1. Introduction
The construction industry is widely recognised as one of the main sources of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to climate change. It is the third largest emitter of carbon dioxide [1], just behind energy production for housing and fuel for transport. In addition, continued population growth in recent years has led to the need for increased infrastructure. This would not be possible without cement.
Cement is a powdery material that forms a plastic binding paste with water or a salt solution, and is capable of binding various substances together when hardening. In a broader sense, it also refers to any material placed between two hard bodies to bind them together.
Cement is thought to have been first invented by the Egyptians, and improved by subsequent civilisations by adding lime to clay. The Greeks of Italy reinforced it with pozzolanic ash (volcanic ash from the Pozzuoli region), and this use was taken up and generalised by the Romans. Until modern times, cement was a binder, often lime, with additives such as crushed tiles or bricks, whose clay had hydraulic properties. Pozzolan (volcanic earth from Pozzuoli in the Naples region of Italy) is widely used as an additive. Cement did not take on its contemporary meaning until the 19th century, when Louis Vicat identified the hydraulic properties of limes in 1817, and that of cements, which he called eminently hydraulic limes, or limit limes, in 1840.
A study of cement production shows that around 4.6 billion tonnes of cement were produced worldwide in 2015 alone [2]. Cement production is costly and ecologically harmful. CO2 (the main gas contributing to the "greenhouse effect"), NOx and SOx are among the dangerous emissions generated in relatively high volumes by the conventional Portland cement process. It should also be noted that around 40% of energy is consumed during the production of clinker, which makes up 90% of the cement's constituents. What's more, cement-based materials account for around 30% of the world's overall use of materials [2].
In light of this, the search for sustainable, environmentally-friendly solutions has become a priority for professionals in the sector.
One area of growing interest concerns the formulation of alternative hydraulic binders, capable of replacing traditional binders while reducing the carbon footprint associated with their production. One of these promising binders is calcined clay-based hydraulic binders, which are said to have physical and chemical characteristics comparable to traditional binders (Portland cement).
The general objective being the formulation of a new calcined clay-based hydraulic binder, the specific objectives are: to compare the characteristics of the formulated binder with those of a traditional binder, focusing on their respective potential for reducing CO2 emissions. To achieve this, a study will be made of the nature of the various constituents of the two types of binder, enabling them to be characterised.
We will then examine the physical characteristics of the two binders, such as specific surface area, residue rate, water content, particle size, as well as their compressive and flexural strength. We will also study the chemical properties of the binders.
2. Material and method
All the experiments were carried out in the laboratory of Dangote Cement Cameroon (DCC).
2.1. Measuring equipment’s
The measuring equipment used were:
. Scales: NETZGERAT scale (with a precision of 10-4) were used to measure the weight of the samples.
. Blain meter: to determine the fineness of the cement.
2.2. Raw material
The raw material used in this experiment were: clay, clinker, limestone, gypsum, standardized sand.
2.3. Material used during the process
. Owen to dry: It was used to dry the clay up to 105°C.
. A small oven: It is used to calcine the clay up to 1340° C.
. A crusher: to reduce the size of the material.
. A ball grinder which is also effective in wet condition.
. A mixer: to homogenized sand, water and cement in order to made the mortar.
. A shaking machine: to homogenized the mortar molds.
. A moisture cabin: to keep mortar prims at a temperature of ± 20°C;
. A water tank: to keep mortar prisms inside water at a room temperature
. Spectrophotometer: to give a qualitative and quantitative description of the elements constituting the sample.
The method is illustrated in the below figure 1
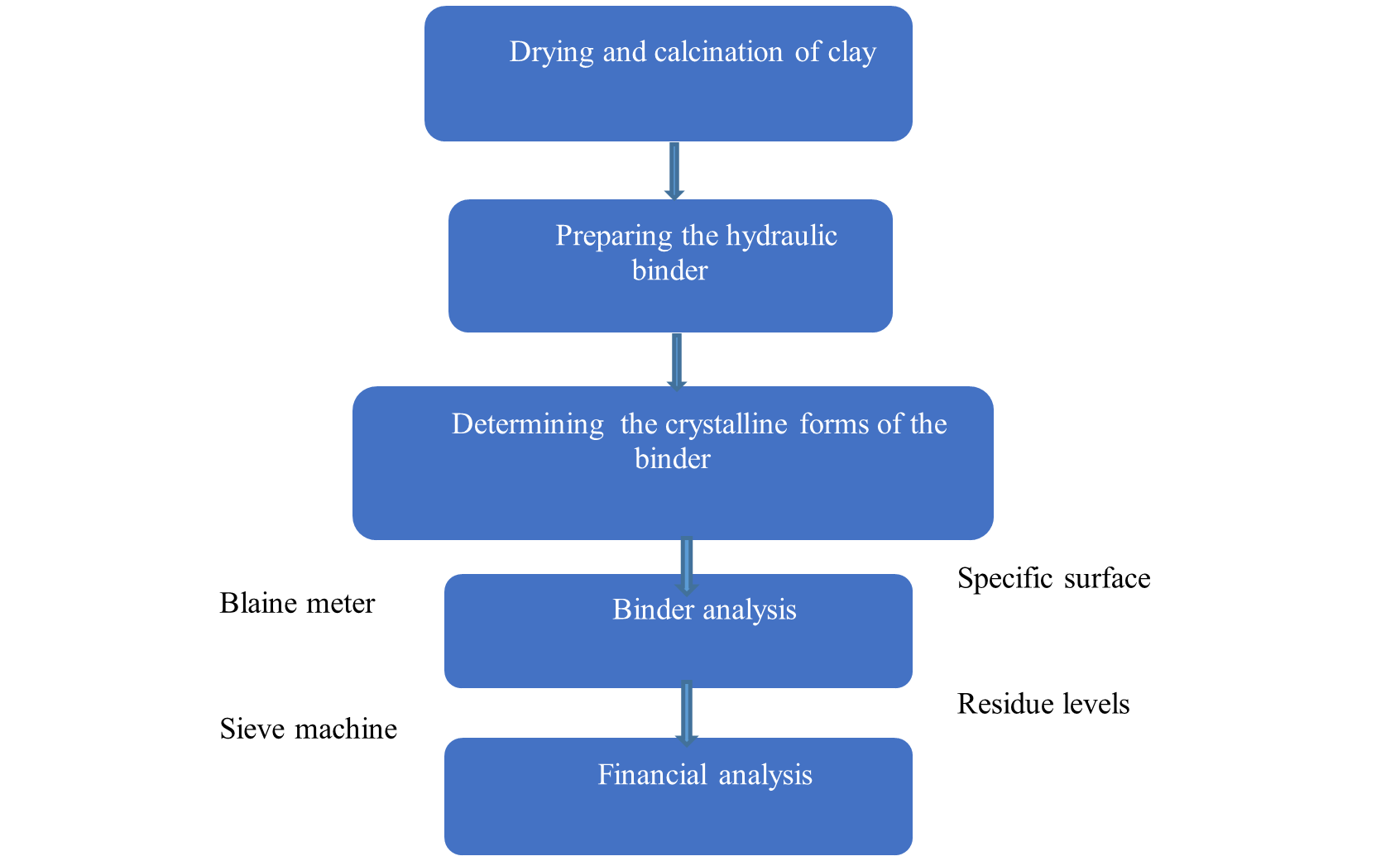
Figure 1. Steps constituting the methodology
2.4. Drying and calcination of the clay
The clay used in this study comes from the Ebimbeh quarry in Kribi. It is dried, calcined and then crushed. When dried at 105° for 24 hours, the clay loses mass. The dried clay is calcined at different temperatures, i.e. 550°C, 650°C, 750°C and 850°C for 2 hours. A change in colour is observed. The calcined clay is pink in colour.

A B
Figure 2. Dried clay (A); calcined clay (B)
2.5. Preparation of the hydraulic binder
The preparation of the hydraulic binder is done as per the below steps
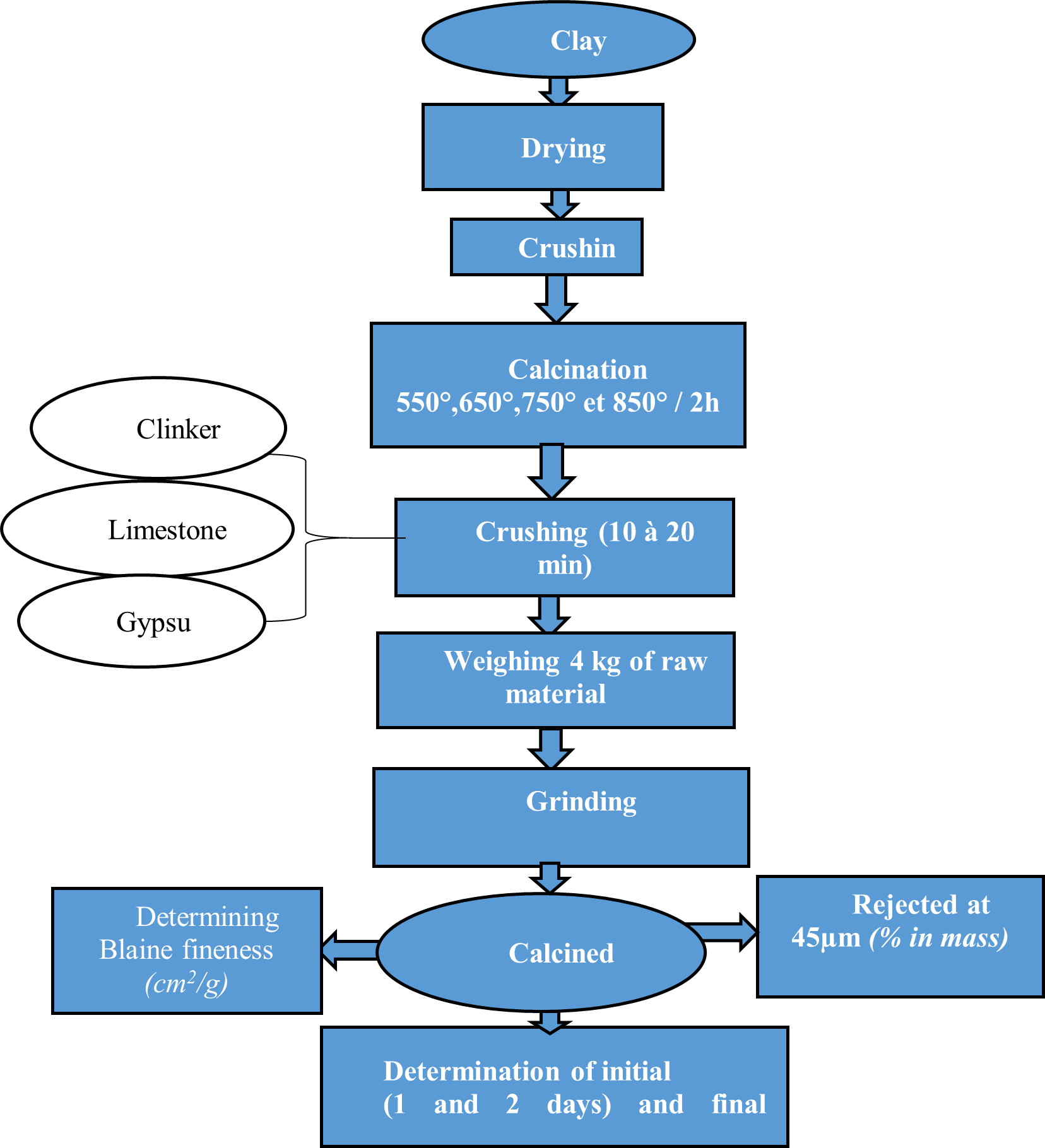
Figure 3. Steps applicable to hydraulic binders
2.5.1. Granulometry analysis of raw materials
Granulometry is the study of the statistical size distribution of a population of finite elements. Its purpose is to measure the size of the elementary particles that make up the grains of various substances. It can also be used to define the statistical frequencies of the different grain sizes in the ensemble studied [4]. To determine grain size, we proceed as follows:
- Measurement of a sample mass;
- Sieving using sieves with various mesh diameters of less than or equal to 25mm,
- Measurement of the mass of the sieves.
• Clinker
The elements in clinker (C3S, C2S, C3A, SO3, CaO (free lime)) play an important role not only in cement manufacture but also in its hydration and strength. This is why we chose these elements for our particle size analysis.
Clinker has a wide range of grain sizes, and the grains produced by clinkerisation are divided into three parts containing four slices:
- A coarse part corresponding to the slice larger than 25 mm
- An intermediate part corresponds to the slice between 10 and 25 mm, and the slice between 5 and 10 mm.
- A fine part corresponds to the slice smaller than 5 mm.
• Clay
Particle size distributions are measured by sieving. This involves placing 100 g in a vibrator fitted with several sieves (63, 125, 180, 250, 300, 425 and 600 μm). At the end of the test, the rejects are weighed in order to deduce the percentage of retention by mass for each sieve.
• Gypsum
The process will be the same as that used for clinker.
2.5.2. Water content
This is the mass of liquid contained per unit mass of dry matter. If this mass is taken in relation to a moist body, it is referred to as the "wet basis" moisture content. If it is relative to anhydrous matter, it is referred to as the "dry basis" moisture content. To determine the water content, we use the formula:
W= \( \frac{E}{Ps} \) = \( \frac{P1-P2}{Ps} \) x 100
E: mass of water in the material
P1: mass of wet material
P2: mass of dry material
In this study, the clinker is weighed at 250g and then weighed again with the mass of the container, and the gypsum is weighed at 105g and then weighed with the mass of the container.
The clinker is placed in an oven at 105°C for 2 hours and the gypsum in an oven at 45°C for 2 hours. After this time, the materials are weighed again and the moisture content can be determined.
2.5.3. Weighing
After crushing the raw materials using a crushing machine, samples are sent to the laboratory for analysis using a spectrophotometer to determine the crystalline forms of each. The materials will then be weighed according to the different proportions and variations in addition. In this study, the proportions of calcined clay added varied between 30% and 40%. The proportions of our reference binder are those of Pouzzolana Portland Cement (PPC): cement made from clinker, gypsum and pozzolana in the proportions defined. The table below shows these different proportions.
Table 1. Pouzzolana Portland Cement (PPC)
Clinker |
Gypsum |
Pozzolana |
|||
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
60 |
2720 |
4 |
160 |
36 |
1120 |
Thus, proportions of the binder are in the below tables:
Table 2. Proportions of 30% clay added
Clinker |
Clay |
Limestone |
Gypsum |
||||
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
50 |
2000 |
30 |
1200 |
15 |
600 |
5 |
200 |
Table 3. Proportions of 40% clay added
Clinker |
Clay |
Limestone |
Gypsum |
||||
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
Percentage (%) |
Mass (g) |
40 |
1600 |
40 |
1600 |
15 |
600 |
5 |
200 |
2.5.4. Analysis of binders
To determine the mineralogical composition, the binders will be analysed at 550°, 650°, 750° and 850° for 30% and 40% addition.
- First, 10g of sample is introduced into the grinder mill for 1 minute.
- Then 3 granite grains are added to make the binder fine,
- Cells are inserted into a pellet press for 1 minute.
- Finally, these cells will be introduced into the spectrophotometer to carry out the analysis for 5 minutes.
The results will be processed by the computer and the different percentages will be calculated.
2.5.5. Physical testing: the fineness
The purpose of fineness is to determine the granulometry of samples, to check sample homogenisation and to check that grinders and separators are working properly. By calculating the time, it takes for the pressurised gas to pass through a given volume of granules, we can deduce the surface area of the granules. The finer the grind, the greater the SSB.
The formula for specific surface area is:
SSB= K√T
It is expressed in Cm2/g where K=341 Cm2.s1/2.g-1 is the constant and T in seconds s is the time measured using the blaine meter.
The measurement procedure is as follows:
- Weigh 2.854 g of binder
- Place in the porous disc
- place in the blaine meter
- measure the time in seconds
2.5.6. Residue rate
The determination of the quantity of residues in the cement is done as per the below stpes:
- Weight 10g of binder
- It is inserted into the sieve machine for 1 minute at 1800 Pa.
- Weight again and obtain a new mass.
The residual rate is computed using the above formulae:
%R= \( \frac{masse obt}{masse att} \) * 100
2.5.7. Mechanical test: bending and compression test
Flexion and compression tests are used to determine the strength of the cement. To do this, moulds are prepared under the precise conditions below:
- Carefully weigh 225g of water into a dried and properly cleaned mixer bowl.
- Weigh out 450g of cement and pour it into the mixer bowl.
- Start the mixer in automatic mode.
- After 30 seconds, for 1350g of standard sand into the top of the bowl.
Bending: used to determine the tensile stress by bending. Breakage is carried out using a press fitted with a device that breaks the mould, displaying the pressure withstood in Megapascals.
Compression: Each half-mould is compressed on its sides between two hard metal plates. Finally, the press device indicates the pressure limit to which the mould has resisted.
The results of these tests are obtained after 28 days.
2.6. Comparative study of the CO2 content of clay-based binders and traditional binders
The aim here is to compare the amount of CO2 emitted during the production of our binder with that emitted by traditional binders, mainly during the production of clinker. The binder is obtained by firing two natural raw materials extracted from quarries in a kiln: limestone and clay. These two materials are crushed and then fed into an inclined rotating tube 50 to 90 metres long. The limestone and clay can only be combined at 1450°C. This results in the production of clinker, the main component of the binder. The decarbonation equation (CaCO3 CaO + CO2) will help to better explain this phenomenon. To manufacture the calcined clay-based hydraulic binder, we have substituted 30% and 40% clinker with calcined clay. An analysis of the clay was carried out before and after calcination, and we found a low level of lime (CaO), which means that the quantity of CO2 emitted is low and therefore smaller than the level of CO2 emitted during the manufacture of clinker.
2.7. Financial
A financial analysis based on 1 ton of product used will be done to evaluate the profitability.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Strength
Strengths of the different binders are summarized in the table below.
Table 4. Compressive strength as a function of temperature
Binders |
30% |
40% |
|||||||
TEMPERATURE |
550 |
650 |
750 |
850 |
550 |
650 |
750 |
850 |
1450 |
1 day strength |
8,5 |
11,5 |
11,4 |
11,3 |
7,6 |
10,9 |
10,3 |
10,4 |
8 |
2 days strength |
16 |
22,3 |
17 |
21 |
13 |
20,4 |
19 |
20,7 |
20 |
7 days strength |
24,8 |
38,9 |
26,5 |
36,5 |
26,5 |
35,2 |
20,9 |
34,7 |
32,5 |
28 days strength |
34,8 |
48,8 |
36,5 |
46 |
42,7 |
45,4 |
44,4 |
44,8 |
42,5 |
The results show that clay has a very positive effect on binder strength after 2 days and especially after 28 days.
An increase in strength was noted when the clay was calcined at 650°C. In the other cases, the strength is also good and is more or less the same as that achieved with the traditional binder.
Compressive strength at 28 days can be maintained and increased by substituting 30% calcined clays containing a high proportion of impurities (over 40% quartz) in the clinker.
The pozzolanic activity of calcined clays is assessed by the compressive strength performed on calcium hydroxide mini-cylinders of calcined clay. They have shown that clays rich in koalinite can have the highest strength and therefore the best pozzolanic activity [3].
Table 5. Flexural strength as a function of temperature
Binders |
30% |
40% |
|||||||
TEMPERATURE |
550 |
650 |
750 |
850 |
550 |
650 |
750 |
850 |
1450 |
1 day strength |
2.1 |
2.3 |
2.2 |
2.3 |
2 |
2.2 |
1.8 |
1.9 |
2 |
2 days strength |
2.9 |
3.2 |
3.1 |
3 |
3 |
3.3 |
3.2 |
3.1 |
3 |
7 days strength |
2.1 |
2.3 |
2.2 |
2.3 |
2 |
2.2 |
1.8 |
1.9 |
2 |
28 days strength |
6.1 |
6.4 |
6.3 |
6.2 |
6.1 |
6.1 |
6.3 |
6 |
6 |
It is observed that at one day and 7 days the flexion is the same because we used the same block. It varies between 1.5 and 2.5; at 2 days it varies between 2.5 and 3.5; at 28 days it is between 6 and 7. Flexural strength varies with temperature and changes over time. In the two variations of addition at 30% and 40%, bending is greatest at 650°C calcination.
3.2. CO2 emission
It is observed that the lime content in the clay before and after calcination is virtually unchanged, whereas in the clinker it is very high. This means that by applying the formulation of the hydraulic binder based on calcined clay, the rate of CO2 emissions decreased.
Table 6. Percentage of CO2 emission per element.
Elements |
Clay before calcination |
Clay after calcination |
Clinker |
Na2O |
0,5532 |
0,3898 |
0,1415 |
MgO |
3,134 |
4,889 |
1,7101 |
Al2O3 |
22,094 |
30,914 |
4,7221 |
SiO3 |
44,914 |
51,907 |
20,423 |
SO3 |
0,1487 |
0,0774 |
1,185 |
K2O |
0,8471 |
1,6158 |
0,7876 |
CaO |
2,6 |
2,0614 |
65,127 |
TiO2 |
2,434 |
3,048 |
0,2319 |
Fe2O3 |
7,881 |
12,154 |
3,722 |
3.3. Financial analysis
The table below provides a financial analysis for the different binders.
Table 7. Evaluation of traditional binder raw materials
Proportions |
Matières |
Prix/tonne ($) |
Masse (tonne) |
Prix ($) |
55% |
Clinker |
95 |
495 000 |
47 025 000 |
40% |
Pouzzolane |
11 |
360 000 |
3 960 000 |
5% |
Gypse |
12 |
36 000 |
432 000 |
TOTAL = 51 417 000 $ |
||||
Table 8. Evaluation of raw materials with 30% clay added
Proportions |
Raw material |
Price/ton ($) |
Mass (ton) |
Price ($) |
50% |
Clinker |
95 |
450000 |
42750000 |
30% |
Clay |
17 |
270000 |
4590000 |
15% |
Limestone |
35 |
135000 |
4725000 |
5% |
Gypsum |
12 |
45000 |
540000 |
TOTAL = 52 605 000 $ |
||||
Table 9. Evaluation of raw materials with 40% added clay
Proportions |
Raw material |
Price/ton ($) |
Mass (ton) |
Price ($) |
40% |
Clinker |
95 |
360000 |
34 200 000 |
40% |
Clay |
17 |
360000 |
6 120 000 |
15% |
Limestone |
35 |
135000 |
4 725 000 |
5% |
Gypsum |
12 |
45000 |
540 000 |
TOTAL = 45 585 000 $ |
||||
From the above tables, we observed that investment cost of the calcined clay-based binder production project is lower than that of the traditional binder. We can say that the substitution of 40% clay is better in terms of savings.
4. Conclusion and outlook
In short, our aim was to formulate a calcined clay-based hydraulic binder with a view to reducing the carbon footprint. This study shows that the use of a calcined clay-based hydraulic binder is a promising solution for reducing the environmental impact of the construction industry.
The results of the X-ray diffraction show that clinker contains a high percentage of lime due to the presence of CaCO3, while in clay the main components are silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3) and iron oxide (Fe2O3). Analyses of clay at different temperatures (550°C, 650°C, 750°C and 850°C) show that the calcination temperature has no influence on the percentage of constituents present. Analyses carried out on the different binders according to their proportions and temperature show that the main constituents are: lime, silica, alumina and iron oxide. Taken together, these elements are conducive to good resistance.
The results of the blaine (between 5000 - 8000 Cm2 /g) are high, unlike the blaine of traditional binders, which is 3800 Cm2 /g, the sieve (34- 56), and the strengths at one day (8- 11.4 Mpa), 2 days (16-22.5 Mpa) and 28 days (48.8 Mpa) show that the calcination temperature and the chemical composition of the clay have a significant impact on greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric pollutants. It is therefore vital to take these factors into account when formulating the hydraulic binder. Financial analysis reveals that the production of calcined clay-based hydraulic binders is less expensive than the production of traditional binders. Further efforts need to be made to develop healthier calcination techniques and explore other alternative materials in order to continue to reduce the construction industry's carbon footprint. All in all, the use of calcined clay-based hydraulic binders represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly construction industry.
References
[1]. Ostnar,TA, Justnes. H, Durabilité du mortier avec la marne calcilnée comme matériau de cimentation supplémentaire. Adv. Cem. Rés,2014, 26, 344-352.
[2]. Cembureau. Revue statistique mondiale ; Cembureau : Bruxelles, Belgiques, 2010. [Google scholar]
[3]. Saiti Issam, Etude d’un procédé d’élaboration d’un béton léger cellulaire à base de sable de dune de la région de Ghardia, décembre 2014.
[4]. Gaamoussi Hajar, Etude granulométrique des tranches de clinker, Université Sidi Mohammed Ben Abdellah, Faculté des Sciences et Technologiques, 2014.
Cite this article
Emmanuelle,M.M.;Paul,K.;Hugues,F.;Bienvenu,A.W.V. (2024). Production of a sustainable cement through the usage of clay as binding element. Advances in Engineering Innovation,7,9-16.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Advances in Engineering Innovation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Ostnar,TA, Justnes. H, Durabilité du mortier avec la marne calcilnée comme matériau de cimentation supplémentaire. Adv. Cem. Rés,2014, 26, 344-352.
[2]. Cembureau. Revue statistique mondiale ; Cembureau : Bruxelles, Belgiques, 2010. [Google scholar]
[3]. Saiti Issam, Etude d’un procédé d’élaboration d’un béton léger cellulaire à base de sable de dune de la région de Ghardia, décembre 2014.
[4]. Gaamoussi Hajar, Etude granulométrique des tranches de clinker, Université Sidi Mohammed Ben Abdellah, Faculté des Sciences et Technologiques, 2014.









