1. Introduction
Nowadays, all kinds of data show explosive growth and the era of big data has arrived, MapReduce as a popular parallel programming model is highly favored due to its wide application in the field of large-scale data processing [1, 2]. However, past research has focused on traditional Hadoop and cluster-based MapReduce frameworks, which provide effective solutions to process and analyze large-scale datasets, but the traditional data processing paradigm is no longer able to meet the needs of researchers [3]. In this context, Serverless architecture brings new ideas for distributed computing [4]. The emergence of Serverless architecture provides users with the ability of dynamic resource allocation and elastic scaling, which greatly simplifies the deployment and management of distributed computing tasks.
This study aims to explore the design, implementation and optimization of MapReduce framework based on AliCloud Serverless platform. By fully utilizing the dynamic resource allocation and elastic scaling characteristics of AliCloud Serverless architecture, an efficient and flexible text data processing system is constructed to provide users with better word frequency statistics solutions. The study not only provides a detailed description of the design and implementation of the MapReduce framework, but also experimentally evaluates the impact of vCPU specification, memory specification, and parallel resource configuration on the system performance, thus providing an important reference for further research and optimization of the MapReduce framework under the Serverless platform.
2. Rationale analysis
2.1. Literature review
In recent years, MapReduce research under Serverless platform has gradually attracted attention. With the computing resources provided by cloud service providers, researchers have started to explore how to design and optimize MapReduce frameworks in Serverless environments to solve the performance bottlenecks and cost problems existing in traditional MapReduce frameworks. Currently, there are some related works at home and abroad that have realized the deployment and execution of MapReduce tasks on Serverless platforms and achieved certain results. For example, Serverless computing services such as AWS Lambda are widely used for the execution of MapReduce tasks [5]. And researchers have proposed different architectures and optimization strategies, e.g., Shweta Das successfully optimized task scheduling in serverless computing by combining the ACO algorithm with MapReduce [6]. Fabian Mahling introduced the BabelMR data processing framework, which provides MapReduce programming model to arbitrary containerized applications on serverless cloud infrastructure to improve the performance and scalability of MapReduce tasks on Serverless platforms [7]. Sebastian Werner's approach to big data processing through serverless computing, using matrix multiplication as an example, reduces costs and improves performance and scalability, providing advantages over traditional cluster computing frameworks [8]. However, MapReduce research based on Serverless platform still faces many challenges and pending issues [9]. Therefore, the design, implementation and optimization of MapReduce frameworks in Serverless environment are still of great research significance. In this study, we explore the reasons for the influence of MapReduce efficiency based on AliCloud serverless on the problem of counting the word frequency of words in large-scale English texts.
2.2. Overview of the methodology
Unlike the traditional MapReduce framework that counts the word frequencies of words in English text, this study aims to design and implement a MapReduce framework based on AliCloud Serverless platform and explore the reasons affecting its efficiency [10]. In this paper, the framework adopts the classical MapReduce programming paradigm, which divides the data processing task into two key phases: Map and Reduce [11]. In terms of concrete implementation, the Map phase is responsible for receiving the original data, dividing the textual data into key-value pairs and performing word frequency statistics; the Reduce phase is responsible for merging and aggregating the key-value pairs outputted from the Map phase, and finally counting the word frequency of each word. The Reduce stage is responsible for merging and summarizing the key-value pairs output from the Map stage, and finally counting the word frequencies. By making full use of the "Function Computation FC" and "Object Storage OSS" functions provided by Aliyun Serverless Platform, the optimization of multi-threaded execution time of functions and the optimization of data loading and transmission speed are achieved.
2.3. Introduction to MapReduce
Map phase and Reduce phase play a key role in the whole MapReduce framework, respectively responsible for the initial processing of raw data and the final summary statistics.
2.3.1. Map phase
In the Map phase, the English text data uploaded by the user is first read by the Map function and the amount of data of the text is determined, including num_files and num_texts. according to the amount of data of num_files, the number of Map functions that need to be allocated is determined in order to carry out a multi-threaded parallel computation, and each thread processes one num_file. during the parallel processing of each text file, the Map function splits and truncates the text to obtain each word, then iterates over each word, checks and modifies the word for formatting errors and symbol errors, then counts the frequency of each word's occurrence in the text and saves the results, categorized according to the first letter, in the word_counts list; specifically, the Map function takes each word as a key and the number of occurrences as a value . After completing the processing of all the text, the Map function generates 26 JSON files from the data that have been grouped according to the first letter in the word_counts list, and each file contains words that start with the same letter and their corresponding word frequency statistics. Finally, the Map function uploads these JSON files to a specified path through the AliCloud OSS API for subsequent Reduce stages.
2.3.2. Reduce phase
The task of Reduce stage is to process the data from the output of Map stage to merge and count the word frequencies of the words. First, the Reduce function reads the 26-text data output from the Map function (these data are generated by the Map phase according to the classification of English initial letters) and determines the data volume of the texts: num_files and num_texts. based on the data volume of num_files, the number of Reduce functions that need to be allocated for parallel computation is determined. Next, the Reduce function accumulates the corresponding values of the same words in all folders to realize the function of word frequency statistics. After confirming that the word frequency counts of all files are complete, the Reduce function saves the generated word_counts as a JSON file. In order to improve the accessibility and persistence of the result, the Reduce function uploads the result file to AliCloud OSS and returns the access link of the file after successful upload. Users can obtain the final statistical results through the API or the AliCloud console interface, and conduct further data analysis and application. Through the above process, a MapReduce framework based on AliCloud Serverless platform is realized, which provides an efficient solution for word frequency statistics by utilizing dynamic resource allocation and elastic expansion characteristics. The specific process is shown in the following figure 1.
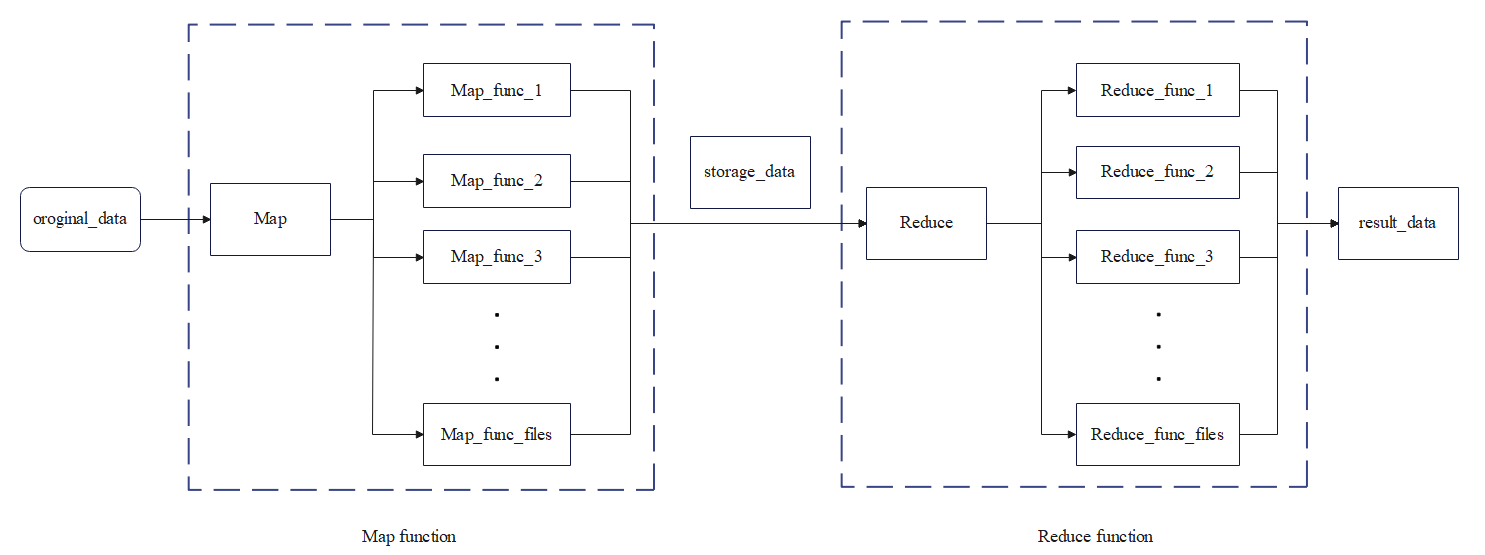
Figure 1. MapReduce flowchart based on AliCloud Serverless
2.4. Introduction to the AliCloud Platform
The AliCloud platform is the core component of the framework, which aims to reduce the time and cost of text data processing. The framework uses AliCloud Serverless platform as the infrastructure, which mainly includes two major parts: data storage layer and technology selection [12]. The data storage layer uses AliCloud OSS to store raw text data and processing results, and the data storage structure is flexibly designed according to the task requirements, such as organizing the storage by date, by task, etc., in order to better manage and organize the data. In terms of technology selection, AliCloud Functional Computing is chosen as the computing engine, which has the characteristics of elasticity and scalability, and is able to dynamically adjust the computing resources according to the task requirements, so as to achieve optimal allocation and utilization of resources. Request security is achieved through AliCloud's RAM, which allows organizations and users to perform fine-grained privilege control of their resources on AliCloud to ensure resource security and compliance. Task scheduling, on the other hand, can utilize timed triggers or automated task scheduling services to manage the execution process and status of tasks to achieve automated task management and scheduling. For logging and monitoring, the monitoring and logging services provided by Aliyun are combined to monitor and analyze the execution status and performance of tasks in real time, so as to identify and solve problems in a timely manner and ensure the smooth execution and efficient operation of tasks. Through the reasonable configuration and implementation of the above technology selection and optimization strategies, an efficient and stable text data processing system is constructed, which is able to meet the needs of various complex data processing tasks, and at the same time greatly simplifies the deployment and management process of the system, improves the system's flexibility and scalability, and further improves the overall processing efficiency.
3. Experimental
3.1. Experimental setup
The test data selected in this paper is the full text of Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, which is split into multiple segments and saved in a total of 10 folders, each containing 1024 txt files. In order to comprehensively evaluate the impact of different computational resource configurations on processing performance, we conducted experiments on AliCloud Serverless Functional Computing (FC) service. In our experiments, we used FC function execution environments with different vCPU specifications (0.3, 0.35, 0.5) and memory specifications (384MB, 512MB, 1024MB). These configurations are designed to simulate low to high resource demands to evaluate the performance of the system under different loads. Each experimental scenario contains both parallel and non-parallel processing to explore the impact of concurrent execution on processing efficiency. In particular, a configuration with a vCPU specification of 0.35 and a memory specification of 512MB is selected as the benchmark parameters for this experiment in order to make a side-by-side comparison under the same network environment. Moreover, in order to simulate the real data volume, we set the number of txt files as 100 and 1024 two kinds of txt file numbers, so as to evaluate the performance difference under different file numbers more precisely. In the experiments, we recorded the key performance indicators such as the execution time, vCPU utilization and memory utilization of the map function and reduce function under the two file sizes respectively.
3.2. Presentation of experimental results
By comparing and analyzing these data, we are able to clearly observe the impact of different vCPU specifications, memory specifications, and parallel processing strategies on the system performance when processing the text segments of Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, and the specific data of the final experiment are shown in table 1 and table 2 below.
Table 1. Parameters when num_file = 10 num_texts = 1024
vCPU rating | Memory Ratings | Parallel or not | vCPU values | vCPU utilisation | Memory values | memory utilisation | Time(ms) |
0.35 | 512 | yes | 0.3318 | 94.80% | 339.46 | 66.30% | 217000 |
no | 0.3178 | 90.80% | 315.39 | 61.60% | 632000 | ||
0.3 | 512 | yes | 0.2576 | 85.85% | 338.94 | 66.20% | 281000 |
no | 0.2277 | 75.90% | 315.39 | 61.60% | 731000 | ||
0.5 | 512 | yes | 0.4815 | 96.30% | 338.94 | 66.20% | 155000 |
no | 0.4925 | 98.50% | 315.39 | 61.60% | 723000 | ||
0.35 | 384 | yes | 0.3294 | 94.10% | 339.46 | 88.40% | 220000 |
no | 0.3469 | 99.10% | 315.26 | 82.10% | 618000 | ||
0.5 | 1024 | yes | 0.4925 | 98.50% | 342.01 | 33.40% | 153000 |
no | 0.4485 | 89.70% | 316.42 | 30.90% | 606000 | ||
0.35 | 1024 | yes | 0.3308 | 94.50% | 342.02 | 33.40% | 222000 |
no | 0.2657 | 75.90% | 316.3 | 30.90% | 770000 | ||
0.3 | 384 | yes | 0.2793 | 93.10% | 326.3 | 85.02% | 249000 |
no | 0.2748 | 91.60% | 315.4 | 81.10% | 999000 |
Table 2. Parameters when num_file = 10 num_texts = 100
vCPU rating | Memory Ratings | Parallel or not | vCPU values | vCPU utilisation | Memory values | memory utilisation | Time(ms) |
0.35 | 512 | yes | 0.3189 | 91.10% | 90.62 | 17.70% | 29400 |
no | 0.299 | 85.42% | 64.51 | 12.60% | 30141 | ||
0.3 | 512 | yes | 0.2766 | 92.20% | 90.62 | 17.70% | 33235 |
no | 0.2507 | 83.58% | 65.54 | 12.80% | 32256 | ||
0.5 | 512 | yes | 0.4443 | 88.85% | 51.20 | 17.56% | 17713 |
no | 0.3474 | 69.48% | 65.54 | 12.80% | 26372 | ||
0.35 | 384 | yes | 0.3196 | 91.30% | 91.01 | 23.70% | 25553 |
no | 0.2902 | 82.90% | 66.05 | 17.20% | 33151 | ||
0.5 | 1024 | yes | 0.4615 | 92.30% | 96.38 | 9.41% | 17584 |
no | 0.3788 | 75.75% | 65.84 | 6.43% | 29433 | ||
0.35 | 1024 | yes | 0.3232 | 92.35% | 94.00 | 9.18% | 27561 |
no | 0.2989 | 85.40% | 68.61 | 6.70% | 33900 | ||
0.3 | 384 | yes | 0.2607 | 86.90% | 91.20 | 23.75% | 38581 |
no | 0.2635 | 87.83% | 65.66 | 17.10% | 35606 |
3.3. Analysis of impact patterns
3.3.1. vCPU influence pattern
The experimental results show that with the increase of vCPU specification, the vCPU utilization tends to increase in both parallel and non-parallel processing. Taking the 512MB memory specification and parallel processing environment as an example, when the vCPU specification is increased from 0.3 to 0.5, the vCPU utilization increases from 85.42% to 88.85% (and from 69.48% to 75.75% under non-parallel processing), while the execution time is shortened from 30 seconds and 141 milliseconds to 17 seconds and 713 milliseconds. The change in usage with vCPU increase under parallel is shown in figure 2.
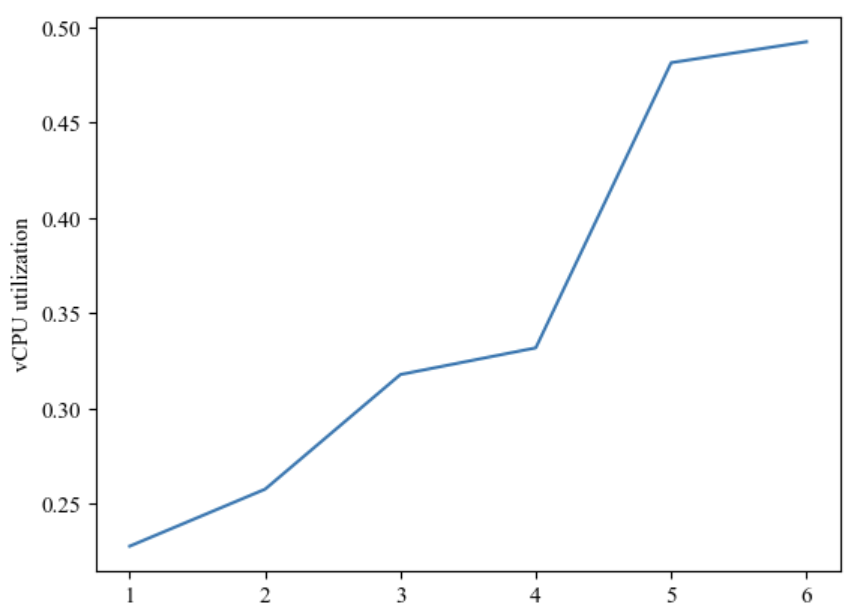
Figure 2. Change in usage with vCPU increase under parallel
This indicates that a higher vCPU specification can handle more workloads, thus increasing the processing power of the system. Under parallel processing, higher vCPU specifications usually result in shorter execution times because multiple vCPUs can work simultaneously to accelerate task processing. In non-parallel processing, although vCPU utilization is lower, higher vCPU specifications also usually result in shorter execution times, probably because higher vCPU specifications allow faster single-threaded processing.
3.3.2. Memory Impact Laws
As can be seen from the experimental results, the memory utilization is not directly proportional to the size of the memory specification. In most cases, the memory utilization is relatively low, probably because the tasks in the experiments are not memory intensive. For example, in an environment with a vCPU specification of 0.35 and parallel processing, when the memory specification was increased from 384MB to 1024MB, the execution time was shortened from 25 seconds 553 milliseconds to 27 seconds 561 milliseconds, despite the decrease in memory utilization (from 23.70% to 9.18%) However, even if the memory utilization is not high, in some cases a larger memory specification still may have a positive impact on performance. For example, in memory-intensive tasks, a larger memory size can reduce performance bottlenecks caused by insufficient memory. Therefore, the choice of memory size needs to be weighed against the actual task requirements. The memory usage under parallel or non-parallel conditions is shown in figure 3.
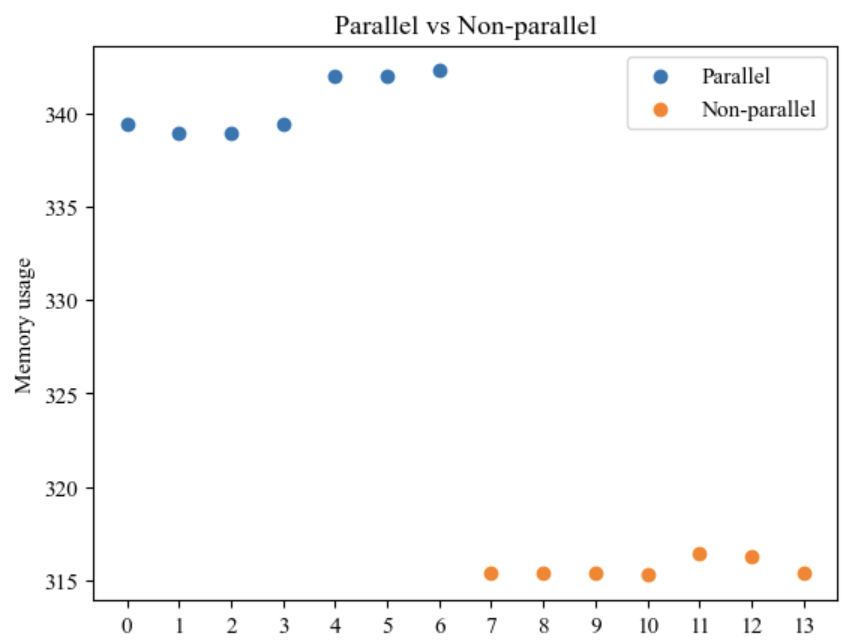
Figure 3. Memory usage under parallel or non-parallel conditions
3.3.3. Laws of parallel influence
The experimental results show that parallel processing has a significant improvement in system performance. With the same vCPU specification and memory specification, the execution time of tasks using parallel processing is generally less than that of non-parallel processing. For example, with a vCPU specification of 0.35 and a memory specification of 512 MB, the execution time for parallel processing is 29 seconds and 400 milliseconds, compared to 30 seconds and 141 milliseconds for non-parallel processing. This result indicates that parallel processing can more fully utilize system resources and improve the processing speed and efficiency of tasks. The time spent in parallel or non-parallel conditions is shown in figure 4.
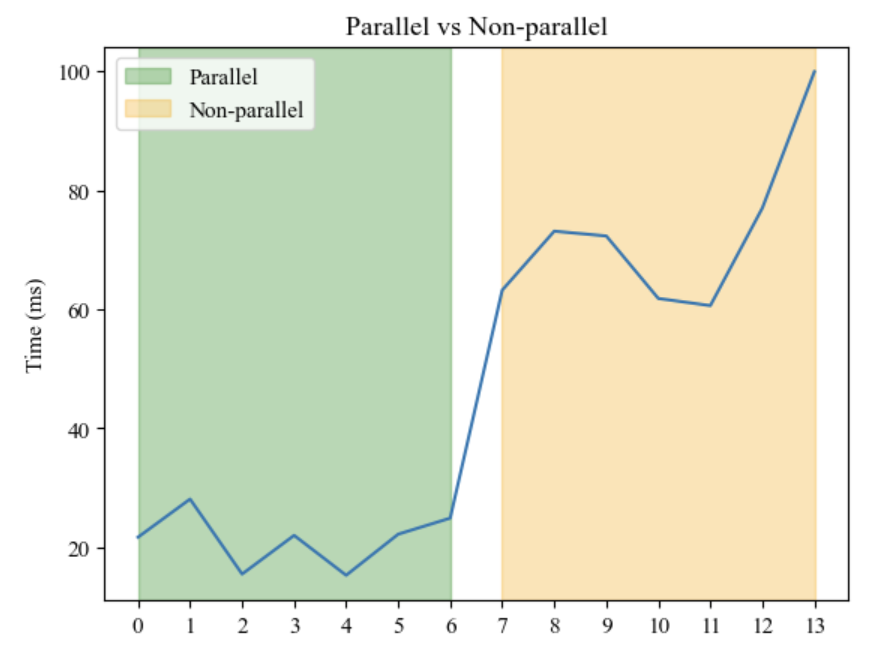
Figure 4. Time spent in parallel or non-parallel conditions
4. Conclusion
In this study, we design and implement a MapReduce framework based on AliCloud Serverless platform for the task of word frequency counting of large-scale English texts. By fully utilizing the dynamic resource allocation and elastic scaling characteristics of the Serverless architecture, we implemented the Map phase and Reduce phase, and conducted experiments to evaluate the system performance. The experimental results show that different computational resource configurations have a significant impact on system performance. As the vCPU specification increases, the processing power and execution efficiency of the system increase, especially in parallel processing environment. Memory specifications have a relatively small impact on system performance, but may still have a positive effect on performance in some cases. Parallel processing provides a significant improvement in system performance, enabling full utilization of system resources and increasing task processing speed and efficiency. Despite the results achieved, there are still some shortcomings in this study, such as the efficiency may not be high when processing very large-scale data, and further optimization is needed for data preprocessing and exception handling. Future research can improve the system performance by introducing efficient parallel computing strategies, such as dynamic task scheduling, graph computing and data flow computing modes, and optimizing resource scheduling in combination with machine learning. At the same time, optimize the error handling and fault tolerance mechanism, and establish an intelligent error warning and handling system through distributed logging, rollback, redundancy calculation, and data validation to enhance the reliability of the system. Improve the data pre-processing process, optimize the data cleaning, conversion and loading steps, and adopt layered storage and caching technology to improve data processing efficiency. In addition, the modular architecture is designed to combine containerization and microservice technologies to achieve flexible expansion and resource management to further enhance the deployment and management efficiency of the system, so that the MapReduce framework based on Serverless architecture is more efficient and stable in processing large-scale data sets.
References
[1]. Kudyba S, Kudyba S. Big data, mining, and analytics. Boca Raton: Auerbach Publications; 2014.
[2]. Dean J, Ghemawat S. MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Communications of the ACM. 2008 Jan 1; 51(1): 107-13.
[3]. Ghazi MR, Gangodkar D. Hadoop, MapReduce and HDFS: a developers perspective. Procedia Computer Science. 2015 Jan 1; 48: 45-50.
[4]. Castro P, Ishakian V, Muthusamy V, Slominski A. Serverless programming (function as a service). In2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS) 2017 Jun 5 (pp. 2658-2659). IEEE.
[5]. Giménez-Alventosa V, Moltó G, Caballer M. A framework and a performance assessment for serverless MapReduce on AWS Lambda. Future Generation Computer Systems. 2019 Aug 1; 97: 259-74.
[6]. Das S. Ant Colony Optimization for MapReduce Application to Optimise Task Scheduling in Serverless Platform (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin, National College of Ireland).
[7]. Mahling F, Rößler P, Bodner T, Rabl T. BabelMR: A Polyglot Framework for Serverless MapReduce.
[8]. Giménez-Alventosa V, Moltó G, Caballer M. A framework and a performance assessment for serverless MapReduce on AWS Lambda. Future Generation Computer Systems. 2019 Aug 1; 97: 259-74.
[9]. Grolinger K, Hayes M, Higashino WA, L'Heureux A, Allison DS, Capretz MA. Challenges for mapreduce in big data. In2014 IEEE world congress on services 2014 Jun 27 (pp. 182-189). IEEE.
[10]. Kong Ruiping. Statistics and sorting of word frequency based on Hadoop and MapReduce. Computer Programming Skills and Maintenance, 2024, (02): 15-17.
[11]. Hashem IA, Anuar NB, Gani A, Yaqoob I, Xia F, Khan SU. MapReduce: Review and open challenges. Scientometrics. 2016 Oct; 109: 389-422.
[12]. Baidu, Alibaba Cloud. https://www.aliyun.com/, 2024.
Cite this article
Wei,P. (2024). Analysis of Aliyun-based serverless on MapReduce efficiency. Applied and Computational Engineering,88,56-63.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Kudyba S, Kudyba S. Big data, mining, and analytics. Boca Raton: Auerbach Publications; 2014.
[2]. Dean J, Ghemawat S. MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Communications of the ACM. 2008 Jan 1; 51(1): 107-13.
[3]. Ghazi MR, Gangodkar D. Hadoop, MapReduce and HDFS: a developers perspective. Procedia Computer Science. 2015 Jan 1; 48: 45-50.
[4]. Castro P, Ishakian V, Muthusamy V, Slominski A. Serverless programming (function as a service). In2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS) 2017 Jun 5 (pp. 2658-2659). IEEE.
[5]. Giménez-Alventosa V, Moltó G, Caballer M. A framework and a performance assessment for serverless MapReduce on AWS Lambda. Future Generation Computer Systems. 2019 Aug 1; 97: 259-74.
[6]. Das S. Ant Colony Optimization for MapReduce Application to Optimise Task Scheduling in Serverless Platform (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin, National College of Ireland).
[7]. Mahling F, Rößler P, Bodner T, Rabl T. BabelMR: A Polyglot Framework for Serverless MapReduce.
[8]. Giménez-Alventosa V, Moltó G, Caballer M. A framework and a performance assessment for serverless MapReduce on AWS Lambda. Future Generation Computer Systems. 2019 Aug 1; 97: 259-74.
[9]. Grolinger K, Hayes M, Higashino WA, L'Heureux A, Allison DS, Capretz MA. Challenges for mapreduce in big data. In2014 IEEE world congress on services 2014 Jun 27 (pp. 182-189). IEEE.
[10]. Kong Ruiping. Statistics and sorting of word frequency based on Hadoop and MapReduce. Computer Programming Skills and Maintenance, 2024, (02): 15-17.
[11]. Hashem IA, Anuar NB, Gani A, Yaqoob I, Xia F, Khan SU. MapReduce: Review and open challenges. Scientometrics. 2016 Oct; 109: 389-422.
[12]. Baidu, Alibaba Cloud. https://www.aliyun.com/, 2024.









