

Volume 16 Issue 8
Published on September 2025
With the growing needs for Extended Reality (XR) products, Apple Vision Pro, being as a creative and emerging equipment in this field, shows the field’s prospects and gives direction to the future interaction between human beings and computers. In this article, it first analyses some cutting-edge products like Microsoft HoloLens2 and some technologies used by XR products, including Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and 3D Modeling. Then this article shows core technologies that make Apple Vision Pro ahead of other XR products. The technologies include dual chips, hand-tracking and eye-tracking system, Micro OLED display and Fully Laminated Triple Pancake Lenses. Last, this article concludes that Apple Vision Pro enhances immersive experience by integrating advanced hardware and it is a role model for future XR products.

 View pdf
View pdf


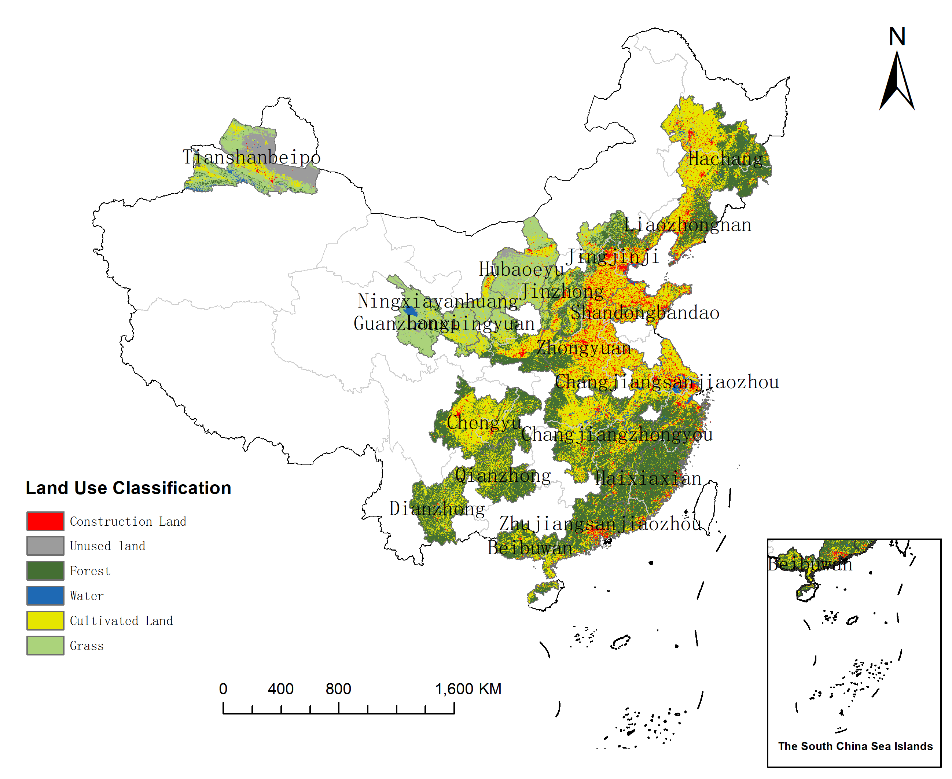
This paper aims to study the spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of land use carbon budget in 19 urban agglomerations in China based on the "dual carbon" goal, and provide a theoretical basis for land use optimization and "dual carbon" decision-making in the development process of China's urban agglomerations. Based on land use data from 19 urban agglomerations in China in 2022, this study calculates the carbon budget for these agglomerations. Spatial autocorrelation analysis and cluster analysis are employed to study the spatial variation pattern of the carbon budget. Furthermore, the influencing factors of the carbon budget are explored from economic, demographic, and energy consumption perspectives, and a regression model for the carbon budget based on key influencing factors is constructed. Research has found that: (1) In 2022, the spatial pattern of the carbon budget across the 19 urban agglomerations in China exhibited characteristics of "higher carbon emissions in the east and lower in the west, higher carbon sequestration in the south and lower in the north." Based on the carbon budget distance, these agglomerations can be roughly clustered into five categories. (2) According to the hot spot analysis of the carbon budget, hot spots for carbon emissions are concentrated around the Bohai Rim in northern China, while hot spots for carbon sequestration are concentrated in northeastern, southeastern, and southwestern regions. (3) Energy consumption, population size, and GDP are the primary factors influencing carbon emissions, while net primary productivity (NPP) of vegetation and precipitation are the main factors influencing carbon sequestration. In summary, the land use of urban agglomerations should be rationally planned, ecological protection should be emphasized, and the carbon sink capacity of urban agglomerations should be consolidated and improved. Formulate differentiated carbon emission reduction measures according to local conditions, focus on optimizing energy consumption and industrial structure, reasonably control the number of population, build urban green space, and give full play to the important role of vegetation in carbon absorption.

 View pdf
View pdf


Aiming at the problems of high computational cost and long optimization cycle in numerical simulation for traditional photonic crystal microcavity design, this study proposes an intelligent inverse design method combining numerical calculation from the MIT Photonic-Bands (MPB) software package and Back Propagation Neural Network (BP Neural Network). Taking two-dimensional photonic crystals with silicon-based dielectric cylinders (permittivity ε=12) as the research object, 55 sets of band structure data are generated using MPB software by systematically adjusting the radius of dielectric cylinders (0.01–0.5 μm with a step size of 0.005 μm), constructing a "structural parameter-optical property" mapping dataset. A three-layer BP neural network model (with 9 neurons in the hidden layer) is designed, optimized and trained using the Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm (LM algorithm), combined with the Hyperbolic Tangent Sigmoid Function (tansig function) to handle nonlinear features. Experimental results show that the coefficient of determination R² of the model on the test set reaches 0.95309, with an average relative error of 0.08183% and a maximum relative error of 0.1419%. The design cycle is shortened from the traditional "day-level" to "second-level", with efficiency improved by more than 3 orders of magnitude.

 View pdf
View pdf


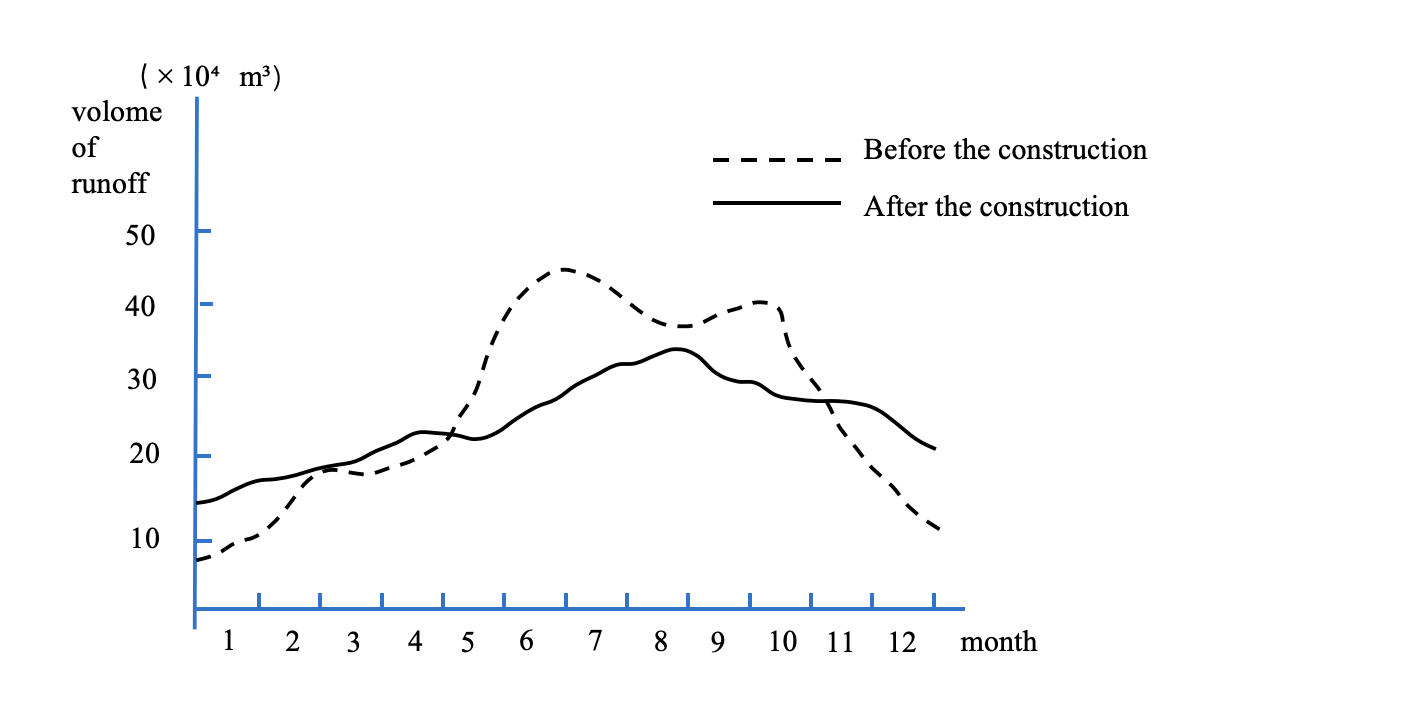
This paper explores the environmental impacts of Water Conservancy and Hydropower Engineering/Projects (WCHE), with a focus on the water pollution caused by construction projects. Rapid urbanization has heightened concerns over water pollution, which threatens ecosystems and human health. This article identifies three primary pollution types- physical pollution, chemical pollution and biological pollution, such as sedimentation, eutrophication and disruption of the hydrological cycle. These impacts are particularly evident in changes in water flow velocity and water quality, which may endanger aquatic organisms and damage the surrounding ecosystem. This article also discusses three main methods for alleviating water pollution - chemical (e.g., flocculants, though risk of secondary pollution), physical (e.g., sedimentation, aeration—costly but effective), and biological (e.g., eco-floating islands, sustainable yet high initial investment). Finally, this study emphasizes the need to formulate comprehensive policies and environmental regulations to balance the benefits of water conservancy projects and water resources protection. By integrating technical solutions with policy frameworks, it is possible to achieve sustainable development while mitigating the environmental impacts of large-scale engineering projects. Under the influence of water environment, water quality management cannot rely solely on technical or engineering solutions. Instead, establishing strict environmental regulations, enhancing law enforcement capabilities, and promoting interdisciplinary cooperation among engineers, environmental scientists, and policy makers are of vital importance.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid growth of the Internet economy and the rising rate of urbanization, urban residents' travel modes have become increasingly diversified, with taxis featuring online booking becoming a common choice for daily commuting. Taxis meet the residents' "door-to-door" travel needs, but their travel modes exhibit significant randomness and uncertainty. Moreover, there are often imbalances in supply and demand, such as "difficult to hail a taxi" and "long-distance orders". Therefore, accurate and rapid prediction of taxi demand is crucial for improving regional transport capacity and achieving a "win-win" situation for platforms, drivers, and passengers. This paper uses the "New York City Taxi and Limousine Commission (TLC) Green Taxi Trip Data for April 2015" dataset, applying data mining techniques based on the LSTM taxi demand prediction model to forecast single-region taxi demand and regional OD matrix. The paper selects real network car order data to validate the model’s effectiveness. Additionally, different prediction models are compared to determine the optimal forecasting model.

 View pdf
View pdf


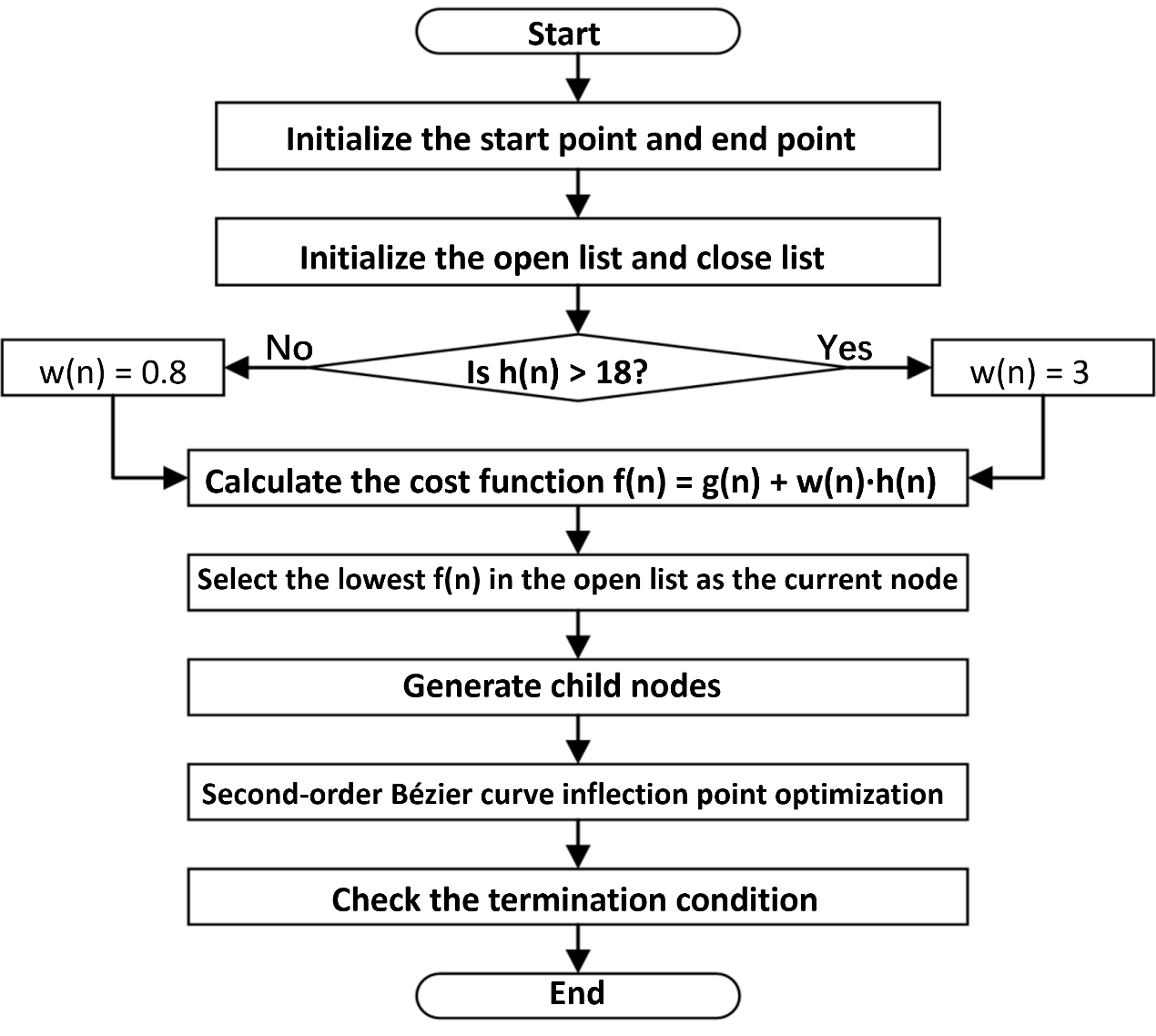
Aiming at the problems of traditional path planning algorithms, such as high computational complexity, low search efficiency, and poor smoothness of planned paths due to non-compliance with kinematic constraints, this paper proposes a path planning method for plant protection Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) based on the fusion of dynamic weight functions and Bézier curves. Firstly, the overall framework of the path planning algorithm is constructed based on the A* algorithm, and a weight function dynamically adjusted with the path is introduced to improve the heuristic function of the A* algorithm, which effectively reduces the number of search nodes and improves the overall search efficiency. Subsequently, the second-order Bézier curve is fused with the improved A* algorithm to reduce the number of turning points in the path planning process of the A* algorithm and improve the smoothness of the path. Finally, the effectiveness of the algorithm is verified based on Python and MATLAB platforms. The research results show that compared with the traditional A* algorithm, the improved A* algorithm fused with the dynamic weight function and Bézier curve can significantly improve the search efficiency and path smoothness; moreover, although the search efficiency of the search algorithm using dynamic weight coefficients is similar to that of the traditional algorithm, its path planning quality is significantly improved.

 View pdf
View pdf


As the importance of hydrogen energy in the global clean energy system becomes increasingly prominent, how to store hydrogen efficiently, safely and economically has become the core bottleneck restricting its large-scale application. This study takes three mainstream hydrogen storage methods, namely high-pressure hydrogen storage, liquid hydrogen storage and solid-state hydrogen storage, as the research objects, and comprehensively compares their advantages and disadvantages in terms of energy density, safety and economy. Through systematic literature review and case analysis, the study finds that high-pressure hydrogen storage has a relatively high mass energy density and technical maturity, and is suitable for mobile transportation scenarios, but its volume efficiency is low and there is a risk of high-pressure leakage; liquid hydrogen storage has the highest volume energy density and is suitable for large-scale transportation, but the liquefaction process has high energy consumption and the equipment cost is expensive; solid-state hydrogen storage performs best in terms of safety and is particularly suitable for portable applications, but the hydrogen storage materials are expensive and the technology is not yet mature. Based on the above comparison, this study proposes suggestions for multi-scenario collaborative optimization and looks forward to the future development direction of hydrogen storage technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


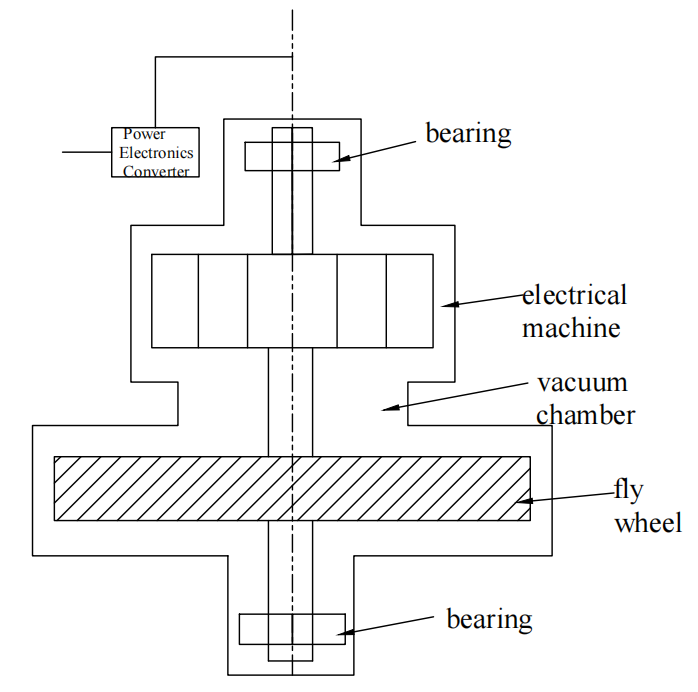
With advantages such as high power density, long cycle life, and environmental friendliness, flywheel energy storage systems hold great promise in applications like renewable energy integration and grid frequency regulation. As the core component for energy storage, the rotor’s stress distribution and evolution under high-speed rotation directly affect the system’s safety and reliability. This paper reviews the stress analysis of rotor materials and structures in flywheel energy storage systems, systematically summarizing current research progress. First, from the perspective of material constitutive properties, it compares the stress responses of conventional metals (e.g., steel and aluminum alloys) and high-performance composite materials (e.g., carbon fiber-reinforced polymers and metal matrix composites) under centrifugal loads, with a focus on the failure mechanisms of anisotropic materials, high-cycle fatigue stress, and thermo-mechanical coupled stress. Second, in terms of structural design, it explores the influence of topology optimization, thin-walled hollow structures, and stiffener configurations on stress concentration and distribution within the rotor, and elaborates on the complex evolution of stress fields under multi-physics coupling (centrifugal force, temperature, and electromagnetic fields). Furthermore, it summarizes the current applications of finite element simulation, experimental methods (strain gauges and digital image correlation), and multi-objective optimization in stress analysis. The study shows that although existing research has revealed the critical influence of material and structural parameters on stress, challenges remain in areas such as refined modeling of multi-field coupling, integrated material-structure optimization, and full lifecycle stress prediction. Future research should integrate the development of novel materials with intelligent design approaches to deepen the understanding of stress mechanisms and provide theoretical support for the lightweight and high-reliability design of flywheel energy storage rotors for engineering applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


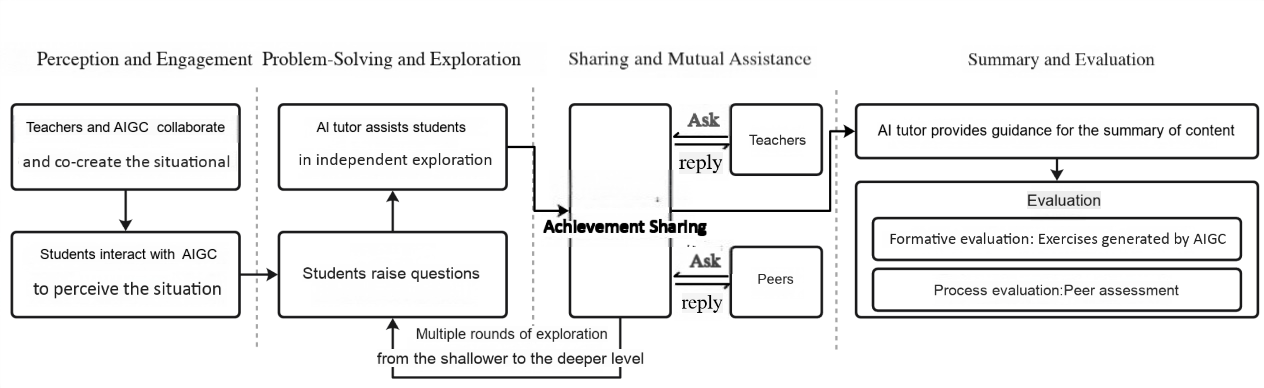
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, the application of Generative AI (AIGC) in education has gradually become a research focus. This study explores the potential of AIGC in programming instruction within high school information technology classes. Based on an in-depth analysis of AIGC’s advantages and potential limitations in education, we propose an innovative programming-teaching approach that integrates AIGC and pilot its use in real classroom practice. Data analysis indicates that the AIGC-integrated approach can, to some extent, enhance students’ classroom engagement. The findings offer new ideas and methods for high school information technology teaching and provide a reference for future innovation and development of programming-instruction models.

 View pdf
View pdf


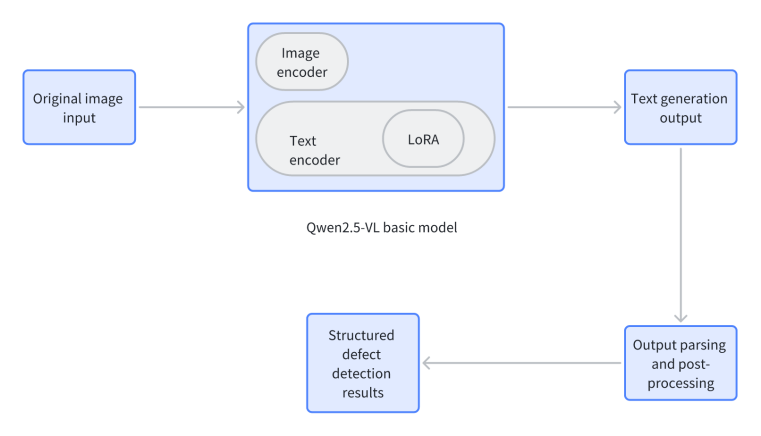
In industrial manufacturing, accurate and efficient identification of product surface defects is essential for ensuring product quality, optimizing the production process and reducing cost. However, complex and diverse defect morphologies and the need for fine-grained description present significant challenges. General image description methods based on large visual language models often struggle to provide accurate defect type and location information for specific areas such as steel surface defect recognition. To address this, a defect identification method for the Qwen2.5-VL-3B large model based on LoRA fine-tuning is proposed. We built a specialized dataset covering six key steel surface defects—cracks, impurities, plaques, pitting, scale penetration, and scratches—and refined the model through efficient low-rank adaptation. Experimental results demonstrate that the fine-tuned Qwen2.5-VL-3B model significantly improves industrial defect recognition, accurately identifying defect types and locations, thus overcoming limitations of general large models and providing an efficient solution for industrial inspection.

 View pdf
View pdf




