1. Introduction
With the rapid development of internet technology, social media platforms have become an indispensable part of people's daily lives. These platforms not only provide users with channels to obtain information and engage in social interactions, but also gradually become an important battleground for businesses to promote their products and services. In the gaming industry, social media platforms have become a key channel for promoting game products and selling virtual goods. However, faced with a sea of information and fierce market competition, how to effectively formulate advertising and marketing strategies, accurately target virtual goods, and enhance users' purchase intentions has become a common challenge faced by game developers and social media platforms.
This study aims to deeply explore advertising and marketing strategies for game products' virtual goods on social media platforms, especially by comparing the effects of official and unofficial promotional videos, and building user profiles to achieve accurate targeting, in order to provide practical guidance and theoretical support for game developers and social media platforms to optimize their advertising effects in the future. The specific objectives include: 1) analyzing the differences in user feedback between official and unofficial promotional videos, exploring the influence of user preferences on advertising effects 2) initially building user profiles and exploring the relationship between potential conversion rates and user profiles 3) proposing advertising optimization strategies based on user preferences and precise targeting technologies.
This study is expected to have important theoretical and practical significance for future research. Theoretically, it enriches the research on social media advertising, user behavior analysis, and precise targeting strategies, providing new perspectives and ideas for related fields of study. Practically, this study provides practical and feasible advertising optimization strategies for game developers and social media platforms, which can help enhance the sales conversion rate of virtual goods, improve user experience, and promote the healthy development of the gaming industry.
This study adopts a combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods, by capturing comment data on new game promotion on Bilibili to conduct word frequency analysis and sentiment analysis to reveal the differences in user feedback between official and unofficial videos. At the same time, a questionnaire survey was designed and distributed to collect users' opinions on different types of promotional videos, further verifying.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Virtual Goods in Social Media and Game Goods
Social Media Virtual Goods: refer to non-physical goods sold on social media platforms, usually in digital form, such as virtual items in games, membership privileges, skins, etc. These goods have no tangible form, but can satisfy users' specific needs in the virtual world, such as enhancing the gaming experience and showcasing individuality.
Game Goods: broadly speaking, they refer to all goods related to games, including both physical goods (such as game discs, merchandise, etc.) and virtual goods. In this study, game goods specifically refer to virtual goods in games, which are digital assets that players can purchase, use, or trade during the gameplay.
Social media virtual goods and game goods differ from ordinary goods in several notable ways: firstly, intangibility, i.e., they exist in digital form and cannot be touched or perceived like physical goods; secondly, immediacy, users can usually obtain and enjoy the value of the goods they purchase immediately; thirdly, interactivity, virtual goods are often closely linked to game or social media platform functions, and users' experience is influenced by the platform environment and the behaviors of other users; fourthly, diversity of value, the value of virtual goods is not only reflected in their direct functions or effects but also may include social identity recognition, emotional attachment, etc. non-direct value.
2.2. User Consumption and Purchase Intentions
User purchase intentions refer to the subjective probability or likelihood that consumers are willing to purchase a certain product or service under certain conditions. In the purchase process of social media virtual goods and game goods, users' purchase intentions are influenced by various factors, including but not limited to the following: the attractiveness of the goods themselves, such as the uniqueness and aesthetics of virtual items; price factors, including price level and the degree of match between price and value; social factors, such as recommendations from friends and the atmosphere of the community; user personal characteristics, such as age, gender, and preference for games; and platform factors, such as the reputation and quality of the platform. These factors interact with each other and jointly influence users' purchase decisions.
2.3. Summary of Previous Studies and Direction of the Current Study
In recent years, the role of social media platforms in promoting virtual goods of game products has become increasingly significant. Scholars have conducted extensive research on advertising strategies in this field from different angles [1]. On one hand, some studies emphasize the importance of content creativity and authenticity in social media advertising, pointing out that users are more inclined to trust and share content that they consider real and interesting [2]. On the other hand, the development of user behavior analysis and precision marketing theory provides a theoretical basis for optimizing advertising strategies, emphasizing the importance of data analysis to identify target user groups and achieve personalized advertising [3].
However, there is still a gap in the comparison of the promotion effects of official and unofficial channels [4]. Most studies focus on optimizing advertising content or strategies, while paying less attention to the impact of promotion subjects (official vs. unofficial) on advertising effectiveness. In addition, although the application of user profiling in precision marketing has been widely recognized, its specific application and effect verification in game product virtual goods advertising are still insufficient.
Therefore, this study aims to fill these research gaps by conducting an empirical analysis of new game promotion cases on BiliBili and comparing the promotion effects of official and unofficial videos. The study also tries to build a profile of potential high-conversion rate users [5]. This study hopes to provide new perspectives and empirical support for the advertising strategies of social media platforms for game product virtual goods.
3. Research Process
This study primarily addresses two issues. The first is the choice of promotion subjects in advertising marketing strategies: the issue of official versus non-official promotion. The second is the issue of precise advertising placement and user profile depiction.
For the first issue, this study takes the newly released Naraka: Bladepoint as the research object. The game is a massive competitive mobile game that was launched on the first day of its public testing at the time of this study. It has a wide audience and a large player base, making it an excellent reference. This study targeted the social media advertising promotion of the game on Bilibili and captured the comment data of ten promotional videos. These videos were released around the same time, all within one day before and after the public testing; and the video content was only about the game, so the users' comments on the videos were also about the game content, reducing the interference of other content and being of great reference value. Among the ten videos, there were four official promotion videos and six non-official promotion videos.
After capturing the comment data of the videos, this study conducted a word frequency analysis on the high-frequency words. This analysis differentiated the official and non-official promotion video comments and conducted a comparison, generating a word cloud for analysis.
This study also conducted sentiment analysis on all comment data for both the official and non-official videos. The sentiment analysis of the official video is shown in Figure 1, and the sentiment analysis of the non-official video is shown in Figure 2.
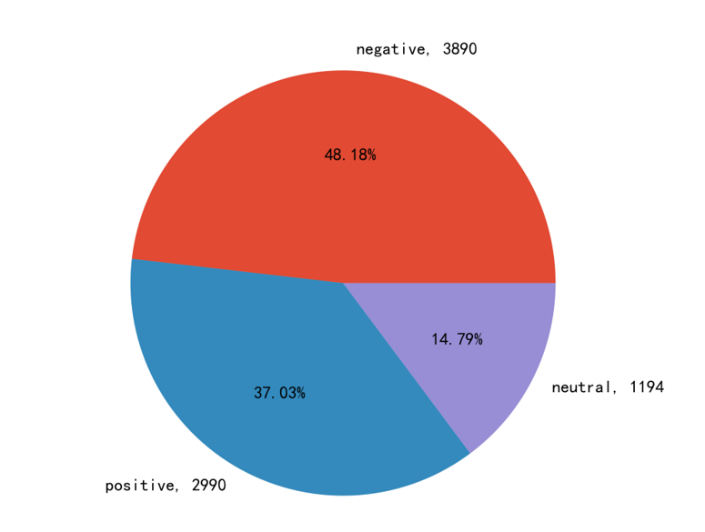
Figure 1: Emotional distribution of official promotional videos
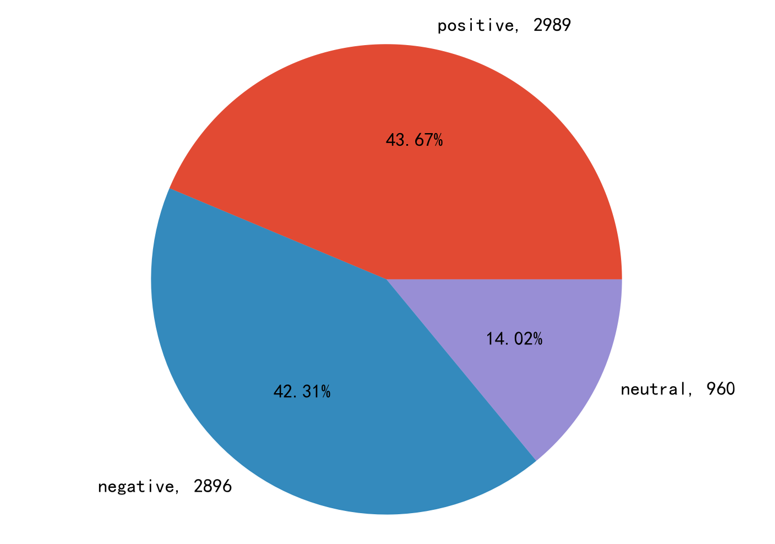
Figure 2: Emotional distribution of unofficial promotional videos
Meanwhile, this study also used a questionnaire survey method to investigate the same issue, namely the users' evaluation of official and unofficial promotion. Since it is in the form of a questionnaire, this study can use a more detailed and flexible classification, dividing unofficial promotion into self-promotion by bloggers and promotion by bloggers hired by the official party. In this study, a questionnaire was used to investigate the impact of users' willingness to watch the three types of videos (as shown in Figure 3) and their willingness to purchase (as shown in Figure 4) on the purchase intention of the product. The data was then analyzed using SPSS for visualization.
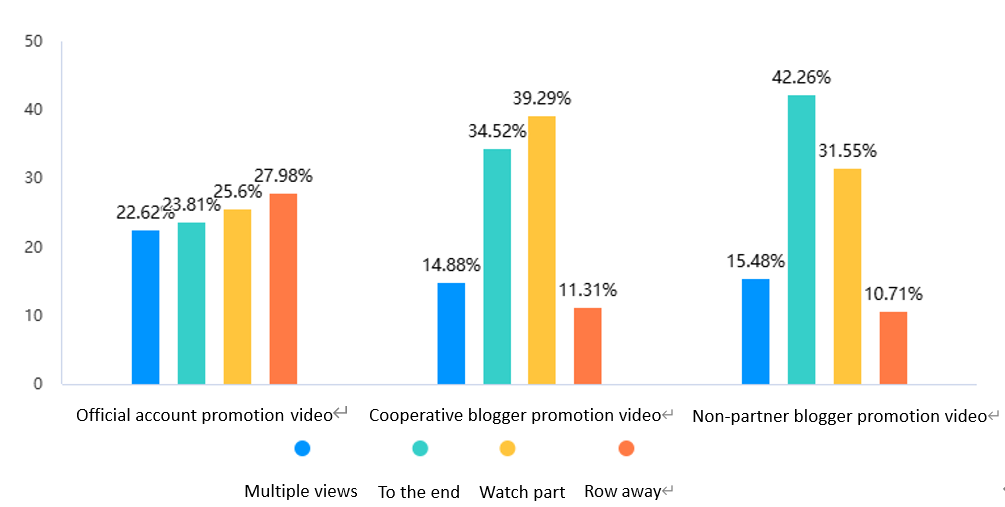
Figure 3: Users' willingness to watch three types of videos
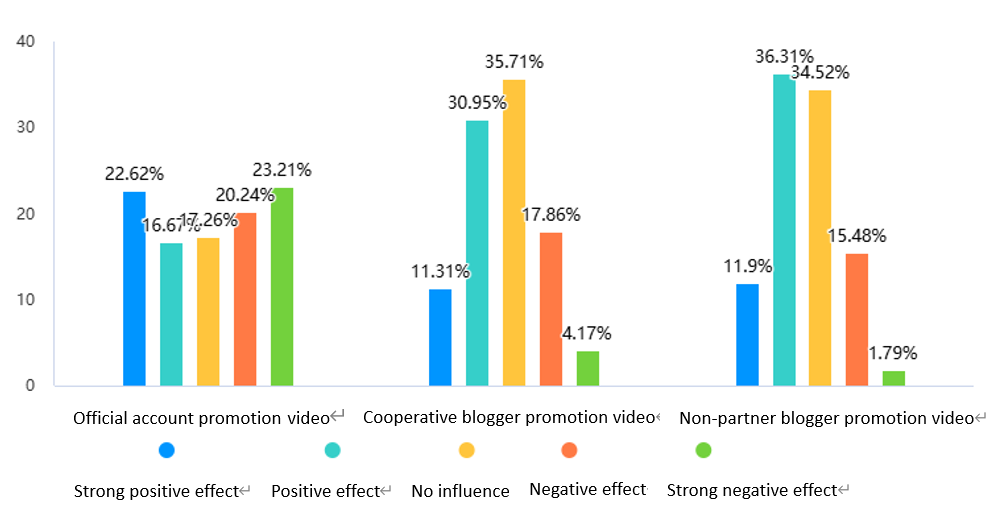
Figure 4: The influence of three kinds of videos on users' consumption intention
For question 2, the research method used in this study is also a questionnaire survey, and data visualization is conducted using SPSS. First, the target of the questionnaire distribution in this study is all game players. In the questionnaire, the study asks questions about the channels through which users learn about new games (see Figure 5), the use of media platforms by users (see Table 1), and the amount of money users spend on games (see Figure 6 and Figure 7).
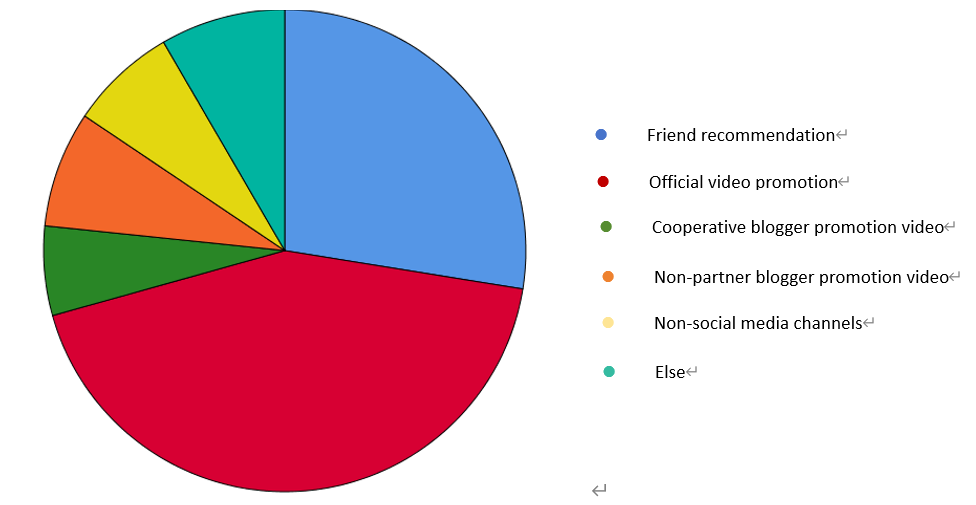
Figure 5: Way for users to know about new games
Table 1: User social media platform usage
Social media | Number | Percentage | Percentage of cases |
TikTok | 61 | 18.3% | 36.5% |
Microblog | 60 | 18.0% | 35.9% |
BiliBili | 54 | 16.2% | 32.3% |
Kuaishou | 48 | 14.4% | 28.7% |
Little red book | 53 | 15.9% | 31.7% |
Else | 58 | 17.4% | 34.7% |
Total | 334 | 100.0% | 200.0% |
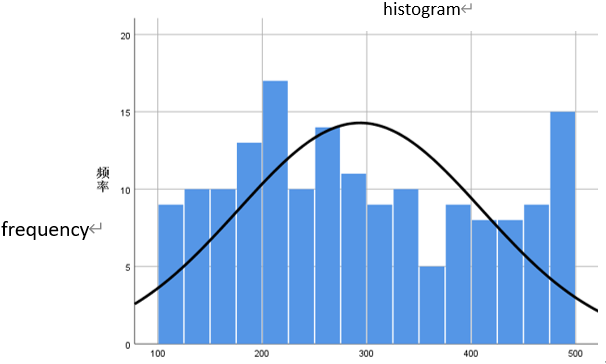
Figure 6: Monthly spending on games
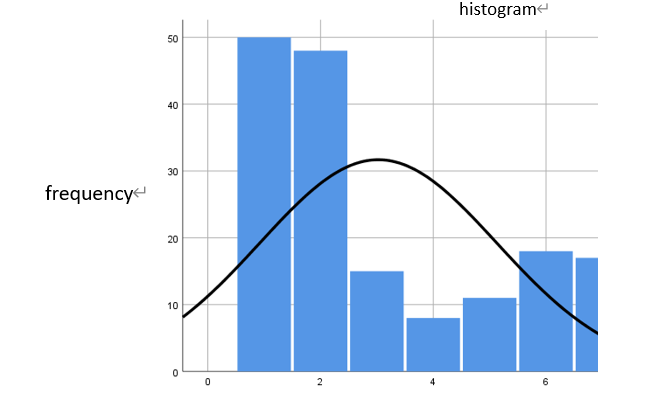
Figure 7: Monthly gaming spending as a percentage of disposable income
4. Research Findings
For the word cloud, this study summarized and analyzed the meanings of the high-frequency words in a brief and concise manner based on their appearance occasions. Among the highest-frequency words in the unofficial video comments: "mobile phone," most of which expressed users' joy at being able to play the game on mobile devices. Among the highest-frequency words in the official video comments: "optimization," which expressed users' skepticism about the optimization performance of this large-scale computer game being ported to mobile devices. As can be seen from Figure 1 and Figure 2, more users discussed the official promotion content negatively, while users often discussed the non-official video content positively. This phenomenon also corresponds to the word frequency analysis. The study found that users tend to discuss negative content in official videos and positive content in non-official videos. They tend to have a worse attitude towards official content and a more tolerant attitude towards non-official content, and are more willing to engage in rational discussion.
In Figure 3 and Figure 4, similar conclusions can be drawn as in the previous study. Figure 3 describes that for the three types of promotion videos, users have an even willingness to watch the official video, and the probability of watching it multiple times is the smallest, while the probability of skipping it is the highest. It is worth mentioning that the probability of watching the official video multiple times is the highest, at 23.62%. Users' willingness to watch the promotion video of the official cooperative blogger is completely different from that of the official video. Users' probability of watching part of the video and finishing it is much higher than that of the official promotion video. Among them, the probability of watching part of the video is the highest among the three videos, accounting for 39.29%. The curve shape of the non-official cooperative blogger's promotion video is similar to that of the official cooperative blogger's promotion video. Among them, the probability of finishing the video is the highest, accounting for 42.26%. It can be seen that the official video is most likely not to attract users to watch, while users are often willing to watch non-official promotion videos, especially willing to finish watching non-official cooperative blogger's promotion. Figure 4's curve distribution is highly similar to that of Figure 3. Compared with that, the most worth analyzing different point is that the negative impact of non-official videos on users' consumption willingness is almost nonexistent, while the negative impact of official videos on users' consumption willingness is as high as 27.98%. It can be seen that the negative impact of official videos is the largest, while the positive impact of non-official videos is relatively obvious.
Regarding issue 2, the survey participants in this study were all game players. Non-game users were not surveyed. Among game users, nearly 60% were minors, which indicates that the young population is a huge user base for the gaming industry. Then, regarding the channels through which survey respondents learned about new games, as shown in Figure 5, the study can conclude that, although official channels are relatively less popular among users, they are still the most widely used channel for learning about new games by the general public. And the majority of people's channels for learning about new games are social media channels. As shown in Table 1, Douyin is the most popular social media platform, but there is little difference in the choices of all platforms. Therefore, it can be considered that advertisements should not be limited to a specific platform, but rather be distributed to as many social media platforms as possible.
This study also examined the respondents' spending on games. Figures 6 and 7 show the monthly game spending and the proportion of disposable income spent on games for respondents. It can be seen that the game consumption behavior of game users exhibits a clear long tail effect, i.e., most users spend less, but a few users spend more; the game consumption behavior of users is related to their disposable income, with most users spending a relatively low proportion of their income on games, and only a small proportion of users spending a higher proportion of their income on games. Therefore, it is worth considering focusing on meeting the needs of small-paying players and providing content and services that are attractive to high-paying players.
5. Conclusion
In the user feedback differences, the sentiment analysis of official video comments shows that more users have a negative attitude towards the official promotion content; the users' discussion in non-official video comments is relatively positive. The willingness to watch the official video is relatively even, but the probability of watching it multiple times is the smallest and the probability of skipping it is the largest; the willingness to watch the non-official video, especially the video promoted by collaborative bloggers, is higher, and it is more likely to generate positive consumption intentions. The strong negative impact on users' consumption intentions generated by the official video is as high as 27.98%, while the non-official video almost has no strong negative impact. Although the official is relatively unpopular, it is still the most widely used channel for new game information, and the majority of people's new game information channels are social media channels. Douyin is the most popular social media platform, but the differences in platform selection are not significant. The game users' game consumption behavior shows a clear long tail effect, that is, most users spend less, but there are also a few users who spend more. The users' game consumption behavior is related to their disposable income, and most users' game spending ratio is relatively low.
This study also has certain limitations. Firstly, the limitation of data sample: This study only selected a part of promotional videos and questionnaire samples on Bilibili, with a limited sample size, which may not be able to fully represent all social media platforms and user groups. The data of video comments may be affected by various factors such as time and platform algorithms, resulting in certain biases. Secondly, the limitation of analytical method: Although sentiment analysis and word frequency analysis can reflect users' partial views and emotions, they are difficult to deeply explore users' deep-level psychological and behavioral motivations. The correlation regression analysis and clustering analysis are not effective in constructing user portraits, which may be limited by data types and questionnaire design.
In future research, it is advisable to expand the data sample as much as possible, including more social media platforms, more types of game products, and a wider range of user groups, to improve the universality and accuracy of the research results. Try to introduce more advanced text mining, sentiment computing, etc. technological means to deeply mine valuable information from user comment data. Improve the questionnaire design to ensure that the problem setting is reasonable and the data collection is comprehensive, so as to better conduct correlation regression analysis and clustering analysis. In addition to official and unofficial promotion effects, it is necessary to deeply explore other factors that may affect advertising effects, such as advertising content creativity, placement strategy, target user positioning, etc., in order to provide more comprehensive empirical support for optimizing the virtual goods advertising strategies of game products. Combine theoretical research with practical application, and based on the research results, propose practical and feasible advertising strategy suggestions and optimization plans, providing valuable reference and guidance for game enterprises and social media platforms.
References
[1]. Wang, L., & Zhang, J. (2023). The Role of Social Media Influencers in Promoting Virtual Goods in Gaming Industry. Journal of Digital Marketing, 15(2), 34-47.
[2]. Smith, J., & Jones, K. (2018). Journal of Advertising Research, 58(3), 123-134.
[3]. Brown, L., Smith, A., & Johnson, P. (2020). Marketing Science, 39(2), 256-274.
[4]. Liu, X., & Chen, H. (2022). A Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Official vs. Non-Official Promotional Videos in Gaming Virtual Goods Marketing. Digital Business Review, 13(4), 78-92.
[5]. Zhang, M., & Wang, Y. (2023). User Profile Construction and Precision Marketing of Virtual Goods in Gaming Industry Based on Social Media Data. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 18(1), 56-73.
Cite this article
Zheng,L. (2024). A Study on Targeted Advertising Strategies for Virtual Goods on Social Media: Exploring Ways to Increase Consumers' Willingness to Purchase in Games. Communications in Humanities Research,63,48-55.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Interdisciplinary Humanities and Communication Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang, L., & Zhang, J. (2023). The Role of Social Media Influencers in Promoting Virtual Goods in Gaming Industry. Journal of Digital Marketing, 15(2), 34-47.
[2]. Smith, J., & Jones, K. (2018). Journal of Advertising Research, 58(3), 123-134.
[3]. Brown, L., Smith, A., & Johnson, P. (2020). Marketing Science, 39(2), 256-274.
[4]. Liu, X., & Chen, H. (2022). A Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Official vs. Non-Official Promotional Videos in Gaming Virtual Goods Marketing. Digital Business Review, 13(4), 78-92.
[5]. Zhang, M., & Wang, Y. (2023). User Profile Construction and Precision Marketing of Virtual Goods in Gaming Industry Based on Social Media Data. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 18(1), 56-73.









