Task-dependent algorithm aversion.Journal of Marketing Research, 56(5), 809-825.
[70]. Hoff, K.A., & Bashir, M.(2015).Trust in automation: Integrating empirical evidence on factors that influence trust.Human factors, 57(3), 407-434.
[71]. Oldmeadow, J.A., Quinn, S., & Kowert, R.(2013).Attachment style, social skills, and Facebook use amongst adults.Computers in human behavior, 29(3), 1142-1149.
[72]. Söllner, M., & Leimeister, J.M.(2013).What we really know about antecedents of trust: A critical review of the empirical information systems literature on trust.Psychology of Trust: New Research, D.Gefen, Verlag/Publisher: Nova Science Publishers.
[73]. Chen, Y.H., Chien, S.H., Wu, J.J., & Tsai, P.Y.(2010).Impact of signals and experience on trust and trusting behavior.Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 13(5), 539-546.
[74]. Prieto, A.G.(2009).From conceptual to perceptual reality: trust in digital repositories.Library Review, 58(8), 593-606.
[75]. Esmaeilzadeh, P., Mirzaei, T., & Dharanikota, S.(2021).Patients’perceptions toward human–artificial intelligence interaction in health care: experimental study.Journal of medical Internet research, 23(11), e25856.
[76]. Chao, P., Fu, H.P., & Lu, I.Y.(2007).Strengthening the quality–loyalty linkage: The role of customer orientation and interpersonal relationship.The Service Industries Journal, 27(4), 471-494.
[77]. Hu, P., & Lu, Y.(2021).Dual humanness and trust in conversational AI: A person-centered approach.Computers in Human Behavior, 119, 106727.
[78]. Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y.(2018).Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of Stimulus-Organism-Response.International Journal of Information Management, 39, 169-185.
[79]. Deriu, V., Pozharliev, R., & De Angelis, M.(2024).How trust and attachment styles jointly shape job candidates’ AI receptivity.Journal of Business Research, 179, 114717.
[80]. Buckley, S.B., & Jakovljevic, M.(2012).Knowledge Management Innovations for Interdisciplinary Education: Organizational Applications.Pennsylvania: IGI Global, 207-232.
[81]. Ma, W.W., & Chan, A.(2014).Knowledge sharing and social media: Altruism, perceived online attachment motivation, and perceived online relationship commitment.Computers in human behavior, 39, 51-58.
[82]. Olan, F., Suklan, J., Arakpogun, E.O., & Robson, A.(2021).Advancing consumer behavior: The role of artificial intelligence technologies and knowledge sharing.IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management.
[83]. Cohen, W.M., & Levinthal, D.A.(1990).Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation.Administrative science quarterly, 35(1), 128-152.
[84]. Bommer, W.H., Miles, E.W., & Grover, S.L.(2003).Does one good turn deserve another?Coworker influences on employee citizenship.Journal of Organizational Behavior, 24(2), 181–196.
[85]. Cabrera, A., & Cabrera, E.F.(2002).Knowledge-sharing dilemmas.Organization Studies, 23(5), 687–1710.
[86]. Evangelista, E., Kale, R., McCutcheon, D., Rameau, A., Gelbard, A., Powell, M., ...& Bensoussan, Y.(2024).Current practices in voice data collection and limitations to voice AI research: a national survey.The Laryngoscope, 134(3), 1333-1339.
[87]. Lefkeli, D., Karataş, M., & Gürhan-Canli, Z.(2024).Sharing information with AI (versus a human) impairs brand trust: The role of audience size inferences and sense of exploitation.International Journal of Research in Marketing, 41(1), 138-155.
[88]. Zierau, N., Flock, K., Janson, A., Söllner, M., & Leimeister, J.M.(2021).The influence of AI-based chatbots and their design on users’ trust and information sharing in online loan applications.In Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS).-Koloa (Hawaii), USA.
[89]. Malik, A., De Silva, M.T., Budhwar, P., & Srikanth, N.R.(2021).Elevating talents' experience through innovative artificial intelligence-mediated knowledge sharing: Evidence from an IT-multinational enterprise.Journal of International Management, 27(4), 100871.
[90]. Park, J., Woo, S.E., & Kim, J.(2024).Attitudes towards artificial intelligence at work: Scale development and validation.Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology.
[91]. Kim, M.J., Lee, C.K., & Jung, T.(2020).Exploring consumer behavior in virtual reality tourism using an extended stimulus-organism-response model.Journal of travel research, 59(1), 69-89.
[92]. Han, S., Kim, K.J., & Kim, J.H.(2017).Understanding nomophobia: Structural equation modeling and semantic network analysis of smartphone separation anxiety.Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 20(7), 419-427.
[93]. Chang, H.H., & Chen, S.W.(2008).The impact of online store environment cues on purchase intention: Trust and perceived risk as a mediator.Online information review, 32(6), 818-841.
[94]. Bock, G.W., Zmud, R.W., Kim, Y.G., & Lee, J.N.(2005).Behavioral intention formation in knowledge sharing: Examining the roles of extrinsic motivators, social-psychological forces, and organizational climate.MIS quarterly, 29(1), 87-111.
[95]. Rosenthal-von der Pütten, A.M., Krämer, N.C., Hoffmann, L., Sobieraj, S., & Eimler, S.C.(2013).An experimental study on emotional reactions towards a robot.International Journal of Social Robotics, 5, 17-34.
[96]. Fu, X.(2019).Existential authenticity and destination loyalty: Evidence from heritage tourists.Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 12, 84-94.
[97]. Osorio, M.L., Centeno, E., & Cambra-Fierro, J.(2023).An empirical examination of human brand authenticity as a driver of brand love.Journal of Business Research, 165, 114059.
[98]. Singh, R.(2022).“Hey Alexa–order groceries for me”–the effect of consumer–VAI emotional attachment on satisfaction and repurchase intention.European Journal of Marketing, 56(6), 1684-1720.
[99]. Wirtz, J., Patterson, P.G., Kunz, W.H., Gruber, T., Lu, V.N., Paluch, S., & Martins, A.(2018).Brave new world: Service robots in the frontline.Journal of Service Management, 29(5), 907–931.
[100]. Lu, V.N., Wirtz, J., Kunz, W.H., Paluch, S., Gruber, T., Martins, A., & Patterson, P.G.(2020).Service robots, customers and service employees: What can we learn from the academic literature and where are the gaps?Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 30, 361–391.
[101]. Tsai, W.H.S., Liu, Y., & Chuan, C.H.(2021).How chatbots' social presence communication enhances consumer engagement: the mediating role of parasocial interaction and dialogue.Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 15(3), 460-482.









