1. Introduction
Most sports consist of fast and precise movements, so it is difficult to track and detect the players and the balls. The advent of computer vision solves this problem. In fact, computer vision(cv) has been widely used in sports now, and it plays a crucial role in both the match and the off-season. For example, in a game, a 3D model is used to show the position of the players and the ball, so that the TV presenter can discuss and analyze the location and trajectory of the players. Also, the referee is able to see what is happening in a second, so the fairest penalty can be given. In team competitions, computer vision allows spectators to see movements that are blocked by other athletes. During the training, coaches can analysis quick technical movements and correct the wrong movements of athletes with the help of computer vision. This paper will focus on the basic technology of computer vision in the field of sports.
2. Application
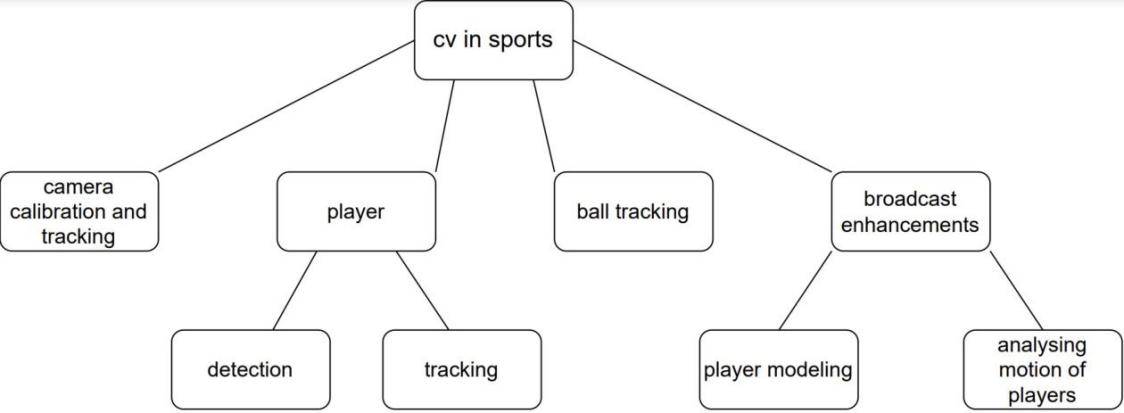
This chapter will focus on different application of computer vision in sports(As shown in Figure 1).
|
Figure 1. Different application of computer vision in sports. |
2.1. Camera calibration and tracking
For systems to render graphics into the image that appear locked to the actual world, camera calibration is required, as well as for the detection and tracking of balls and players(as shown in Figure. 2) [1]. The relationships between the pixel coordinates in each image and the world(court) coordinates must be understood in order to perform measurements based on the acquired images. These relations are obtained by the camera calibration. Sports have strict rules that exactly define the locations and sizes of key landmarks on the playing field, simplifying the process [2]. The original systems measured the camera’s pan and tilt on a fixed mount, as well as the zoom and focus settings on the lens, using mechanical sensors. These lens encoders’ “raw” outputs will have an impact on the calibration information for the lens. The ideal situation would be for lens distortion and nodal shift to be evaluated during calibration and taken into account when generating images(movement of the notional position of the pinhole in a simple camera model, primarily along the direction of vision). It is also required to make an educated guess as to where the camera mounting will be in relation to the playing surface, perhaps using surveying tools like a theodolite or rangefinder. In a photo, a lens and camera with sensors for creating virtual graphics are depicted. Instead of the conventional approach, computer vision is now used for the majority of camera calibration. Line-based trackers can be utilized directly in sports like basketball, which already have distinct lines denoting well-defined positions(as shown in Figure. 3). A feature point tracker can even be utilized for sports that don’t have any evident line features. Computer vision using can eliminate the need for extra lenses or mounts.
|
Figure 2. Camera with sensors on lens and pan [1]. |
|
Figure 3. Basketball field with lines. |
2.2. Detection and Tracking of player
The first step is to determine the specific position of the player at a specific time. The above is the first step of player tracking. Commercial broadcast analysis systems use a variety of methods, from manually selecting parts of athletes in calibrated camera images to automated techniques [3][4]. When tracking these indoor athletes, it requires two high-quality digital cameras, and a set tracking algorithm. This algorithm is based on template matching, and also takes into account the assumption of indoor tracking. The above is the whole video tracking system. The following assumptions can be used to define the closed world assumption: (1) There are two fixed cameras that provide a full field view; (2) The field is bounded; and(3) Two players cannot occupy the same position at the same time-step [5]. Background detection should be done first, then tracking. Background detection uses background subtraction to categorize each pixel in the current scene as either foreground or background, allowing the foreground items to be the main subject of processing. A template is a sub image that contains the shape you want to find. Then, utilize the template matching technique to track. The template is centred on an image point throughout the template matching procedure, and the matched pixels are tallied. The head and shoulders are typically tracked in part when tracking an athlete because it is simpler and more visible [5]. When tracking numerous athletes, divide the image into N distinct parts, with just one player in each zone. This portioning is called Voronoi partitioning [6].
2.3. Ball tracking
In team sports, it is more difficult to track a ball since it might be obstructed by players and can be in between their hands or feet. It is simpler to create the ball’ s trajectory in a sport like tennis because the ball is usually visible. The location of the ball can be difficult to determine in some ball games since players may obstruct it, so it can be modeled by integrating the position relationships between the ball and players [1]. To monitor cricket balls in 3D, Hawk-Eye developed one of the first multi-camera computer vision systems that was commercially available in 2001. Later, it was used in tennis; at first, the images were provided via broadcast cameras. But in recent years, the system is typically used with up to 10 cameras placed around the field to record live images at up to 340 frames per second. They can be used with short shutter times and greater frame rates because they are static and easier to tune. The algorithm may leverage a lot of prior knowledge about tennis, such as the dimension and appearance of the ball and its movement(once it is struck, the rules of physics can be used to forecast its motion.),as well as the area that has to be tracked [1].
2.4. Broadcast enhancements
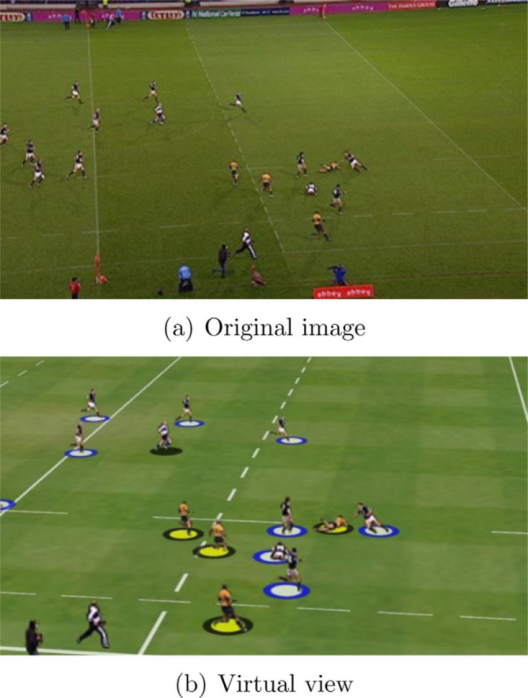
2.4.1. Player modeling. Once the position of the player is determined, the current sports graphics systems use various methods to improve the visualization of key moments from a different perspective. Modeling players is one way to improve visualization. Later, some smoothly moving viewpoints will be copied from one or more fixed cameras. This process is realized by some algorithms of computer vision. A basic 3D rendering of the scene can be created from a single camera using a billboard technique by isolating the players from the background and putting them as features on flat surfaces placed at the predicted places in a 3D model of a sports field [7]. The picture provides an illustration of this strategy, which was initially applied in 2004(as shown in Figure 4) [8]. Using positions other than the actual camera position, we are able to build virtual views of the game. For instance, we may show the field when a linesman determines whether a player is on or offside [1]. This technique of building a model with a single camera works well in many circumstances, but it limits the virtual camera’s range of motion. The players’ planar nature becomes clear when the viewing direction shifts by over 15 degrees. It is also difficult to distinguish between two players when their positions overlap. Add one or more cameras, make a “2.5D” model, and require seamless merging of several billboard images. The above is the solution [1].
|
Figure 4. Generation of a virtual view from a single camera image [9]. |
2.4.2. Analyze motion of players. Trainers and broadcasters can learn a lot about players’ movements at crucial times in a game by analyzing or visualizing them. Usually, in some important training(such as elite level), athletes will be placed with more cameras and markers. Of course, these are calibrated. This is also achieved through a dedicated motion capture system. However, using such marker-based systems in lower-level training and during competition is impracticable. By superimposing a series of “snapshots” on the background to generate a motion “trail,” foreground objects or human movements can be visually segmented, which can be realized. This allows the movement of objects or people in the foreground to be observed. This creates a result that is comparable to what can be obtained by lighting the scene with a stroboscope and taking a picture with a camera that has a long exposure. The snooker analysis tool takes advantage of the relatively non threatening characteristics of the game. Specifically, when the ball is separated from a simple green background, the camera is usually fixed. This is an early example [10].
2.5. Correcting of distortion
Due to the distortion produced by the fisheye lenses, the footage that was utilized for the visualization should be adjusted. The following equations serve as the foundation for the transformation of the distorted to the undistorted image:
\( {r_{Defish}}=ftan(\frac{{r_{Fisheye}}}{f}) \) (1)
\( {r_{Fisheye}}=farctan(\frac{{r_{Defish}}}{f}) \) (2)
Where \( {r_{Defish}} \) is the distance to the center of the corrected (Defish) image, \( {r_{Fisheye}} \) is the distance to the center of the distorted(Fisheye) image and \( f \) is the focal length(in pixels). This transformation is carried out under the assumption that the lens is spherical and that the distortion is radial but not tangential [5].
Interpolation is necessary because the restored image is larger than the distorted one. Reverse mapping can avoid interpolation by copying a few of the original, deformed image’s pixels into the corrected image. In the approach, look-up tables are used, and each camera’s mapping is only calculated once. To transform a pixel p’ at location (x′, y′) from distorted image to a pixel p at location (x, y) in the undistorted image we use the following equations:
\( {X_{Fisheye}}=(X-{X_{center}})\frac{{r_{Fisheye}}}{{r_{Defish}}}+{X \prime _{Center}} \) (3)
\( {Y_{Fisheye}}=(Y-{Y_{center}})\frac{{r_{Fisheye}}}{{r_{Defish}}}+{Y \prime _{Center}} \) (4)
\( {r_{Defish}}=\sqrt[]{{(X-{X_{center}})^{2}}+{(y-{y_{center}})^{2}}} \) (5)
Where the center of the distorted image is at pixel \( {P \prime _{center}}=({X \prime _{Center}},{Y \prime _{Center}}) \) and the center of the undistorted image is \( {P_{center}}=({X_{Center}},{Y_{Center}}) \) [5].
3. Discussion
The progress of the sport has embraced computer vision, which is widely used and adored by spectators, coaches, and commentators. However, computer vision also has some limitations, such as the fact that some remote locations lack the resources and technology necessary to employ computer vision. The rhythm of some fast-paced sports will be disrupted by the repeated use of computer vision for replay, which will also have an impact on player performance and spectator sentiment. Despite the fact that computer vision technology has been applied in numerous sports, many of its performances still need to be enhanced. How can the target be tracked when it is obscured? Fully automated player tracking is also a very difficult problem to achieve. Some deep analysis of sports is worth researching, for example, according to the events in progress, infer the kinds of sport, or according to the scene situation, automatically generate the highlight time and save the video file. Any facet of development in sports has the potential to create a sizable market, whether it be before practice, during the actual game, or postgame analysis, which means computer vision has a great commercial value.
4. Conclusion
This paper introduces the basic application of computer vision in sports field, including tracking and detection of ball and player, broadcast enhancement. In fact, computer vision is much more than that. Some application are still immature, such as accurate tracking of athletes over a long period of time, which is still an area need to be improved, but there are also lots of technologies that have been recognized and used. Future research in computer vision remains positive, and it will undoubtedly significantly enhance sports viewing.
Acknowledgments
My teachers, who have given me invaluable advice at every stage of the composition of this thesis, have my sincere gratitude. I also want to thank my parents and all of my friends for their help and support.
References
[1]. Thomas G, Gade R, Moeslund T B, et al. 2017. Computer vision for sports: Current applications and research topics[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 159: 3-18.
[2]. Perš, J., & Kovacic, S. (2000). A system for tracking players in sports games by computer vision. Electrotechnical Review, 67(5), 281-288.
[3]. Bialik, C. (2014). The people tracking every touch, pass and tackle in the world cup. Fivethirtyeight. com.
[4]. Tamir, M., & Oz, G. (2008). U.S. Patent Application No. 11/909, 080.
[5]. Monier, E., Wilhelm, P., & Rückert, U. (2009). A computer vision based tracking system for indoor team sports. In The fourth international conference on intelligent computing and information systems.
[6]. Lewis, J. P. 1995. Fast normalized cross-correlation. In Proceedings of Vision Interface 95, Canadian Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Society, pp.120-123.
[7]. Grau, O., Price, M. C., & Thomas, G. A. (2000, December). Use of 3d techniques for virtual production. In Videometrics and Optical Methods for 3D Shape Measurement (Vol. 4309, pp. 40-50). SPIE.
[8]. R&D, B., 2017. Piero Sports Graphics System. http://www.bbc.co.uk/rd/projects/piero.Accessed 12 Feb 2017.
[9]. Ericsson, 2016. The PieroTMSports Graphics System. http://www.ericsson.com/broadcastandmedia/what-we-do/piero. Accessed 2 May 2016.
[10]. Storey, R., 1984. TELETRACK - A Special Effect. BBC Research Department Report 1984-10, Available as BBC R&D White Paper 033.
Cite this article
Shao,X. (2023). Review of computer vision in sports. Applied and Computational Engineering,5,28-33.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Thomas G, Gade R, Moeslund T B, et al. 2017. Computer vision for sports: Current applications and research topics[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 159: 3-18.
[2]. Perš, J., & Kovacic, S. (2000). A system for tracking players in sports games by computer vision. Electrotechnical Review, 67(5), 281-288.
[3]. Bialik, C. (2014). The people tracking every touch, pass and tackle in the world cup. Fivethirtyeight. com.
[4]. Tamir, M., & Oz, G. (2008). U.S. Patent Application No. 11/909, 080.
[5]. Monier, E., Wilhelm, P., & Rückert, U. (2009). A computer vision based tracking system for indoor team sports. In The fourth international conference on intelligent computing and information systems.
[6]. Lewis, J. P. 1995. Fast normalized cross-correlation. In Proceedings of Vision Interface 95, Canadian Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Society, pp.120-123.
[7]. Grau, O., Price, M. C., & Thomas, G. A. (2000, December). Use of 3d techniques for virtual production. In Videometrics and Optical Methods for 3D Shape Measurement (Vol. 4309, pp. 40-50). SPIE.
[8]. R&D, B., 2017. Piero Sports Graphics System. http://www.bbc.co.uk/rd/projects/piero.Accessed 12 Feb 2017.
[9]. Ericsson, 2016. The PieroTMSports Graphics System. http://www.ericsson.com/broadcastandmedia/what-we-do/piero. Accessed 2 May 2016.
[10]. Storey, R., 1984. TELETRACK - A Special Effect. BBC Research Department Report 1984-10, Available as BBC R&D White Paper 033.