1. Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a important branch of computer science, Its core purpose is to use machines to simulate human thought processes and thereby replace humans in performing related tasks [1]. It efficiently processes data, analyzes patterns and provides decision recommendations, increasing efficiency and reducing task time. In recent years, AI has developed rapidly in various fields and promoted the progress of the industry. Over several decades, AI technologies have been extensively applied in numerous agricultural fields, such as plant protection, soil fertility and water management, facility horticulture management, crop cultivation management, livestock and poultry farming, aquaculture, and agricultural product sales decision-making [2].In agricultural production, AI technologies analyze the growth of crops by processing the collected data, calculating the environmental demands of crops, predicting the future status of crops, then helping people make an optimal decision in order to enhance the quality of crops production. Machine learning is a subfield of AI which focuses on using computers to simulate human learning activities. It constitutes a methodology for investigating computer recognition of existing knowledge, acquisition of novel knowledge, continuous enhancement of performance, and the attainment of self-perfection [3]. Recently, machine learning has demonstrated widespread applicability across various social domains due to its self-improving capabilities. It enhances production efficiency and collaborates with other emerging production tools to promote high-quality development across industries. The core essence of machine learning lies in its learning mechanisms [4]. The main approaches of machine learning include supervised learning, semi-supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. By applying algorithms to process collected data, this technology assists individuals in making optimal decisions under given conditions. In agricultural contexts, machine learning leverages its robust statistical analysis and data processing capabilities, combined with Internet of Things technologies, to analyze and process vast amounts of collected data statistically. This integration optimizes agricultural decision-making processes and improves production efficiency.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the emerging technologies of this century. IoT refers to a network system that connects any object to the internet through information sensing devices and specified protocols, which enables information exchange and communication to achieve intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring, and management [5]. The Internet of Things technology enables sensors to be connected to the network, allowing any object to be interconnected through this technology, in order to achieve intelligent recognition, querying, tracking, and supervision. The use of IoT technology can achieve automation in production, conserve human resources, and promote efficiency in production. The advantages of the Internet of Things lie in its real-time, automatic, and intelligent capabilities, as well as its ability to reduce work costs and energy consumption, and adapt to personalized needs. The use of IoT technology in agricultural production will save a significant amount of labor costs and obtain real-time data. Combined with artificial intelligence technology, it can achieve planting automation, adapt to the actual production environment, and automatically adjust planting strategies.
Data processing serves as an indispensable component in fields such as machine learning. Its operations including data cleansing, anomaly removal, and modeling to extract inherent patterns from datasets, thereby laying the foundation for subsequent analytical processes. In agricultural production, data processing and analysis provide a robust decision-making support tool for agricultural product quality management [6]. With the exponential growth of data volumes, the role of machine learning and AI applications in agricultural product quality analysis has got more and more critical [6]. Through these processes, data processing can analyze crop growth patterns, establish qualification criteria for agricultural products, and ensure compliance with quality standards. A typical application in agricultural production includes big data processing through smart agricultural cloud platforms, which processes real-time feedback data to ensure the proper functioning of crop production operations and facilitate optimal decision-making in cultivation practices. Furthermore, data-derived solutions in agricultural production help resource conservation through reduced pesticide usage, intelligent irrigation allocation, and enhanced production intelligence, ultimately improving operational efficiency.
Smart Agriculture, supported by IoT and Data processing technologies, has got rapid development these days. As a modern agricultural form, smart agriculture belongs to the category of agricultural informatization along with computer-aided agriculture, precision agriculture, and digital agriculture. It is a product resulting from the developmental progression of modern information technology [7]. This innovative approach significantly enhances agricultural production efficiency while providing real-time feedback on farming operations, facilitating the summarization of crop growth patterns. From the perspective of systems engineering, smart agriculture can be conceptualized as a transformative innovation in agricultural production modes resulting from the systematic integration of advanced productivity elements [8]. The key of smart agriculture lies in its combination with emerging electronic technologies like the IoT, thereby promoting the transformation of agricultural production from traditional extensive forms to modern efficient, labor-saving, and intelligent paradigms. Smart agriculture reduces resource waste, saves the cost, optimizes the quality of agricultural products and reduces pesticide contamination [9]. In addition, the data collected through smart agricultural technologies ensures food safety and minimizes the food safety incidents’ occurrence This technological revolution profoundly indicates how AI is reshaping agricultural development, presenting both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges. Therefore, conducting in-depth research on smart agriculture has become an urgent need.
2. The application of Artificial Intelligence in agricultural production
AI is a scientific technology that enables machines to simulate human intelligence. The main researches of AI involve machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision and so on. AI can be generalized as an Input/Output (I/O) paradigm. By simulating human cognitive patterns, AI processes collected information and generates corresponding outputs through three sequential phases. Firstly, data acquisition and preprocessing. Secondly, machine learning implementation. Thirdly, reasoning, prediction, or operational execution. Throughout this process, data quality and processing logic constitute critical determinants. During the input phase, AI integrates with technologies such as IoT to collect data through diverse modalities including human radar systems, visual sensors, soil moisture sensors, manual inputs, and web crawlers. The preparatory phase involves rigorous data cleaning and organization to ensure completeness, usability, and accessibility of datasets. In the processing phase, AI employs advanced data analysis methods to identify patterns and construct predictive models. The output phase enables the deployment of trained models for forecasting future trends and generating optimized decision-making recommendations. As illustrated in Figure 1, the core of AI lies in knowledge representation, which extends to four main directions: cognitive, augmentation, physical, and intelligentization. Based on these directions, the application fields of artificial intelligence can be further categorized. In terms of Replacing human and Cognitive, applications includes image recognition, speech recognition, natural language, logic and reasoning, computer gaming; In terms of Human assistance and Cognitive, applications includes hyper-personalization, precision personalized recommendations, adaptive customized manufacturing; Regarding Replacing human and Physical, applications involves Auto driving, smart manufacturing, various robots, drones, robotic arms, etc.; With regard to Human assistance and Physical, AI is applied in wearable devices, AR/VR and smart home. "Therefore, these applications shows that AI can imitates human and assist people. In agricultural production, it collects data through sensors, then processes the data and ultimately achieving the dual objectives of facilitating human involvement in production processes and enhancing production efficiency.
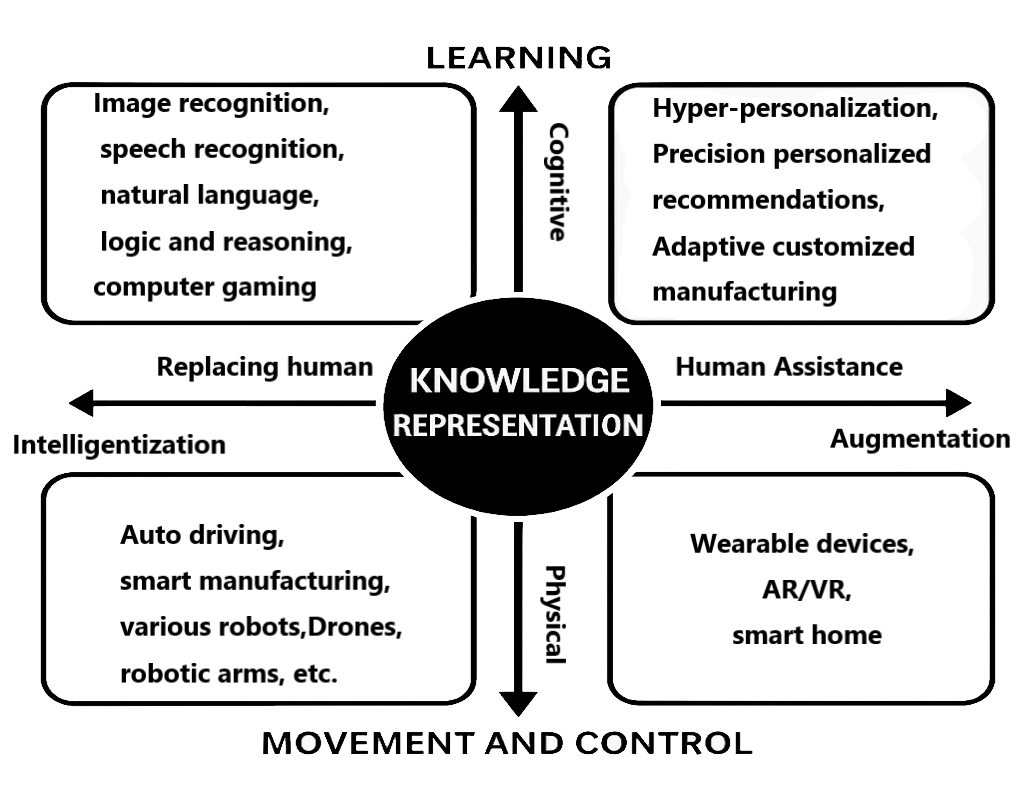
Figure 1. Application scenarios of Artificial intelligence
Machine learning is a discipline that enables machines such as computers to learn from data, serving as a branch of AI. It allows computers to achieve learning purposes by accumulating data processing experience like a human without explicit programming. Its application fields are very extensive, including object detection, natural language processing, recommendation systems, and financial risk management, and so on. Among these fields, object detection is used in cultural production frequently. The object detection’s function is to identifying all specified targets (objects) within an image and then determining their categories and positions. This process mainly involves four primary tasks, classification that determines object categories, localization that pinpoints object positions in images, detection that simultaneous localization and classification, segmentation which can be divided into instance segmentation and scene segmentation, it resolves the issue of assigning each pixel. The operation principle of object detection realizes the classification and localization of objects through the collaborative effort of feature extraction, bounding box, object classification, and localization these three components.
Feature extraction typically use Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) as feature extractors. As the framework illustrated in Figure 2, when an image is input into CNN (a zebra photo as an example), the CNN framework sequentially executes feature extraction, classification, and probability distribution, the three critical stages. The image first undergoes feature mapping through convolutional layers and ReLU activation, where essential characteristics are extracted via pooling operations. After multi-layer pooling, these features are flattened into one-dimensional vectors which makes subsequent processing easier. These vectors then pass through fully connected layers that link feature vectors to neurons for classification, ultimately yielding probabilistic outputs (Horse: 0.2, Zebra: 0.7, Dog: 0.1 in this case), which demonstrates the data was categorized successfully.
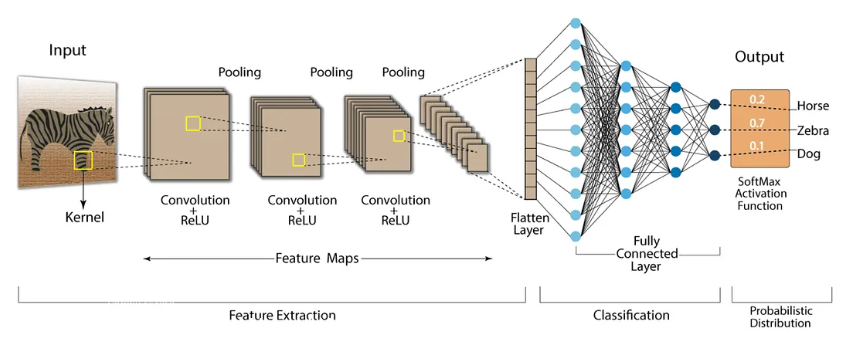
Figure 2. CNN framework (source:https://nafizshahriar.medium.com/what-is-convolutional-neural-network-cnn-deep-learning-b3921bdd82d5)
Bounding box employs regression algorithms to refine box positions and dimensions, it also adopts the Intersection over Union metric that quantifies overlap between predicted and actual boxes, thereby enhancing positional and dimensional precision. In terms of object classification and localization, predominant models like YOLO, SSD, and R-CNN employ distinct algorithmic approaches while achieving comparable objectives. The YOLO (You Only Look Once) algorithm, which is known for its real-time performance, processing images through four critical stages as depicted in Figure 3: image input, grid division, bounding box prediction, and category probability output. Initially dividing the input image into S×S grids, each cell autonomously detects objects within its spatial domain. The algorithm's uniqueness manifests in its unified regression-based approach to bounding box prediction and class probability estimation. By framing detection as a regression task, YOLO achieves accelerated computation while maintaining contextual awareness through global image perception. During prediction phases, each grid cell generates B bounding boxes containing positional coordinates, dimensional parameters, and confidence scores, alongside C class probability distributions. Final outputs synthesize these predictions across all grid cells, constructing comprehensive object descriptions. Notably, YOLO's architecture supports real-time end-to-end training through a single neural network, delivering superior processing speeds compared to R-CNN frameworks, making it particularly suitable for sustained recognition tasks.
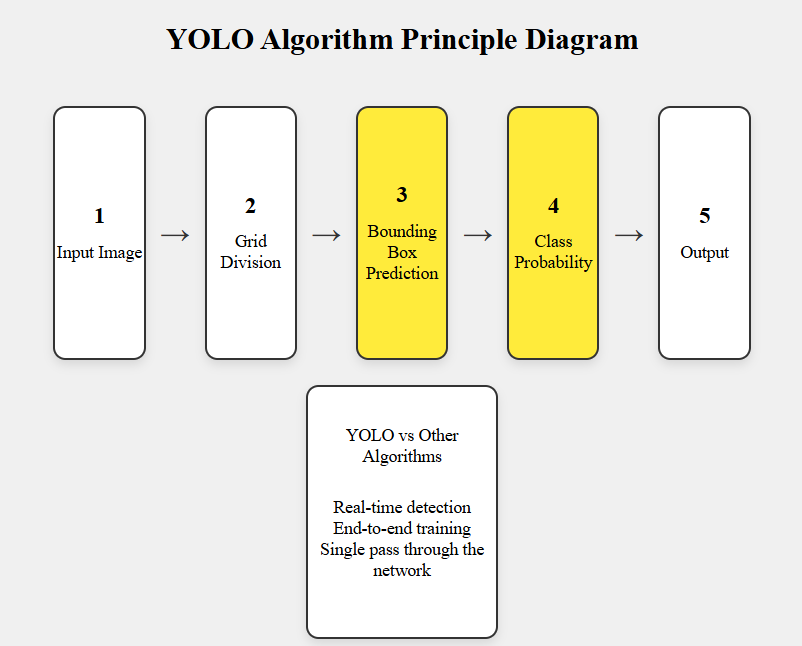
Figure 3. YOLO algorithm principle diagram
SSD (Single Shot MultiBox Detector) is a single-stage object detection algorithm. Compared to other algorithms, it absorbs the advantages of YOLO and Faster R-CNN algorithms and regression is adopted to address classification problems as well. In addition, SSD Introduces the unique Anchor Boxes mechanism. SSD predicts target offsets and class confidence scores for each anchor box, instead of directly predicting the absolute coordinates of bounding boxes as in other algorithms. It demonstrates characteristics of high efficiency, superior accuracy, and broad applicability. Machine learning-based object detection algorithms exhibit multiple advantages. As shown in Table 1, machine learning-based object detection algorithms outperform traditional methods in aspects like feature extraction, detection approach, classifier, process, accuracy and real-time performance, date dependency, generalization capability, application scenarios. It is suitable for today’s complex application scenarios, enabling effective adaptation to modern requirements for efficient and precise detection across diverse domains.
Table 1. Comparison of traditional object detection and machine learning-based object detection
Feature/Algorithm Type | Traditional Object Detection Algorithms | Machine Learning-based Object Detection Algorithms |
Feature Extraction | Manually designed features | Deep networks automatically learn features |
Detection Approach | Sliding window | Proposals (e.g., RPN) or direct regression |
Classifier | Traditional classifiers (e.g., SVM, Adaboost) | Deep networks (e.g., CNN) |
Process | Multi-stage (feature extraction, classification, localization, etc.) | End-to-end (unified training and prediction) |
Accuracy & Real-Time Performance | Lower accuracy and slower real-time performance | Higher accuracy and better real-time performance |
Data Dependency | Relies on small datasets and simple features | Relies on large datasets and complex features |
Generalization Capability | Weaker generalization capability | Stronger generalization capability |
Application Scenarios | Suitable for simple scenarios and small-scale datasets | Suitable for complex scenarios and large-scale datasets |
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that interconnects various physical devices, software, and sensors through the internet, enabling mutual communication and data exchange. Its applications are extensive, spanning diverse domains includes smart homes, urban infrastructure, industrial systems, agricultural operations, and healthcare services. The operational mechanism of IoT, as illustrated in Figure 4, involves cloud services (IoT platforms) collecting data from devices, transmitting it to the Iot platform, and relaying it back to applications (APPs) subsequently. Commands issued by the APPs are routed through the IoT platform to the devices. IoT employs numerous algorithms, mainly focusing on security and information processing. In terms of security, mainstream algorithms include the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA). The SHA algorithm is a message digest algorithm, which ensures data integrity by detecting unauthorized modifications. It encompasses multiple versions, with SHA-0 being the earliest iteration and SHA-256 widely adopted in recent years for enhanced security. The SHA algorithm operates through several steps. First, the input data undergoes padding to expand its length to 512 bits. Subsequently, 64 rounds of transformations are applied, where mathematical functions and constants are utilized to obfuscate the information. During these transformations, intermediate hash values are generated. The final hash result is derived by performing a bitwise XOR operation on all intermediate hash values. By comparing the computed hash digest with the generated one, data integrity is verified. For information processing, decision tree algorithms are predominantly employed, which are categorized into classification decision trees and regression decision trees.
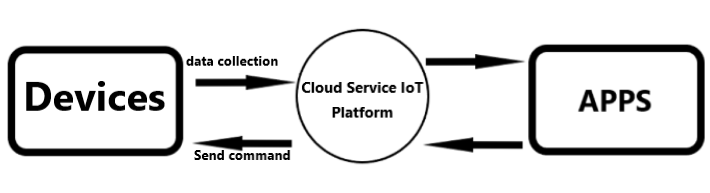
Figure 4. The operation principle of IoT
In the Internet of Things (IoT), the most commonly utilized decision tree algorithm is the Classification and Regression Tree (CART). As Figure 5 illustrates, the CART framework comprises classification CART trees and regression CART trees. Both variants follow feature selection, tree generation, and pruning these three sequential steps in data processing. The difference is that the classification CART tree uses the Gini coefficient in the feature selection step to select features from the data, while the regression CART tree uses the residual sum of squares method for feature selection. The use of Gini coefficient for feature selection focuses more on maximizing the purity of the categories to be classified, while the use of residual sum of squares aims to minimize prediction error.
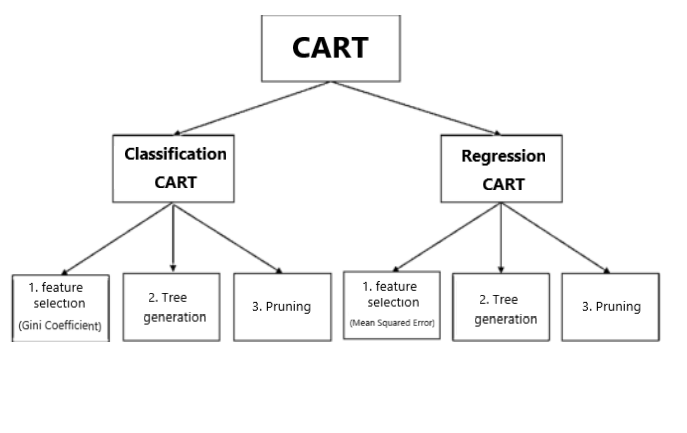
Figure 5. CART’s principle and framework
Use IoT technologies have a lot of advantages. As Table 2 shows, IoT combine physical entities with smart technologies, enabling mass data procession. It is a network with generalization capability, safer and isomerized technologies. Compared to traditional internet technologies, which are human-centric, handle limited-scale data processing, and prioritize user privacy through centralized architectures capable of holistic system management, IoT technologies exhibit apparent advantages. In agricultural applications, IoT enables macro-level regulation, data-driven precision analytics, operational efficiency acceleration, and robust information security assurance. Effective utilization of IoT technologies can significantly enhance production efficiency.
Table 2. Comparison between IoT and traditional internet
Internet of Things (IoT) | Traditional Internet |
Integration of physical entities and intelligent technologies | Human-centric information interaction |
Massive data processing capability | Small-scale data processing |
Ubiquitous network connectivity | Single-mode information transmission |
Enhanced security | Focus on user privacy protection |
isomerized technologies | Centralized traditional technologies |
Data processing is an essential concept in information technology, playing a crucial role in fields such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and machine learning. Here is a detailed explanation of data processing in the field of machine learning. The steps of data processing are shown in Figure 6. Firstly, the data is collected, followed by preprocessing such as cleaning, transformation, and partitioning. Then, data features are extracted (feature engineering), and finally the data is visualized.
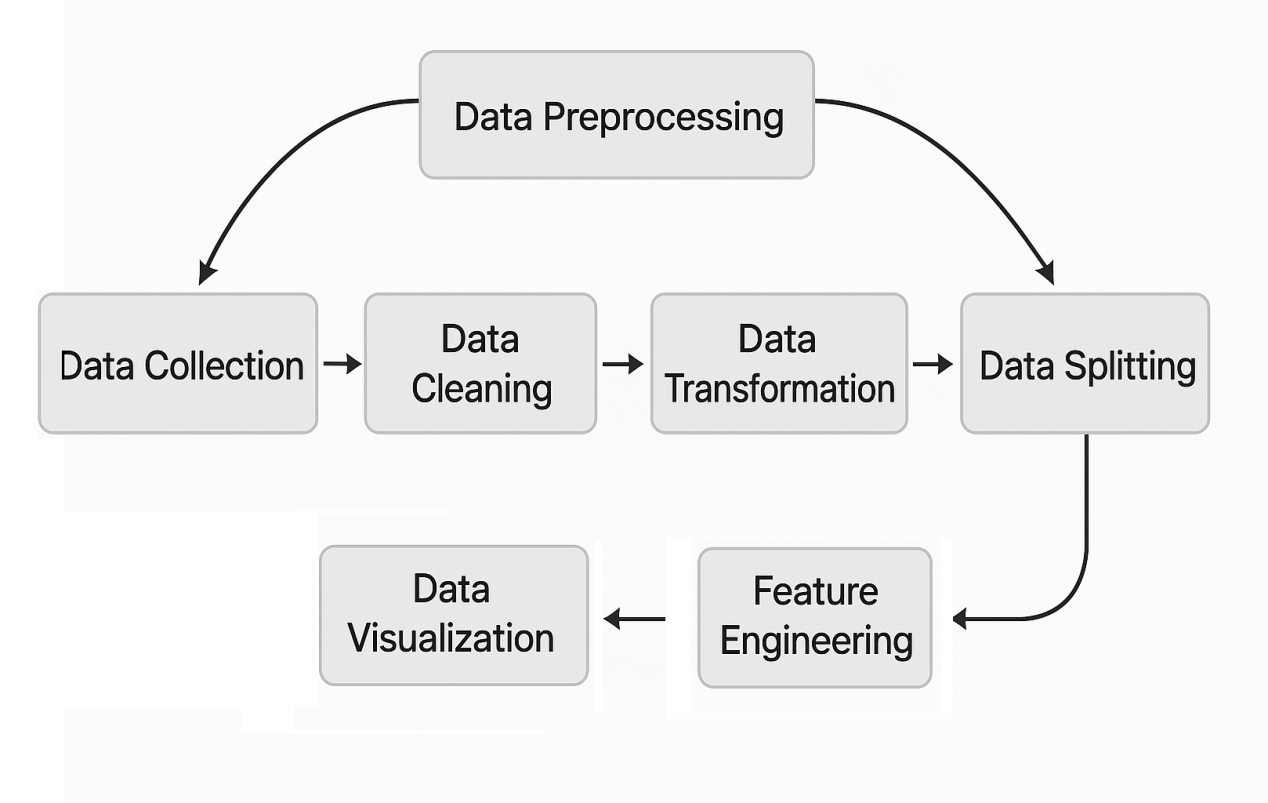
Figure 6. Basic steps of data processing
One of the most important parts is the data preprocessing section. Data cleaning mainly involves filling in data, removing duplicate values, smoothing data noise, and handling outliers. These operations standardize the collected data for further processing; Data conversion, also known as data transformation, usually involves data normalization and standardization, which refers to adjusting data to a unified scale, expanding the scale of data usage, and accelerating the calculation speed of the model; Similarly, data partitioning is the process of normalizing data and further formatting it into a format that is easy to manipulate. The main algorithms used in data processing include minimum maximum normalization, normalization (Z-score normalization), Box Cox transformation, etc. For scenarios involving large-scale data design in agricultural production, Box Cox transformation is used to perform data changes. Its basic idea is to transform the data to make it more in line with the characteristics of normal distribution. Its formula is as follows:
\( {y^{~}}=\begin{cases} \begin{array}{c} {y^{λ}}-1, λ≠0 \\ ln y, λ=0 \end{array} \end{cases} \) (1)
According to this formula, \( {y^{~}} \) represents the processed data, y is the raw data, and λ is the data transformation parameter. By using this formula, a normally distributed variable can be effectively constructed from the observed values of a set of random variables x, enabling subsequent data analysis based on this normal distribution. The algorithm improves prediction accuracy of the model, smooths heteroscedastic data more effectively, and demonstrates sensitivity to dataset characteristics. As illustrated in Figure 7, the original data exhibit sharp peaks and uneven density distribution, whereas the transformed data are concentrated within the approximate range of -5 to 5 on the horizontal axis, with smoother density variation. This transformation facilitates subsequent data processing steps.
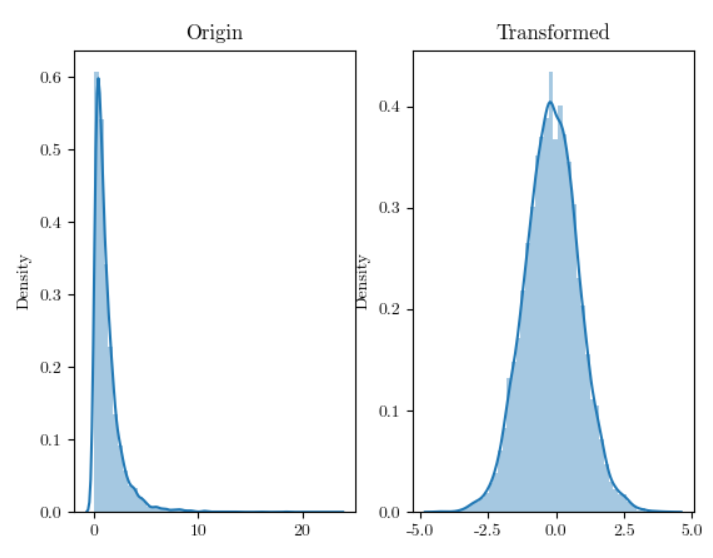
Figure 7. Box-Cox transformation effect diagram
Data processing has obvious advantages in today's massive data situation. As shown in Table 3, machine learning data processing is superior to traditional data processing methods in terms of data volume, data type, processing speed, real-time performance, analysis ability, and scalability. It plays a significant advantage in the massive data scenario, and integrating machine learning processing methods into agricultural production will accelerate agricultural production, improve efficiency, and promote its high-quality development.
Table 3. Comparison between traditional data processing and machine learning data processing methods
Comparison Dimension | Traditional Data Processing | Machine Learning Data Processing |
Data Volume | Small data volume | Massive data volume |
Data Type | Primarily structured data | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data |
Processing Speed | Limited by single-machine performance | Distributed computing for high-speed processing |
Real-Time Capability | Offline processing with no real-time support | Real-time stream and batch processing support |
Analytical Capability | Suitable for descriptive statistics and simple predictions | Complex data mining and predictive analytics |
Scalability | Poor scalability for handling massive data | High scalability |
Applicable Scenarios | Small-scale, structured data analysis | Large-scale, complex data analysis |
Smart agriculture represents a transformative agricultural paradigm that comprehensively applies modern information technologies such as internet of things, big data, and cloud computing to revolutionize the entire agricultural industry chain. It involves domains like agricultural production, computer science, and various other domains, which demonstrates extensive content. Typically smart agriculture is integrated with IoT technologies, establishing a comprehensive agricultural management system. As illustrated in Figure 8, this system generally comprises application layer, network layer and perception layer. Taking smart irrigation systems as an example. Data is collected by sensors in the perception layer initially and subsequently transmitted to the network layer. This intermediary layer incorporates multiple information transmission platforms including Beidou satellite navigation systems, NB-IoT/LoRa WAN networks, wireless bridges, IoT information platforms, and 4G/5G communication networks. After information is processed through the network layer, the information ultimately reaches the application layer. At this layer, the processed data facilitates various agricultural functions such as water measurement in irrigation districts or water-efficient irrigation management.
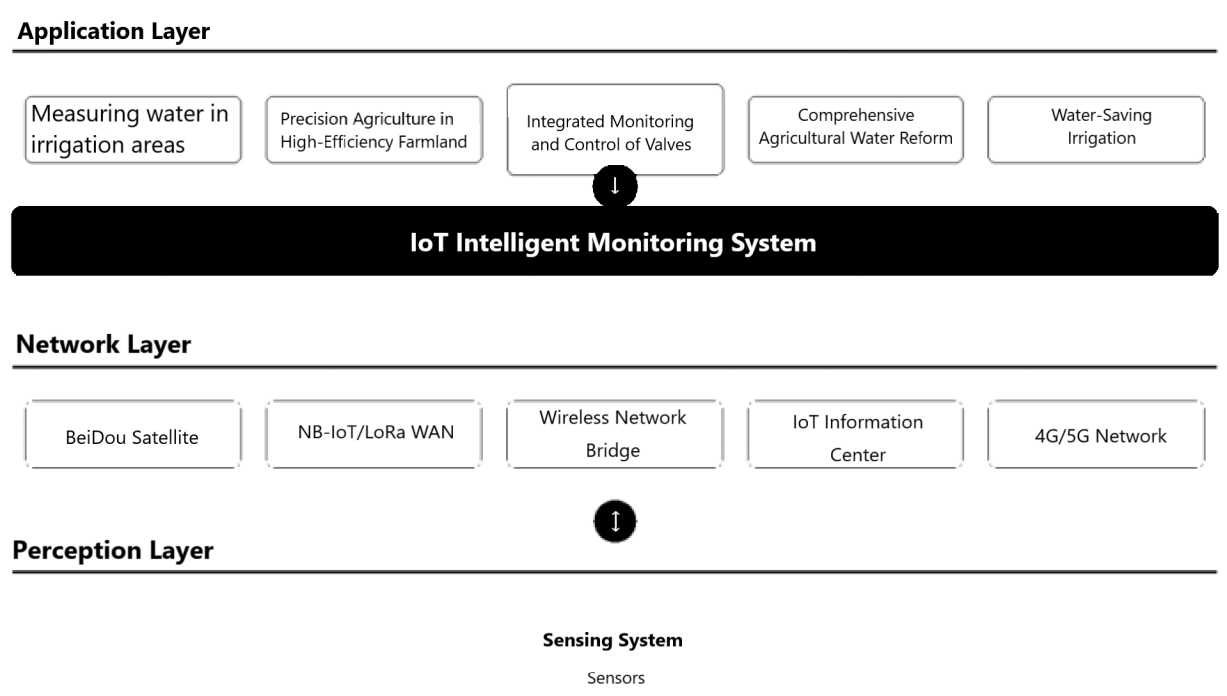
Figure 8. Structure of the internet of things in smart agriculture
In smart agriculture, machine learning algorithms are commonly used to model crop data for predicting future developmental trends. For example, the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network, a specialized recurrent neural network architecture, demonstrates exceptional capability in capturing long-range temporal dependencies within sequential data, making it particularly suitable for time-series analysis tasks. Its principle is shown in Figure 9, temporal steps-enhanced data is processed through LSTM units (memory cells), where each input undergoes processing through three gating mechanisms: the forget gate, input gate, and output gate. The forget gate determines redundant information to discard and critical features to retain, while the input gate regulates valuable data for memory updates. Through these gating operations, the algorithm dynamically updates its cell state - the core memory component. The output gate subsequently filters the cell state to generate hidden states that encapsulate essential temporal patterns. This architecture enables systematic learning from historical growth records when applied to agricultural production, facilitating accurate predictions of future crop development trajectories and enabling data-driven cultivation strategy optimization.
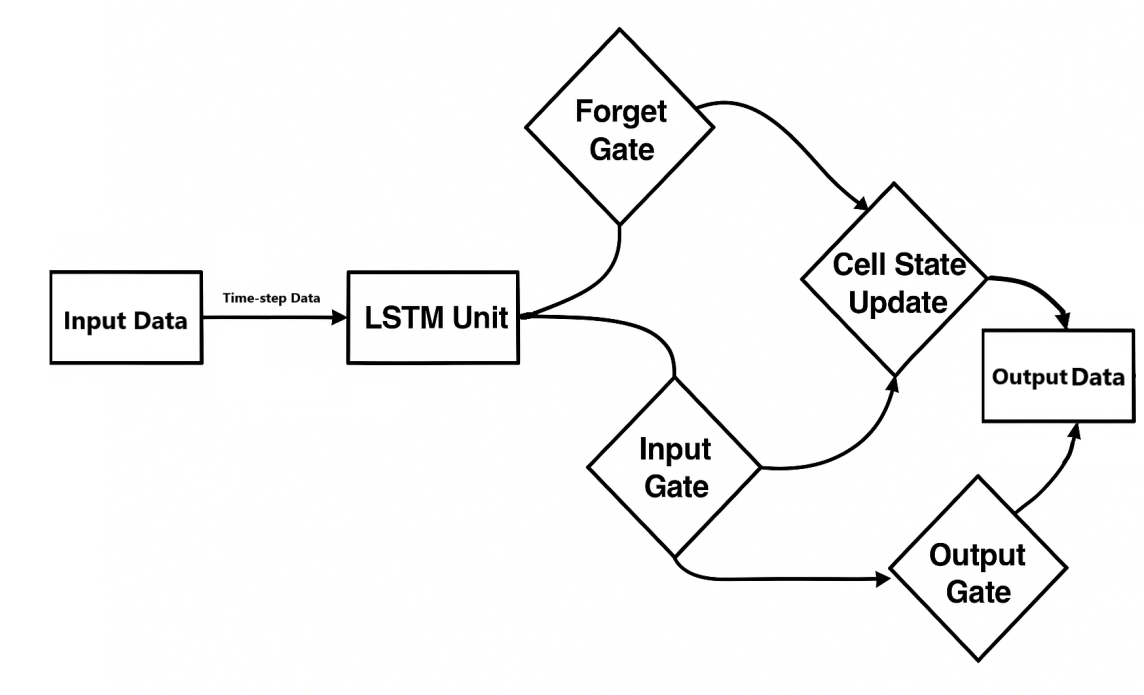
Figure 9. LSTM algorithm’s principle
Compared to traditional agriculture, smart agriculture have a lot of advantages. As Table 4 shows, smart agriculture outdoes traditional agriculture in production management, resource utilization, environmental impact, production efficiency, decision support, product quality, market adaptability, labor input, and sustainability aspects. Through data-driven management approaches, it achieves rational and optimized utilization of agricultural resources.
Table 4. Comparison between smart agriculture and traditional agriculture
Comparison Dimensions | Traditional Agriculture | Smart Agriculture |
Production Management | Manual operations | Data-driven management |
Resource Utilization | Low resource efficiency | Precision fertilization/irrigation; High resource efficiency |
Environmental Impact | Environmental pollution | Eco-friendly production; Pollution reduction |
Production Efficiency | Low efficiency; High labor intensity | High automation efficiency; Low labor intensity |
Decision Support | Subjective decision-making | Big data analytics; Scientific decision models |
Product Quality | Unstable quality; Low added value | High-quality outputs; Enhanced added value |
Market Adaptability | Poor adaptability; Weak risk resistance | Flexible adjustments; Strong risk resilience |
Labor Input | High labor demand; Low skill requirements | Reduced labor demand; High skill requirements |
Sustainability | Low sustainability | High sustainability |
3. Conclusion
The application prospects of artificial intelligence in the agricultural field are promising. Combining and applying technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things in agricultural production will reduce labor consumption, scientifically regulate resources, and ensure crop yield and quality while also reducing the waste of pesticides and other resources and their pollution to the environment. From this, it can be seen that the field of smart agriculture is rapidly developing towards intelligence under technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. However, there are still some shortcomings in the research on the application of artificial intelligence in agriculture. This only considers crop production in agricultural production and does not take into account other types of agricultural production, so the argument here may have some limitations in agricultural production. In addition, IoT technology updates and iterates rapidly, and technologies such as SHA256 will be phased out in the future due to their lagging security with the development of computer technology. Therefore, during the development of smart agriculture, sufficient consideration of diverse production scenarios should be prioritized, accompanied by continuous technological iteration and timely adoption of emerging technologies. These measures ensure agricultural safety and production stability while enhancing intelligent agricultural capabilities through stable implementation and practical application. Such advancements ultimately contribute to the innovative transformation and high-quality development of the agricultural sector.
References
[1] Wang, Z. H., & Yang, Z. (2017). Research on artificial intelligence technology and reflections on future intelligent information service systems. Telecommunications Science, 33(5), 1-11.
[2] Wang, Y., & Zheng, Z. H. (2019). Application directions and development pathways of artificial intelligence technology in agriculture. Information and Communications Technology and Policy(6), 29-31.
[3] Chen, K., & Zhu, Y. (2007). A review of machine learning and its related algorithms. Statistics and Information Forum(5), 105-112.
[4] Yan, Y. B., & Chen, Y. Y. (2004). A review of major strategies in machine learning. Application Research of Computers(7), 4-10+13.
[5] Sun, C. N., & Zhang, X. (2010). Overview of Internet of Things concepts and key technologies. Fujian Computer, 26(12), 39-41.
[6] Feng, S. H., & Li, Y. (2024). Data processing and application practices in agricultural product quality analysis. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 44(8), 36-37. https://doi.org/10.16815/j.cnki.11-5436/s.2024.08.012
[7] Li, D. L. (2012). Internet of Things and smart agriculture. Agricultural Engineering, 2(1), 1-7.
[8] Zhao, C. J. (2021). Development status and future prospects of smart agriculture. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 42(6), 1-7.
[9] Yang, D. R. (2014). Development strategies for China's smart agriculture industry. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 42(4), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.04.138
References
[1]. Wang, Z. H., & Yang, Z. (2017). Research on artificial intelligence technology and reflections on future intelligent information service systems. Telecommunications Science, 33(5), 1-11.
[2]. Wang, Y., & Zheng, Z. H. (2019). Application directions and development pathways of artificial intelligence technology in agriculture. Information and Communications Technology and Policy(6), 29-31.
[3]. Chen, K., & Zhu, Y. (2007). A review of machine learning and its related algorithms. Statistics and Information Forum(5), 105-112.
[4]. Yan, Y. B., & Chen, Y. Y. (2004). A review of major strategies in machine learning. Application Research of Computers(7), 4-10+13.
[5]. Sun, C. N., & Zhang, X. (2010). Overview of Internet of Things concepts and key technologies. Fujian Computer, 26(12), 39-41.
[6]. Feng, S. H., & Li, Y. (2024). Data processing and application practices in agricultural product quality analysis. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 44(8), 36-37. https://doi.org/10.16815/j.cnki.11-5436/s.2024.08.012
[7]. Li, D. L. (2012). Internet of Things and smart agriculture. Agricultural Engineering, 2(1), 1-7.
[8]. Zhao, C. J. (2021). Development status and future prospects of smart agriculture. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 42(6), 1-7.
[9]. Yang, D. R. (2014). Development strategies for China's smart agriculture industry. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 42(4), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.04.138
Cite this article
Zhang,Z. (2025). The application of AI in agricultural production. Advances in Engineering Innovation,16(5),44-53.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Engineering Innovation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang, Z. H., & Yang, Z. (2017). Research on artificial intelligence technology and reflections on future intelligent information service systems. Telecommunications Science, 33(5), 1-11.
[2]. Wang, Y., & Zheng, Z. H. (2019). Application directions and development pathways of artificial intelligence technology in agriculture. Information and Communications Technology and Policy(6), 29-31.
[3]. Chen, K., & Zhu, Y. (2007). A review of machine learning and its related algorithms. Statistics and Information Forum(5), 105-112.
[4]. Yan, Y. B., & Chen, Y. Y. (2004). A review of major strategies in machine learning. Application Research of Computers(7), 4-10+13.
[5]. Sun, C. N., & Zhang, X. (2010). Overview of Internet of Things concepts and key technologies. Fujian Computer, 26(12), 39-41.
[6]. Feng, S. H., & Li, Y. (2024). Data processing and application practices in agricultural product quality analysis. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 44(8), 36-37. https://doi.org/10.16815/j.cnki.11-5436/s.2024.08.012
[7]. Li, D. L. (2012). Internet of Things and smart agriculture. Agricultural Engineering, 2(1), 1-7.
[8]. Zhao, C. J. (2021). Development status and future prospects of smart agriculture. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 42(6), 1-7.
[9]. Yang, D. R. (2014). Development strategies for China's smart agriculture industry. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 42(4), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.04.138









