1. Introduction
Ensuring regulatory compliance is an important principle in the financial industry as it allows financial institutions to operate within the legal framework and maintain the integrity of financial markets, as well as their stakeholders protection. However, with the ever-expanding and constantly changing requirements on the part of regulators, growing in complexity and amount, it has become hugely challenging for financial institutions to keep up with them. When it comes to the processes, regulatory compliance is more and more expensive, complicated, and difficult to implement in the financial institutions. This is why newer technologies are highly sought after by the industry. One of the most prominent technological breakthroughs with a focus on regulatory compliance is the RegTech sector. RegTech imply the measures taken to automate the regulatory processes and improve the compliance procedures, using state-of-the-art technological solutions. It has become apparent that automation and AI-driven software solutions are capable of dealing with an exponential increase in regulatory loads because of their procedural nature. Moreover, by shifting regulatory processes to algorithms based on machine learning and natural language processing, the compliance experts in the financial industry can adapt to changes in regulatory frameworks quickly, leading to reduced costs of compliance, and minimizing human error in administrative work which may result in time-related delays and inefficiencies [1]. This work provides an analysis of modern AI as a part of the RegTech sector and its possible role in regulating the financial industry by automating regulatory reporting, Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, real-time transaction monitoring, as well as predictive analytics, and enforcement investigation for fraud, money laundering and terrorist financing detection. AI's strength lies in its exceptionally fast and precise calculations, allowance to analyze millions of data points, and advanced machine learning that overcomes biases and errors inherited from human agents. Natural language processing (NLP) helps to identify language peculiarities and develop a highly precise linguistic model to control the information discourse and respond to changes in regulations and the international financial sector market. AI in RegTech also involves robotic process automation (RPA), modern software with human-like capabilities such as speech recognition and input. This innovative technology has tremendous potential to ensure the reduction of not only costs of operations and regulatory compliance in the financial industry, but also multiple other risks accompanying business management in general. The deployment of such technology also helps to automate specific processes, including checking, classification, verification and, indeed, regulatory reporting which is one of the critical aspects for any financial company's operations. Importantly, all the empirical data will be supported by case studies on the financial industry practices and cases.
2. Enhancing Compliance Efficiency with AI
2.1. Automating Regulatory Reporting
The use of AI in RegTech helps to reduce the time, errors and cost of regulatory reporting which also helps with meeting deadlines faster and without human errors. Delivering compliance reports in the required format, deadline and content is a challenge for financial institutions. They often face issues with the manual preparation of the compliance reports as these require more time and often human errors. Using AI algorithms, these regulatory reports will be prepared in time due to the fast ability of AI tools in recognizing valuable data from large volumes of data and producing a detailed report in the required format by the regulatory authorities. For instance, transaction records and allocations in financial statements of a firm contain a large amount of data but most of them are simple and do not require human intervention. Instead of humans analyzing this information, machine learning models can be trained to see which transactions contain the key data points and how to classify it, which is done by using algorithms. Once they have been trained, machine learning tools can extract the relevant visual patterns and output it into a report that complies with the regulatory guidelines. Any innovation or changes in the regulatory requirements will automatically need to be inserted in the reports, automating the changes in format and content [2]. Table 1 illustrates how AI significantly reduce the time, errors and the cost spent in preparing and submitting the regulatory reports compared to manual intervention over 4 years, showing the actual benefit of this implementation in the automation in regulatory reporting process using AI.
Table 1. Automating Regulatory Reporting Data
Year | Manual Reporting Time (hours) | AI Reporting Time (hours) | Manual Reporting Errors | AI Reporting Errors | Manual Reporting Cost ($) | AI Reporting Cost ($) |
2021 | 5000 | 3000 | 250 | 50 | 200,000 | 120,000 |
2022 | 4800 | 2500 | 200 | 40 | 190,000 | 100,000 |
2023 | 4600 | 2000 | 180 | 30 | 180,000 | 90,000 |
2024 | 4500 | 1800 | 170 | 25 | 175,000 | 85,000 |
2.2. Streamlining Know Your Customer (KYC) Processes
KYC procedures are essential in safeguarding financial institutions from fraudulent clients and ensuring that operators do not engage with illicit parties. These KYC processes often involve an extensive collection of documentation and verification steps. Every single transaction with no missing KYC data is time-consuming for all parties, especially if it involves cross-border transfers and consequently, costs. For instance, conducting such reviews for companies publicly listed on US stock exchanges can be incredibly expensive, with high license fees, personnel costs and other associated expenses to handle. Current AI technologies can be used to perform KYC processes faster and cheaper than ever before. For example, natural language processing (NLP) and optical character recognition (OCR) make it possible to automate the extraction of relevant customer information from their own documents, as well as verify that information against multi-layer databases to ensure the integrity of the data and final verification. AI can also be used to log and monitor customer behaviours, and identify any suspect activities that would otherwise be undetected. As an example, AI KYC solutions can easily flag any information discrepancies that ensure total compliance and prevent any cases of fraud [3].
2.3. Reducing Operational Costs
The incorporation of AI within RegTech significantly improves the operational efficiency of compliance operations. Typically, these activities have been associated with high costs related to human involvement and investments. With most compliance processes carried out manually, human intervention has been the predominant approach for handling compliance queries. However, the incorporation of AI-powered RegTech into compliance operations allows for seamless automation, thus resulting in significantly reduced operational costs by eliminating the need for substantial human involvement. In this aspect, too, the RegTech revolution is imminent, as compliance queries and complaints can be handled 24 hours a day by an AI system that can operate without human intervention, thus avoiding errors and addressing issues in real time – an attribute that human monitors are unable to replicate. Similarly, AI systems can process more information and transactions simultaneously, and in real time [4]. For example, consider a large private bank that is growing and onboarding new clients every day. With a more traditional manual approach to onboarding new clients, the cost of hiring more staff to cope with the increasing operational demands would also increase proportionately. However, the advantage of RegTech is that it can scale up operations among financial institutions, without increasing costs by the same proportion. The considerable cost savings achieved through the incorporation of AI within RegTech can be illustrated through this formula, which accounts for the direct cost savings, reduced cost of human intervention, and minimised regulatory penalties associated with AI-powered compliance functions:
\( Cost Reduction=({C_{m}}-{C_{ai}})+({H_{m}}-{H_{ai}})+({P_{m}}-{P_{ai}}) \) (1)
Where Cm is the cost of manual compliance processes. Cai is the cost of AI-driven compliance processes. Hm is the human resources cost for manual compliance. Hai is the human resources cost for AI-driven compliance. Pm is the potential fines and penalties from manual compliance errors. Pai is the potential fines and penalties from AI-driven compliance.
3. Automating Compliance Processes
3.1. Intelligent Workflow Automation
AI-powered intelligent workflow automation reimagines compliance by integrating these regulatory requirements into standardised workflows. AI algorithms can translate the required obligations in regulatory guidelines into the logic behind checklists, task assignments, and timelines. A key aspect of intelligent automation is the ability to classify regulatory requirements into distinct categories of compliance requirements. For instance, internal control automation can logically cascade cash limits or tolerances across the operational lifecycle. In a similar vein, either qualitative or quantitative risk criteria can be used to classify transactions. High-risk activities can be automatically flagged for further scrutiny and review while low-risk transactions can be expedited. Ongoing regulatory changes can also be handled dynamically. Intelligent workflow automation responds to these changes, automatically updating processes to maintain compliance, without having to manually reconfigure processes every time.
3.2. Dynamic Policy Management
AI can also manage these policies dynamically by tracking changes in regulatory environment and updating compliance protocols – which are continuously changing and can consist of hundreds of thousands of pages of regulations and amendments. Manually keeping track of all the changes is time-consuming and increases the likelihood of breaching compliance requirements. AI-driven RegTech solutions can monitor changes in regulatory environment from various sources, interpret new regulations and their implications, and automatically update compliance policies and procedures. This dynamic approach can increase the likelihood of compliance and decrease the risk of inadvertent breaches in regulations [6]. Moreover, AI can provide compliance officers with automated alerts and recommendations. Natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning can help to track regulatory changes and narrow down relevant information, enabling AI to quickly flag the effects of changes in regulatory environment on new or existing policies, allowing firms to respond in a timely and effective manner.
3.3. Real-Time Transaction Monitoring
Transaction monitoring is a necessary part of compliance for financial institutions to identify and flag suspicious behaviour. AI-powered RegTech analyses and makes predictions on real-time transactions using complex machine learning models. Insights derived from huge volumes of transaction data can be leveraged to detect patterns and anomalous outcomes that are likely to be criminal related and to combat money laundering and terrorism financing more effectively. AI models on transaction monitoring can easily process large volumes of transactions in real time, as AI is a non-stop processing engine with no need for time delays or waiting for an analysis period to complete. AI transaction monitoring is also designed to continuously learn from the historical data or alerts raised by clients, enabling them to improve the detection rate of criminal activity over time. Figure 1 shows the proportion of suspicious activity detected when using a manual vs AI-powered-system [7].
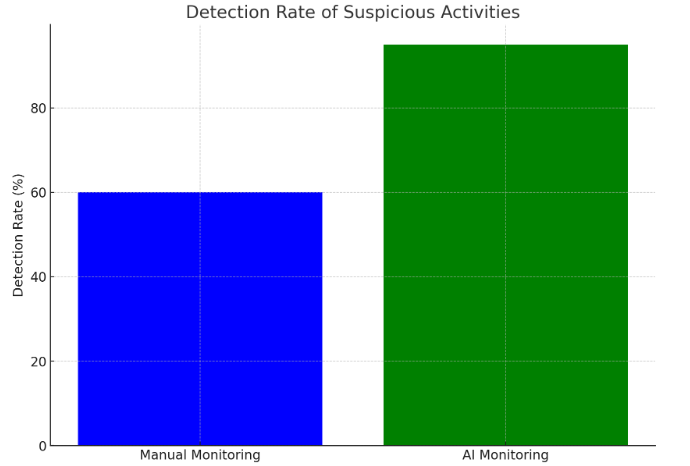 Figure 1. Detection Rate of Suspicious Activities
Figure 1. Detection Rate of Suspicious Activities
4. Monitoring and Analysis of Transaction Data
4.1. Predictive Analytics for Risk Assessment
A critical approach in risk assessment is the identification and prediction of potential compliance problems using predictive analytics capable of processing large amounts of historical transaction data to predict risk. Supervised machine-learning algorithms that identify and classify complex patterns in historical data are employed to spot specific trends and moves that help identify and predict the probability of potential fraud, incredibly useful to preventive interventions. To illustrate, specific machine-learning code can detect different categories of suspicious patterns and, ultimately, identify the probability of committing fraud based on the nature and sequence of transactions observed in the data. This capability is extremely relevant to a bank’s compliance with laws, as it provides insight into which transactions need to be monitored and assigned to relevant business professionals. [8] One of its distinguishing features is that it typically harvests data from multiple sources. Transactional history, customer profiles, demographic data, and external information about market trends and economic indicators can all be used to feed predictive models. By bringing together this diverse range of datasets, predictive models can provide a rich assessment of risk that considers multiple dimensions of the threat. This multi-faceted approach ensures that financial institutions are not relying on a simplified view of risk computed solely from historical data, but are also considering current trends and changes that could impact risk profiles. Predictive analytics can also improve the granularity of risk assessment. AI models can cluster new customers’ and old customers’ spending behaviour into different categories, and these categories can represent different types of fraud or violation of compliance. For example, they can differentiate regular transactional patterns from anomalous irregular ones.
4.2. Anomaly Detection and Fraud Prevention
Anomaly detection is one of the key AI applications for analysing transactional data, and is critical in the detection of fraudulent activity. Through careful analysis of patterns in past transactional data, AI algorithms can identify departures from normal patterns that might indicate fraud. This can be done through the use of both supervised and unsupervised machine learning to build models that, after being trained on pattern examples, can discern normal from anomalous activity. The most common type of supervised learning is training the AI models on historical data which is labelled into normal and fraudulent. This helps the models learn the features associated with each category. For example, an AI system could be trained on typical spending patterns for a customer, such as the nominal amount, transaction frequency and their geographical location. When there is a transaction that deviates significantly from the learned patterns, such as a large purchase in a foreign country, far away from the customer’s last few transactions, that transaction’s probability of being fraudulent increases significantly. Imagine a system can learn the behaviour of transactions from historic data, and compared with future transactions you can tell the difference. Unsupervised learning does not rely on labelled data, thereby allowing the AI models to detect patterns and clusters within the data autonomously. This type of training allows institutions to detect new forms of fraud instead of relying solely on models that have seen the same frauds before. Using unsupervised learning, AI-developed anomaly-detection systems might automatically detect unusual spikes of transactions in a short period, such as a 40 per cent increase in transaction volumes in a couple of hours driven by a coordinated fraud. By clustering anomalies together, unsupervised learning models can point out patterns worthy of investigation for compliance teams. Early detection is the secret sauce to prevent and reduce fraud. Anomalies identified early in the transaction chain right at the very start can prevent massive amounts of fraud. Imagine an anomaly system detects a series of high-value transactions that are much higher than one’s average spending vicinity from the customer. The institution could freeze the account and investigate these transactions. [10].
5. Conclusion
The use of AI in RegTech is a game-changer that will transform the way financial institutions approach compliance. AI-enabled RegTech offer significant advantages – they will enable firms to improve the efficiency, automate the processes and strengthen the monitoring and analysis of data associated with compliance activities. Evidence from the industry, with empirical data and case studies, also suggest that AI-enabled RegTech generate repeated financial benefits in the form of improved accuracy, cost reduction and risk management. Nonetheless, there are some concerns that need to be addressed for the ecnhanced use of AI in finance, specifically for its application in RegTech development. There are issues regarding the availability of trusted data to work with, as well as the challenges of data security and system integration of AI into operational processes. Looking ahead, while it will continue to evolve alongside other FinTech, the role of AI in RegTech will be instrumental in shaping the future of financial compliance. The introduction of AI-based RegTech will undoubtedly be a game changer to transform the way financial institutions approach compliance – improving its efficiency and cost as well as improving the risk management capability.
References
[1]. Black, Geoffrey, et al. "Prospects for nuclear microreactors: a review of the technology, economics, and regulatory considerations." Nuclear Technology 209.sup1 (2023): S1-S20.
[2]. Padmanaban, Harish. "Revolutionizing regulatory reporting through AI/ML: Approaches for enhanced compliance and efficiency." Journal of Artificial Intelligence General science (JAIGS) ISSN: 3006-4023 2.1 (2024): 71-90.
[3]. Costinot, Arnaud, and Iván Werning. "Robots, trade, and luddism: A sufficient statistic approach to optimal technology regulation." The Review of Economic Studies 90.5 (2023): 2261-2291.
[4]. Bradford, Anu. Digital empires: The global battle to regulate technology. Oxford University Press, 2023.
[5]. Ezeigweneme, Chinedu Alex, et al. "Review of telecommunication regulation and policy: comparative analysis USA and Africa." Computer Science & IT Research Journal 5.1 (2024): 81-99.
[6]. Teichmann, Fabian, Sonia Boticiu, and Bruno S. Sergi. "RegTech–Potential benefits and challenges for businesses." Technology in Society 72 (2023): 102150.
[7]. Bolton, Mitzi, and Michael Mintrom. "RegTech and creating public value: opportunities and challenges." Policy Design and Practice 6.3 (2023): 266-282.
[8]. Kurum, Esman. "RegTech solutions and AML compliance: what future for financial crime?." Journal of Financial Crime 30.3 (2023): 776-794.
[9]. Uzougbo, Ngozi Samuel, Chinonso Gladys Ikegwu, and Adefolake Olachi Adewusi. "Cybersecurity compliance in financial institutions: a comparative analysis of global standards and regulations." International Journal of Science and Research Archive 12.1 (2024): 533-548.
[10]. Olawale, Olufunke, et al. "RegTech innovations streamlining compliance, reducing costs in the financial sector." GSC Advanced Research and Reviews 19.1 (2024): 114-131.
Cite this article
Liang,P. (2024). Leveraging artificial intelligence in Regulatory Technology (RegTech) for financial compliance. Applied and Computational Engineering,93,166-171.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Black, Geoffrey, et al. "Prospects for nuclear microreactors: a review of the technology, economics, and regulatory considerations." Nuclear Technology 209.sup1 (2023): S1-S20.
[2]. Padmanaban, Harish. "Revolutionizing regulatory reporting through AI/ML: Approaches for enhanced compliance and efficiency." Journal of Artificial Intelligence General science (JAIGS) ISSN: 3006-4023 2.1 (2024): 71-90.
[3]. Costinot, Arnaud, and Iván Werning. "Robots, trade, and luddism: A sufficient statistic approach to optimal technology regulation." The Review of Economic Studies 90.5 (2023): 2261-2291.
[4]. Bradford, Anu. Digital empires: The global battle to regulate technology. Oxford University Press, 2023.
[5]. Ezeigweneme, Chinedu Alex, et al. "Review of telecommunication regulation and policy: comparative analysis USA and Africa." Computer Science & IT Research Journal 5.1 (2024): 81-99.
[6]. Teichmann, Fabian, Sonia Boticiu, and Bruno S. Sergi. "RegTech–Potential benefits and challenges for businesses." Technology in Society 72 (2023): 102150.
[7]. Bolton, Mitzi, and Michael Mintrom. "RegTech and creating public value: opportunities and challenges." Policy Design and Practice 6.3 (2023): 266-282.
[8]. Kurum, Esman. "RegTech solutions and AML compliance: what future for financial crime?." Journal of Financial Crime 30.3 (2023): 776-794.
[9]. Uzougbo, Ngozi Samuel, Chinonso Gladys Ikegwu, and Adefolake Olachi Adewusi. "Cybersecurity compliance in financial institutions: a comparative analysis of global standards and regulations." International Journal of Science and Research Archive 12.1 (2024): 533-548.
[10]. Olawale, Olufunke, et al. "RegTech innovations streamlining compliance, reducing costs in the financial sector." GSC Advanced Research and Reviews 19.1 (2024): 114-131.









