1. Introduction
Macroeconomic regulation and legal adjustments are integral components of modern economic development and play an irreplaceable role in maintaining economic stability and promoting sustainable growth. Macroeconomic regulation refers to the management and adjustment of the overall economy through government macro-control measures to achieve goals such as stable economic growth, price stability, and employment promotion. Legal adjustments, on the other hand, involve the formulation and modification of laws and regulations to adapt to and guide changes in economic development, ensuring the adaptability and effectiveness of the legal system. [1]
Under a market economy system, the relationship between macroeconomic regulation and legal adjustments is becoming increasingly interconnected. Macroeconomic regulation relies on legal adjustments to provide institutional safeguards and legal support, while legal adjustments need to be coordinated with macroeconomic regulation to ensure the implementation and effectiveness of laws. Therefore, studying the relationship between macroeconomic regulation and legal adjustments is of great significance in deepening our understanding of economic regulation and improving the legal system. By reviewing relevant literature, we can further analyze the goals, means, and effects of macroeconomic regulation, as well as explore the role and challenges of legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation. Based on this, some suggestions for legal adjustments can be proposed to better support macroeconomic regulation.
2. Goals and Means of Macroeconomic Regulation
Macroeconomic regulation refers to the measures taken by the government to influence the operation and development of the entire economic system, with the aim of achieving goals such as economic growth, stable employment, and price stability. Therefore, in macroeconomic regulation, the objectives of regulation should be clearly defined, and appropriate means should be chosen to achieve these objectives. These means can include fiscal policy, monetary policy, etc., aiming to influence aggregate demand and aggregate supply, thus promoting economic stability and growth.
2.1. Goals of Macroeconomic Regulation
The goals of macroeconomic regulation typically include the following aspects:
2.1.1. Economic Growth
Economic growth is one of the primary goals of macroeconomic regulation. Economic growth can improve people’s living standards, increase employment opportunities, and promote social stability. In regulation, it is necessary to focus on the speed and quality of economic growth, ensuring sustainable and healthy growth.
2.1.2. Stable Employment
Stable employment is another important goal of macroeconomic regulation. Maintaining employment stability can enhance people’s income levels, reduce social instability factors, and promote social harmony. Therefore, measures need to be taken to promote employment, increase employment rates, and prevent mass unemployment.
2.1.3. Price Stability
Price stability is another crucial goal of macroeconomic regulation. Both inflation and deflation have negative impacts on the economy and society. Therefore, measures need to be taken to control price increases and decreases, maintaining price stability.
2.1.4. Fair Income Distribution
Fair income distribution is an important goal of macroeconomic regulation. Unequal income distribution can lead to increased social instability and exacerbate unfair phenomena. Thus, promoting fair income distribution, reducing wealth gaps, and improving social fairness and justice are necessary steps.
2.2. Means of Macroeconomic Regulation
The means of macroeconomic regulation typically include monetary policy and fiscal policy. Monetary policy influences economic operations by adjusting the money supply and interest rates, while fiscal policy affects economic operations by adjusting government expenditures and taxation.
2.2.1. Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to the use of adjustments in the money supply and interest rates to influence economic operations and development. Adjustments in the money supply can affect price levels and economic growth, while adjustments in interest rates can impact investment and consumption behavior. In monetary policy, the central bank serves as the primary implementing institution, utilizing tools such as open market operations and reserve requirement adjustments to implement monetary policy.
2.2.2. Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the use of adjustments in government expenditures and taxation to influence economic operations and development. Adjustments in government expenditures can stimulate economic growth, while adjustments in taxation can affect consumption and investment behavior. In fiscal policy, the Ministry of Finance serves as the main implementing institution, employing measures such as budget formulation and tax policy adjustments to implement fiscal policy.
2.3. Effects of Macroeconomic Regulation
The effects of macroeconomic regulation depend on the choice of objectives and means of regulation, as well as the effectiveness of implementation. In macroeconomic regulation, it is crucial to consider the complexity and uncertainty of the economy, as well as the lag effects and coordination of policies.
The effects of macroeconomic regulation can be evaluated using various indicators, such as economic growth rate, unemployment rate, inflation rate, etc. By analyzing the changes in these indicators, the effectiveness of regulatory policies can be assessed, and policy measures can be adjusted timely to achieve desired goals.
2.4. Role and Challenges of Legal Adjustments in Macroeconomic Regulation
Legal adjustments play a vital role in macroeconomic regulation. In the face of challenges such as economic complexity and uncertainty, difficulties in coordinating interests, and alignment with international economic and trade rules, the formulation and revision of laws are essential to ensure the implementation of regulation and clarify objectives, means, and scope.
To better support macroeconomic regulation, research and practice in legal adjustments should be strengthened to enhance their scientificity and effectiveness. In this process, the importance of international cooperation is self-evident as it helps better adapt to the trends of globalization and economic integration. [2]
3. Evaluation of the Effects of Macroeconomic Regulation
Macroeconomic regulation refers to the process in which a country adjusts and controls economic operations through the use of monetary policy, fiscal policy, industrial policy, etc. In macroeconomic regulation, the accuracy and timeliness of evaluating the effectiveness of regulation are crucial. This section will analyze the methods and indicators used to evaluate the effects of macroeconomic regulation, with a focus on economic growth rate and inflation rate, and discuss their advantages, disadvantages, and application scope.
3.1. Evaluation of Economic Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is an important indicator of the speed of economic growth in a country or region, usually expressed by the annual change rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). When evaluating the effectiveness of macroeconomic regulation, the economic growth rate is a key reference indicator.
There are various methods to evaluate the economic growth rate, including:
Comparative method: This method compares the economic growth rate before and after the implementation of regulatory measures to evaluate their effectiveness. By comparing the economic growth rates during different time periods, the effectiveness of regulatory measures can be assessed. However, the limitation of the comparative method is that it cannot completely isolate the influence of other factors on the economic growth rate, thus requiring a comprehensive analysis in conjunction with other evaluation methods.
Trend method: This method evaluates the effectiveness of regulation by observing the long-term trend of the economic growth rate. It is suitable for evaluating the long-term effects of macroeconomic regulation. The advantage of the trend method is that it can eliminate the influence of short-term fluctuations, but it cannot promptly reflect the short-term effects of regulatory measures.
Capacity method: This method evaluates the contribution of regulatory measures to economic growth by analyzing the gap between the economic growth rate and the potential economic growth rate. The potential economic growth rate refers to the rate at which the economy can sustainably grow without considering inflation and other short-term factors. The advantage of the capacity method is that it can evaluate the contribution of regulatory measures to economic growth, but determining the accurate value of potential economic growth rate is challenging.
In addition to the above methods, the decomposition method can be used to decompose the economic growth rate into contributions from factors such as labor, capital, and productivity. This method allows for a more in-depth assessment of the impact of regulatory measures on economic growth.
3.2. Evaluation of Inflation Rate
The inflation rate is an indicator that measures the speed at which prices are rising and is typically represented by the annual change in the Consumer Price Index (CPI). When evaluating the effectiveness of macroeconomic regulation, the inflation rate is also an important reference indicator.
The methods for evaluating the inflation rate mainly include the absolute method, relative method, and expectation method.
The absolute method directly compares the changes in the inflation rate before and after regulation to evaluate the effectiveness of the regulatory measures. By comparing the inflation rates during different time periods, it is possible to determine whether the regulatory measures are effective. However, the limitation of the absolute method lies in its inability to exclude the influence of other factors on the inflation rate. Therefore, it is necessary to combine other evaluation methods for comprehensive analysis.
The relative method compares the inflation rates before and after regulation with those of other countries or regions to evaluate the effectiveness of the regulatory measures. By comparing the inflation rates in different regions, it is possible to determine whether the regulatory measures are internationally competitive. [3] The advantage of the relative method is that it allows for comparison with international standards, but the disadvantage is that it needs to consider the influence of the international environment.
The expectation method evaluates the effectiveness of regulatory measures by investigating and analyzing the market participants’ expectations of future inflation rates. The advantage of the expectation method is that it can reflect the market’s response to regulatory measures in a timely manner, [4] but the disadvantage is that the accuracy of expectations is uncertain.
In addition to the above methods, the decomposition method of the inflation rate can be used to assess the impact of regulatory measures on inflation by decomposing the inflation rate into contributions from demand pull and supply push factors. This method allows for a more in-depth evaluation of the impact of regulatory measures on inflation.
3.3. Comprehensive Evaluation Method
In order to comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness of macroeconomic regulation, indicators such as economic growth rate and inflation rate can be considered together. The evaluation results obtained from different evaluation methods can be compared in a tabular form to judge the overall effectiveness of the regulatory measures. Please refer to Figure 1 and Table 1 for details.
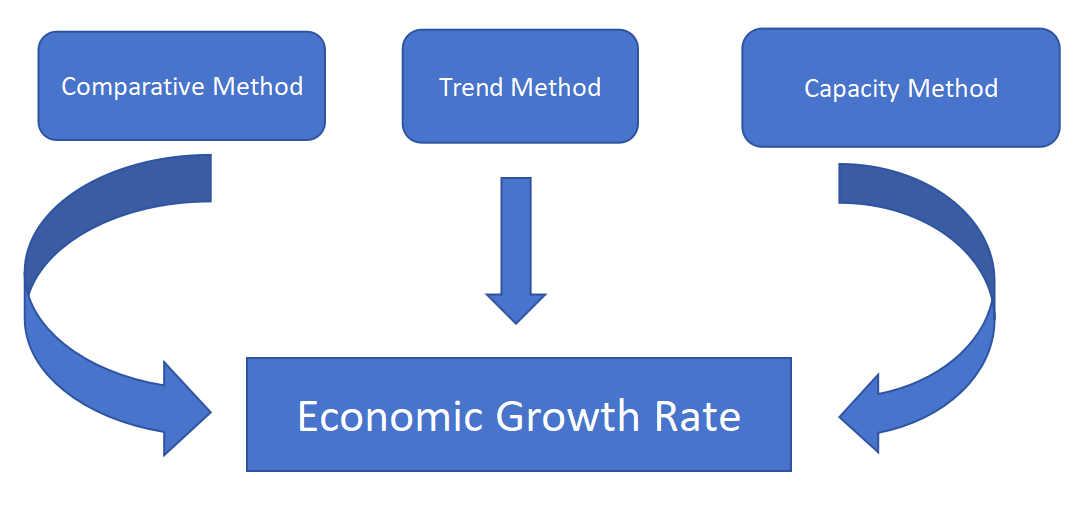
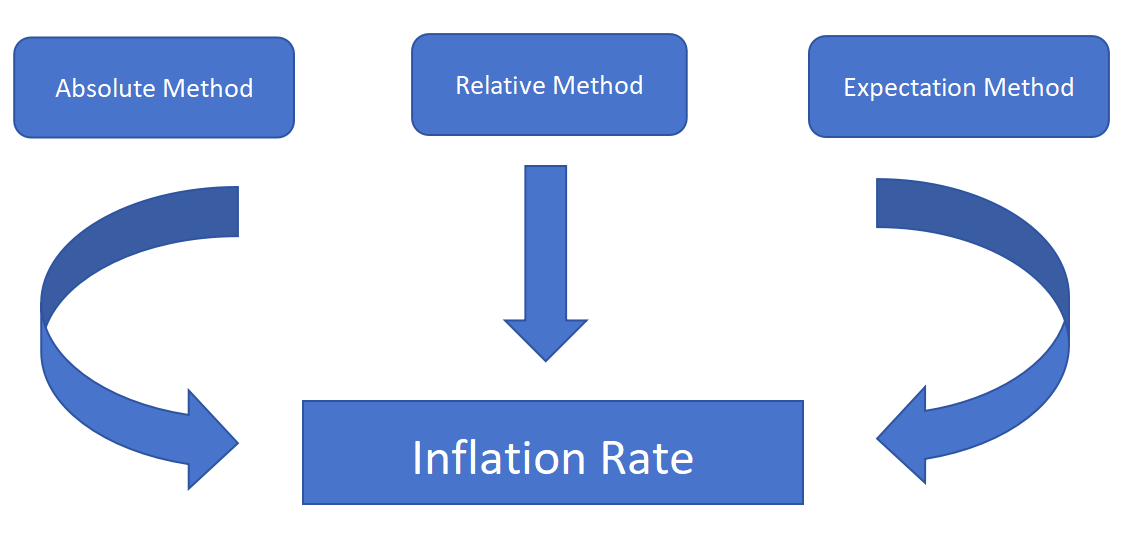
Figure 1: Analysis Process.
Table 1: Comprehensive Evaluation Method.
Evaluation Method | Economic Growth Rate | Inflation Rate |
Comparative Method | Result 1 | |
Trend Method | Result 2 | |
Capacity Method | Result 3 | |
Absolute Method | Result 4 | |
Relative Method | Result 5 | |
Expectation Method | Result 6 |
By using the comprehensive evaluation method, a more comprehensive understanding of the effectiveness of macroeconomic regulation can be obtained, providing a basis for regulatory decision-making.
The evaluation of the effectiveness of macroeconomic regulation is a complex and important issue. Economic growth rate and inflation rate are commonly used evaluation indicators, and multiple evaluation methods can be used for comprehensive analysis. However, each evaluation method has its own advantages, disadvantages, and scope of application, so it is necessary to use different evaluation methods in combination and make judgments based on the actual situation. [5] At the same time, tools such as tables and charts can be used to clearly present the evaluation results, thereby better supporting the decision-making process of macroeconomic regulation.
4. The Role of Legal Adjustments in Macroeconomic Regulation
In this section, we will explore the role and impact of legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation. Macroeconomic regulation aims to promote economic stability and sustainable growth through government intervention. Legal adjustments serve as an important means to achieve macroeconomic regulation. In this context, legal adjustments play a role in regulation, guidance, and protection, by adjusting and regulating the behavior of economic entities to achieve the goals of macroeconomic regulation.
4.1. Formulation and Enforcement of Laws and Regulations
The first role of legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation is to regulate the behavior of economic entities through the formulation and enforcement of laws and regulations. The government formulates relevant laws and regulations to regulate the behavior of market entities, in order to prevent market failures and unfair competition. For example, anti-monopoly laws are enacted to regulate monopolistic behavior in the market, environmental protection laws are established to regulate the environmental behavior of enterprises, and labor laws are enacted to protect the rights and interests of workers. The formulation and enforcement of these laws and regulations ensure that economic entities abide by the rules of the market economy, ensuring fair competition and stable economic development.
4.2. Support for Macroeconomic Policies
The second role of legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation is to support macroeconomic policies. Macroeconomic policies refer to the government’s use of fiscal policy, monetary policy, and industrial policy, among other means, to influence the overall direction and pace of economic operation. Legal adjustments establish and improve corresponding legal systems, providing legal basis and protection for the government’s implementation of macroeconomic policies. [6] For example, the formulation of fiscal laws and regulations regulates the implementation of fiscal policies, the formulation of monetary laws and regulations regulates the execution of monetary policies, and the formulation of industrial laws and regulations guides the implementation of industrial policies. These measures of legal adjustment provide a solid legal foundation for the government’s macroeconomic policies, ensuring the smooth implementation of these policies.
4.3. Challenges and Countermeasures of Legal Adjustments
However, legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation also face challenges. Firstly, the complexity and diversity of macroeconomic regulation pose challenges to legal adjustments. As macroeconomic regulation involves multiple sectors, entities, and interests, the formulation and enforcement of legal adjustments need to consider various complex situations and changes. Secondly, the timeliness and flexibility of legal adjustments are also challenged. Macro-economic regulation requires timely responses, while the formulation and enforcement of legal adjustments often require a considerable amount of time, which may result in insufficient timeliness and flexibility. Lastly, the execution and supervision of legal adjustments also face certain challenges. Due to the involvement of numerous economic entities and interests in macroeconomic regulation, higher demands are placed on the execution and supervision of legal adjustments.
To address these challenges, several countermeasures can be taken to strengthen the role of legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation. Firstly, it is necessary to enhance research and theoretical development in legal adjustments, improving their scientific and adaptive nature. Secondly, the legislative and enforcement capabilities of legal adjustments need to be strengthened, enhancing their timeliness and flexibility. Lastly, the execution and supervision of legal adjustments should be strengthened to ensure their effective implementation. [7]
In summary, legal adjustments play a crucial role in macroeconomic regulation. Through the formulation and enforcement of laws and regulations, legal adjustments regulate the behavior of economic entities. By supporting macroeconomic policies, legal adjustments provide the legal basis and protection for the government’s macroeconomic regulation. However, legal adjustments also face challenges in macroeconomic regulation. Therefore, it is essential to improve regulatory policies to enhance the effectiveness of legal adjustments in supporting the implementation of macroeconomic regulation.
5. Challenges and Recommendations of Legal Adjustments
Legal adjustments play a crucial role in macroeconomic regulation, but they also face several challenges. This section will first analyze the challenges of legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation and provide corresponding recommendations and improvement measures. Please refer to Figure 2 and Table 2 for details.
5.1. Challenges of Legal Adjustments
In macroeconomic regulation, legal adjustments face the following main challenges:
5.1.1. Institutional Challenges
Macro-economic regulation relies on a comprehensive legal framework to ensure the effective implementation and enforcement of regulatory policies. However, the existing legal system for macroeconomic regulation still has some deficiencies, such as an inadequate legal system and unclear legal provisions. These institutional challenges pose certain difficulties for legal adjustments and affect the effectiveness and efficiency of macroeconomic regulation.
5.1.2. Adaptability Challenges
Macro-economic regulation requires timely and effective responses to changes in economic conditions and the market. However, the existing mechanisms for legal adjustments have certain shortcomings in terms of adaptability. On one hand, the procedures for legal adjustments are relatively lengthy, often involving a series of legislative, amendment, and deliberation procedures, which results in insufficient timeliness of adjustments. On the other hand, legal adjustments often fail to keep up with changes in the economic situation, leading to ineffective implementation of regulatory measures.
5.1.3. Regulatory Challenges
Macro-economic regulation requires the establishment of an effective regulatory mechanism to ensure the effective implementation and enforcement of regulatory policies. However, the current regulatory mechanisms have some issues, such as insufficient regulatory intensity and inflexible regulatory means. These regulatory challenges create certain pressure for legal adjustments and also have an impact on the effectiveness and efficiency of macroeconomic regulation.
5.2. Recommendations and Improvement Measures for Legal Adjustments
5.2.1. Enhancing the Legal System
To enhance the comprehensiveness and adaptability of the legal system for macroeconomic regulation, it is necessary to strengthen legislative work and improve the basic framework and specific provisions of laws related to macroeconomic regulation. At the same time, it is also important to strengthen the evaluation and monitoring of the legal system, timely identify and resolve institutional issues, and ensure the effectiveness and operability of legal adjustments.
5.2.2. Improving the Flexibility and Timeliness of Legal Adjustments
To improve the flexibility and timeliness of legal adjustments, the following measures can be taken: First, simplify the procedures for legal adjustments, reduce lengthy legislative, amendment, and deliberation procedures, and enhance the timeliness of adjustments. Second, establish a rapid response mechanism to promptly adjust to changes in economic conditions and the market, improving the adaptability and implementation effectiveness of regulatory measures.
5.2.3. Strengthening Regulatory Intensity and Means
To strengthen the regulation of macroeconomic regulation, the following measures can be taken: First, increase regulatory intensity by enhancing comprehensive supervision of the entire process of macroeconomic regulation policies, ensuring the effective implementation of policies. Second, innovate regulatory means by introducing information technology and big data analysis, enhancing the precision and efficiency of regulation.
By addressing the challenges through the improvement of the legal system, enhancing the flexibility and timeliness of adjustments, and strengthening regulatory intensity and means, legal adjustments can better support macroeconomic regulation and promote economic stability and sustainable development.
Figure 2: Challenges.
Table 2: Challenges and Recommendations Faced by Legal Adjustments.
Challenges of Legal Adjustments | Recommendations | |
Institutional Challenges | 30% | Enhancing the Legal System |
Adaptability Challenges | 40% | Improving the Flexibility and Timeliness of Legal Adjustments |
Regulatory Challenges | 30% | Strengthening Regulatory Intensity and Means |
6. Conclusion
The intrinsic mechanisms and influencing factors of macroeconomic regulation are diverse and complex, and legal adjustments play a key role in this process. In the current economic environment, legal adjustments in macroeconomic regulation face some problems and challenges, including an inadequate legal system and weak enforcement. To address these issues, proactive measures should be taken to improve relevant laws and regulations and policy-making work. Additionally, it is important to establish a comprehensive information disclosure system and introduce more market mechanisms to further optimize the effectiveness of macroeconomic regulation.
References
[1]. Xu, G. J. (2005). Strengthening structural adjustments and maintaining overall balance: Analysis of the expected goals of macroeconomic regulation in 2005 and recent economic trends. *Price Theory and Practice*, (4), 6-7.
[2]. Xu, M. Z. (2001). Thoughts on the formulation of the “Macroeconomic Regulation Law”. *Law Journal*, (3), 15-17.
[3]. Chen, J. H. (2005). From implementing macroeconomic regulation to successful “soft landing”. *Research on the History of the Communist Party of China*, (2), 3-18.
[4]. Li, D. H. (1988). Strengthening macroeconomic regulation and promoting the strategic transformation of county-level economy: Reflections from the implementation of economic development plans in Huazhou County. *Academic Research*, (3), 20-22.
[5]. Wang, J. G. (2016). Institutional dilemma of the legal liability mechanism for financial macroeconomic regulation: Perspective from the “uncertainty” of financial macroeconomic regulation. *Journal of Qiqihar Normal University*, (1), 83-85.
[6]. Chen, G. (2012). *Public Finance* (5th ed.). Beijing: Renmin University of China Press. 190-196.
[7]. Bai, B., Yang, X. W., & Li, Y. (2008). *Macroeconomics Tutorial*. Chengdu: Sichuan People’s Publishing House. 220-230.
Cite this article
Sun,Z. (2023). A Study on the Relationship of Macroeconomic Regulation and Its Legal Adjustments. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,26,149-157.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the International Conference on Global Politics and Socio-Humanities
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Xu, G. J. (2005). Strengthening structural adjustments and maintaining overall balance: Analysis of the expected goals of macroeconomic regulation in 2005 and recent economic trends. *Price Theory and Practice*, (4), 6-7.
[2]. Xu, M. Z. (2001). Thoughts on the formulation of the “Macroeconomic Regulation Law”. *Law Journal*, (3), 15-17.
[3]. Chen, J. H. (2005). From implementing macroeconomic regulation to successful “soft landing”. *Research on the History of the Communist Party of China*, (2), 3-18.
[4]. Li, D. H. (1988). Strengthening macroeconomic regulation and promoting the strategic transformation of county-level economy: Reflections from the implementation of economic development plans in Huazhou County. *Academic Research*, (3), 20-22.
[5]. Wang, J. G. (2016). Institutional dilemma of the legal liability mechanism for financial macroeconomic regulation: Perspective from the “uncertainty” of financial macroeconomic regulation. *Journal of Qiqihar Normal University*, (1), 83-85.
[6]. Chen, G. (2012). *Public Finance* (5th ed.). Beijing: Renmin University of China Press. 190-196.
[7]. Bai, B., Yang, X. W., & Li, Y. (2008). *Macroeconomics Tutorial*. Chengdu: Sichuan People’s Publishing House. 220-230.









