1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Significance
Alongside the rapid continuous improvement of Internet coverage and the popularization of smart devices, the various forms of games have gradually become an inseparable part of everyday life. The development scale of digital educational games is also considerably remarkable. According to Metaari's publication, ‘The 2019-2024 Global Game-based Learning Market Report’, it’s evident that game-based learning has become a mainstream trend in the education industry. To illustrate, the global five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of industry-related products and services has already reached an unprecedented 33.2%. It’s estimated that the industry revenue will more than quadruple to $24 billion by 2024, and the global educational game market is undoubtedly in its boom stage of development [1]. Similarly, the overseas market share of Chinese-style games has also undergone tremendous evolution. According to the "2021 China Game Industry Report", last year’s sales revenue of China's self-developed games in overseas markets was US$18.013 billion. Comparatively, the overseas revenue of Chinese game manufacturers in 2012 was only 570 million yuan [2].
It is also worth mentioning that Chinese culture in recent years has gradually increased in its popularity, and the number of individuals learning and taking an interest in Chinese characters and Chinese culture has also seen a steady increase. The above report referred that before the epidemic, that is, in 2018, the Confucius Institute enrolled a total of 1.86 million face-to-face Chinese language students, an increase of 810,000 over the previous year [3]. The Confucius Institute is a non-profit educational institution that teaches Chinese in different countries
Under these contextual changes, certain digital educational games for learning Chinese characters have received heavy popularization, for example, the online game "Chinese Character Room" developed by South Korea's NHN Corporation. Compared with some other mature commercial games on the market, the game developed within this paper focuses significantly more on the artistic style and immersive 3D scene experiences. It aims to develop a game that not only improves the efficiency of players in learning Chinese characters but also deepens their knowledge of Chinese culture. Furthermore, the mechanisms within this game place comparatively more attention on the balance between educational functions and entertainment. In these designs, players are expected to learn in relaxation, improving learning efficiency and increasing their general interest in education. Conjunctively, it is ways also designed with the goal of commemorating and inheriting Chinese culture in a modern and popular fashion to protect cultural heritage.
1.2. Research Content
The game was mainly developed based on the foundations of the Unity system, utilizing Sketchbook and Ps to complete the illustrations with the game interface. Modeling and texturizing were completed through Maya and Substance Painter, with the 3D scene graphics developed through Unity. During the development process, the game referred to the Unity User Manual to implement various game functions through C# scripts. The specific stages can be understood as follows:
1)Theoretical Background and Case Study:
Based on the determined purpose of certain games, the related theories circling digital education games and language teaching were collected and compared for a detailed analysis. Which lays the foundation for subsequent game design. Online games are advantageous for the stress relief of individuals, allowing beautiful illustrations and sounds to satisfy people's aesthetic needs to obtain users' preferences and loyalty [4]. Based on previous research, individuals also learn more efficiently within a relaxed state [5].
2)Project Brief and User Analysis:
The project brief is an essential element that provides a plan for the project in its entirety and ensures that the project is accurately instigated in a timely fashion. Furthermore, user positioning is also a critical feature of a quality product [6]. Before game development begins, it is necessary to determine the main target, user groups. It would be beneficial to identify these target groups’ hobbies, special requirements, and motivations [7]. With regard to this paper, the main users are foreigners who wish to learn Chinese characters and improve their understanding of Chinese culture.
3)Rules and Logic of the Game:
A reasonable background story must be developed for the game while also determining the corresponding rules. That is, players collect the required items by completing different tasks to move past the next level.
4)Game Material Preparation
By collecting reference materials, building 3D models, and preparing digital mapping, the researcher could design game interaction interfaces and prepare the extra required materials for the hot update.
5)Scenario Building and Scripting
Various 3D model scenes were designed through Unity, the interactive interface was managed through Panel, and scripts were devised to enable more connection and emotion to the game.
6)User Test
Conduct user tests and interviews and optimize the game for the second generation based on feedback.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Description
2.1.1. Definition of the problem
As digital game-based learning became popular, various digital educational games emerged across numerous disciplines, including science, nature, engineering, history, and humanities. Digital game-based learning refers to using entertainment created through playing digital games to serve educational purposes [8]. There are very few Chinese educational games developed by China for foreign students. Far more literature discusses the design of educational games from a theoretical perspective instead of actual development. For example, the project of Professor Zhang Yi's Beijing Hutong, though its theoretical research was complete, it did not eventuate to the market. A well-designed digital game-based learning tool about Chinese culture would be helpful to fill this gap in the market.
Additionally, Chinese cultural knowledge and characters are often complex and difficult to understand. In Professor Zhang Yi's questionnaire survey, nearly 50% of the international students believed that Chinese language education games could increase their interest in studying Chinese [9]. In the Chinese teaching classes at Beijing Language and Culture University, teachers often utilize PowerPoint to set up simple games to increase their students' interest in learning. Therefore, a well-designed game should be entertaining while satisfying educational purposes and provide players with an efficient and engaging learning process. Essentially, it is what underpins the concept of digital game-based learning.
Furthermore, discovering modern cross-cultural knowledge-sharing methods is an important societal concern. Chinese civilization has an extensive history full of relics, and its ability to be preserved and shared across different cultures is bolstered through modern technology. In addition to restoring history in virtual museums [10], which began to develop as early as this century, educational games are also becoming increasingly popular. For example, the Palace Museum has released numerous online educational games and gaming applications [11]. Recently, in China, interactive, experiential educational games have become a key method museums use to promote learning. In addition, some large museums will often cooperate with games to jointly produce and present traditional knowledge [12].
2.1.2. Audience orientation
The solution to this problem is designed for people interested in Chinese culture, specifically those seeking to learn Chinese characters and cultural knowledge. Scientific evidence suggests that the brain works more efficiently when experiencing pleasure, attributed to chemicals produced by positive emotions [13]. Using this philosophy, the game seeks to mitigate the difficulties associated with learning Chinese characters and Chinese culture by making the process fun and engaging. This may be especially helpful for students studying during the advent of Covid-19 who would otherwise travel to China to be immersed in the culture but cannot due to travel restrictions. Their inability to interact with teachers in real time in class may be ameliorated by immersive learning through the game. At the same time, the game can record and disseminate Chinese traditional culture in the form of emerging technologies.
2.2. Theory of Digital game-based learning
The concept of educational games has a deep-seated presence in Chinese history; there has been an idiom of learning with entertainment. Although Plato proffered the idea of marrying the concepts of learning and gaming initially, the birth of digital educational gaming was established in the United States in the 1980s, boasting games such as Number Munchers and Reader Rabbit [14]. As technological advancement has accelerated the prevalence and necessity of smart devices, such as computers and mobile phones, in our regular routine, digital educational games have evolved concomitantly [15]. For example, driving simulation games are now expressly utilized to aid learners in obtaining a license. Particularly in the current era, Digital game-based learning has become an indispensable technical education means. Marc Prensky, a famous American game designer and education expert, conducted an in-depth analysis and discussion on this concept. He believes that digital games will be a fully recognized method of learning, as they have the capacity to meet the needs of the modern learner, are not limited by disciplines, and are uniquely stimulating [16].
In addition to the prevalence of various online courses and online teaching resources, schools have moved more rapidly toward digitalization. Microsoft and MIT's Games to Teach project designed ten game concept prototypes to support learning in advanced math, science, and engineering [17]. Sid Meiers Civilization III guides students to learn about history and how to manage the balance between infrastructure, resources, diplomatic relations, trade skills, technological progress, city and empire management, culture, and finally, military power [18]. The element of fun is one of the essential attributes of digital game-based learning, especially when people learn new skills. Having fun promotes a more effective way to learn [19]. This paper will analyze four theories related to Digital game-based learning, namely ‘Constructivism Learning Theory,’ ‘Humanistic Learning Theory,’ and ‘Situated Cognition and Flow Theory.’
2.2.1. Constructivism Learning Theory
Constructivism Learning Theory teaches students to actively explore, recognize, and learn independently rather than passively accepting the already established content [20]. By directly participating in problem-solving activities, discovering problems, and acquiring the skills to solve them, the differences among individuals become much more evident [21]. Digital educational games manifest the direct application of constructivism learning theory. Educational games create a virtual environment for learners, integrate learning into situational tasks, and enable learners to learn and master new skills through exploration. To elaborate, Sid Meiers Civilization III built a world for players to create and expand their empires. Here, players can explore and solve problems by themselves and intuitively experience the impact of political, military, and foreign education policies within a civilization’s history [18]. This allows them to develop a sound knowledge system about the development of society.
2.2.2. Humanistic Learning Theory
The Humanistic Learning Theory denotes that students should not be considered products on the production line, and by the same token, the teaching unit should not be the workers. Teachers should stimulate students' interest in learning, and students should make their own determination on how they learn [22]. Humanistic learning theory is pertinent to both the intellectual and emotional, as well as psychological, creative, social, physical, and even spiritual levels of learning [23]. Digital educational games can generate a natural learning environment. They recognize the complexity of students' specific emotional needs and provisions in the learning process. Through empathy design, the analysis of customer needs, and other directions, the primary purposes of fun and learning are balanced to guide students in their development. Digital educational games provide students with guidance via positive feedback and reward mechanisms. It does not have fixed results, and there is no unequivocal right or wrong. Instead, its focal point is the learning process itself.
2.2.3. Situated Cognition Theory
Situational Cognition Theory argues that events cannot be independent of learning and that knowledge is not merely a collection of facts and rules. Knowledge should be intertwined between people and their environment, a constructive interaction state [24]. It is very similar to the Constructivism Learning Theory, and both philosophies share the belief that students should actively interact with their environment as opposed to passively receiving information. Scholars of Situated Cognition Theory believe that knowledge is, to an extent, the product of actions, situations, and cultures as they exist in the context of the knowledge holder [25]. These scholars have demonstrated through experiments that creativity and context are integral to the learning process.
This theory provides a strong theoretical basis to support the use of digital educational games to teach Chinese written and cultural studies outlined in this paper. Brown cites many instances of Situated Cognition in his article, including language acquisition. He emphasizes that words and sentences are not islands. The educational game developed in this paper aligns with the Situated cognition learning theory and creates an immersive virtual environment for students to develop their language skills. The game rejects the concept of isolated rope learning by encouraging students to actively engage with new information while drawing on their existing knowledge to achieve the desired learning outcomes.
2.2.4. Flow Theory
The Flow Theory is a psychological concept proposed by Csikszentmihalyi. Broadly, it describes a mental state of fulfilment and excitement that results or “flows” from being totally immersed and focused on a particular activity. This state of mind may be likened to an artist or athlete who is engaged and focused on their respective performances. The central element of Flow Theory is perceiving challenges and their skill level; the participant achieves immersion only when these two elements are in equilibrium [26]. Flow Theory provides a reference for the design of digital educational games. Game designers must set tasks and reward mechanisms relevant to the average skill level of players. The game should not set excessively difficult tasks, causing players anxiety, nor set overly simplistic tasks that fail to stimulate players [27]. A well-designed educational game should allow the player to continue to feel stimulated and immersed for extended periods of time without the player consciously noticing the fact that time has elapsed. In the Chinese cultural teaching game studied in this paper, the level of existing elementary Chinese textbooks should be thoroughly analyzed. Further, the game should refrain from setting complex literacy and cultural tasks to ensure the digital educational game successfully stimulates its players' interests.
2.3. Theory about culture teaching
2.3.1. The Pedagogy of Performing Another Culture Theory
The Pedagogy of Performing Another Culture, as shown in Figure 1, is an essential theoretical concept in teaching Chinese as a foreign language. It combines both the attributes of physical performance and practice, integrating certain situational scenes and daily observations into teaching practices to achieve an improvement in students' material performance culture. Students will practice a scene and then learn how to practically respond the next time it occurs [28]. The Pedagogy of Performing Another Culture subscribes to the idea that learning cultures, wherein learning stories account for a large part of memory content, can support learners in learning the target culture [29].
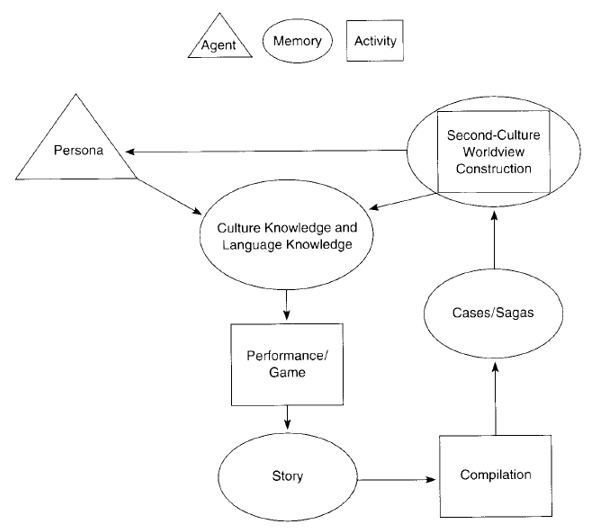
Figure 1: Cycle of Compilation [29].
Chengo Chinese is regarded as one of the most famous international Chinese teaching materials. It employs situations as the basis of each lesson’s learning content and teaches accordingly. Many games about international Chinese education generate relevant situations to allow students to experience and practice a particular situation repeatedly. ‘Han Jamaru,’ a Chinese game launched by South Korea in 2009, uses contextual settings that allow players to hear and see Chinese characters, instigating a method to learn Chinese in natural, realistic circumstances. The integration of Chinese culture in educational games, ‘Emperor's Day,’ illustrates the different situations of the emperor's daily life, allowing players to also learn traditional Chinese cultural knowledge through repeated experience [30].
2.3.2. Task-based Language Teaching
Task-based Language Teaching is teaching students to learn language by setting tasks in the classroom. It is a pivotal second language teaching technique [31]. It emphasizes learning via interactive communication, introducing authentic texts into learning situations, and enabling learners to pay greater attention to the language and learning process. The methodology of Task-based language teaching shares many aspects of constructivist theory and emulates many of the core principles of educational games. Various tasks connect the game itself through the background story. After comparing results, the game processes and skills learned through situational experience will gradually be discovered.
2.4. Research Summary
In light of vast technological progression and evolving trends in learning methods, traditional classroom teaching is becoming increasingly antiquated. In addition to the popularization of online classrooms, digital educational games have gradually entered the public's field of vision [15]. The industry of digital educational games consists of various subjects such as mathematics, biological engineering, and history. These modern learning methods and innovative game designs penetrate many educational spheres, including language study. Still, in China, in terms of international Chinese education, there is a lack of digital educational games that are officially released in the game market that target foreign language groups. Most are theoretical research and design and do not use Unity or Unreal to develop a real executable, well-designed digital educational game. This paper analyzes four theories of digital game-based learning and discusses them in conjunction with modern digital educational games. In addition, two approaches to language and Chinese teaching methods are also discussed in support of the game theory. At last, feasible game development was designed and user-tested based on the theory.
3. First-generation game prototype
3.1. Project Brief
The purpose of this graduation project is to develop an educational game for learning Chinese characters and celebrating Chinese traditional culture (the Four Great Inventions). This will be a provision for international students interested in Chinese culture. It will be an inheritance and development of China's intangible cultural heritage. At present, the interactive experience of digital gaming and intangible cultural heritage both have prominence in China. Many museums have launched corresponding interactive games to promote their collections. The Palace Museum has developed digital educational applications like ‘Emperor's Day,’ ‘The Daily Forbidden City,’ the ‘Chinese Treasures Museum,’ and the ‘Forbidden City Ceramics Museum’ [11]. The following three components are integral in constructing these digital education games: education, fun, and cultural inheritance.
In terms of education, according to the questionnaire survey conducted by Zhang Yi on international students in China, more than 40% of the students hope to improve their ability to recognize characters. That is, they wish to completely understand the meaning of Chinese characters when they see them. This has proven to be the most difficult learning facet for students who seek to learn Chinese characters [9].
Considering that the game's fun element can aid players in enhancing their knowledge, this digital education game will present the teaching content in the mechanisms of mini-games so as not to make the learning process tedious. As for cultural inheritance, the project selects the four most representative Chinese cultural innovations and introduces them: papermaking, compass, printing, and gunpowder. With changes over time, they continue to develop, but these inventions shocked the world at the time, and they play a role in significantly improving people's lives. This project hopes to pass on and record them in fresh, ingenious ways. Finally, the feedback from selected game-testers will be collated and analytically deconstructed to refine further and improve the game.
3.2. Analysis of user requirements
This part of the paper presents user personas and scenarios in user needs analysis, an important design step in designing software and games. A persona is somewhat similar to a personal profile; it describes one’s personal background. Further, it analyzes the user's psychological desires and subsequently carries out an appropriate game design. Each persona is equipped with specific scenarios and situational portraits, highlighting which circumstances will make the user more willing to play the game.
3.2.1. Initial Level of Chinese Learning
This type of player has a particular interest in Chinese culture. They have commenced learning some Chinese characters and culture, but due to the complexity of Chinese characters, they have encountered significant obstacles to their learning, impeding their progress and motivation. They expect to learn some Chinese characters quickly and efficiently. Figure 2 shows this persona.
3.2.2. Interest in Chinese culture
This type of player is interested in Chinese culture and may even be able to communicate fluently but does not read Chinese characters. They expect to experience Chinese culture and gain knowledge in an immersive learning environment. Figure 3 shows this persona.

Figure 2: User1 persona.

Figure 3: User2 persona.
3.3. Game Design
3.3.1. Story background
Amber is a businessman from Britain. He took a boat to China to sell goods but unfortunately encountered a tsunami before completing his voyage. Thankfully, as he drifted afloat at sea, clinging to life by holding a wooden board, he was discovered by some returning Chinese businessmen who rescued him. After listening to Amber recount his experience, they suggested that Amber disembark in Gusu, the most prosperous southern city in China, where Amber could find tools such as a compass, map, and other much-needed equipment to return home safely. After Amber learns some simple Chinese, the merchants give him money and deliver him just outside the city of Gusu.
3.3.2. Game Mechanics
Eamon Slevin once said, “The Core Mechanics and Gameplay of games are the centre stone of what a game is.” By designing game mechanics, the designer is also creating interactions and achieving different emotional outcomes [32]. In the beginning, the numbers 1-10 were selected as the initial card game content with reference to the textbook on international Chinese education. Because the educational function of literacy is one of the game's key focuses, Unity's Streaming Assets will be implemented so that players can modify the learning content they need locally after downloading the game. This better facilitates the practice and exercise of their memory. After succeeding in the card game, players can enter the Gusu scene and explore cultural knowledge about the four great inventions.
After the game launches, the player enters the game while on a ship. The player is required to find a dictionary, learn Chinese characters, and then pass the test. If it fails, the player can re-challenge and return to study the content anytime. Once this challenge is successful, the player can enter the Gusu City game scene to explore and search for further tools. The compass and map are hidden within the game scene of Gusu City. Players must travel to the corresponding position through exploration and complete the related tasks before obtaining the tools. The game will end when the players have successfully collected all the tools. Table 1 is an illustration of the rules.
Table 1: Illustration of the rules.
1 | The player enters the game scene on the ship and finds the dictionary to start learning. |
2 | Players perform a timed memory card game challenge. |
3 | Before the timer ends, the player passes and enters the Gusu scene to begin looking for tools. |
4 | If the timer expires, the player fails and must restart the game or re-learn the content. |
5 | After entering the Suzhou scene, complete the corresponding task to collect tools. |
6 | Game ends. |
There is no limit to the number of times each mini-game and task may be played, provided it is successful at the end. The player can receive a clue about the game.
3.3.3. Game balance
After adjusting the game balance, the functional version will be adjusted to maintain a deep, fair, and interesting nature [33]. According to the simple feedback from players, the initial selection of 9 pairs of inspections from 25 pairs of paired memories was changed to the choice of 6 from 10. Subsequent user testing will also be used to make subtle adjustments to ensure the game efficiently balances fun and challenging elements. In addition, when designing game balance, the following aspects will be considered [34].
3.3.4. Immersion
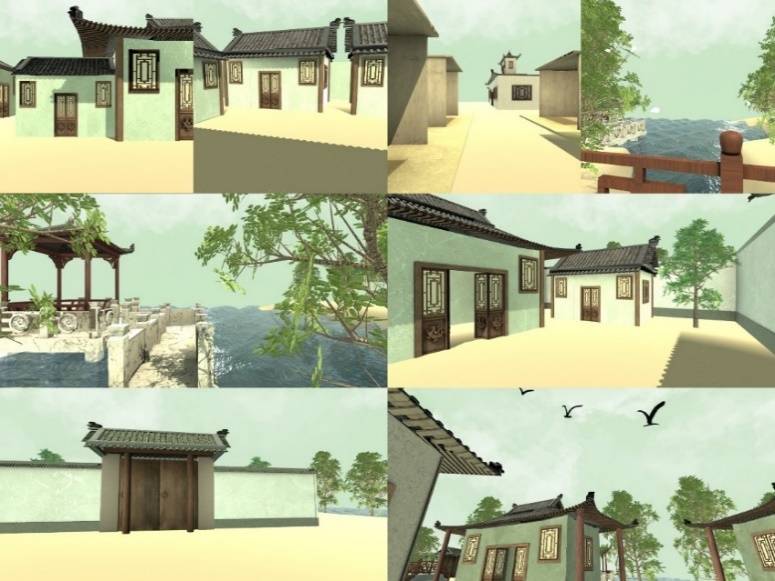

Figure 4: Aesthetic style of the game scene.
When considering the immersion element of the game, the desired outcome is to achieve the feeling of presence in the setting and culture when the player/learner is at the helm of this digital learning device. Presence is a subjective state or mental perception people feel there [35]. This can be achieved using some physical means. For example, when people are watching a 3D movie, the chair will shake, and the wind will blow above them, making people feel immersed in the movie’s setting as much as they do their own. Although the presence aspect of this graduation project faces its limitations, it will be significantly developed from the sensory perspective to its achievable capacity, namely the implementation of aesthetics and audio [36-38]. Figure 4 shows the whole aesthetic style of the game.
3.4. Technology Realization with Unity
3.4.1. Development and Work Conclusion
The development of this game is divided into four primary segments. First, developing the models required for the game through Maya, making textures according to the determined theme and style, and constructing them in Unity. Prepare UI interface Images by using Procreate and Ps. Establish game Rules, outlining the core logic design of the game through flowcharts and pseudocodes. Secondly, according to the overall logic flow chart and the pseudo-code of each function, each script was implemented in detail, and the realization of various functions, such as hot updates, timer, real-time map system, card game, etc., was completed. Preliminary testing of implemented functions and optimization after testing. Thirdly, designing realistic sound effects according to the plot requirements and atmosphere of the scene, producing appropriate background music using the materials collected. Finally, seek users for game testing, conduct interviews with regard to their game experience, analyze and collect data, and perform second-generation optimization of the game.
3.4.2. Execution logic
This game is a typical stand-alone man-machine game. The basic logic flow of the game is shown in the figure 5. The core logic of the game implementation includes a timer, card game, hot updates, text input and processing, scene switching, puzzle game, paper-making game, gunpowder game, composing game, and other components. Additionally, through the hot update module, users, after downloading the game, can customize the Chinese character card game they wish to practice by modifying the character text and corresponding pictures to accommodate the different needs of players.
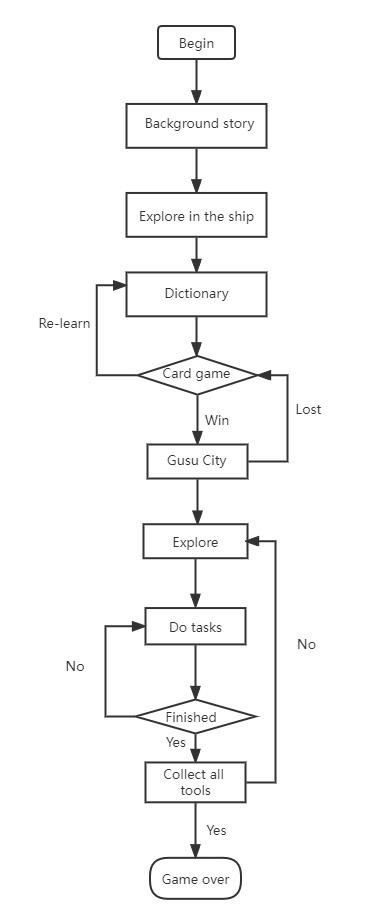
Figure 5: Basic logic flow.
4. User Test & Evaluation
4.1. Heuristic Evaluation
Heuristic evaluation is a methodology frequently used to assess software usability. The method is primarily based on literature reviews or author introspection rather than elaborating on in-game design issues [39]. By referring to the literature on heuristic evaluation, this paper conducts an author’s reflective evaluation of the Unity three-dimensional game developed within this project. Initial game optimization was performed based on the evaluation results and then entered the user testing phase.
4.2. User Test
Excluding the heuristic evaluation, user testing is also another popular software evaluation method [40]. Digital educational games should be designed for players; therefore, user experience should be prioritized. Under these assumptions, to better evaluate and improve this game, the researcher invited two individual users to participate in a game testing, where short interviews were conducted based on their game experience. The interview questions are shown in the appendix. According to the obtained interview feedback data, positive evaluations are displayed in Table 2.
Table 2: Positive evaluation.
Number | Positive evaluation |
1 | Enjoyed the setting and art style of the game |
2 | The game is very intriguing. |
3 | The design of the mini-games helps with regard to learning and understanding Chinese characters and Chinese culture, further deepening user impression. |
4 | Become noticeably more interested in Chinese culture after playing the game. |
As previously stated, this project is a digital educational game designed for foreigners to understand and learn Chinese culture. The game focuses on many educational functions and mechanics in hopes that players are entertained when attempting to learn and understand Chinese culture. Conjunctively, it also facilitates the inheriting and spreading of Chinese cultural heritage. From the positive evaluation results, the user test shows that this game meets the previous project requirements. Furthermore, the user test can also be used for second-generation game optimization, which Is why, during the test, the researcher executed empath design to gain further insight into the special customer needs [41]. As such, test players also expressed certain issues they encountered with the game. The following list encompasses problems that must be optimized within the game, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Problems to be solved.
Number | Problems to be solved |
1 | Some mini-games are too simple and lack a sense of challenge. |
2 | In some places, the game controls are not very smooth. |
3 | The character walks rather slowly. |
4 | The rules are not given a clear enough description. |
5 | The trigger range is too small in some locations. |
4.3. Game optimization
The game submitted by this project has been optimized based on the feedback from the above interview questions. Specifically, large adjustments were made with regard to the difficulty level of mini-games and the walking speed of the characters. The triggers and introduction pages were also been revised. In addition, many elements depicting ancient Chinese daily life were incorporated into the scene's layout. This decision mainly came to fruition as test players during interviews mentioned their curiosity about ancient Chinese life. In dealing with game manipulation fluency, the smoothness of game operations was improved by reducing the number of mesh faces in the overall model. However, due to the numerous diverging scenes and complex model designs, this game still has extremely high requirements for the configuration of a computer.
5. Conclusion
The project outlined within this paper completed the required original project planning while also completing the project goals with regard to the learning of Chinese characters, as well as the understanding and promotion of Chinese culture. Within the interview, both test players expressed that after incorporating the game into their learning strategies, they were able to both recognize Chinese characters 1 to 10, and also learn knowledge about Chinese culture. Through this game, the players experienced an increased interest in Chinese culture and expressed a desire to travel to China.
Due to this game being independently produced within three months, with the completion of modeling, hand-painting, script writing, scene construction, thesis writing, etc., certain intricacies of the game were not finalized to perfection. For example, there is no 3D character model designed in the scene for NPC guidance, which reduces the overall intuitiveness of the game, forcing players to unnecessarily waste time understanding the rules. Additionally, the southern China street scene could require further polishing, but due to time constraints, no more detailed models were constructed. Specific reference needs to be made with regard to the fluency and speed of the game, which is a major issue for this graduation project. Although different in-game scenes have been separated and the number of mesh face model appearances reduced, the game still requires a high level of computer configuration. Unfortunately, this means not all players can run the game smoothly, inevitably reducing overall game popularity.
When considering future game development, this paper suggests increased research into finding methodologies to ensure game smoothness without the complete dependence on computer configuration, potentially increasing game popularity. Additionally, in specific reference to this game, more details could be added to Jiangnan Street View and 3D characters, allowing the game to depict the Chinese landscape. Also, one of the purposes of the game is to introduce common cultural sense related to the four great inventions in ancient China. However, due to time constraints, only papermaking has completely replicated the process. In future work, the other three games can be improved as close as possible to restore their whole process. As previously mentioned, to improve the immersion experience of players, this game focuses on constructing three-dimensional scenes and art styles. Based on this design, the game can also be developed in virtual reality, further intensifying the player’s immersive experience. In virtual reality, players can manipulate the 5 mini-game functions through movement, generating a more interactive experience for payers with Chinese traditional culture.
References
[1]. Serious Play Conference. (2019) The 2019-2024 Global Game-based Learning Market. https://seriousplayconf.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Metaari_2019-2024_Global_Game-based_Learning_Market_Executive_Overview.pdf.
[2]. M.thepaper.cn. (2022) The game goes out to sea, and the "national style" is getting stronger. https://m.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_16986040.
[3]. Statista. (2022) China: students' number at Confucius Institutes worldwide by class type 2018 | Statista.https://www.statista.com/statistics/879730/number-of-students-at-confucius-institutes-worldwide-by-class-type/.
[4]. Tian, W. (2009) The Educational Potential of Online Games from a psychological perspective. [online] Kns8.zh.eastview.com. Available at: http://kns8.zh.eastview.com/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=CQGY200902110&dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2009&v=.
[5]. JENSEN, E., n.d. (2020) BRAIN BASED LEARNING. CORWIN SAGE.
[6]. Cooper, R., (1998) Benchmarking new product performance:. European Management Journal, 16(1), pp.1-17.
[7]. Mauroner, O. (2019) Gamification in Management and Other Non-Game Contexts—Understanding Game Elements, Motivation, Reward Systems, and User Types. Open Journal of Business and Management, 07(04), pp.1815-1830.
[8]. All, A., Nuñez Castellar, E. and Van Looy, J. (2016) Assessing the effectiveness of digital game-based learning: Best practices. Computers & Education, 92-93, pp.90-103.
[9]. Zhang, Y., Lin, Y., & Zhang, F. (2013). Research and development of educational games from the perspective of EDR. Science Publishing House.
[10]. C. Yang, D. Peng and S. Sun. (2006) "Creating a Virtual Activity for the Intangible Culture Heritage," 16th International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence--Workshops (ICAT'06) pp. 636-641, doi: 10.1109/ICAT.2006.52.
[11]. The Palace Museum. (2022) Game Museum - The Palace Museum. https://www.dpm.org.cn/games_hall.html.
[12]. 163.com. (2021) 35 Case Studies of Cooperation between Museum and Game. https://www.163.com/dy/article/G49DQSG705466ZM9.html.
[13]. Rose, C. and Nicholl, M. (1998) Accelerated learning for the 21st century. New York: Dell, p.30.
[14]. PCMag UK. (2017) 10 Educational PC Games Every 80s Kid Loved. https://uk.pcmag.com/features/61595/10-educational-pc-games-every-80s-kid-loved.
[15]. Manesis, D. (2020) 'Digital Games in Primary Education', in I. Deliyannis (ed.), Game Design and Intelligent Interaction, IntechOpen, London. 10.5772/intechopen.91134.
[16]. Prensky, Mark. (2001) Digital Game-Based Learning / Mark Prensky. New York ;: McGraw-Hill, 2001. Print.
[17]. Report, A., Gallery, I., Kit, P. and Prize, i. (2022) [online] iCampus. http://icampus.mit.edu/projects/project/?pname=GamesToTeach.
[18]. Burns A., J. (2022) Civilization III: Digital game-based learning and macrohistory simulations. Australian Foresight Institute/Disinformation. http://alexburns.net/Files/CivilizationIII.pdf.
[19]. Bisson, C. and Luckner, J. (1996) Fun in Learning: The Pedagogical Role of Fun in Adventure Education. Journal of Experiential Education, 19(2), pp.108-112.
[20]. Bada S O, Olusegun S., J. (2015) Constructivism learning theory: A paradigm for teaching and learning. Journal of Research & Method in Education, 5(6): 66-70.
[21]. Srivastava, K. (2021) Constructivist Theory of Learning. Technolearn An International Journal of Educational Technology, 11(1).
[22]. Johnson A P., J. (2014) Humanistic learning theory. Education psychology: Theories of learning and human development,: 1-10.
[23]. DeCarvalho, R. (1991) The humanistic paradigm in education. The Humanistic Psychologist, 19(1), pp.88-104.
[24]. Roth, W. and Jornet, A. (2013) Situated cognition. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 4(5), pp.463-478.
[25]. Brown, J., Collins, A. and Duguid, P. (1989) Situated Cognition and the Culture of Learning. Educational Researcher, 18(1), pp.32-42.
[26]. Shernoff, David & Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly &Shneider, Barbara &Shernoff, Elisa. (2003). Student Engagement in High School Classrooms from the Perspective of Flow Theory. School Psychology Quarterly. 18. 158-176. 10.1521/scpq.18.2.158.21860.
[27]. Egbert, J. (2003) A Study of Flow Theory in the Foreign Language Classroom. The Modern Language Journal, 87(4), pp.499-518.
[28]. WeiKe Wu (2010) The Pedagogy of Performing Another Culture Theory.
[29]. Walker, G., & Noda, M. (2000). Remembering the future: Compiling knowledge of another culture. Reflecting on the past to shape the future, 187-212.
[30]. Emperor's Day. App Store. (2014).https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/huang-di-yi-tian-gu-gong-chu/id893942155?l=zh&ls=1&mt=8.
[31]. Ellis, R. (2009) Task-based language teaching: sorting out the misunderstandings. International Journal Of Applied Linguistics, 19(3), 221-246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-4192.2009.00231.x
[32]. Slevin, E. (2022) Core mechanics and gameplay. [online] Ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub. https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/gamedesigndevelopmenttextbook/chapter/core-mechanics-and-gameplay/.
[33]. Jaffe, A., Miller, A., Andersen, E., Liu, Y. E., Karlin, A., & Popovic, Z. (2012, October) Evaluating competitive game balance with restricted play. In Eighth Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment Conference.
[34]. Schell, J. and Lu, J. (2015) The Art of Game Design.
[35]. Ispr.info. (2022) Presence defined. https://ispr.info/about-presence-2/about-presence/.
[36]. Nordin, A. Imran &Denisova, Alena. (2014) Too Many Questionnaires: Measuring Player Experience Whilst Playing Digital Games.
[37]. Blog.krybot.com. (2022) Unity3D hot update plan (collection of experts) – Krybot. https://blog.krybot.com/a?ID=00500-27b3a00a-6792-4e85-8e81-35ba504f596e.
[38]. Technologies, U. (2022) Unity - Manual: Streaming Assets. [online] Docs.unity3d.com. https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/StreamingAssets.html.
[39]. Pinelle, D. and Wong, N. (2008) Heuristic evaluation for games. Proceeding of the twenty-sixth annual CHI conference on Human factors in computing systems - CHI '08,.
[40]. Tan, W., Liu, D. and Bishu, R. (2009) Web evaluation: Heuristic evaluation vs. user testing. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 39(4), pp.621-627.
[41]. Harvard Business Review. (2022) Spark Innovation Through Empathic Design. https://hbr.org/1997/11/spark-innovation-through-empathic-design%20In%20such%20a%20context,%20researchers%20can%20gain%20acce.
Cite this article
Zhang,J. (2024). Unity-based Chinese Digital Education Game: Journey to Cultural Relics of Ancient China. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,49,119-132.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Interdisciplinary Humanities and Communication Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Serious Play Conference. (2019) The 2019-2024 Global Game-based Learning Market. https://seriousplayconf.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Metaari_2019-2024_Global_Game-based_Learning_Market_Executive_Overview.pdf.
[2]. M.thepaper.cn. (2022) The game goes out to sea, and the "national style" is getting stronger. https://m.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_16986040.
[3]. Statista. (2022) China: students' number at Confucius Institutes worldwide by class type 2018 | Statista.https://www.statista.com/statistics/879730/number-of-students-at-confucius-institutes-worldwide-by-class-type/.
[4]. Tian, W. (2009) The Educational Potential of Online Games from a psychological perspective. [online] Kns8.zh.eastview.com. Available at: http://kns8.zh.eastview.com/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=CQGY200902110&dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2009&v=.
[5]. JENSEN, E., n.d. (2020) BRAIN BASED LEARNING. CORWIN SAGE.
[6]. Cooper, R., (1998) Benchmarking new product performance:. European Management Journal, 16(1), pp.1-17.
[7]. Mauroner, O. (2019) Gamification in Management and Other Non-Game Contexts—Understanding Game Elements, Motivation, Reward Systems, and User Types. Open Journal of Business and Management, 07(04), pp.1815-1830.
[8]. All, A., Nuñez Castellar, E. and Van Looy, J. (2016) Assessing the effectiveness of digital game-based learning: Best practices. Computers & Education, 92-93, pp.90-103.
[9]. Zhang, Y., Lin, Y., & Zhang, F. (2013). Research and development of educational games from the perspective of EDR. Science Publishing House.
[10]. C. Yang, D. Peng and S. Sun. (2006) "Creating a Virtual Activity for the Intangible Culture Heritage," 16th International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence--Workshops (ICAT'06) pp. 636-641, doi: 10.1109/ICAT.2006.52.
[11]. The Palace Museum. (2022) Game Museum - The Palace Museum. https://www.dpm.org.cn/games_hall.html.
[12]. 163.com. (2021) 35 Case Studies of Cooperation between Museum and Game. https://www.163.com/dy/article/G49DQSG705466ZM9.html.
[13]. Rose, C. and Nicholl, M. (1998) Accelerated learning for the 21st century. New York: Dell, p.30.
[14]. PCMag UK. (2017) 10 Educational PC Games Every 80s Kid Loved. https://uk.pcmag.com/features/61595/10-educational-pc-games-every-80s-kid-loved.
[15]. Manesis, D. (2020) 'Digital Games in Primary Education', in I. Deliyannis (ed.), Game Design and Intelligent Interaction, IntechOpen, London. 10.5772/intechopen.91134.
[16]. Prensky, Mark. (2001) Digital Game-Based Learning / Mark Prensky. New York ;: McGraw-Hill, 2001. Print.
[17]. Report, A., Gallery, I., Kit, P. and Prize, i. (2022) [online] iCampus. http://icampus.mit.edu/projects/project/?pname=GamesToTeach.
[18]. Burns A., J. (2022) Civilization III: Digital game-based learning and macrohistory simulations. Australian Foresight Institute/Disinformation. http://alexburns.net/Files/CivilizationIII.pdf.
[19]. Bisson, C. and Luckner, J. (1996) Fun in Learning: The Pedagogical Role of Fun in Adventure Education. Journal of Experiential Education, 19(2), pp.108-112.
[20]. Bada S O, Olusegun S., J. (2015) Constructivism learning theory: A paradigm for teaching and learning. Journal of Research & Method in Education, 5(6): 66-70.
[21]. Srivastava, K. (2021) Constructivist Theory of Learning. Technolearn An International Journal of Educational Technology, 11(1).
[22]. Johnson A P., J. (2014) Humanistic learning theory. Education psychology: Theories of learning and human development,: 1-10.
[23]. DeCarvalho, R. (1991) The humanistic paradigm in education. The Humanistic Psychologist, 19(1), pp.88-104.
[24]. Roth, W. and Jornet, A. (2013) Situated cognition. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 4(5), pp.463-478.
[25]. Brown, J., Collins, A. and Duguid, P. (1989) Situated Cognition and the Culture of Learning. Educational Researcher, 18(1), pp.32-42.
[26]. Shernoff, David & Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly &Shneider, Barbara &Shernoff, Elisa. (2003). Student Engagement in High School Classrooms from the Perspective of Flow Theory. School Psychology Quarterly. 18. 158-176. 10.1521/scpq.18.2.158.21860.
[27]. Egbert, J. (2003) A Study of Flow Theory in the Foreign Language Classroom. The Modern Language Journal, 87(4), pp.499-518.
[28]. WeiKe Wu (2010) The Pedagogy of Performing Another Culture Theory.
[29]. Walker, G., & Noda, M. (2000). Remembering the future: Compiling knowledge of another culture. Reflecting on the past to shape the future, 187-212.
[30]. Emperor's Day. App Store. (2014).https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/huang-di-yi-tian-gu-gong-chu/id893942155?l=zh&ls=1&mt=8.
[31]. Ellis, R. (2009) Task-based language teaching: sorting out the misunderstandings. International Journal Of Applied Linguistics, 19(3), 221-246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-4192.2009.00231.x
[32]. Slevin, E. (2022) Core mechanics and gameplay. [online] Ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub. https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/gamedesigndevelopmenttextbook/chapter/core-mechanics-and-gameplay/.
[33]. Jaffe, A., Miller, A., Andersen, E., Liu, Y. E., Karlin, A., & Popovic, Z. (2012, October) Evaluating competitive game balance with restricted play. In Eighth Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment Conference.
[34]. Schell, J. and Lu, J. (2015) The Art of Game Design.
[35]. Ispr.info. (2022) Presence defined. https://ispr.info/about-presence-2/about-presence/.
[36]. Nordin, A. Imran &Denisova, Alena. (2014) Too Many Questionnaires: Measuring Player Experience Whilst Playing Digital Games.
[37]. Blog.krybot.com. (2022) Unity3D hot update plan (collection of experts) – Krybot. https://blog.krybot.com/a?ID=00500-27b3a00a-6792-4e85-8e81-35ba504f596e.
[38]. Technologies, U. (2022) Unity - Manual: Streaming Assets. [online] Docs.unity3d.com. https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/StreamingAssets.html.
[39]. Pinelle, D. and Wong, N. (2008) Heuristic evaluation for games. Proceeding of the twenty-sixth annual CHI conference on Human factors in computing systems - CHI '08,.
[40]. Tan, W., Liu, D. and Bishu, R. (2009) Web evaluation: Heuristic evaluation vs. user testing. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 39(4), pp.621-627.
[41]. Harvard Business Review. (2022) Spark Innovation Through Empathic Design. https://hbr.org/1997/11/spark-innovation-through-empathic-design%20In%20such%20a%20context,%20researchers%20can%20gain%20acce.









