1. Introduction
In modern times, the popularity of the Internet of Things has brought many conveniences to people's lives. The Internet of Things and its applications are very dependent on real-time data processing and transmission. This data processing and transmission method usually adopts the cloud computing model. However, people are now increasingly pursuing low latency, so that this traditional cloud computing model can no longer meet people's requirements. This requires finding a new method to replace the traditional cloud computing model. Edge computing, as one of the alternative methods, can just make up for the shortcomings of cloud computing.
Edge computing technology differs from cloud computing in the way it processes data, which is in the devices that process data. Cloud computing usually uploads all data to the cloud and then processes them one by one. However, if the data to be processed is complex and the processing end is unique, it is easy to cause network congestion. The method used by edge computing is sends data to the nearest edge node for processing in a decentralized manner. This method could avoid the delay which is caused by long-distance transmission of large amounts of data. And in the other hand, it is also reducing bandwidth usage and thus network congestion [1][2]. With these advantages, edge computing has been widely used. Especially in scenarios that require strict real-time response, such as smart cities and intelligent transportation systems (ITS). In addition, data processing at edge nodes could reduce energy consumption [3]. This advantage is particularly evident in wireless sensor networks, because their unique distributed nature amplifies these effects. In addition, the power source of the devices in wireless sensors is batteries. Battery life is determined by the energy consumption of the device [4]. In addition, edge computing can also protect user privacy and security. Since data is mainly processed on the local edge device, data leakage can be avoided when it is transmitted to the remote server. Therefore, edge computing is also common in industrial IoT and smart grids where the risk of data leakage is high [2]. However, edge computing is not perfect. This imperfect characteristic is largely due to its limited computing power. Therefore, some studies have combined machine learning models such as TinyML with edge computing to improve its computing power. This trained model can make intelligent decisions locally without continuous communication with cloud resources.
This article will introduce an embedded smart sensor network architecture based on edge computing. The architecture is mainly discussed from three aspects. The first is the real-time processing part of edge computing. This part will analyze how edge computing processes data in real time through edge nodes. The second part will focus on how the architecture efficiently allocates tasks. The last part is some new attempts in the field of edge computing. This architecture provides an effective way to address common challenges in IoT applications, including reducing latency, improving energy efficiency and protecting privacy.
2. Embedded smart sensor network architecture
2.1. The commonality of edge computing in different applications
As IoT technology is widely used, people are increasingly pursuing more efficient real-time data processing and transmission. The problem that needs to be solved for more efficient real-time data processing and transmission is the delay in data processing. The data processing method of cloud computing is to integrate data into the cloud for processing. This method is easily affected by network congestion. As an alternative to cloud computing, one of the advantages of edge computing is that it can effectively alleviate the impact of delays on real-time data processing. It advocates transferring complex computing tasks from the cloud to local devices. This enables the system to respond faster. For industrial environments that have high requirements for real-time processing, edge computing can provide a good processing environment. It can help avoid the time loss when data needs to be connected to the cloud for processing. This helps improve the responsiveness of the system. In addition, edge technology greatly alleviates the pressure on network bandwidth by processing data locally, thereby reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over long distances.
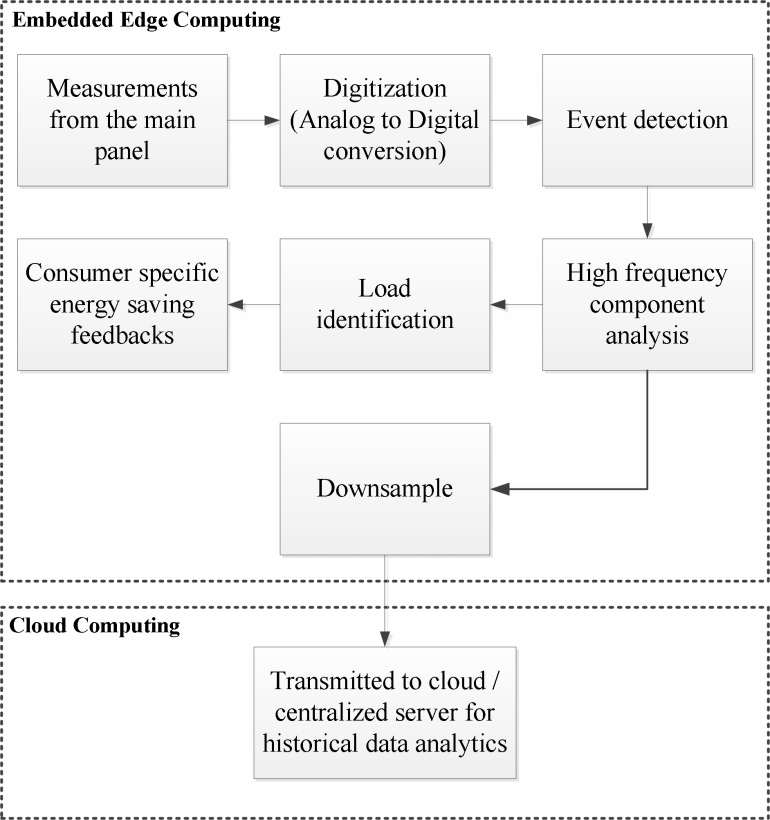
Edge technology emerges as a highly reliable solution for wireless sensor networks with stringent latency requirements, offering a paradigm shift in data processing approaches. In a working system, the system's devices and sensors usually need to process a large amount of complex data. If these data are uploaded to the cloud for processing through long-distance transmission, they will be affected by network congestion. These effects are often reflected as delays in data processing. This will not meet the needs of wireless sensor networks for real-time data processing. Edge technology does not need to transmit data over long distances. It only needs to use local devices for processing. Therefore, it does not rely too much on network transmission, but only needs to perform computing tasks on edge nodes. This can effectively alleviate the delay of data transmission. For example, in a smart grid system, the system needs to monitor power load data in real time. When the data fluctuates abnormally, it needs to be processed immediately. The traditional cloud computing model is easily affected by network delays, resulting in low efficiency of real-time processing [5]. However, by applying edge computing technology to smart meters, data can be processed locally. This can effectively avoid network congestion. Figure 1 shows the structure of a smart meter that uses embedded edge computing to process data in real time. In this picture, it can be clearly see the relationship between data collection, local processing and central grid communication.
Figure 1: Smart Meter Data Analysis System [5]
In addition to real-time processing, low energy consumption is also a major advantage of edge computing. Most sensor nodes and some IoT devices rely on batteries for power supply. Batteries also face the problem of battery loss. Traditional cloud data processing methods transmit data to remote servers for processing. This approach not only devours bandwidth but also drains the energy reserves of sensor devices, presenting a dual challenge in resource management. Edge computing processes this data through local devices. Local processing can reduce energy consumption by reducing the frequency of transmission [6]. Especially in wireless sensor networks, system operation will be directly affected by battery life. If the system's working efficiency can be improved and battery loss can be reduced, the sensor's working time can be extended. This can also effectively reduce the maintenance cost of the entire system.
In terms of protecting user data privacy and security issues, edge technology is also widely used. With the development of network communications, the number of IoT devices is increasing day by day. What follows is a huge amount of data transmission. In most common network architectures, data transmission is always carried out through shared channels. In public channels, data security is difficult to guarantee. Edge computing allows data processing on local devices. This can effectively avoid the risk of data leakage. In industrial environments, edge computing can be used to monitor multiple sensor data. And detect abnormal behavior on local edge devices without uploading all data to remote servers [7]. When data is processed by local devices, it is more difficult for attackers to obtain data. Especially in industrial Internet of Things and some smart manufacturing systems, the consequences of information leakage are often fatal. These core data maintain the rise and fall of the entire enterprise. This information is directly related to the core competitiveness of the enterprise [8].
2.2. The same implementation method of edge computing
Distributed computing architecture is a cornerstone of edge computing, characterized by its approach of offloading data processing from central servers to edge devices situated near data sources. This can reduce the burden on the cloud server and improve the efficiency of the system. In smart meter systems, for instance, devices leveraging edge computing technology can process data locally, thereby significantly reducing reliance on remote servers and enhancing system autonomy. In large-scale IoT applications, the distributed architecture enables each edge node to process data independently, rather than waiting for a response from a central server. In intelligent transportation systems, the distributed architecture can help each traffic monitoring camera independently process local data to analyze road traffic conditions [9][10]. Based on the conditions of these roads, the local camera will feed back the situation to the central system. This can effectively reduce the amount of data transmission. Similarly, in smart cities, each edge node (street lights, monitoring) has the ability to process local data on its own. The multi-MCU architecture is detailed in Figure 2. It shows the flow of sensor data, embedded databases, and communication modules in a distributed system.
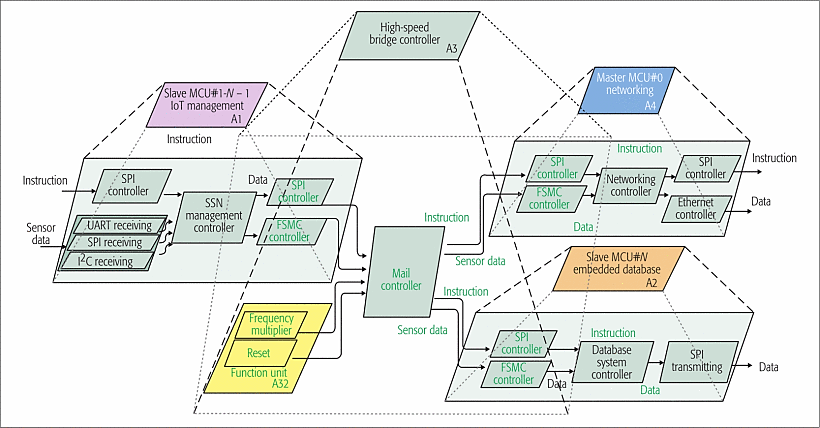
Figure 2: IoT Gateway Architecture for Edge Computing [6]
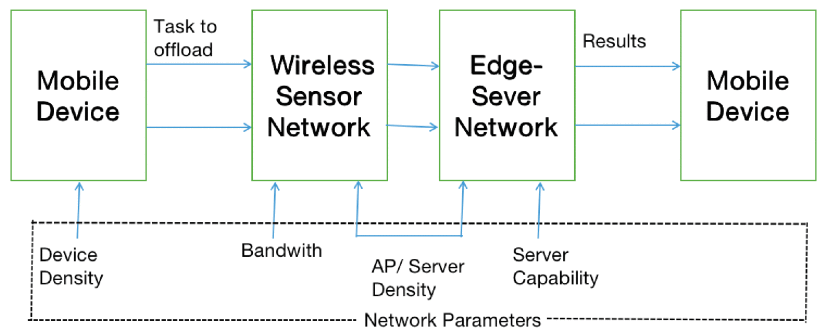
While distributed architecture forms the backbone of edge computing, task offloading emerges as another crucial component in this paradigm. Numerous studies have delved into the optimization of resource allocation through intelligent task offloading across various application scenarios [11][12]. In wireless sensor networks, the computing power of sensor nodes is limited. Task offloading can intelligently allocate these processing tasks to edge devices with stronger processing power for processing. This intelligent allocation not only minimizes energy consumption by alleviating the processing burden on sensor nodes, but also significantly extends their operational lifespan, effectively killing two birds with one stone [11][12]. In some underwater sensor networks, the authors proposed using autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) as mobile edge nodes to collect and process data [12]. The propagation distance of wireless signals in water is very limited and the bandwidth is low. The mobile processing capabilities of AUVs can help mobile edge nodes cover a wide range of underwater areas. AUVs can not only move to the vicinity of sensors to obtain important data such as ocean temperature and salinity, but also pre-process the data in real time and send it to receivers on the sea surface through short-distance transmission. This avoids the cost of establishing local edge devices in various places underwater. Such mobile edge computing is more flexible than traditional static computing nodes. In addition, AUVs can perform path planning and task allocation based on real-time conditions. This can improve the efficiency of data collection. Figure 3 shows the multi-access edge computing (MEC) network model. This figure clearly shows that the tasks of mobile devices are offloaded to the wireless sensor network and edge server network for processing.
Figure 3: MEC network model [13]
At the forefront of technology integration, researchers have made some attempts to explore the combination of edge computing and machine learning. Due to the limitations of edge device computing power and memory, edge nodes have difficulty processing large-scale machine learning models. This innovative combination method is to embed lightweight machine learning models directly into edge nodes. For example, some researchers have developed lightweight machine learning models (TinyML) [14]. This can provide real-time data analysis and processing capabilities for local devices. These developed lightweight models are the result of applying complex compression techniques to traditional models. Through methods such as pruning (removing less important connections), quantization (reducing the precision of calculations) and other advanced technologies, researchers have managed to create compact yet powerful models suitable for edge devices. The lightweight machine learning models embedded on edge nodes are used for reasoning tasks (making decisions and predictions on collected real-time data). For example, smart cameras can use machine learning models on edge nodes to process images. This video data does not need to be uploaded to the cloud. In addition, the edge device will synchronize the latest optimized model with the cloud when connected to the Internet [6]. This makes full use of the data resources of each edge node.
2.3. Different implementation methods of edge computing
Building upon the foundation of edge computing and machine learning integration, researchers have developed an even more sophisticated approach: edge collaborative learning. This advanced method leverages federated learning principles, enabling edge devices to share model parameters without directly exchanging sensitive data. In this innovative paradigm, each edge node independently trains its model using local data, after which the resulting model parameters are securely uploaded to a central server for aggregation and refinement. The central server will organize these parameters and update the existing model. The updated model will be transmitted to each edge node. This method can protect the data to a great extent and can effectively combine the data of each node to optimize the system [15]. The introduction of this technology helps to improve the flexibility of the network, especially in complex industrial networks.
Recent studies have explored innovative network architectures to address the challenges of real-time data processing. One such approach involves the collaboration of multiple microcontroller units, working in tandem to handle large volumes of data efficiently [10]. This architecture is often used in industrial automation. Another article proposed an architecture that combines fog computing with edge computing [9]. It can effectively solve the resource problem in large-scale IoT systems. This architecture achieves dynamic load management in large-scale IoT applications through distributed computing nodes. This innovative architecture achieves efficient resource allocation between edge nodes and the cloud, facilitating dynamic load management in complex systems such as smart cities and intelligent transportation networks, all through strategically distributed computing nodes. This architecture can reduce dependence on cloud computing.
3. Conclusion
This article introduces the use of edge devices in IoT environment, distributed network architecture and the independently trained machine learning model introduced. This architecture effectively addresses both latency issues in IoT environments and reduces potential data security risks. In the distributed computing architecture, one of the main reasons for network congestion is that complex computing tasks require more processing time. Task offloading addresses this challenge by redistributing complex computations to nearby edge devices with superior processing capabilities.
However, this method of allocating tasks according to task complexity without state detection also has some disadvantages. When allocating tasks, factors such as network bandwidth and processing status also need to be considered. To further improve the function of the architecture, an adaptive system that can dynamically detect the network transmission status and make real-time adjustments to task allocation based on this status is necessary. Such an adaptive system can prevent the overloading of any single edge device with complex tasks. In addition, quantum computing-assisted TinyML models can also reduce the power consumption of complex device operations. This adaptive hybrid architecture will make the edge network smarter and more efficient. However, while current technological limitations pose challenges in manufacturing lightweight quantum computing chips for embedded and edge devices, ongoing research and development show promising potential for future breakthroughs.
References
[1]. Cao, K., Liu, Y., Meng, G., & Sun, Q. (2020). An overview on edge computing research. IEEE Access, 8, 85714-85728. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991734
[2]. Zhang, Z. (2023). The analysis of distributed computing systems with machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Networking, Informatics and Computing (pp. 67-70).
[3]. Arthurs, P., Gillam, L., Krause, P., Wang, N., Halder, K., & Mouzakitis, A. (2022). A taxonomy and survey of edge cloud computing for intelligent transportation systems and connected vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 23(7), 6206-6221. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3084396
[4]. Alalawi, A., & Al-Omary, A. (2020). A survey on cloud-based distributed computing system frameworks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (pp. 1-6).
[5]. Sirojan, T., Lu, S., Phung, B. T., & Ambikairajah, E. (2019). Embedded edge computing for real-time smart meter data analytics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (pp. 1-5).
[6]. Chen, C. H., Lin, M. Y., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Edge computing gateway of the industrial internet of things using multiple collaborative microcontrollers. IEEE Network, 32(1), 24-29. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1700146
[7]. Islam, A., Debnath, A., & Ghose, M. (2021). A survey on task offloading in multi-access edge computing. Journal of Systems Architecture, 118, 102225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2021.102225
[8]. Anantha, A. P., Daely, P. T., Lee, J. M., & Kim, D. S. (2020). Edge computing-based anomaly detection for multi-source monitoring in industrial wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (pp. 1890-1892).
[9]. Omoniwa, B., Hussain, R., Javed, M. A., Bouk, S. H., & Malik, S. A. (2019). Fog/edge computing-based IoT (FECIoT): Architecture, applications, and research issues. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(3), 4118-4135. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875544
[10]. Chen, C. H., Lin, M. Y., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Edge computing gateway of the industrial internet of things using multiple collaborative microcontrollers. IEEE Network, 32(1), 24-32. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1700146
[11]. Hou, X., Hu, Y., & Wang, F. (2023). Overview of task offloading of wireless sensor network in edge computing environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (pp. 1018-1022).
[12]. Cai, S., Zhu, Y., Wang, T., Xu, G., Liu, A., & Liu, X. (2019). Data collection in underwater sensor networks based on mobile edge computing. IEEE Access, 7, 65357-65367. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918213
[13]. Chen, Y., Liu, J., & Siano, P. (2021). SGedge: Stochastic geometry-based model for multi-access edge computing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 9, 111238-111248. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3103003
[14]. Oliveira, F., Costa, D. G., Assis, F., & Silva, I. (2024). Internet of intelligent things: A convergence of embedded systems, edge computing, and machine learning. Internet of Things, 26, 101153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2024.101153
[15]. Wang, A., Zha, Z., Guo, Y., & Chen, S. (2019). Software-defined networking enhanced edge computing: A network-centric survey. Proceedings of the IEEE, 107(8), 1500-1519. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2019.2924377
Cite this article
Li,X. (2025). Embedded Smart Sensor Network Architecture Based on Edge Computing. Applied and Computational Engineering,127,134-140.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Cao, K., Liu, Y., Meng, G., & Sun, Q. (2020). An overview on edge computing research. IEEE Access, 8, 85714-85728. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991734
[2]. Zhang, Z. (2023). The analysis of distributed computing systems with machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Networking, Informatics and Computing (pp. 67-70).
[3]. Arthurs, P., Gillam, L., Krause, P., Wang, N., Halder, K., & Mouzakitis, A. (2022). A taxonomy and survey of edge cloud computing for intelligent transportation systems and connected vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 23(7), 6206-6221. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3084396
[4]. Alalawi, A., & Al-Omary, A. (2020). A survey on cloud-based distributed computing system frameworks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (pp. 1-6).
[5]. Sirojan, T., Lu, S., Phung, B. T., & Ambikairajah, E. (2019). Embedded edge computing for real-time smart meter data analytics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (pp. 1-5).
[6]. Chen, C. H., Lin, M. Y., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Edge computing gateway of the industrial internet of things using multiple collaborative microcontrollers. IEEE Network, 32(1), 24-29. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1700146
[7]. Islam, A., Debnath, A., & Ghose, M. (2021). A survey on task offloading in multi-access edge computing. Journal of Systems Architecture, 118, 102225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2021.102225
[8]. Anantha, A. P., Daely, P. T., Lee, J. M., & Kim, D. S. (2020). Edge computing-based anomaly detection for multi-source monitoring in industrial wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (pp. 1890-1892).
[9]. Omoniwa, B., Hussain, R., Javed, M. A., Bouk, S. H., & Malik, S. A. (2019). Fog/edge computing-based IoT (FECIoT): Architecture, applications, and research issues. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(3), 4118-4135. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875544
[10]. Chen, C. H., Lin, M. Y., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Edge computing gateway of the industrial internet of things using multiple collaborative microcontrollers. IEEE Network, 32(1), 24-32. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1700146
[11]. Hou, X., Hu, Y., & Wang, F. (2023). Overview of task offloading of wireless sensor network in edge computing environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (pp. 1018-1022).
[12]. Cai, S., Zhu, Y., Wang, T., Xu, G., Liu, A., & Liu, X. (2019). Data collection in underwater sensor networks based on mobile edge computing. IEEE Access, 7, 65357-65367. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918213
[13]. Chen, Y., Liu, J., & Siano, P. (2021). SGedge: Stochastic geometry-based model for multi-access edge computing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 9, 111238-111248. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3103003
[14]. Oliveira, F., Costa, D. G., Assis, F., & Silva, I. (2024). Internet of intelligent things: A convergence of embedded systems, edge computing, and machine learning. Internet of Things, 26, 101153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2024.101153
[15]. Wang, A., Zha, Z., Guo, Y., & Chen, S. (2019). Software-defined networking enhanced edge computing: A network-centric survey. Proceedings of the IEEE, 107(8), 1500-1519. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2019.2924377