1.Introduction
The world today is in a period of significant change and adjustment. With the continuous emergence and application of new technologies and the increasing development of the information society, the era of new media has emerged, widely and profoundly affecting human thinking and activities. In this context, people try to grasp the overall trend, use media means reasonably, and help and promote the dissemination and development of culture. This information operation has also led to varying degrees of cultural substitution and promotion, Collision and confinement of ideas, and Economic changes. It is worth noting that the media significantly impacts Generation Z youth in these aspects [1-3]. Generation Z is the first group of “digital natives” and a group growing up in the development of network technology. This group has experienced significant events in which technology and media have grown from scratch to strength. Therefore, there are significant differences in the usage habits, thinking habits, values, and other aspects of media among this group compared to previous generations [4].
A data survey showed 4.62 paid social media users worldwide in January 2022. This number is equivalent to 58.4% of the world’s total population. In the past 12 months, global social media users have increased by over 10%, with 424 million new users starting their social media magazine in 2021. In Charlotte Bond’s survey, globally, people spend an average of 6 hours and 37 minutes per day using screens. This is especially true for Generation Z people.
Many social media platforms on the internet are highly “tribal” and have no commonality with so-called “outsiders,” including those from other generations [5]. Many older adults are isolated from the internet culture of young people, and the social media tools used by young people are even different from those familiar to general society and not compatible with others. The culture they share and value often differs significantly from the general forms of society. Because of this, “Generation Z” has formed its views on society under the impact and integration of new and old and Eastern and Western cultures.
Besides, the consumption characteristics of Generation Z often reflect their pragmatic attitude towards money and education, and they believe in social undertakings and strong individualism. This generation is an “informed consumer” and typically studies variable choices before purchasing [7,8]. They only rely a little on specific brands but prefer to shop around to retain the most cost-effective items. They attach great importance to brand ethics and corporate responsibility and will likely shop through social media. A survey by IBM found that product selection, availability, conservation, and value are the main influencing factors when Generation Z chooses an Interested product. Generation Z significantly influences the market more than their actual consumption capacity [9]. This is based on their online purchasing decisions and trends towards their parents, significantly impacting this generation. Therefore, studying the media’s impact on Generation Z’s culture and the economic and ideological changes it drives will help us better understand the changes in society and provide valuable references for cultural inheritance, economic development, and ideological breakthroughs [10].
Due to the strong consumption ability and personalized and differentiated consumption demand of Generation Z, there are different consumption circles in the group of Generation Z, such as the famous “ootd,” hot-blooded E-sports games, cosplay, kpop culture lovers, and the eating and broadcasting of food all over the world. The emergence of the consumption circle not only stems from Generation Z’s own hobbies and social needs but also dramatically stimulates the consumption potential of Generation Z in all circles through the dissemination of various media and the exposure of traffic. As more and more Generation Z enter society as students, their income will be further improved, and their consumption ability will be further strengthened. Generation Z consumers are avant-garde, open-minded, and like trendy things. They have a stronger desire to consume than previous generations and have formed consumption concepts such as internal and external cultivation, willingness to taste fresh food, and personalized goods. For them, consumption is not only a way to meet the needs of daily life but also a way to pursue personalization. Consumption pursues good quality and low price, but additional experiences like product appearance, quality, and sense of technology. Similarly, this brand or business should have sustainability and social responsibility, such as the rise of “domestic products” in China. Commodities or businesses have particular significance and social significance. It is worth noting that this generation needs more brand loyalty. This generation is better at comparing goods and trying to get the lowest price and the best quality. This generation is relatively assertive or different. Gen Z will not stick to brand, region, and propaganda tactics. What they want more is relatively transparent, authentic, and sincere goods. This generation is also relatively casual in work. Without a long social experience, there is no shortage of food and clothing, which leads to a higher turnover rate than previous generations.
This paper is focused on the age group of Generation Z, which is the largest population group at present and the most critical consumer group expected in the future. Through a questionnaire survey, this paper collects people’s views on Generation Z and analyzes them. The detailed results will be stated in the second section.
2.Questionnaire Data Analysis
In terms of the questionnaire, there are four questions: the advantages of Generation Z (Figure 1), the disadvantages of Generation Z (Figure 2), the differences between Generation Z and previous generations (Figure 3), and the impact of Generation Z on the future development trend (Figure 4).
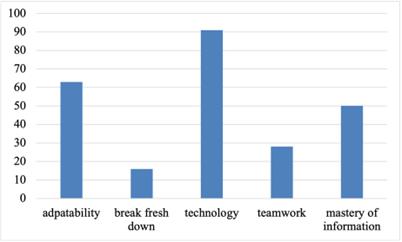
Figure 1: The advantages of generation Z.
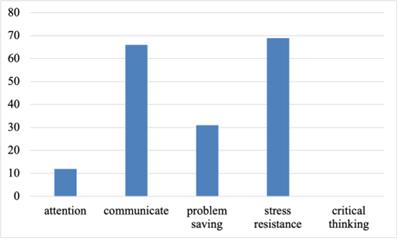
Figure 2: The disadvantages of generation Z.
For the advantage of this generation, 51.1% felt that it was in the application of science and technology. The ability to quickly adapt to the environment accounts for the second largest proportion in this field. For the lack of this generation, most people think it is the ability to communicate and withstand pressure. Similarly, communication has become where people feel the most significant gap with the concept of Generation Z. This also led the respondents to believe that the most significant impact of Generation Z on the future was in the mode of thinking and ideological education. The gap between this idea and concept has been gradually reflected, such as gender inclusiveness, differences in family concepts of several generations, and individual personalization. Secondly, Generation Z will significantly improve technology. This generation lives in what can be called a new era based on the Internet. Generation Z’s mastery of the Internet is much higher than that of other generations, leading to people’s guessing about this concept.
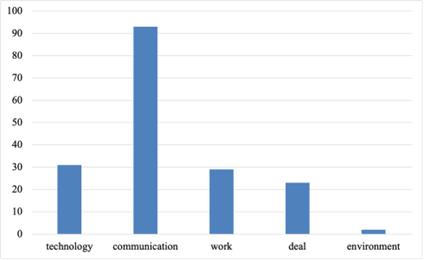
Figure 3: The differences between generation Z and previous generations.
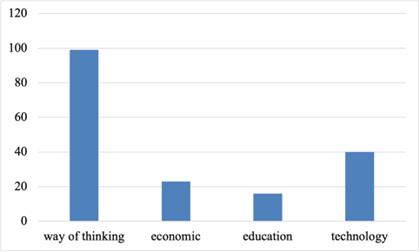
Figure 4: The impact of generation Z on the future development trend.
3.Discussion
Due to the influence of new media, this generation can learn more and broaden their knowledge. Online access to current events and news, as well as access to the latest knowledge and information, plays a guiding role in the learning and life of this generation. This is also why the Generation Z will be the first voice and call of much social news. The call and voice for social news, on the one hand, is the passion of young people; on the other hand, it is the ideological collision and developmental thinking brought by the media.
Similarly, many cases and promotions are related to the economy on the Internet. They are good at shopping around. This is also why the Generation Z has a more significant impact on the socio-economy. Opening an online store and conducting commercial publicity is relatively easy for the current generation of Z because they have a good grasp of media and technology. It is susceptible and accurate for business opportunities and commodity value. Because they are familiar with the Internet, they can quickly spread their product usage descriptions to netizens worldwide or their family and friends nearby. In the questionnaire, people mentioned a significant difference in thinking between this generation and previous generations.
The Generation Z has its own logic and philosophy because of globalization. Unlike the M generation, this generation emphasizes collective consciousness on the moral level, such as the rise of feminist consciousness. However, at the same time, they are not rigidly adhering to rules and traditions. In the concept of this generation, tradition and rules are not a value that should be fully respected. The Generation Z will be more idealistic, pursuing cultural equality between men and women. They also pay more attention to traditional culture and national spirit. Based on their social media mastery, this generation will rationally use various platforms and resources to promote their culture. They hope that in the era of globalization, every place can preserve its unique ethnic customs and traditional culture. Also, because, this generation is more focused on product and corporate culture. Take China as an example; “domestic products” are rapidly rising and being sought after by many Generation Z people. The reason is that these brands have a simple culture, affordable value, and high product quality. At the same time, these brands also retain China’s own culture and elements.
4.Conclusion
Based on the current data, new media significantly impacts the Z generation. Similarly, this generation will have an impact on the future. Z generation broadens its horizons based on more multimedia consulting and enriches its education. Also, more actively respond to social news and consultation. Those who are capable will help, and those who are still young will use their mastery of social media to help more people. Also, this generation has more social responsibility and morality. They pursue equality and fairness and dare to speak for the weak. Generation Z also pays more attention to developing and disseminating local culture. They are experienced in globalization and realize that the culture that is not strong will be swallowed up and disappear. In this era, media and social platforms will promote local culture. Attaching importance to culture is also a primary reason for changing commodities. Regarding commodity selection, generation Z attaches great importance to creativity and beauty and emphasizes function and quality. The current popular national fashion goods are designed to combine fashion and traditional delicacy. Hence, they are very popular with Generation Z. Generation Z has a more significant impact on commodities or the economy, and this impact will be greater and greater. This generation covers a wide range of fields and has a high degree of active participation in different fields. Based on the Internet and new media, they are knowledgeable and good at shopping. This generation is also not loyal to the brand because of this. Generation Z is no longer satisfied with essential living consumption for practical purposes. Pleasing itself has become the first driving force of Generation Z’s consumption. Consumption with entertainment as the main content has become an essential part of Generation Z’s consumption structure. Also, based on the Internet and new media, they are good at delivering information and telling people their true feelings. The cultural transmission of new media has led this generation to prefer personalized services. Generation Z accepts the social way of tagging and is willing to show their tags and shape their personas. They do not care much about the labels or stereotypes that others put on themselves. “If others are willing to label me, just stick it” and “it does not matter what others say” are more representative attitudes. At the same time, they are tolerant and open to different lifestyles, respect differences, and understand each other.
References
[1]. Seemiller, C., & Grace, M. (2015). Generation Z goes to college. John Wiley & Sons.
[2]. Dolot, A. (2018). The characteristics of Generation Z. E-mentor, 74(2), 44-50.
[3]. Dimock, M. (2019). Defining generations: Where Millennials end and Generation Z begins. Pew Research Center, 17(1), 1-7.
[4]. Singh, A. P., & Dangmei, J. (2016). Understanding the generation Z: the future workforce. South-Asian journal of multidisciplinary studies, 3(3), 1-5.
[5]. Shatto, B., & Erwin, K. (2016). Moving on from millennials: Preparing for generation Z. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 47(6), 253-254.
[6]. Wood, S. (2013). Generation Z as consumers: trends and innovation. Institute for Emerging Issues: NC State University, 119(9), 7767-7779.
[7]. Gabrielova, K., & Buchko, A. A. (2021). Here comes Generation Z: Millennials as managers. Business Horizons, 64(4), 489-499.
[8]. Törőcsik, M., Szűcs, K., & Kehl, D. (2014). How generations think: research on generation z. Acta universitatis Sapientiae, communicatio, 1(1), 23-45.
[9]. Williams, A. (2015). Move over, millennials, here comes Generation Z. The New York Times, 18, 1-7.
[10]. Moore, K., & Frazier, R. S. (2017). Engineering education for generation Z. American Journal of Engineering Education (AJEE), 8(2), 111-126.
Cite this article
Zhu,Y. (2023). The Impact of Media on Generation Z and Possible Future Social Changes. Communications in Humanities Research,22,36-41.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Interdisciplinary Humanities and Communication Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Seemiller, C., & Grace, M. (2015). Generation Z goes to college. John Wiley & Sons.
[2]. Dolot, A. (2018). The characteristics of Generation Z. E-mentor, 74(2), 44-50.
[3]. Dimock, M. (2019). Defining generations: Where Millennials end and Generation Z begins. Pew Research Center, 17(1), 1-7.
[4]. Singh, A. P., & Dangmei, J. (2016). Understanding the generation Z: the future workforce. South-Asian journal of multidisciplinary studies, 3(3), 1-5.
[5]. Shatto, B., & Erwin, K. (2016). Moving on from millennials: Preparing for generation Z. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 47(6), 253-254.
[6]. Wood, S. (2013). Generation Z as consumers: trends and innovation. Institute for Emerging Issues: NC State University, 119(9), 7767-7779.
[7]. Gabrielova, K., & Buchko, A. A. (2021). Here comes Generation Z: Millennials as managers. Business Horizons, 64(4), 489-499.
[8]. Törőcsik, M., Szűcs, K., & Kehl, D. (2014). How generations think: research on generation z. Acta universitatis Sapientiae, communicatio, 1(1), 23-45.
[9]. Williams, A. (2015). Move over, millennials, here comes Generation Z. The New York Times, 18, 1-7.
[10]. Moore, K., & Frazier, R. S. (2017). Engineering education for generation Z. American Journal of Engineering Education (AJEE), 8(2), 111-126.









