

Volume 5
Published on December 2023Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has gained widespread usage in the treatment of various chronic wounds due to its ease of preparation and high safety profile. But not every treatment can achieve satisfactory results. The quality of PRP is based on individual biological characteristics. Autologous PRP technology is greatly affected by the patient himself. Individual responses to PRP treatment are different and will produce different therapeutic effects. Especially in patients with uncontrollable factors such as aging, diabetes, and coronary heart disease, the use of antiplatelet drugs may potentially reduce the quality of autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP). When treating related diseases, it is important to consider the impact of factors such as age, gender, and the specific disease. Currently, many researchers are focusing on the development of allogeneic PRP technology to avoid the inconvenience of collecting autologous blood and reduce potential negative effects that may exist in the patient's disease itself. In this review, we explore the factors generally recognized in current research which influence the efficacy of PRP.

 View pdf
View pdf


Blockchain technology, primarily acclaimed for its instrumental role in underpinning cryptocurrencies, has seen rising prominence in a multitude of applications outside the digital currency realm. Its decentralized infrastructure coupled with cryptographic integrity offers solutions to longstanding challenges across various industries, including supply chain, healthcare, and finance. This research endeavor delves into these multifarious applications, providing insights into the potential benefits and the existing impediments in the broader adoption of blockchain technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the evolving landscape of software development, Human-Centric Software Engineering (HCSE) is emerging as a pivotal paradigm, prioritizing human needs and experiences at the core of software engineering processes. This research delves into the fundamental principles of HCSE, its implications on software quality, and the enhanced user satisfaction it promises. Through comprehensive surveys, case study analyses, and user feedback sessions, this study reaffirms the increasing significance of HCSE in modern software development. Despite its evident benefits, the research also sheds light on the organizational barriers hindering its broad adoption. As software systems continue to intertwine with our daily lives, the research underscores the imperative shift from mere functionality to creating holistic, human-centered software experiences.

 View pdf
View pdf


The realm of education is witnessing a transformative integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI), poised to redefine the contours of pedagogical strategies. Central to this transformation is the emergence of personalized learning experiences, where AI endeavors to tailor educational content and interactions to resonate with individual learners' unique needs, preferences, and pace. This paper delves into the multifaceted dimensions of AI-driven personalized learning, from its potential to enhance e-learning modules, the advent of AI-powered virtual tutors, to the ethical challenges it surfaces. As the tapestry of education becomes more intertwined with digital innovations, understanding AI's role in individualizing learning becomes paramount.

 View pdf
View pdf


The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with the Internet of Things (IoT) devices has led to the emergence of Edge AI, a transformative solution that enables data processing directly on the IoT devices or "at the edge" of the network. This paper explores the benefits of Edge AI, emphasizing reduced latency, bandwidth conservation, enhanced privacy, and faster decision-making. Despite its advantages, challenges like resource constraints on IoT devices persist. By examining the practical implications of Edge AI in sectors like healthcare and urban development, this study underscores the paradigm shift towards more efficient, secure, and responsive technological ecosystems.

 View pdf
View pdf


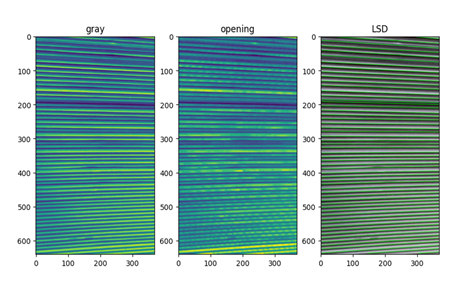
In industrial, the modern intelligent degree of board counting is relatively low. Some small manufacturers still count by hand, but for large factories, manual counting needs a lot of human resources, and the accuracy of counting is low. With the rapid development of modern intelligence, image recognition is becoming more mature, some traditional algorithms keep emerging, such as Hough Transform, Fast Line Detector (FLD), Line Segment Detector (LSD) and other line detection algorithms, they have their own advantages and disadvantages, and are summarized and tested, compare which algorithm has higher accuracy and better effect in the field of board linear detection and counting. Finally, the operation mechanism, advantages and disadvantages are summarized, and the process and trend of the further optimization and development of the traditional algorithm line detection technology in the future are prospected, which provides some reference for the research in related fields.

 View pdf
View pdf


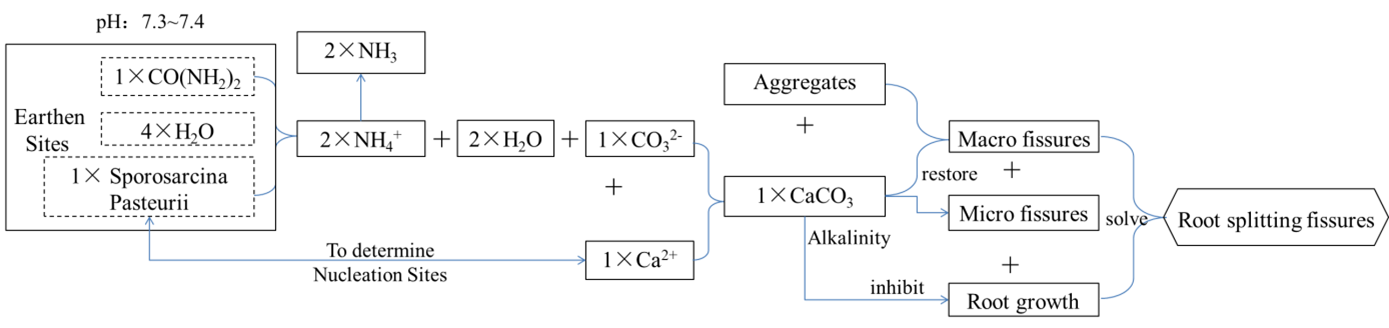
To master the culture optimization and regulation mechanism of Sporosarcina Pasteurii, this study explored the adaptability of MICP technology for restoring root splitting fissures of plants, and used single factor comparative experimental method to study the characteristics of growth curves and urease activity of Pasteurii in different conditions in earthen sites of Jinyang Ancient City. The conclusions are as follows. The technology of MICP was an ideal method for restoring root splitting fissures of plants, which could meet the requirements of restoring earthen sites by sealing surface fissures, inhibiting root growth of plants and preserving the physical morphology of damaged plant roots and stems. It was recommended to use the medium of M1, with an initial pH of 7.25, a culture temperature of 30 ℃, inoculation age range of 12-13h, and inoculation amount of 3%. The suggestion was to select Pasteurii as restoration solution when the urease activity was at peak period. The conclusions can provide suitable breeding conditions for Pasteurii, providing an important reference for MICP technology to restore root splitting fissures of plants for earthen sites.

 View pdf
View pdf


The transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the realm of smart cities is an evolving landscape of innovation and challenges. This research undertook a comprehensive exploration of AI's impact, harnessing both quantitative and qualitative methodologies. Detailed analyses were performed on data from select smart cities globally, focusing on sectors such as energy, traffic, health services, and waste management. Additionally, perceptions and experiences of urban stakeholders were captured through interviews. The results solidified AI's tangible benefits in enhancing urban life quality, while also bringing forth concerns about data privacy, algorithmic biases, and socio-economic implications. The study concludes with a call for holistic AI frameworks, heightened public engagement, and interdisciplinary collaborations to ensure the ethical and sustainable evolution of AI-integrated smart cities.

 View pdf
View pdf




