

About AEIAdvances in Engineering Innovation (AEI) is a peer-reviewed, fast-indexing open access journal hosted by Tianjin University Research Centre on Data Intelligence and Cloud-Edge-Client Service Engineering and published by EWA Publishing. AEI is published monthly, and it is a comprehensive journal focusing on multidisciplinary areas of engineering and at the interface of related subjects, including, but not limited to, Artificial Intelligence, Biomedical Engineering, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Materials Engineering, Traffic and Transportation Engineering, etc.For the details about the AEI scope, please refer to the Aims and Scope page. For more information about the journal, please refer to the FAQ page or contact info@ewapublishing.org. |
| Aims & scope of AEI are: · Artificial Intelligence · Computer Sciences · Aerospace Engineering · Architecture & Civil Engineering · Biomedical Engineering · Electrical and Electronic Engineering · Energy and Power Engineering · Materials Engineering · Mechanical Engineering · Traffic and Transportation Engineering |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

Chicago, US
momar3@iit.edu

New York, United States

Quanzhou, China

Eskişehir, Turkey
Latest articles View all articles
In today’s digital era, a sweeping wave of informatization is transforming the education sector. It is imperative to advance educational informatization and to improve the quality of teaching and learning. Over the past two years, guided by an innovation-driven, service-oriented philosophy, the institution has steadily promoted practical applications of educational information systems and explored effective approaches to deeply integrate informatization with pedagogy, yielding a series of notable achievements. The smart campus system has served as a platform for teacher–student connectivity, and the institution continues to innovate its information models. While smart campus systems offer significant advantages in streamlining and integrating information, data security remains a critical issue that cannot be overlooked in campus operations. This paper examines the current status of the smart campus and provides a comprehensive analysis along with constructive recommendations for future informatization development strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rise of Virtual Reality (VR) and metaverse concepts, high-fidelity virtual human interaction systems have become a hot research topic. Motion capture technology, as a key bridge connecting the real world and virtual environment, plays a central role in driving avatars in the VR metaverse. The purpose of this paper is to explore the application of motion capture technology in constructing a high-fidelity virtual human interaction system in the VR metaverse. By reviewing the technical classification of motion capture technology, comparing and studying its core breakthrough points, and analyzing its innovative principles in the system architecture model, this paper mainly focuses on the key features of low latency, high fidelity, and multimodality. The research results show that motion capture technology can effectively capture and reconstruct user movements, realize real-time driving of virtualized bodies, and enhance the immersion and realism of VR interaction. Meanwhile, to address the high cost of current motion capture technology, the research is committed to exploring the use of fewer sensors to realize whole-body motion reconstruction, which will provide a more economical and practical solution for future VR applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


Animal behavior analysis plays a pivotal role in neuroscience, behavioral ecology, animal welfare, and precision agriculture. However, traditional manual observation methods are often subjective, labor-intensive, and insufficient for large-scale quantification. The advent of deep learning has revolutionized this field, enabling automated, high-throughput and accurate analysis particularly in complex group settings. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in deep learning-based animal group pose estimation and behavior analysis. It systematically outlines the key stages from data acquisition to behavior interpretation, including object detection, multi-animal tracking, pose estimation, and individual identification. Representative models and tools are critically evaluated, along with their applications across various species and experimental contexts. While notable advancements have been attained—including refined occlusion handling via part affinity fields and augmented temporal behavior recognition through video transformers—several core challenges persist. These include robustness in wild environments, rare behavior detection and long-term identity preservation. Future research should focus on end-to-end joint modeling, data-efficient learning paradigms and multimodal data integration for advancing robust and intelligent systems. This review aims to provide researchers with a panoramic view of the field, highlighting key methodologies and directions for future development.

 View pdf
View pdf


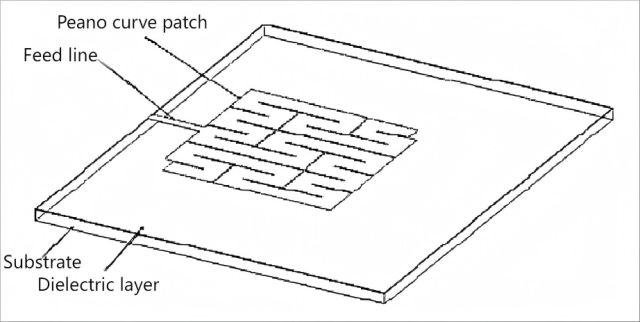
With the development of millimeter-wave technology, the miniaturization and integration of antennas have become key requirements. This paper presents a millimeter-wave second-order fractal antenna, including its structural design, fabrication method, and application in a silicon-based three-dimensional integrated structure. This antenna realizes a miniaturized structure with a Peano fractal curve on the substrate, featuring a novel structure, small size, and compatibility with other devices and chip processes. Meanwhile, a large-thickness BCB dielectric layer is adopted, which contributes to the miniaturization and integrated integration of the system. By elaborating on the design principle, fabrication steps, and performance of the antenna in the three-dimensional integrated structure, this paper provides a valuable reference for the development of millimeter-wave three-dimensional integration technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
2025
Volume 16November 2025
Find articlesVolume 16April 2025
Find articlesVolume 16March 2025
Find articles2024
Volume 14December 2024
Find articlesVolume 13November 2024
Find articlesVolume 12October 2024
Find articlesAnnouncements View all announcements
Advances in Engineering Innovation
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Advances in Engineering Innovation
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Advances in Engineering Innovation (AEI) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:





