

Volume 108
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Global Politics and Socio-Humanities
The effectiveness of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) has declined significantly in recent decades, weakening its ability to address contemporary security challenges. This paper examines the underlying causes of this decline, with a particular emphasis on the Council's structural inflexibility and the escalation of geopolitical competition among the P5 member states. It explores the ways in which these factors have impeded timely and effective decision-making, resulting in impasse and protracted humanitarian crises, through a comparative analysis of the Kosovo crisis, the Syrian civil war, and the Ukrainian conflict. The study underscores the challenges presented by the evolving multipolar world, the detrimental consequences of the frequent and strategic use of the veto, and the UNSC's failure to reform its decision-making mechanisms and membership structure. Lastly, the study demonstrates the pressing necessity of targeted reforms to fortify the Council's adaptive capacity and re-establish its role in the preservation of global peace and security in an international system that is becoming increasingly fragmented.

 View pdf
View pdf


The International Criminal Court (“ICC”) is an important international institution for dealing with international crimes. The ICC has always been at the front line for pursuing international criminal justice and has accomplished several influential cases. However, problems emerged within the ICC’s legal process and need to be solved. This paper focuses on the obstacles encountered during the Pre-Trial and Trial stages of the ICC, which are two critical parts in the whole legal process. The research question is: "What are the major obstacles in the ICC's Pre-Trial and Trial stages?" This research question is fundamental as it could enhance the efficiency of the ICC's legal process and reduce extensive time commitments. This paper uses the case study methodology, analyzing cases from the ICC and ad hoc tribunals. The analysis concludes that limited state cooperation and the strict standards for proving Genocide are the primary challenges in these stages. Addressing these issues can enhance the ICC's ability to prosecute international crimes effectively.

 View pdf
View pdf


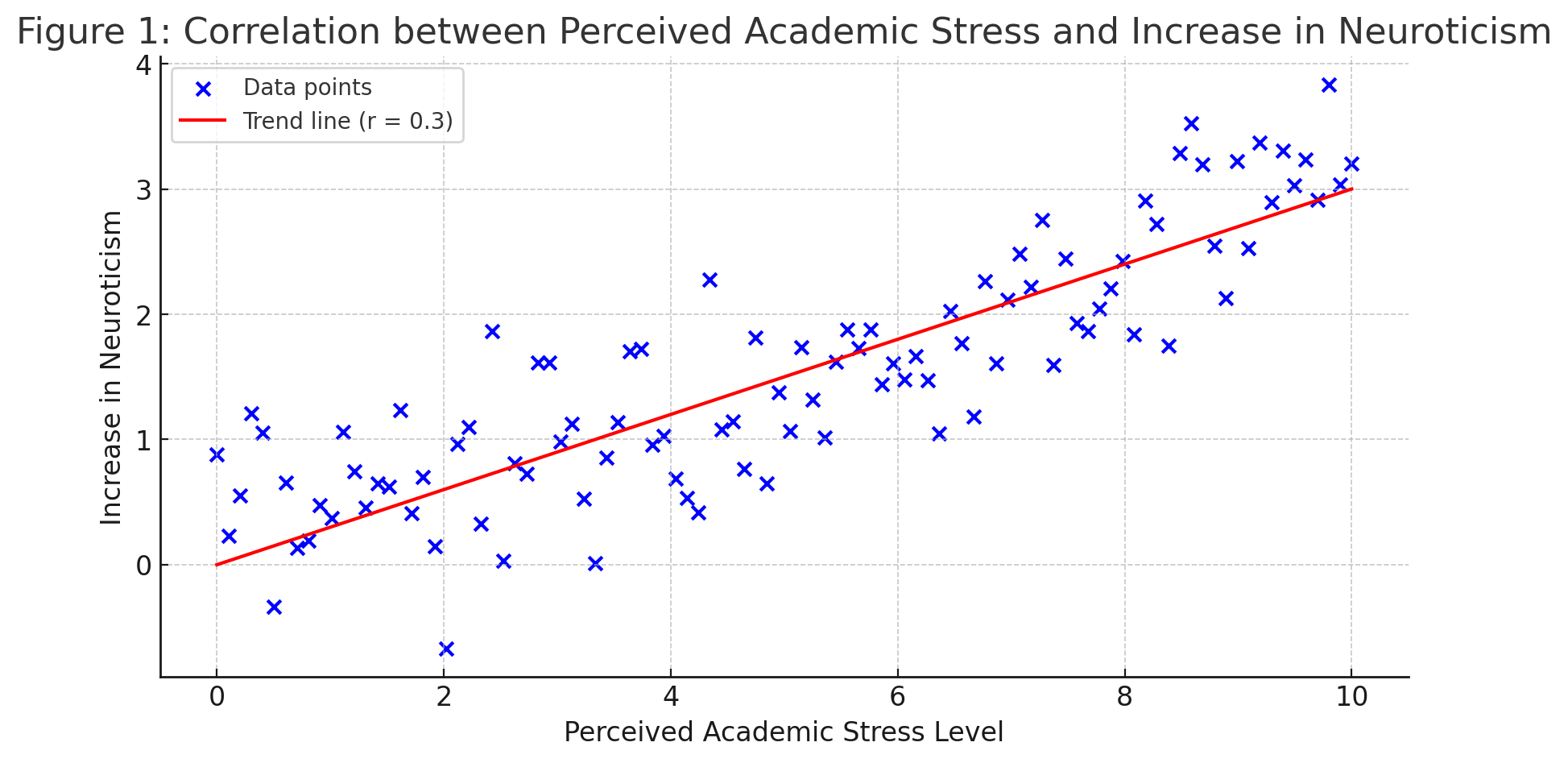
This study aims to investigate the impacts of perceived academic stress levels and mindsets on the personality trait development of neuroticism. It has importance for guiding adolescents’ personality development and academic success and addressing the existing gap in the current literature. I plan to conduct a longitudinal study and recruit 352 high school seniors as participants. Each participant will complete three questionnaires to measure their perceived academic stress level, mindsets, and neuroticism level, first at the start of the academic year, and again at the end of the year. I predict that higher levels of perceived academic stress will correlate with increased neuroticism, but that this relationship may vary depending on the type of mindset held by the individual. This study emphasizes the importance to recognize the relationship between perceived academic stress, mindsets, and neuroticism, which is essential for promoting mental well-being in adolescents. Raising awareness of how stress perception and mindsets affect development could lead to more effective mental health intervention from parents and educators. Additionally, by focusing on how we interpret stress and how that interpretation can affect our futures, we can be more aware of the power of our internal belief systems and include positive stress interpretations and coping strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


The main research is working memory, long-term memory, and integrated study of memory. Most modern research barely covered the study of short-term memory. Nevertheless, short-term memory can let your life change in many ways, such as forgetting the key or forgetting your idea in a discussion. As an important part of memory, we decided to research its correlation with Neuroticism in Big Five personality traits. We will ask participants to watch a video and do a Big Five personality traits test for data measure and use the questionnaire to collect their data of ability in Neuroticism and short-term memory. We will also do related tests of other personality traits’ correlation with short-term memory. For the data analysis part, we will use cor-test to calculate the data. The result shows there is a negative correlation between Neuroticism and short-term memory, which means people who have low levels of neuroticism should have better short-term memory. Extraversion has a positive correlation with short-term memory.

 View pdf
View pdf


Attachment-related avoidance is known to hinder emotional closeness, self-disclosure, and relationship identification in intimate relationships. This study examines how individual differences in attachment-related avoidance predict variations in self-disclosure and relationship identification, particularly when moderated by perceived appreciation and understanding from partners. Drawing on attachment theory, the study hypothesizes that avoidantly attached individuals who feel appreciated or understood by their partners will report higher levels of self-disclosure and relationship identification. Participants involved in intimate relationships will be recruited from China and randomly assigned to groups experiencing varying levels of partners’ appreciation or understanding through controlled interaction tasks. The study will employ self-reported measures before and after these interactions to assess changes in self-disclosure and relationship identification. The results are expected to show that higher levels of perceived appreciation and understanding lead to greater improvements in relationship outcomes. Secondary analyses will explore the effects of gender and partner attachment styles. Findings will have both theoretical and practical implications, contributing to a deeper understanding of attachment theory and offering insights for therapeutic interventions that aim to foster appreciation and understanding in relationships, particularly for individuals with avoidant attachment styles.

 View pdf
View pdf


The primary goal of this research is to investigate the benefits and risks associated with AI-driven personalization on social media platforms. This technology enhances user experiences by expanding services, increasing user engagement, and improving the economic value of platforms. However, it also introduces challenges, such as limiting user choice and potentially worsening decision-making. The study also examines the risk of privacy invasion, particularly when users cannot access or control their personal data. The objective of this research is to inform policymakers about the need for enhanced data security regulations. Social media platforms should empower users with greater control over their data and be more transparent about its use. Individuals must also exercise caution in sharing personal information online.

 View pdf
View pdf


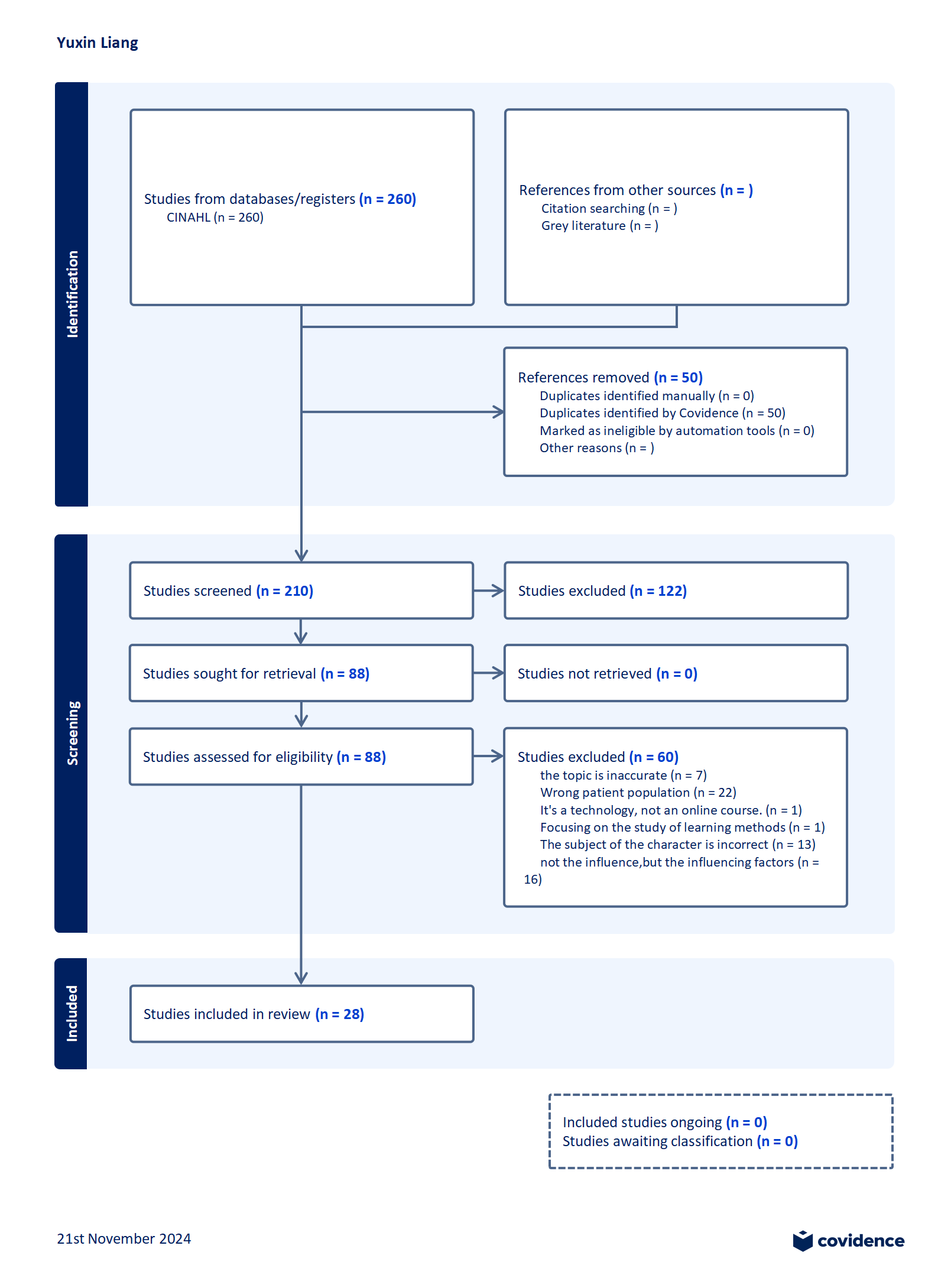
With the rapid development of science and technology and the far-reaching impact of the COVID-19 epidemic, online courses have grown significantly and expanded their coverage in various educational environments. This transformation has not only reshaped the traditional teaching and learning model but also brought new opportunities and challenges to educators and learners. Given the increasing importance of online education, this study systematically explored the existing literature on the impact of online education on Chinese students and teachers, hoping not only to provide valuable insights for teaching reform and help improve educational practice but also to provide a helpful reference for future research in this area. The researcher classified and screened 260 articles and finally explored 28 articles in detail. The research results showed that more articles were used to study the impact of online courses on students while neglecting their impact on teachers. This imbalance highlights an important research gap that deserves attention. The results of this study may contribute to a deeper understanding and provide some favorable information for the future development and research direction of online education.

 View pdf
View pdf


Obesity, recognized as a chronic disease, imposes enormous economic and health burdens on Chinese society. In examining obesity rates across various age groups in China, this study identifies a paradox: An observation has been made that obesity rates among university students are comparatively lower than those seen in high school. Despite extensive research on the factors contributing to obesity and strategies for its reduction, there has been limited exploration into why university students are less affected by obesity than high school students. This paper addresses this gap by conducting a comprehensive review of the literature, focusing on socioeconomic status (SES) as a critical factor. We categorize the determinants of this phenomenon into external factors, such as urban-rural disparities, income, and educational attainment, and internal factors, including gender differences and behavioral responses to stress. By offering academic insights and policy implications, this review aims to contribute to the early prevention and management of obesity, ultimately improving public health in China.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article demonstrates the ability of nations with great power to ignore structural barriers implemented, using such to rectify action directed to be in positive correlation to their interests. While the original barriers were implemented by limiting factors such as the United Nations, the lack of effectiveness was exemplified by rooted historical interdictions alongside policies and rules commodified to benefit great powers. An important goal of great powers would be to develop these modern structures, a tool for neo-imperialist standings, eliminating justification and logic by developing structures embodying their own structure. While a direct approach to eliminate such a mindset developed by great powers includes a solution from the United Nations themselves, this paper offers a junction in which the development of decolonizing thought must be accepted and integrated within the United Nations. As such, later in the paper, I suggest that the implementation of a decolonial mindset would act as a prerequisite to an effective curtailment of modern great powers. Further, great powers must be scrutinized under the historical precedent of established systems permitting abuse of power and possible reform regarding solutions to be of progressive movement in the direction of decolonization. To decolonize the United Nations through the removal of the idealization of the state in conjunction with the individual would be vital reform. Scrutinizing such states to end the perpetuation of the settler state corroborates the decolonial mission.

 View pdf
View pdf


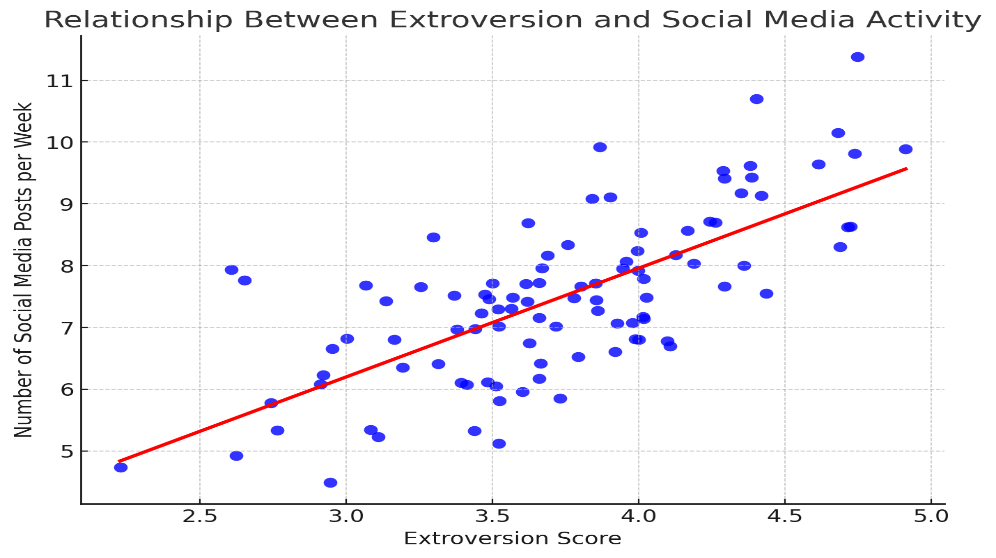
This study explores how extroversion affects an individual's frequency of interaction and self-presentation behavior on social media platforms. The importance of this research question is that with the popularity of social media, especially the rise of short video platforms, more and more people are starting to post less frequently on social media. The significance of this study is not only on the personal level but also on the theoretical and practical level. When we understand the relationship between personality traits and social media use, we can better optimize the user experience and help content creators tailor their content to the audience's preferences. There is relatively little research on personality traits and social media use in the existing literature, so this study is expected to provide new perspectives and insights. This study adopted a quantitative approach, using questionnaires to investigate participants' personality traits (mainly extroversion) and social media behavior. The extraversion scale and social media Behavior scale were used to measure subjects' frequency of Posting, liking, and commenting. Data were analyzed using Pearson correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis to assess the relationship between extroversion and social media behavior. The study also took into account moderating factors such as age, gender, and cultural background. The expected results showed that individuals with higher extroversion were more active on social media, in the form of more frequent posts, likes, and comments. In addition, people who are more extroverted are more likely to post selfies or self-presentations. The results of this study will provide a reference for the optimization of user interaction and content creation on social media platforms, and also provide a basis for future research on personality traits and digital behavior.

 View pdf
View pdf




