

Volume 4 Issue 2
Published on October 2025Purpose: This study aims to discuss the application value of the synergistic herb pairing concept of traditional Chinese medicine in treating Parkinson's disease and analyses its differences from and potential advantages over conventional Western therapies. From the perspective of synergistic herb pairings, this study takes three classic herb pairings, including the Tianma-and-Gouteng (Gastrodia-and-Uncaria) pairing, the Shudi-and-Yurou (Rehmannia-and-Cornus) pairing, as well as the Shaoyao-and-Gancao (Paeonia-Glycyrrhiza) pairing, as examples to examine and summarize the pairing rules, chemical pharmacology, and clinical efficacy. Results: Through different formula combinations, it is found that mutually reinforcing herb pairings can enhance clinical efficacy. Meanwhile, new active compounds formed during the decoction process, such as 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol extracted from Gastrodia elata and Rehmannia glutinosa polysaccharide produced during the processing of prepared Rehmannia root, exhibit stronger anti-neuronal apoptosis and neuroprotective effects. Conclusion: The concept of synergistic herb pairings in traditional Chinese medicine exerts therapeutic effects through multi-target mechanisms, showing unique advantages in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. In particular, it demonstrates clinical value in slowing disease progression and alleviating non-motor symptoms such as sleep disturbances and constipation. By integrating modern extraction technologies with optimized herb pairings, it can further enhance clinical efficacy and improve patients' quality of life.

 View pdf
View pdf


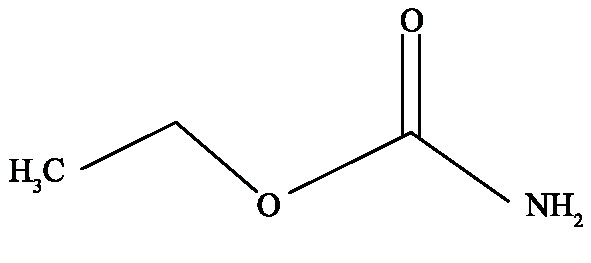
Ethyl carbamate (EC) is a multi-site carcinogen produced in the fermentation and storage process of food, which is widely found in soy sauce, wine (liquor, rice wine, wine, etc.), cereal or bean fermented food, lactic acid bacteria fermented beverage and other products. EC is able to be quickly and completely absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and skin, which poses a potential threat to the life and health of consumers. This paper systematically reviews the formation mechanism, limit standards and detection methods of EC in food in recent years, aiming to provide a scientific basis for the food industry to reduce the impact of EC on public health.

 View pdf
View pdf


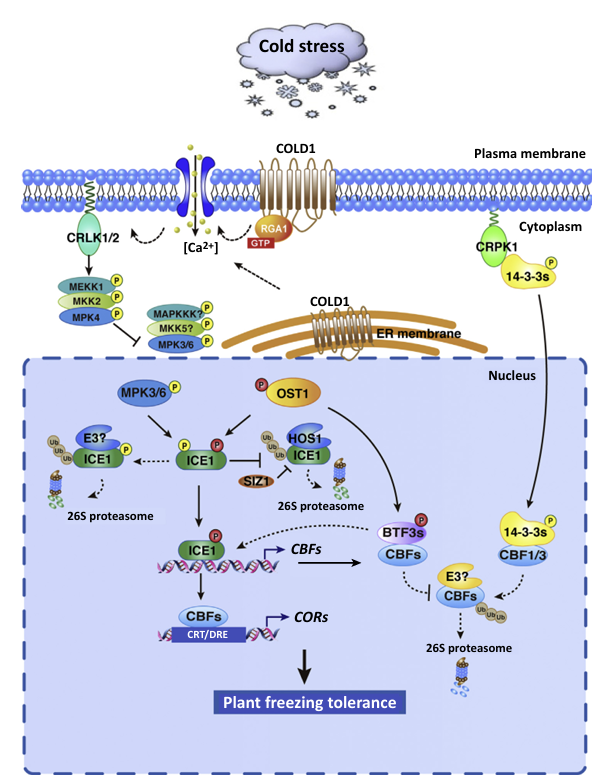
Tropical fruits are highly sought after for their unique flavor and nutritional value, but their cultivation is limited by warm climatic conditions. With global climate change and frequent extreme weather events, they need to breed cold-resistant tropical fruit varieties that are becoming increasingly urgent. Gene editing technologies, especially the CRISPR-Cas9 system, provide powerful tools for precise improvement of crop traits. However, due to challenges such as genome complexity and ecological impacts, few cases of gene editing in tropical plants have been grown in agriculture, and most of the studies are still in the laboratory or field trial stage. This topic investigates the mechanism of action during the response to low temperature stress and explores how these mechanisms can be utilized to better improve plant varieties, as well as how to accurately edit the genes related to cold tolerance discovered from the mechanisms. We are optimistic about the future development of new varieties that retain tropical characteristics and are cold-tolerant, and with the advancement of gene function analysis and editing tools, these new varieties are expected to expand their cultivation area and economic valuation.

 View pdf
View pdf


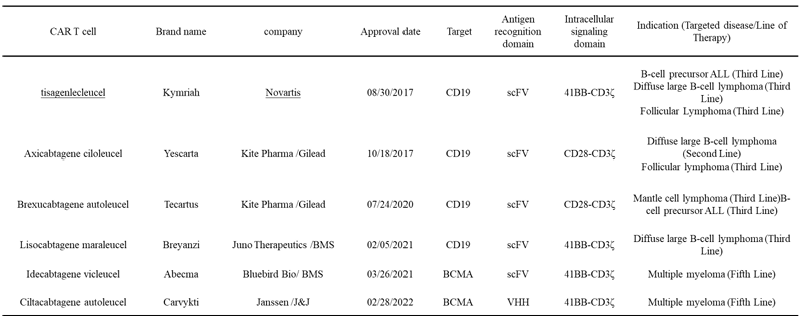
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is an innovative method of tumor immunotherapy. It has achieved excellent results in treating hematological malignancies and has been applied in a number of clinical situations. However, its therapeutic effect in solid tumors is still limited by multiple factors, including immunosuppression of the neoplastic microenvironment, target heterogeneity, insufficient penetration ability of CAR-T cells and poor persistence, etc. This study aims to explore effective approaches for enhancing the cytotoxicity of CAR-T cells against strong tumors. Through literature review and comprehensive analysis, this paper focuses on evaluating various enhancement methods, including optimizing the design of CAR structures (such as using costimulatory domain improvement, dual/multi-target CAR construction), synergistic therapy with combined immunomodulatory factors (such as IL-12, IL-18, IL-15) or antibody molecules, and targeting the tumor microenvironment, etc. Studies have pointed out that constructing CAR-T cells with stronger penetration, persistent activation ability and anti-exhaustion characteristics is a key direction to break through the bottleneck for treating strong tumors.This project provides theoretical assistance and strategic guidance. It helps us understand more deeply about the potential and problems of CAR-T cell therapy for solid neoplasms.

 View pdf
View pdf


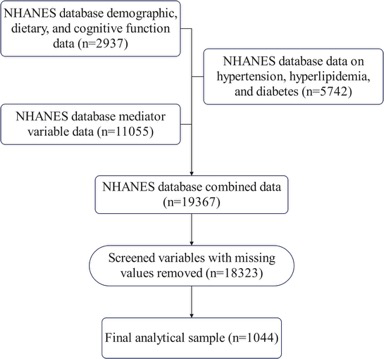
Objective: To examine the relationship between older adults’ diet-and-lifestyle oxidative balance score (Oxidative Balance Score, OBS) and cognitive function, and to investigate whether oxidative stress mediates that relationship. Methods: A total of 1,044 adults aged 60 years and older were included from the 2011–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Cognitive function was assessed by four tests: the Immediate Recall Test (IRT), Delayed Recall Test (DIR), Animal Fluency Test (AFT), and the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST). Weighted multivariable linear regression and restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses evaluated the associations between OBS and cognitive outcomes. Mediation analysis using structural equation modeling (SEM) tested the indirect effects of oxidative-stress biomarkers on these associations. Results: OBS was positively associated with IRT, DIR, AFT, DSST, and overall cognitive function; the β estimates (95% CI) were 5.83 (5.10–6.56), 0.38 (0.17–0.59), 15.37 (13.64–17.09), 45.22 (40.97–49.46), and 66.79 (61.48–72.11), respectively. RCS analyses revealed approximately linear dose–response relationships between OBS and IRT, DSST, and overall cognitive function. The 75th percentile and the highest quartile of scores on these three measures were also significantly associated with OBS. OBS directly and positively predicted overall cognitive ability, and was positively correlated with serum albumin and vitamin D levels while negatively correlated with uric acid. OBS may indirectly influence memory performance by modulating albumin, uric acid, and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels. Conclusions: We propose a four-dimensional regulatory model — “diet → lifestyle → oxidative microenvironment → cognitive function” — and provide evidence that multifactorial, synergistic antioxidant interventions have cumulative protective effects on cognition in older adults via a biomarker-network mediation mechanism. These findings support the development of personalized, oxidative-balance-based cognitive interventions and underscore the public-health value of whole-diet pattern adjustment combined with lifestyle optimization for preventing cognitive decline.

 View pdf
View pdf


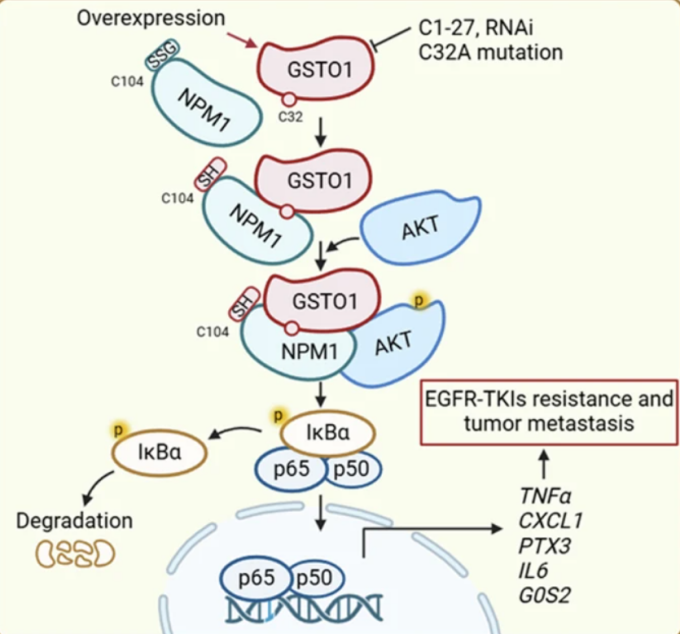
This study focuses on lysine-targeted covalent inhibitors of Glutathione S-Transferase Omega 1 (GSTO1). As a member of the glutathione enzyme family, GSTO1 is mainly involved in Phase II detoxification. Its expression is upregulated in various cancers, enhancing the drug resistance of cancer cells, thus making it a potential target for cancer therapy. Inhibiting GSTO1 can suppress the proliferation of tumor cells and promote their apoptosis without affecting the growth of normal cells. Therefore, we can select a small-molecule covalent inhibitor to inhibit the activity of GSTO1. Covalent small-molecule inhibitors have attracted significant attention due to their high selectivity and long-lasting efficacy. Currently, the cysteine-targeted inhibitors under research suffer from short half-lives and poor stability, making it difficult to achieve breakthroughs in clinical applications. Future research should focus on targeting lysine and employ a variety of technical approaches to develop highly active and stable lysine-targeted covalent small-molecule inhibitors for GSTO1, with the aim of achieving breakthroughs in cancer treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


Pruritus is a highly complex sensory disorder with a large proportion of the population experiencing chronic pruritus. Its occurrence involves multi-level signal transduction of skin receptors, peripheral nerves, central regulation and effectors. Persistent pruritus can lead to scratched skin lesions, pigmentation, and secondary infections, and may even cause sleep disorders, anxiety, and depression, significantly impairing patients’ quality of life. In this paper, the physiological and pathological process of pruritus is systematically analyzed based on the reflex arc pathway of "receptor → afferent nerve → nerve center → efferent nerve → effector"; At the same time, it introduces the non-classical signaling mechanisms found in recent years and the clinical research progress of emerging targeted neuromodulators, and pays attention to the psychological, Chinese medicine and physical intervention from multiple dimensions. Such multidisciplinary intervention means can further improve the well-being of patients. At present, there is still a lack of highly effective clinical guidelines for doctors' reference, which makes the prognosis of patients treated with doctors’ experience potentially poor. Therefore, the update of guidelines needs to be further strengthened after the publication of new studies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Fennel is the dry and mature fruit of the Umbelliferae plant (Foeniculum vuLgare Mill). It is widely distributed and does not require a high growth environment; Fennel was first recorded in Tang materia medica and was originally named Huaixiang. Throughout its long history, people not only used it as a delicacy in their diet, but also discovered its medicinal value and widely applied it in clinical treatment of diseases. In China, fennel is commonly used as a food and seasoning, as well as traditional Chinese medicine; Internationally, fennel is mainly used in cosmetics and food additives. With the improvement of living standards, people are increasingly focusing on the high-yield cultivation and active ingredient research of fennel, which has given rise to some research on its components and how to achieve high-yield cultivation; Meanwhile, the variety and quantity of products related to fennel are increasing day by day. This review aims to summarize the ingredients of fennel, the research progress in cultivation methods, and the fennel products currently available on the market.

 View pdf
View pdf


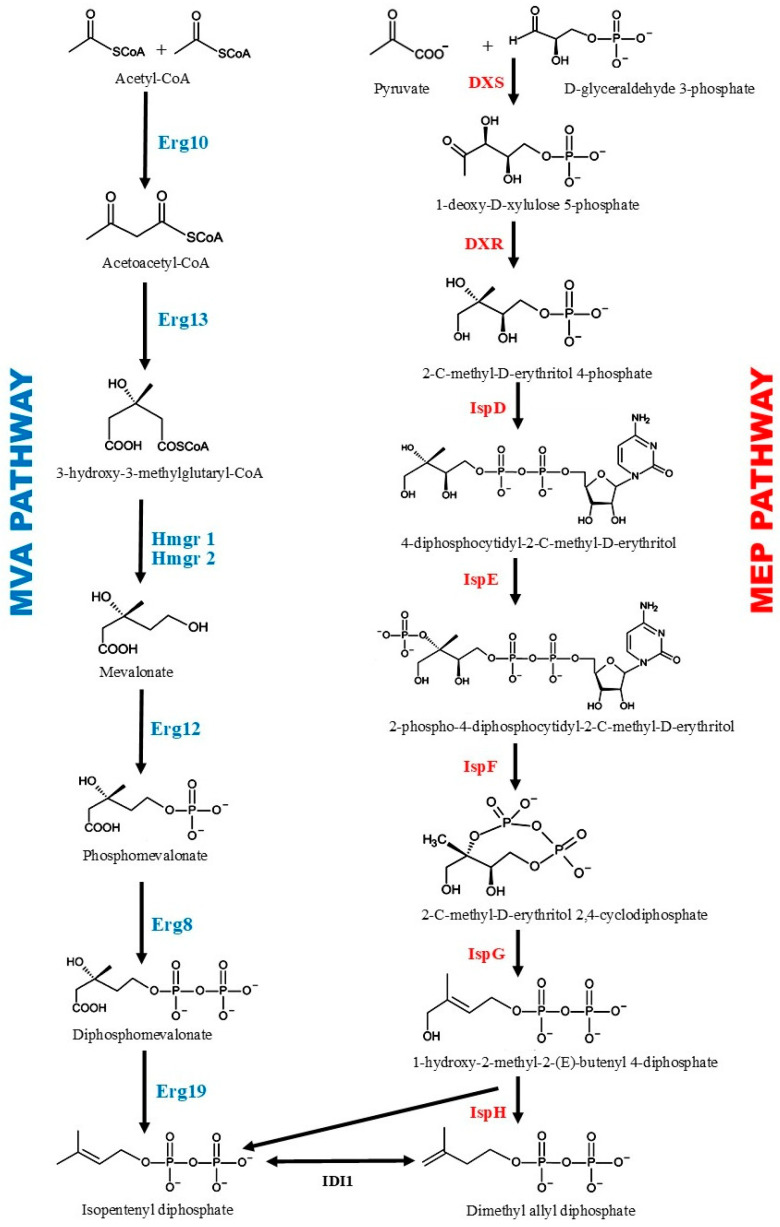
Santalene, as a major sesquiterpene component of sandalwood oil, possesses broad pharmacological activities and considerable commercial value. However, traditional plant-extraction methods are inefficient, costly and unsustainable. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to achieve biological synthesis of santalene has emerged as a highly promising alternative. This review summarizes key recent advances in the field, including reconstruction and optimization of the mevalonate (MVA) pathway to enhance precursor supply; redirecting metabolic flux toward santalene by suppressing competing branch pathways such as ERG9 and DPP1, achieving 3.4- and 5.9-fold increases; optimization of cofactor regeneration systems (e.g., NADPH and acetyl-CoA); and fermentation-process improvements that raised α-santalene titers to 163 mg·L⁻¹. These systemic modifications have led to significant yield improvements. Finally, we discuss future directions for combining systems biology and synthetic biology tools to further optimize cell-factory performance and advance industrial-scale production.

 View pdf
View pdf




