1.Introduction
Social media has become an integral part of daily life for many individuals in the United States. With the rise of social media platforms such as Tik tok, Instagram, and Snap chat, people are more connected than ever before. With this phenomenon being observed as the usage of social media has increased, there are concerns about its impact on mental health. The current dominant problem would be FMO (Fear of Missing Out) and, psychological problems such as depression and loneliness. This paper aims to explore the effects of social media on the mental health of young adults, a group that has been found to be particularly vulnerable to negative outcomes associated.
2.Literature Review
Previous research on social media and mental health has found mixed results. While some studies have found positive effects of social media, including increased social support and self-esteem, others have found negative effects, such as increased anxiety, depression, and loneliness. Additionally, studies also suggest that excessive social media usage can lead to addiction and an increase in mental health disorder FMO. [1] For example, a study gives an insight on how social media has affected mental health. The study surveyed a group of eighth-grade students and found that eighth-graders who spend more than 10 hours per week on social media are 56% more likely to be dissatisfied than those who spend less time on social media [2]. The connection between mental health and social media could not be seen as a straight influence but the content contained in social media, such as time, could be the main cause. According to a n 2019 study, kids who spend more than three hours per day on social media are more likely to struggle with mental health issues like sadness, anxiety, hostility, and antisocial conduct.[3] However, on the contrary, some researchers believe that social media itself cannot be the cause of mental health problems, but rather how students use it and the people they interact with it. A broad study examines the features that social media users look at most. Results showed that the users who look at Instagram photos tend to have eating disorders and anxiety. Due to the fact that Instagram photos only share the best moments of a user’s life, by looking at them, viewers tend to think that they are not good enough. [4] Likewise, Richard B. Lopez and Isabel Pollett conclude that a higher loss of self-worth on Instagram was associated with multiple content control activities, including spending more time annotating images and videos and changing captions, as well as being more apprehensive in social circumstances [5]. These recent studies have shed light on how social media may have a detrimental impact on people's mental health. A limitation of past studies would be that they mostly focused on the relationship between social media and mental health but not necessarily on the users' own psychological perspectives and application methods towards social media. This means that there are still major gaps in our knowledge of the connection between social media use and mental health. Previous research has not taken into account the variety of user viewpoints and application styles, instead concentrating on the general relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes. The knowledge of whether users themselves may have particular psychological vulnerabilities that interact with their experiences on social media is thus lacking. Subsequent investigations need to probe more deeply into the subtleties of how social media affects mental health, taking into account the varied viewpoints and strategies utilized by individuals. This more sophisticated knowledge can assist in identifying usage trends, enhance mental health care, and provide users with more confidence when utilizing social media. Without succumbing to its potential negative influences.
3.Methodology
The experiment was performed as a survey and was conducted to assess the association between SM use and depression in a nationally representative sample of young adults. The experiment and result are from [6]. It was used to identify what caused SM to affect mental health. In this experiment, the quantitative method was used, according to Importance Of [7]." Quantitative research on social platforms tells us the "what," giving you objective information about the habits of a population based on the sample." Social media is a widely used object around the world, and using surveys, it helps gather information more efficiently and effectively. Additionally, the relationship between SM and mental health has a definite linear relationship, but usually, the longer the time spent in that activity, the worse the outcomes [8]. The process of gathering and interpreting numerical data can help identify trends and averages. Meaning that by using quantitative research, the patterns of time spent, age population, and locational patterns are being able to be seen [9]. This survey contains a large variety of social media users and contains In this case, the survey results allow us to conclude that the time spent on social media affects mental health. The survey is intended to gather information on participant demographics, social media usage habits, and experiences with mental health. This survey also includes an accurate and detailed SM visit time, up to date. which gives the audience a more direct insight on the data. The poll will be completely secret, as will the replies. Closed-ended questions will be used in the survey to make data analysis easier. A survey was conducted to gather data on social media usage and mental health outcomes. The survey was a second handed survey and was performed by random digital and addressed based sample. In the study, 1,787 people between the ages of 19 and 32 completed a survey on social media use and depression. Self-reported visits per week, daily time spent on SM, and a global frequency score based on the Pew Internet Research Questionnaire were used to measure SM use. Address-based sampling and random digit dialing were used to find participants. The Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Depression Scale Short Form was used to measure depression.
4.Results
50.3% of the sample was female and 57.5% of it was White. Participants in the highest quartile of daily social media time spent had significantly higher odds of depression (AOR = 1.66, 95% CI = 1. 14–2.42) compared to those in the lowest quartile after adjusting for all covariates [6]. Individuals in the highest quartile of social media site visits per week and those with a higher global frequency score both had significantly higher odds of depression when compared to those in the lowest quartile (AOR = 2.74, 95% CI = 1.86-4.04; AOR = 3.05, 95% CI = 2.03-4.59, respectively) [6]. The use of social media was strongly linked to elevated depression. Given the widespread use of social media, understanding the causes and trends of this association is essential for developing effective SM use and depression interventions[6]. The findings show a significant link between social media use and poor mental health outcomes. Comparing participants who used social media for less than an hour per day to those who used it for more than two hours per day, it was shown that the latter group experienced considerably higher levels of anxiety and depressive symptoms. Participants who said they felt lonely also said they used social media more frequently.
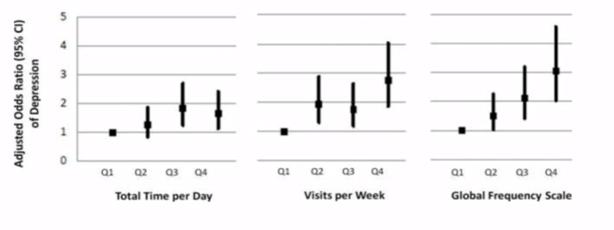
Figure 1: The quartiles for each social media use indicator are arranged from lowest (Q1) to highest (Q4). Vertical bars show the adjusted odds ratio point estimates and the 95% confidence interval. For each social media use variable, the P value for the overall linear effect was.002, <.001, and <.001, respectively. [6].
Any research involving human subjects must take ethics into account. The anonymity and privacy of study participants must be safeguarded at all times, according to researchers. Participants will be informed of the research's purpose and offered the choice to leave at any time during the course of the investigation. Participants will be made aware that all replies will remain anonymous and confidential.
5.Discussion
The results corroborate earlier research that suggested that excessive social media use, particularly among individuals, may have detrimental effects on mental health. The main risk factors for depression, anxiousness, and emotional distress are identified by this research included screen time, behaviors like checking for messages repeatedly, looking at perfect photos, addicted use. Even though there is proof that using social media for extended periods of time and engaging in related activities can lead to depression, other research has found the opposite to be true. For instance, this article from Harvard have found that time use could not be the factor that caused mental health. The three outcomes are adversely correlated with emotional attachment to social media, such as excessive app checking out of a fear of missing out, feeling let down by, or feeling distant from friends while not hooked into social media. In a broader sense, these findings imply that frequent usage might not necessarily be a issue as long as we are thoughtful users. Social media use can be positive for mental health and well-being [10].The aforementioned confounding variables, intermediaries, and editors, among others, may help to explain these contradictory results.
6.Limitations
Although this data did reflect how social media connects to metal health and suggested the core relationship between each other, it also helped note key points for further research. However, this data is from seven years ago, and the data could be different if it were assessed again today. Moreover, the advances in technology in recent years could have caused a more positive or negative relationship between social media and mental health. As the technology is different now, the people themselves could have a different point of view towards social media, and the factors that affect social media could be more than just the time used. Hence, the findings were also not able to give the names of all the participants or the type of social media they used. psychological distress among individuals who are at higher risk of developing anxiety and depression, the results of this systematic review added significantly to the body of literature that already exists on the subject. which could mean that some participants may already have a potential mental disorder that is not caused by social media but merely triggered by it. Only one study has given an insight on the side that mental disorder may be a trigger but is not caused by SM. [11] examined whether there had previously been any evidence of a connection between problematic social media use and shifts in depressive mood. However, the scope of this study was restricted to demonstrating the causality of social media. As well, no professional scientific research or data comparisons were done on this subject. As a result, this article is only meant as a reference. Additionally, if some participants visit social media that contains more emotional and aggressive content, they may be more affected than others who don’t. It seems that most depression involves emotional numbness, especially sadness, fear, anger, and shame. So when these emotions cycle back to oneself, such as seeing a situation similar to one's own, it can cause patients to experience these emotions again and feel their feelings, which can lead to depression [12]. So in the future, it might be best to let participants visit specific or similar social media content. Only [11] have invested the specific amount. However, these small flaws did not effect the overall investigation and still brought out the main points of this investigation and helps give an insight on how time could be a great factor in social media. Reviewing the research, there happen to be some important findings. One finding suggested that specific types of social media content may cause a greater degree of psychological disorder than others. This type of social media involves great connections between people and the reviews they get back from peers online. Examples are Instagram, TikTok, and Snap chat. Additionally, these social media sites allow users to have greater access and communication with strangers, which brought up the possibility of cyberbullying that may also be a factor in mental disorders like anxiety and depression. Which forms of cyberbullying involve threatening or intimidating individuals online, uploading images or videos meant to incite disgust or anguish, encouraging others to make offensive remarks about someone, or sending offensive text messages on a smartphone. The incidence of cyberbullying across seven European countries among children aged 8–16 increased from 8% to 12% between 2010 and 2014 [13]. This being found gives us a more clear insight on the time spent on different content on social media could have a greater or lesser effect on mental health. Not just negative outcomes of social media studies have confirmed that social media Social media can connect people who might not have a strong social support network in person, which is an important example of how it can benefit mental health [14]. The paper concludes with suggestions for individuals and social media companies to encourage healthier use of social media, such as limiting screen time and moderating content.
7.Conclusion
This study provides evidence for the negative effects of excessive social media usage on mental health among individuals. It’s reasonable to claim that there is a "link" between the usage of social media and mental health problems, so in order to improve individual mental health, we need to grasp this "connection." Moreover, this research will serve as a foundation for future studies on social media and its effect on mental illness. The current study could not analyze the previous potential mental disorders on social media. If the content has a greater effect on mental health than the time used, while social media can provide benefits, it is important for individuals and companies to be aware of the potential risks and take steps to promote healthier usage. Hopefully, this study help identify the main reasons of social media and its effect towards mental health. In Future research should continue to explore the relationship between social media and mental health outcomes and how best to promote positive use of social media.
References
[1]. Karim, F., Oyewande, A. A., Abdalla, L. F., Ehsanullah, R. C., & Khan, S. (2020, June 15). Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health: A Systematic Review. Cureus; Cureus, Inc. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.8627
[2]. Davies, J. (2022, March 20). Social Media And Mental Health Statistics - Mind Essential. Mind Essential. https://mindessential.net/social-media-and-mental-health-statistics/
[3]. Social Media and Teen Mental Health. (2023, August 10). The Annie E. Casey Foundation. https://www.aecf.org/blog/social-medias-concerning-effect-on-teen-mental-health
[4]. Social Media and Mental Health. (n.d.). https://www.rpc.senate.gov/policy-papers/social-media-and-mental-health
[5]. Lopez, R. B., & Polletta, I. (2021, August 25). Regulating Self-Image on Instagram: Links Between Social Anxiety, Instagram Contingent Self-Worth, and Content Control Behaviors. Frontiers in Psychology, 12.
[6]. Lin, L. Y., Sidani, J. E., Shensa, A., Radovic, A., Miller, E., Colditz, J. B., Hoffman, B. L., Giles, L. M., & Primack, B. A. (2016, January 19). ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SOCIAL MEDIA USE AND DEPRESSION AMONG U.S. YOUNG ADULTS. Depression and Anxiety, 33(4), 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22466
[7]. Ward, R. M., Steers, M. N., Das, A., Speed, S., & Geyer, R. B. (2023, January 1). Applications of social media research in quantitative and mixed methods research. Elsevier eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-95630-7.00004-4
[8]. Lopes, L. S., Valentini, J. P., Monteiro, T. H., Costacurta, M. C. D. F., Soares, L. O. N., Telfar-Barnard, L., & Nunes, P. V. (2022, November 1). Problematic Social Media Use and Its Relationship with Depression or Anxiety: A Systematic Review. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 25(11), 691–702. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2021.0300
[9]. Larnyo, Ebenezer. (2023). Research Design & Methods. 10.13140/RG.2.2.17112.98566. This presentation discusses the different types of research methods.
[10]. Social media use can be positive for mental health and well-being. (2020, May 28). News. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/features/social-media-positive-mental-health/#:~:text=Indeed%2C%20there%20is%20some%20empirical%20evidence%20supporting%20this.,to%20increased%20risk%20of%20depression%20and%20anxiety%20symptoms.
[11]. Desk, T. (2020, October 31). Social Media: Its Effects on Depression and How to Fix It. News18. https://www.news18.com/news/lifestyle/social-media-its-effects-on-depression-and-how-to-fix-it-3027992.html
[12]. Naslund, J. A., Bondre, A., Torous, J., & Aschbrenner, K. A. (2020, April 20). Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Opportunities for Research and Practice. Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science; Springer Science+Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00134-x
[13]. Srivastava, K., Chaudhury, S., Prakash, J., & Dhamija, S. (2019). Social media and mental health challenges. Industrial psychiatry journal, 28(2), 155–159. https://doi.org/10.4103/ipj.ipj_154_20
[14]. Edwards, B. R. (2022, February 25). 9 Reasons Why Social Media Is Actually Good for You. MUO. https://www.makeuseof.com/why-social-media-good-for-you/
Cite this article
li,A. (2024). The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health: A Study of Young Adults in the United States. Communications in Humanities Research,27,171-176.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Interdisciplinary Humanities and Communication Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Karim, F., Oyewande, A. A., Abdalla, L. F., Ehsanullah, R. C., & Khan, S. (2020, June 15). Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health: A Systematic Review. Cureus; Cureus, Inc. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.8627
[2]. Davies, J. (2022, March 20). Social Media And Mental Health Statistics - Mind Essential. Mind Essential. https://mindessential.net/social-media-and-mental-health-statistics/
[3]. Social Media and Teen Mental Health. (2023, August 10). The Annie E. Casey Foundation. https://www.aecf.org/blog/social-medias-concerning-effect-on-teen-mental-health
[4]. Social Media and Mental Health. (n.d.). https://www.rpc.senate.gov/policy-papers/social-media-and-mental-health
[5]. Lopez, R. B., & Polletta, I. (2021, August 25). Regulating Self-Image on Instagram: Links Between Social Anxiety, Instagram Contingent Self-Worth, and Content Control Behaviors. Frontiers in Psychology, 12.
[6]. Lin, L. Y., Sidani, J. E., Shensa, A., Radovic, A., Miller, E., Colditz, J. B., Hoffman, B. L., Giles, L. M., & Primack, B. A. (2016, January 19). ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SOCIAL MEDIA USE AND DEPRESSION AMONG U.S. YOUNG ADULTS. Depression and Anxiety, 33(4), 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22466
[7]. Ward, R. M., Steers, M. N., Das, A., Speed, S., & Geyer, R. B. (2023, January 1). Applications of social media research in quantitative and mixed methods research. Elsevier eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-95630-7.00004-4
[8]. Lopes, L. S., Valentini, J. P., Monteiro, T. H., Costacurta, M. C. D. F., Soares, L. O. N., Telfar-Barnard, L., & Nunes, P. V. (2022, November 1). Problematic Social Media Use and Its Relationship with Depression or Anxiety: A Systematic Review. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 25(11), 691–702. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2021.0300
[9]. Larnyo, Ebenezer. (2023). Research Design & Methods. 10.13140/RG.2.2.17112.98566. This presentation discusses the different types of research methods.
[10]. Social media use can be positive for mental health and well-being. (2020, May 28). News. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/features/social-media-positive-mental-health/#:~:text=Indeed%2C%20there%20is%20some%20empirical%20evidence%20supporting%20this.,to%20increased%20risk%20of%20depression%20and%20anxiety%20symptoms.
[11]. Desk, T. (2020, October 31). Social Media: Its Effects on Depression and How to Fix It. News18. https://www.news18.com/news/lifestyle/social-media-its-effects-on-depression-and-how-to-fix-it-3027992.html
[12]. Naslund, J. A., Bondre, A., Torous, J., & Aschbrenner, K. A. (2020, April 20). Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Opportunities for Research and Practice. Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science; Springer Science+Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00134-x
[13]. Srivastava, K., Chaudhury, S., Prakash, J., & Dhamija, S. (2019). Social media and mental health challenges. Industrial psychiatry journal, 28(2), 155–159. https://doi.org/10.4103/ipj.ipj_154_20
[14]. Edwards, B. R. (2022, February 25). 9 Reasons Why Social Media Is Actually Good for You. MUO. https://www.makeuseof.com/why-social-media-good-for-you/









