

Volume 16 Issue 9
Published on October 2025
Against the backdrop of worsening global energy crises and environmental pollution, the civil aviation industry, which relies heavily on kerosene, faces severe challenges due to its massive annual fuel consumption and significant emissions, searching for new energy alternatives to aviation kerosene an urgent issue. This paper focuses on researching next-generation energy sources for the aviation industry, aiming to identify alternative energy options to kerosene and their development prospects. By reviewing the development history of passenger aircraft and the technical principles of new energy aircraft, and integrating the current development status, it conducts in-depth exploration into the applications of electric aircraft, hydrogen-powered aircraft, and Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) in the aviation sector. It analyzes their technical maturity, applicable scenarios, bottlenecks, and future trends, intending to provide references for the green transformation of the aviation industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


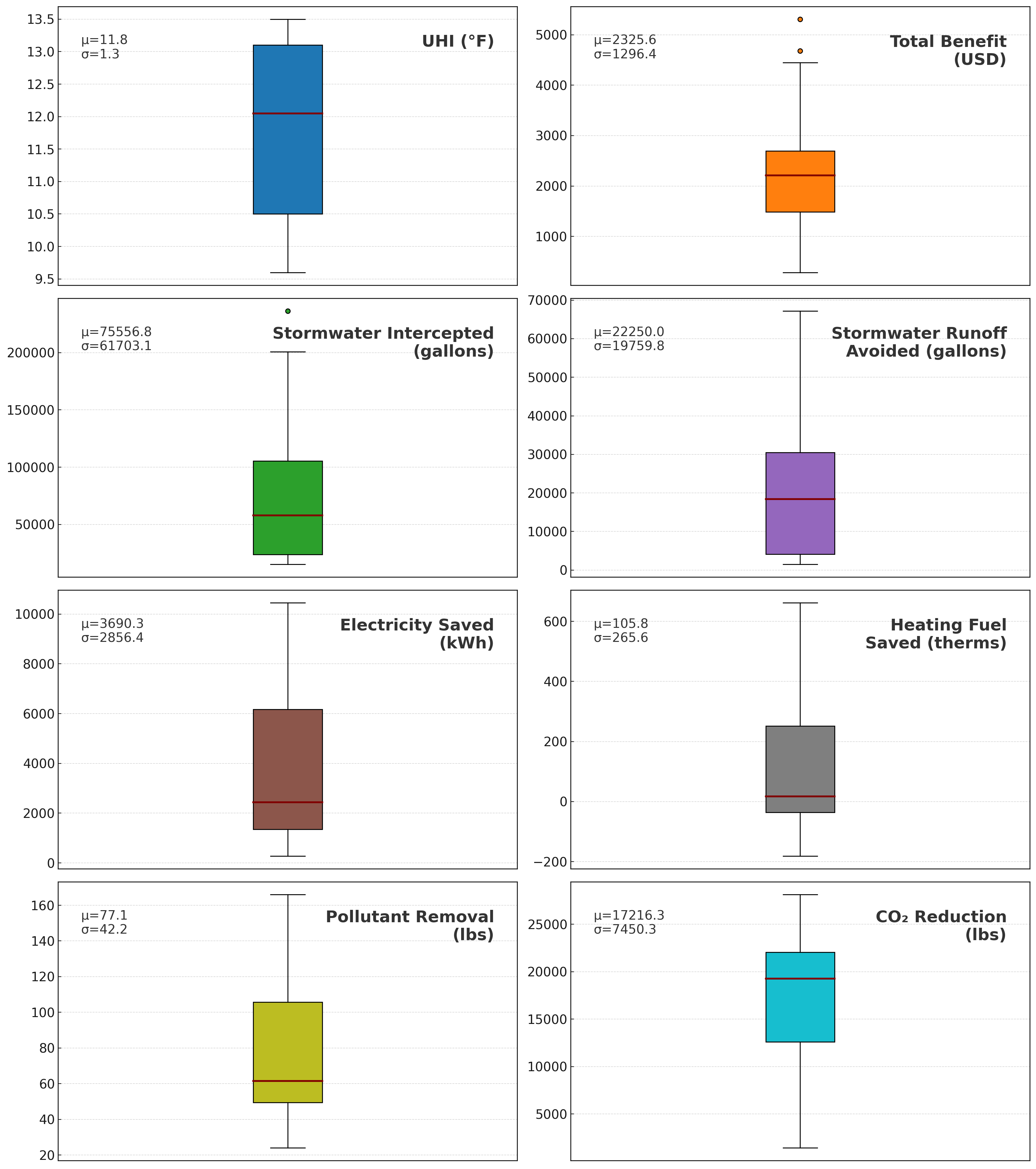
Urban Heat-Island (UHI) hotspots concentrate heat risk and may offer outsized returns from strategic greening. This study evaluates the eco-benefits of planting a single street tree at the maximum UHI hotspot in 20 U.S. cities. Hotspots are identified using a composite UHI index and per-tree services are estimated for their eco-benefits. Results show relatively uniform UHI levels across cities (mean ≈12 °F) but large variability in co-benefits. Hydrological services vary most (stormwater interception spanning an order of magnitude), and energy savings separate along climate lines: hot-summer cities are cooling-dominated (higher electricity savings), whereas colder cities are heating-dominated (greater therm savings, sometimes offsetting cooling gains in warm regions). CO₂ reduction and pollutant removal track interception, and total monetary benefits range widely from a few hundred to several thousand dollars per tree. Multivariate analyses group cities into high-benefit coastal hubs, temperate cooling-dominant sites, and warm-climate locations with winter penalties. Overall, targeted tree planting at UHI hotspots consistently mitigates heat, but realized hydrologic, energy, and carbon returns are strongly place dependent.

 View pdf
View pdf


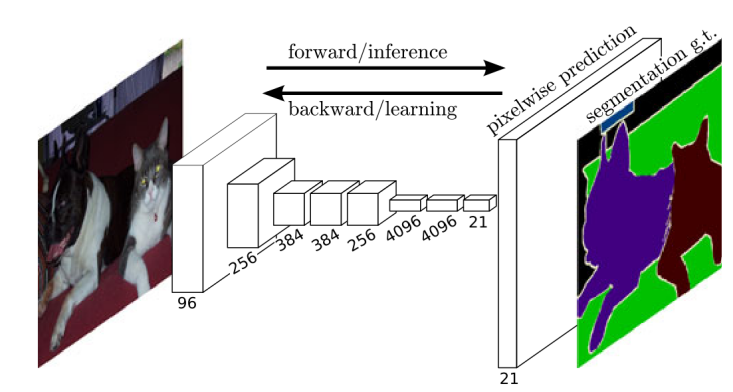
Remote sensing images contain a wealth of geospatial information. To accurately identify different geospatial categories and extract relevant data, image semantic segmentation plays a crucial role. In recent years, deep learning technology has brought significant breakthroughs to semantic segmentation of remote sensing images, significantly enhancing its performance. This paper investigates the application of deep learning technologies in remote sensing image semantic segmentation, based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Transformer-based semantic segmentation methods. It conducts an in-depth comparison of their structural characteristics and applicable scenarios, summarizes the achievements and shortcomings of existing research, and provides technical references and theoretical support for future studies, thereby contributing to the further development of deep learning technology in the field of remote sensing. Research results indicate that CNN-based semantic segmentation methods still hold advantages in extracting local features and achieving efficient segmentation, whereas Transformers address CNN's limitations in global context modeling and long-range dependency capture. Therefore, the collaborative integration of CNN and Transformers will become an important research direction for enhancing model performance in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


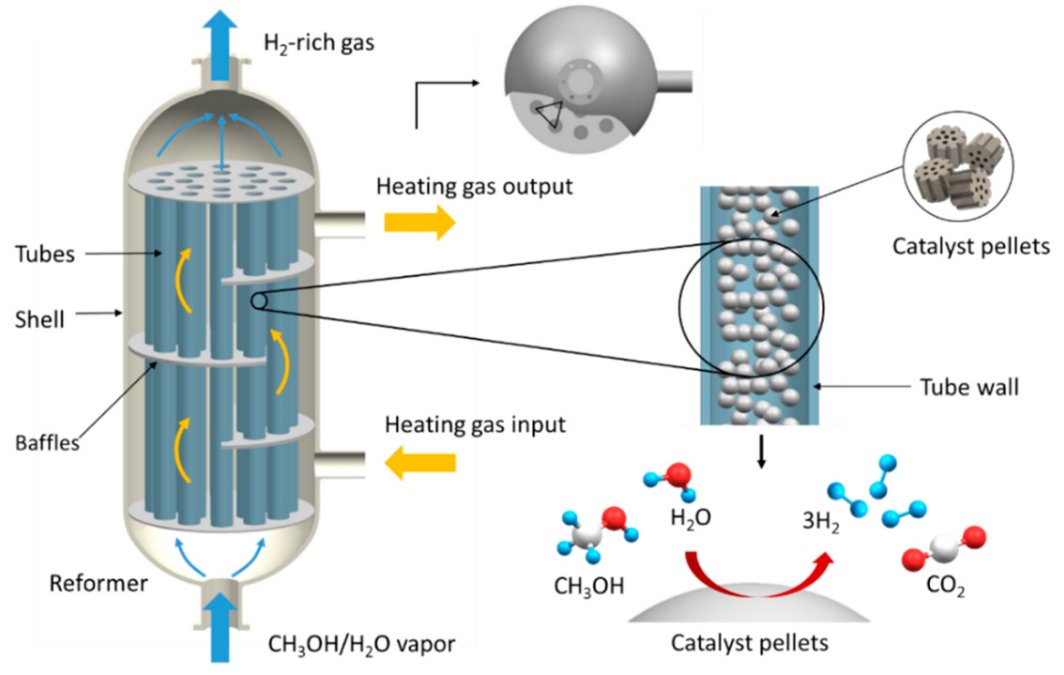
Waste heat recovery is a method of minimizing energy usage and environmental pollution by using various methods to recover energy lost and unused in industrial production. As one of China's major metallurgical industries, the pollution and resource waste generated by the steel industry make it necessary to improve the efficiency of waste heat recovery. In this dissertation, the difficulties currently encountered by waste heat recovery can be summarized from two aspects: the difficulty in obtaining patent licenses and the continued lack of increase in low-temperature waste heat recovery efficiency. Among them, the difficulty in obtaining patents not only increases the cost of steel manufacturers economically, but also makes it difficult to carry out research to improve the efficiency of waste heat recovery smoothly, because the research process may involve patented technologies. As the cooling medium used in the organic Rankine cycle, the performance in safeguarding the environment and energy-saving effect of R236ea coincide with the current difficulties encountered in China in the utilization of waste heat recovery. The achievement of the Kalina cycle in recovering low-grade waste heat makes it a possible alternative to the organic Rankine cycle. However, the problem of difficulty in obtaining patent licenses is difficult to solve. In the subsequent promotion process, the current imbalance in the scale advancement of the steel and metallurgical industry in different regions and the scale gap of Chinese steel mills may lead to differences in the applicable waste heat recovery methods. In the future, the conclusions of this dissertation need to be tested to confirm the feasibility of alleviating China's rapid energy consumption.

 View pdf
View pdf


Over the past decades, the growing demands for disease management have spurred advancements in wearable electronics, enabling more comprehensive and precise monitoring of vital signs. The integration of these devices with artificial intelligence has not only enhanced detection efficiency and user interaction but also deepened research in this field. This article provides a comprehensive review of the up-to-date development of wearable electronics while attach importance to its relation with health care. The application of wearable electronics in monitoring both human’s and animal’s condition are also discussed. The findings reveal that wearable devices can not only bring revolutionary innovations to the medical and health field, but also promote the coordinated development of industries such as AI and wireless communication. It also demonstrates that while future challenges will exist, it is still promising for wearable electronics to change humanity’s life positively with the assistance of policies, technical breakthrough and market requirement. And the conclusion is that wearable electronics will develop further than health monitoring devices to be a comprehensive platform generating human health, animal and environmental protections.

 View pdf
View pdf


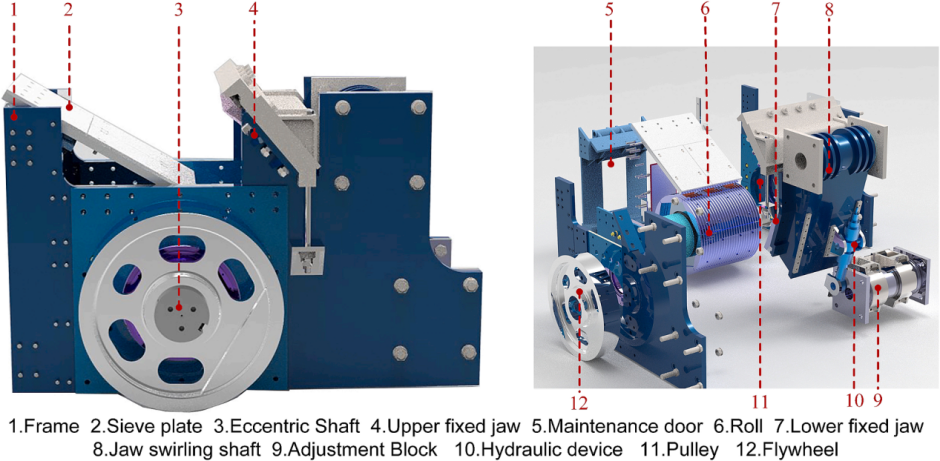
Under the strategic framework of “dual-carbon” goals (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality), high efficiency, energy conservation, and intelligence have become imperative trends in the development of ore-comminution equipment. In sectors such as mining, construction, and metallurgy, crushers serve as the critical hardware for particle-size reduction, and their performance directly governs downstream productivity and operating costs. Ongoing industrial progress is placing ever-stricter demands on crusher efficiency, reliability, and energy consumption. The eccentric roll crusher (ERC)—a novel primary crushing machine—offers marked advantages over conventional jaw, gyratory and cone crushers, including superior efficiency, a more compact overall envelope, lower specific energy consumption, and superior dynamic balance, thereby constituting a subject of exceptional research value. In this study, the influences of key operational parameters—eccentric shaft rotational speed, closed-side setting (CSS), and eccentric throw—on throughput, power draw, and roll reversal velocity are systematically investigated by means of coupled discrete-element method (DEM) and multi-body dynamics (MBD) simulations, complemented by rigorous kinematic modelling and experimental validation. Subsequently, a multi-objective optimization framework integrating genetic algorithms and response-surface methodology is employed to achieve an optimized design. The outcomes establish a sound theoretical and experimental foundation for the intelligent design of eccentric roll crushers within the context of the dual-carbon era.

 View pdf
View pdf


As an emerging industrial paradigm, the low-altitude economy is rapidly developing, with electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft as a key enabling platform. This paper reviews major advances in eVTOL technologies, including configuration design, distributed electric propulsion, and flight-control and autonomous-navigation systems. It also analyzes the progress of representative companies and products, application scenarios, demonstration projects, and supporting infrastructure and operational systems. Current challenges include flight safety and noise control, delayed airworthiness certification and airspace management, and unclear business models. In the future, the integration of artificial intelligence, cooperative low-altitude traffic management, and standardized regulatory frameworks is expected to enable autonomous and large-scale eVTOL operations, driving the low-altitude economy toward maturity.

 View pdf
View pdf


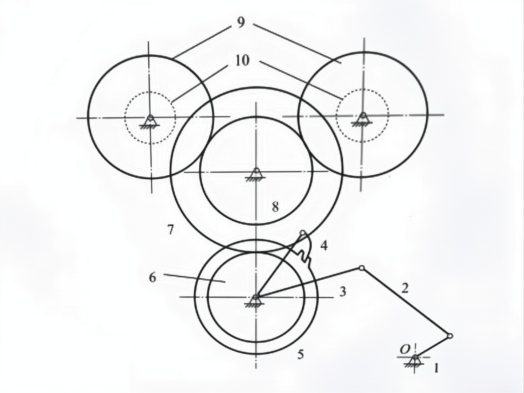
Textile machinery is an indispensable piece of equipment in modern manufacturing, and the proper operation of a machine’s cotton-feeding mechanism directly affects product quality and production efficiency. Based on a physical intermittent clamp-type cotton-feeding machine with take-up rollers, this paper conducts kinematic analysis and optimization of its drive mechanism (including the slotted-wheel mechanism, the ratchet anti-reverse mechanism, and the take-up roller assembly). Using basic principles of planar mechanism kinematics, the degrees of freedom of the drive mechanism are calculated and the determinacy of the motion is verified. Mathematical models are established for the angular displacement, angular velocity, and angular acceleration of the clamp plate’s pivot; SolidWorks is then used to simulate and analyze the motion characteristics of the guide rod under variations of the link-length ratio (l4/l1). From problems such as errors in degree-of-freedom calculations and the difficulty of modeling compound motions, this paper proposes solutions to the identified issues. The study provides a theoretical reference for subsequent structural optimization and performance improvement of cotton-feeding mechanisms in textile machinery, and demonstrates that kinematic analysis methods offer useful guidance for mechanical design.

 View pdf
View pdf


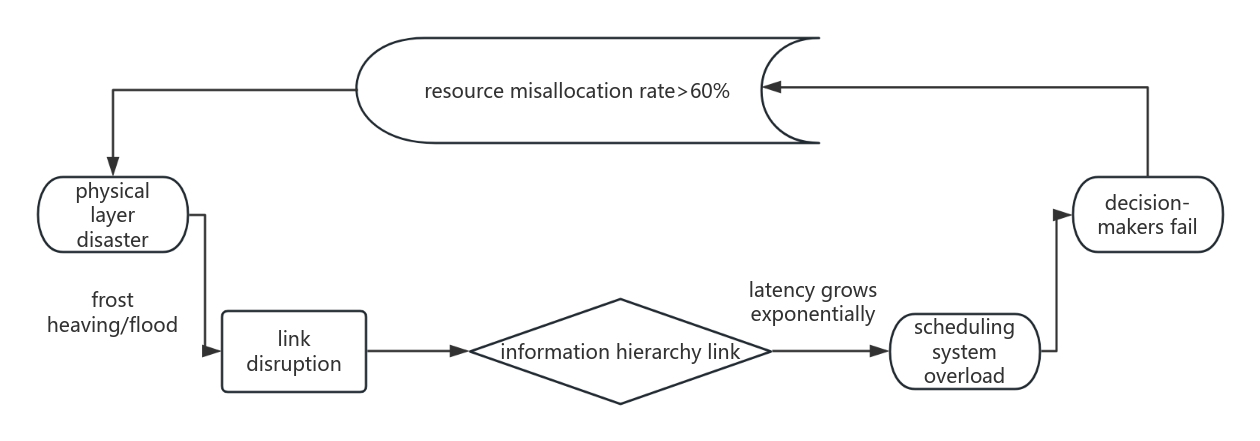
Against the backdrop of China's high-speed rail (HSR) network achieving global leadership in scale (48,000km, 70% worldwide) yet facing structural fragility, disaster-chain coupling, and regional imbalance, this study constructs a "structural resilience-propagation dynamics-intelligent governance" trinity framework. By integrating multi-layer coupled network theory, this paper develop: (1).A spatiotemporal-weighted betweenness centrality algorithm dynamically identifying critical nodes using Beidou data; (2).A multi-layer SEIR model quantifying epidemic-economic dual diffusion with linear threshold mechanisms; (3).A reinforcement learning framework optimizing anti-siphoning policies. Key findings reveal: Wuhan hub fault recovery time reduced by 50% through backup topology, Beijing West Station achieved 89% epidemic blocking via dual-channel quarantine, and the Chengdu-Chongqing regional Gini coefficient decreased 29% via frequency regulation. The paradigm shift from static planning to real-time adaptive governance offers a "China solution" for global railway resilience, evidenced by magnetic levitation standards (e.g., 18% energy savings in Saudi NEOM line) and multi-disaster defense systems (35% faster ASEAN flood recovery).

 View pdf
View pdf


In today's rapidly developing field of science and technology, autonomous driving technology—a pivotal development direction in the intelligent transportation sector—is profoundly transforming traditional travel modes. As the "eye" of autonomous driving, environmental perception provides a basis for its decision-making and is a part of the autonomous driving process that cannot be ignored. Breakthroughs and developments in the field of sensors have also driven the progress of environmental perception technology. This paper will start from the definition and principle of autonomous driving environmental perception technology, study the advantages and disadvantages of sensors such as cameras and millimeter-wave radar, and point out that environmental perception technology is vulnerable to complex environments and extreme weather, and the perception system is vulnerable to network attacks. In the future, the development of environmental perception technology should focus on mitigating the impact of environment and weather, and enhance the ability of the perception system to resist cyber attacks.

 View pdf
View pdf




