1. Introduction
Since the end of 2019, the virus has gradually spread and eventually spread around the world. The COVID-19 epidemic has caused a great impact on People's Daily life and the world's economic development [1]. The impact on China is as follows: decreased output, decreased consumption, decreased investment, restricted foreign trade, great losses in industrial development, increased risks of financial institutions, and fierce fluctuations in the capital market in the short term [2]. In this context, rapid control of the spread of COVID-19 is very important [3]. However, the detection and identification of COVID-19 is usually carried out by nucleic acid detection, which requires a long period of time, preventing people from cutting off the source of the spread of COVID-19 in the first time. Current computer vision technology has made breakthrough progress in the recognition of medical films, such as the segmentation and recognition of cancer cell microscopic images, the recognition of red blood cells based on multi-feature fusion, and the automatic recognition of breast cancer cells by computer [4],etc. This project tries to use artificial intelligence method to identify the CT photos of the lungs of COVID-19 patients, to assist rapid screening of COVID-19 patients. Therefore, the main focus of this research is on using artificial intelligence based on deep learning of model transfer to identify whether patients are infected with novel coronavirus through the lung images of patients [5].
For the recognition of CT photos, many works have put forward their own methods, especially in the medical field. For example, the uCT760 64-slice spiral CT is used for chest scanning, and the original data is imported into the uAI COVID-19 intelligent auxiliary analysis system for AI calculation after the scanning is completed. To observe the CT signs of COVID-19 patients, including lesion distribution and image characteristics, and compare the lesion volumes of the left and right lungs. SPSS 19.0 software was used for data analysis [6], CT was used for automatic identification and classification of upper emphysema [7], or convolutional neural network deep learning was used to help brain CT image classification to achieve intelligent image classification and provide convenience for clinical screening of Alzheimer's disease [8].
Different from the traditional methods mentioned above, the difficulty of this task is that the number of lung images of COVID-19 patients is very limited due to the privacy protection of COVID-19 patients by governments of various countries [9], which brings great difficulties to the training of traditional neural networks. Traditional computer vision deep learning to extract image features requires a large number of sample data for model training. If the number of images in the data set is too small, the model will be overfitted, which cannot achieve a relatively accurate effect of COVID-19 recognition [10].
In order to solve the above problems, this paper studies the novel coronavirus identification of patients' lung CT photos based on the deep learning method of model transfer. We established a model based on similar types of problems -- deep learning to identify pneumonia patients [11] [12], and stored the established model[13] (when training this model, the sample pictures of the training set are sufficient, so a relatively stable model can be obtained), and then made fine adjustments on this basis. Eventually, a model was trained to recognize images of the lungs of COVID-19 patients.
We tested the method in a publicly available COVID-19 data set, and the test results show that the recognition accuracy of the method is about 70%.
2. Methodology
In the existing dataset, we have two types of images available, the first of which is the X-ray image of the lung, which is used to identify whether the image is the lung image of a patient with viral pneumonia. The images were classified into training set, test set and validation set according to the quantity proportion. The test set contained a total of 624 images, 234 of which were non-pneumonia images and 390 of which were pneumonia patient images. There were 5232 images in the training set, including 1349 images of normal lungs and 3883 images of pneumonia patients. There are 23 images in the validation set, including 8 images of normal lungs and 15 images of pneumonia patients. The second category is the CT images of the lungs, which are used to identify whether the patients are infected with novel coronavirus. (It should be noted that these images are divided into those of COVID-19 patients and those of non-COVID-19 patients, in which the images of non-COVID-19 patients include the lung images of patients with possible common pneumonia and those of normal people.) They were proportioned into training set, test set and validation set. There were 200 images in the test set, 100 images in the lungs of COVID-19 patients and 100 images in non-COVID-19 patients. There are 400 images in the training set, including 200 lung images of COVID-19 patients and 200 lung images of non-COVID-19 patients. A total of 98 images were included in the validation set, including 200 lung images of COVID-19 patients and 200 lung images of non-COVID-19 patients. Up to this point, all the data needed to build the model have been classified locally on the computer.
The next step is to train a model that can identify patients with pneumonia from this first type of data. It is important to note that the sizes of all the images are not equal, and we need to process them again after reading them into the program:
from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical
from keras import layers
from keras import models
import matplotlib.image as processimage
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
First import the packages you need from Keras into your program, then set a uniform value for the image size:
IMG_SIZE_WIDTH = 128
IMG_SIZE_HEIGHT = 128
Similarly, considering that the file types of each image are different, it is necessary to establish a file extension that includes all possible file names to facilitate the program to identify all data in the data set later:In the available data sets, there are four image types with the extensions JPG, PNG, BMP, and JPEG
The following process is to read the picture data in the folder. The process of reading the training set data here is the same as that of reading the test set data in general format and content, only the path of reading the file needs to be modified:we set up two empty lists storing images and image labels in turn (img_list = []lab_list = []) then read the required contents from the local data set, and then resize all of these images to the size we set. Note that when we append them to the tag list, in order to distinguish the labels of pneumonia and non-pneumonia images, The label of non-pneumonia image is 0, and the label of pneumonia image is 1
After reading the data, the steps to be carried out are the preprocessing of all the data. Firstly, the pictures that have been unified into the same size should be flattened and converted into language forms that can be recognized by the computer. In this case, they are converted into a three-dimensional shape:
x_train = x_train.reshape((-1, IMG_SIZE_WIDTH, IMG_SIZE_HEIGHT, 1))
x_test = x_test.reshape((-1, IMG_SIZE_WIDTH, IMG_SIZE_HEIGHT, 1))
In order to facilitate the analysis of the final calculation accuracy and loss rate of the program, normalization can be added to scale the feature attributes of the data to a unified dimension:
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255
According to the purpose of programming, there are two types of images to be finally identified this time -- lung images of patients with pneumonia and lung images of patients without pneumonia. Therefore, labels for reading data need to be divided into two categories:
y_train = to_categorical(y_train, num_classes=2)
y_test = to_categorical(y_test, num_classes=2)
Next, we start to build the model of the entire neural network. In this program, we use the sequential model in Keras, which has single input and single output, and only neighboring relationships between layers, without cross-layer connections. This model is fast to compile and easy to operate, so it is suitable for simple classification tasks. For the construction of this model, most layers use alternating stacking of convolution layer and pooling layer, and finally Dense layer is used as the output layer:It should be noted that since we use Dense layer as the output layer, it will be more effective to use 'sigmoid' as the activation function here.
After each layer of the model is set, the compilation mode of the model needs to be defined. In this model, Rmsprop is chosen as our optimizer, which usually has good results in the training of recurrent neural network (RNN). The loss function uses the binary cross-entropy function, and the metrics of the model uses accuracy, which we need:
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['acc'])
Finally, we set batch_size for each gradient update as 32, and epoch for iteration of the training model as 10. By now, the establishment and compilation of the whole model are basically finished. Since this model will be used in the future, we use the model.save function to save it for subsequent reading:
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=32)
So far identified COVID - 19 basic training needed to use the model has finished, the next step work began to model migration to handle COVID - 19 patients with pulmonary image recognition, for data preprocessing COVID - 19 data set, the way we use the same as the above basic, here is not much, agree to handle the same or pictures into 128 * 128 size, Then the data is flattened into the format of (-1,128,128,1). It should be noted that since this program needs to read the previously trained model, model.load function is needed to read the model saved above before compilation (see bold font) :
model = keras.models.load_model("pneu_model.h5")
3. Experiment
The following part will specifically describe the experimental process after compiling the program and analyze the experimental results.
Following on from what was described in the previous section, we have compiled two complete programs. For ease of understanding, we have named the program recognizing lung images of Pneumonia patients "Pneumonia" and the program recognizing images of COVID-19 patients "COVID". The following part will specifically describe the experimental process after compiling the program and analyze the experimental results.
Following on from what was described in the previous section, we have compiled two complete programs. For ease of understanding, we have named the program recognizing lung images of Pneumonia patients "Pneumonia" and the program recognizing images of COVID-19 patients "COVID". The program runs on a ThinkPad X1 Carbon laptop without GPU. The CPU model is Intel(R) Core(TM) I7-6500U CPU @ 2.50ghz 2.59ghz, and the RAM is 8GB.
The virtual environment configured when compiling the Python language is as follows:
• |
Figure 1. The virtual environment. |
Epoch was set to 10 in the Pneumonia program with ten training batches:
Epoch 1/10: loss: 0.3941 - acc: 0.8385
A total of 164 images were processed in the first training batch, and the total time was 155s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.3941, and the recognition accuracy was about 83.85%.
Epoch 2/10: loss: 0.1694 - acc: 0.9421
In the second training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 150s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.1694, and the recognition accuracy was about 94.21%.
Epoch 3/10: loss: 0.1101 - acc: 0.9622
In the third training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 147s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.1101, and the recognition accuracy was about 96.22%.
Epoch 4/10: loss: 0.0917 - acc: 0.9677
In the fourth training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 149s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0917, and the recognition accuracy was about 96.77%.
Epoch 5/10: loss: 0.0788 - acc: 0.9727
In the fifth training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 115s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0788, and the recognition accuracy was about 97.27%.
Epoch 6/10: loss: 0.0606 - acc: 0.9792
In the sixth training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 144s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0606, and the recognition accuracy was about 97.92%.
Epoch 7/10: loss: 0.0498 - acc: 0.9822
In the seventh training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 131s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0498, and the recognition accuracy was about 98.22%.
Epoch 8/10: loss: 0.0473 - acc: 0.9830
In the eighth training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 111s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0473, and the recognition accuracy was about 98.3%.
Epoch 9/10: loss: 0.0414 - acc: 0.9859
In the ninth training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 134s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0414, and the recognition accuracy was about 98.59%.
Epoch 10/10: loss: 0.0423 - acc: 0.9859
| |
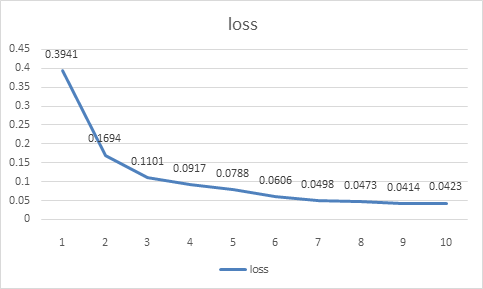
Figure 2. Curver of loss when training model. | |
In the tenth training batch, a total of 164 images were processed, and the total time was 145s. The error calculated by the loss function was about 0.0423, and the recognition accuracy was about 98.59%。
| |
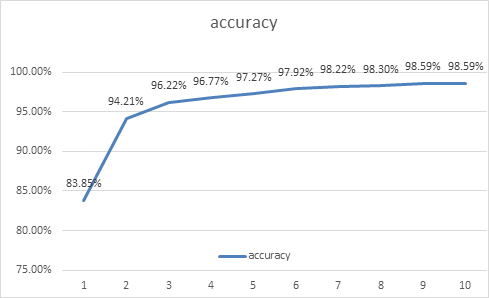
Figure 3. Curve of accuracy when training model. | |
In order to facilitate finding the changing trend of the above data, we specially draw the broken line statistical charts of two variables, Loss and accuracy, for analysis. It can be seen that the accuracy of model identification in the first epoch is significantly lower than that in subsequent epochs, and the loss value is as high as 39.41%. The ability to recognize images is crude. With the increase of training batches.it can be seen that the change trend of loss value is decreasing continuously until the ninth epoch of training reaches the lowest value. The accuracy of recognition image is also gradually increasing, and finally can be stable at 98.59%.
It can be seen that the performance of the neural network model trained in "pneumonia" program is reliable and can correctly identify the lung images of most pneumonia patients. Next, we can use the same method to analyze the image recognition of COVID-19 patients in the "Covid" program.Here, we omit the lengthy data presentation of each epoch, and directly draw the obtained result data into the same broken line statistical graph to analyze the specific data change trend:
| ||||
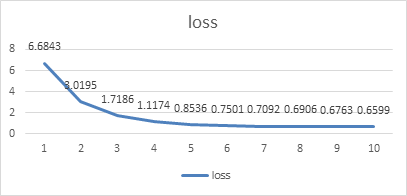
Figure 4. Curver of loss value when training model 2. | ||||
| ||||
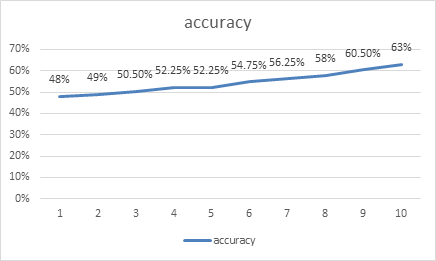
Figure 5. Curve of accuracy when training model 2. | ||||
From the data in the figure above, we clearly found that the loss of recognition of lung images of COVID-19 patients by the model in this program was significantly higher than the loss of recognition of lung images of pneumonia patients in the "pneumonia" program. The same model had a peak recognition accuracy of 63%, about a 30% difference compared to the previous program. The reasons for this phenomenon have been mentioned above. One of the important reasons is that the sample data are too small to achieve the best results during training, which is also one of the reasons for using model migration to train this program. If the model trained by "Pneumonia" program was not used as the basis, the correct rate might have been lower. As a result, the efficiency of the procedure cannot meet the requirements of identifying COVID-19 patients. There is a potential problem is that, in recognition of pneumonia patients with lung images when images are used in the X-ray image, and at the time of 19 patients with pulmonary image recognition COVID - read images are lung CT images, two types of special clinic image itself has certain difference, can lead to positive optimization model after the migration effect is not obvious.
4. Conclusion
This paper describes the procedure of deep learning based on model transfer for COVID-19 recognition. Its innovation lies in the pretrained model as the basis to help build the recognition model of COVID-19 images, which solves the potential problem of overfitting caused by insufficient samples of COVID-19 lung images. Finally, after training, the recognition rate of the program can reach about 70 percent, there is a certain recognition efficiency, to achieve the goal of this topic.
References
[1]. Dolbneva D V . The Impact of COVID-19 on the World's Economies[J]. THE PROBLEMS OF ECONOMY, 2020, 1(43):20-26.
[2]. Chengying, Wen Yuechun, Chang Yali, et al. Analysis on the impact of novel coronavirus pneumonia epidemic on Chinese economy [J]. Journal of Quantitative and Technical Economics, 2020, 37(5):20.
[3]. Jiang Rong, Xie Huarong, Duan Yongsheng. Prevention and control strategies of nosocomial infection in COVID-19 medical institutions [J]. Chinese Contemporary Medicine, 2020, 27(30):3.
[4]. Hu Xiaobo, Zhang Peng, An Ji, et al. Research on automatic medical image recognition technology based on computer vision [J]. Microcomputer Information, 2012(10):2.
[5]. Shi Xiangbin, Fang Xuejian, Zhang Deyuan, et al. Image classification based on Deep Learning Hybrid model transfer learning [J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2016, 28(1):8.
[6]. Zhang Zhenhua, Jixiang, Zhang Jinsong, et al. Analysis of CT image characteristics of COVID-19 based on AI technology [J]. Medical Equipment, 2020, 41(5):4.
[7]. S M Humphries, A M Notartary, J P Caceno, et al. Deep learning can realize automatic classification of emphysema on CT [J]. International Journal of Medical Radiology, 2020, V. 43(02):120-120.
[8]. Hui Rui, Gao Xiaohong, Tian Zengmin. CT brain image classification method based on deep learning for preliminary screening of Alzheimer's disease [J]. China Medical Equipment, 2017, 32(12):5.
[9]. Zhang Weiqi, Jiang Yufei, Yuan Huiyun. Research on privacy protection of COVID-19 patients [J]. Chinese Medical Ethics, 2021, 34(10):5.
[10]. [10]LI H. Analysis of overfitting phenomenon based on deep learning [J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2020(14):2. (in Chinese)
[11]. Chen Yufeng, Chen Jianwen, Hou Jiayi. Radiological image recognition of viral pneumonia based on deep learning framework KERAS [J]. Electronic Components and Information Technology, 2021.
[12]. Rajpurkar P , Irvin J , Zhu K , et al. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-Rays with Deep Learning[J]. 2017.
[13]. Yuan Jianyong, Yu Yuanming, Wang Chao. A Training model saving method and driver based on Tensorflow, Computing server: ,CN108446173A[P].2018.
Cite this article
Li,M. (2023). Deep learning based on model migration for COVID-19 identification. Applied and Computational Engineering,4,111-118.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Dolbneva D V . The Impact of COVID-19 on the World's Economies[J]. THE PROBLEMS OF ECONOMY, 2020, 1(43):20-26.
[2]. Chengying, Wen Yuechun, Chang Yali, et al. Analysis on the impact of novel coronavirus pneumonia epidemic on Chinese economy [J]. Journal of Quantitative and Technical Economics, 2020, 37(5):20.
[3]. Jiang Rong, Xie Huarong, Duan Yongsheng. Prevention and control strategies of nosocomial infection in COVID-19 medical institutions [J]. Chinese Contemporary Medicine, 2020, 27(30):3.
[4]. Hu Xiaobo, Zhang Peng, An Ji, et al. Research on automatic medical image recognition technology based on computer vision [J]. Microcomputer Information, 2012(10):2.
[5]. Shi Xiangbin, Fang Xuejian, Zhang Deyuan, et al. Image classification based on Deep Learning Hybrid model transfer learning [J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2016, 28(1):8.
[6]. Zhang Zhenhua, Jixiang, Zhang Jinsong, et al. Analysis of CT image characteristics of COVID-19 based on AI technology [J]. Medical Equipment, 2020, 41(5):4.
[7]. S M Humphries, A M Notartary, J P Caceno, et al. Deep learning can realize automatic classification of emphysema on CT [J]. International Journal of Medical Radiology, 2020, V. 43(02):120-120.
[8]. Hui Rui, Gao Xiaohong, Tian Zengmin. CT brain image classification method based on deep learning for preliminary screening of Alzheimer's disease [J]. China Medical Equipment, 2017, 32(12):5.
[9]. Zhang Weiqi, Jiang Yufei, Yuan Huiyun. Research on privacy protection of COVID-19 patients [J]. Chinese Medical Ethics, 2021, 34(10):5.
[10]. [10]LI H. Analysis of overfitting phenomenon based on deep learning [J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2020(14):2. (in Chinese)
[11]. Chen Yufeng, Chen Jianwen, Hou Jiayi. Radiological image recognition of viral pneumonia based on deep learning framework KERAS [J]. Electronic Components and Information Technology, 2021.
[12]. Rajpurkar P , Irvin J , Zhu K , et al. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-Rays with Deep Learning[J]. 2017.
[13]. Yuan Jianyong, Yu Yuanming, Wang Chao. A Training model saving method and driver based on Tensorflow, Computing server: ,CN108446173A[P].2018.