1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence, as the hottest word in recent years, has been widely concerned by people. It has been applied in various fields from the original branch of computers and has gone deep into people's lives. However, with the continuous development of artificial intelligence, especially after the appearance of AlphaGo, more and more people begin to worry whether artificial intelligence will surpass human beings shortly, and even enslave and replace human beings like in the movie Terminator.
This article will discuss whether artificial intelligence will surpass the human brain completely from the current development status of the four aspects of artificial intelligence: listening(Speech recognition and natural language processing), speaking (human-computer dialogue), looking(image identification), thinking and learning(man-machine game, Machine learning).
2. Artificial intelligence
In 1956, the concept of "artificial intelligence" was first proposed at the Dartmouth conference. At first, people focused on the reasoning system used to solve logic problems. Humans wanted to convert their inner thoughts and process knowledge into precise forms and inform artificial intelligence with symbols and rules, which was called symbolic artificial intelligence. Based on this, people have created an expert system, which is a kind of computer intelligence program system with special knowledge and experience. It generally uses knowledge representation and knowledge reasoning techniques in artificial intelligence to simulate complex problems that are usually solved by domain experts. [1] It is now widely used in medical applications.
However, with the continuous development of symbolic artificial intelligence, people find that more and more problems cannot be solved by pure symbolic reasoning. Examples include natural language processing and image recognition. So, the development of AI has hit a plateau.
In the past two decades, with the development of artificial neural networks and the popularity of deep learning, more and more problems that cannot be solved by symbolic artificial intelligence have been well solved.
3. Artificial neural network
An artificial neural network abstracts the brain neuron network from the perspective of information processing, and forms different networks according to different connection modes, to establish different operation models. It consists of a large number of nodes, or neurons, connected, each representing a specific output function, called the activation function. Each connection between two nodes represents a weighted value for the signal passing through the connection, called the weight, which is equivalent to the memory of the artificial neural network.
Therefore, people can give the machine the ability to learn by having the artificial neural network model constantly train and change the value of the weights. It is also because of the emergence of artificial neural networks so that machines can hear, see, learn and think become a reality.
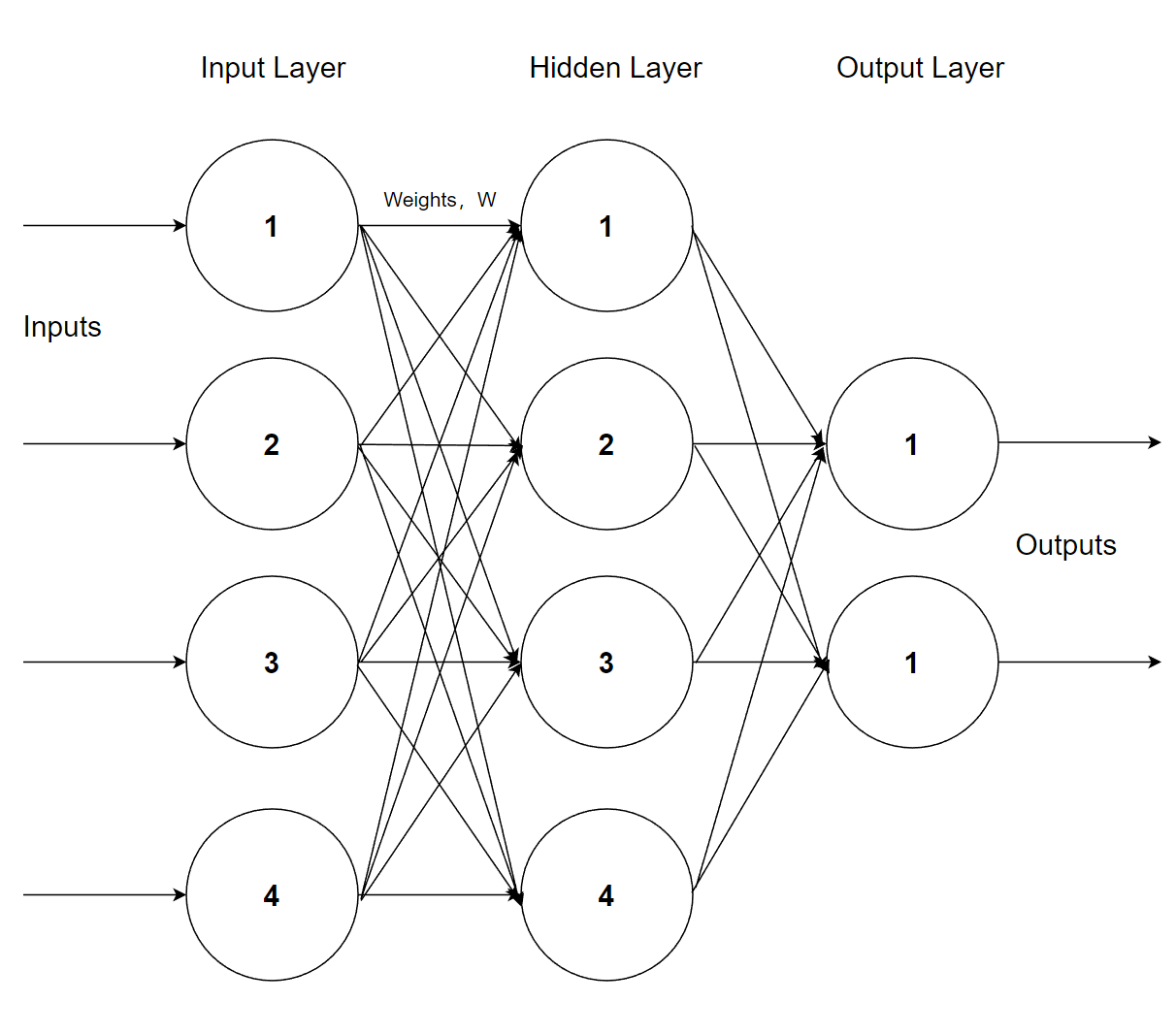
Figure 1. Artificial Neural Network.
3.1. Listening(automatic speech recognition and natural language processing)
When we want to learn a language, listening is often the main part. For example, when we learn a foreign language, the first thing we need to do is to hear each word clearly and then understand the meaning of the paragraph. The same is true of machines. If we want to communicate better with machines, we first need to make machines understand our language.
Automatic Speech recognition (ASR) and natural language processing (NLP) are the main approaches to making machines hear and understand human speech. Speech recognition technology is to let the machine through the process of recognition and understanding speech signals in the corresponding text, while natural language processing is to let the machine understand the content of the text.
ASR can be basically divided into three steps: building an acoustic model, building a language model, and speech recognition.
Building acoustic model: For the machine to recognize more human voices, a large number of original user voices need to be input when building the acoustic model. Then, special features are extracted for each person's pronunciation, intonation, and speaking speed, to build the acoustic model database.
Building language model: The language model is designed to adjust the illogical words processed by the acoustic model to make the recognition result smoother and more correct.
Speech recognition: Both the speech model and language model can be called preprocessing for automatic speech recognition. Speech recognition is a real-time process. After encoding the user's speech input and extracting features, the extracted features will be matched in the acoustic model database to get a word, and then put into the language model database to query, to get the most matched word.
Although automatic speech recognition is now mature for commercial use, the high error rate in some speech recognition areas is still one of the major obstacles to the widespread use of speech technology [2].
In People's Daily communication, most of the time we are unable to speak out what we want to say directly and fluently, which is often accompanied by thinking, interruption, hesitation, or repetition. Including sometimes poor pronunciation and accents, which do not affect human communication, but are undoubtedly very difficult for machines to recognize. Therefore, the error rate is up to 50% for large vocabulary continuous speech recognition (LVCSR) in the presence of these conditions [3].
To solve this problem, people begin to study the automatic error detection and correction of Automatic Speech recognition.
In a 2018 paper, Rahhal Errattahi et al. summarized several ASR automatic detection and error correction methods. For example, Sarm et al. used co-occurrence analysis to construct ASR error detectors and correctors. They introduce an unsupervised learning method for detecting and correcting unidentified words in document collections with high accuracy. Similarly, Bassil et al. proposed an ASR error correction method based on the Microsoft N-gram dataset. Firstly, error correction suggestions are generated for the detected word errors, and then the best option is selected to correct according to the context correction algorithm. Then they selected five speakers to read five different articles in English. The final identification error rate was only 2.4%[4].
However, Rahhal et al [2] found that only a few studies addressed the error correction process of ASR, and more studies focused on manual error correction of error fragments. Therefore, the automatic error correction of ASR still needs more research.
In addition to human factors, recording equipment, transmission channel signals, environmental noise, and other issues will also affect the accuracy of speech recognition.
After using ASR to make the machine hear what people are saying, the next step is to make the machine understand it. This is where Natural Language Processing (NLP)techniques come in. But clearly, getting a machine to understand is more complicated than hearing clearly.
The general processing pipeline of NLP is relatively complex. It is divided into corpus acquisition, data preprocessing, feature extraction, model building, and evaluation.
The first step is to obtain a corpus and then pre-process the corpus to clean the characters that do not make sense, such as some special symbols (!,?). Or stop words (a an the), then split the text into words, and finally label the words such as adjectives, and verbs (this is very important in analyzing language sentiment, and reasoning). After that, appropriate features are selected and the segmented words are vectorized. Finally, the appropriate model is selected and established, and the model output results are evaluated after continuous training.
This is a basic NLP process and there are many algorithms in each flow. For example, string matching algorithms, statistical word segmentation methods, or rule-based word segmentation algorithms are used in word segmentation. In Chinese part-of-speech tagging, we will use the maximum entropy-based part-of-speech tagging or the statistical maximum probability-based part-of-speech tagging. It is also necessary to choose different representation models when converting words into vectors, such as Word2Vec and Seq2Seq. Similarly, when building the final model training, it is also necessary to choose different machine learning or deep learning models according to the requirements, while paying attention to overfitting, underfitting, gradient explosion, and other issues. Therefore, the proper selection of algorithms and models is also the most critical one to solving NLP problems.
However, there are many problems when the machine is dealing with language problems. Language is the essence of human civilization. It has no rules. In other words, its rules are complicated. Different language systems have different grammatical structures. Take English and Chinese for example, English words have multiple forms, so when NLP processes English sentences, it needs some unique processing steps, such as Lemmatization and Stemming. Lemmatization: goes, went, going needs to revert to go. Stemming: feet, teeth need to revert to foot, tooth.
These two steps are not necessary for Chinese NLP. But Chinese also has a unique problem, that is, sentence segmentation. A Chinese paragraph is completely connected, and different sentence segmentation will produce a completely different meaning.
There are two very different problems with just two languages, not to mention the fact that there are nearly 7,000 languages in human civilization[5], and it is of course an unprecedented challenge for a machine to fully understand all of them. Of course, if a machine could do it, it would undoubtedly surpass all humans in language understanding.
In addition to the complex rules of language, open compositional expression in spoken language is equally a problem. In daily communication, people do not speak according to the rules of language, and they can even create some new expressions arbitrarily, including different expressions for different emotions. This is a difficult problem to overcome both for speech recognition and natural language processing.
Similarly, the use of language requires context, and different words may have different meanings in different contexts. How to make the machine understand the text according to the context is also a problem that people are currently trying to solve. For example, QUAN YI Hu et al. designed the CF-MUG framework to solve the cross-language translation barriers caused by context relationships in machine translation, which draws on the idea of collaboration. Each word is tagged with a unique ID, and the document exchange is converted to ID exchange, which ensures machine readability, improves the generality of the system, and minimizes missing information from the source to the target language [6]. However, this framework is not perfect and needs to be further improved.
Thus, there are still a variety of problems in speech recognition and natural language processing, whether it is the adaptation of different language systems, the recognition, and understanding of complex semantic articles, or the understanding of people's spoken language expressions that are waiting for people to solve.
3.2. Speaking(human-computer dialogue)
With the development of natural language processing, machines can understand people's speech, people began to try to make machines and people start a dialogue based on NLP, so the human-machine dialogue technology was born.
At present, man-machine dialogue is mainly divided into two kinds, one is written dialogue, and one is voice dialogue. For these two types, chatbots and intelligent voice assistants like SIRI are the most common things in people's lives. Fig2 is the basic process of human-machine dialogue.
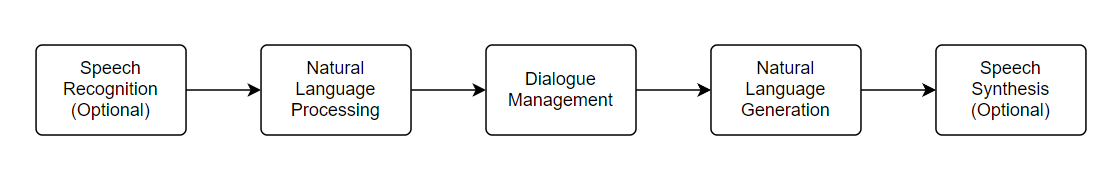
Figure 2. Human-machine dialogue process.
Chatbot responses are usually categorized into retrieval and generation. At present, most of the chat assistants that have been used are usually retrieval types. This kind of robot is mostly proposed to solve a certain kind of specific problem, all the answers are set in advance, through the rule engine, knowledge graph, pattern matching, machine learning model, and other data media, and select the best response in the knowledge base to the user. For such chatbots, the most common thing people see is intelligent customer service. People can ask questions about the service, such as what's the weather today, how do I return my purchase, etc., but these questions are limited to basic questions, so it is often the case that people say a lot of things, but the machine can't understand or can't match the answer
Even Siri, our familiar voice assistant, is the same. When people use Siri, most of Siri's answers are based on a pre-set corpus. Therefore, when people's questions are out of the scope of the corpus, Siri will not be able to answer.
Therefore, we can find that the retrieving-based chatbot has a very clear task orientation, and it appears completely to help people solve a certain problem because the answer it gives must be clear and straightforward, it has strong efficiency and relevance [7]. So, businesses that want to give users a better experience only need to set more answer options for their service types. But such chatbots will never be able to match or surpass humans in conversation because they are designed to serve humans in a specific domain
The other way is based on generation. Instead of relying on pre-defined answers, a large corpus is used to train the supervised model [8], so that the model can automatically generate a reply after the user's question is input. Therefore, the chatbot based on this method can answer questions in any field, but it is prone to syntactic errors and incoherent sentences. The classic example of this type is the AI article automatic generator. When people type in a paragraph, the AI can write a story based on the context. Compared to the former, generation-based chatbots have more possibilities in terms of conversation.
Asbjorn et al. [9] have done such an experiment by letting users use a task-oriented retrieval-based chatbot and a free-text-oriented chatbot, respectively. Then share their user experience. The final feedback is that task-oriented chatbots can usually solve their problems clearly, but they do not have a sense of communication with a human, in other words, it is more like instruction. Whereas free-text-oriented chatbots are more like communicating with them.
Chatbots deliberately imitate human social communication and communicate with users through context emotion recognition [10]. However, limited by the development of natural language processing, it is often possible to identify the wrong emotion and give the user a poor or ambiguous answer. And such robots are also limited by domain problems. A chatbot based on the medical direction will not be able to give users appropriate answers to questions in other fields. But it is obvious that generative chatbots are the main direction of future development to make machines better communicate with humans.
3.3. Looking(image identification)
Image recognition is an important field of artificial intelligence, which refers to the use of computers to process, analyze and understand images to identify a variety of different patterns of objects.
Since the generation of image recognition technology is based on artificial intelligence, the process of computer image recognition is generally the same as the process of human brain image recognition. When we see a picture, our brain will quickly sense whether we have seen this picture or a similar picture. In this process, our brain will have determined according to the memory, which can identify the category of the see if any and the feature of the image with the same or similar memory, to identify whether seen the image, so the computer image recognition technology induces mainly includes image acquisition, image processing, image recognition, and result output four parts. For the stage of image recognition, the most commonly used model is the convolutional neural network (CNN).
Nowadays, image recognition technology has been successfully applied in many fields, such as face recognition and fingerprint recognition in security, satellite image processing in aerospace and military, imaging precision guidance, target detection, and so on. In medicine, there is medical image analysis; Industry has a variety of monitoring systems. therefore, the application of image processing has been involved in all aspects of human life and work and compared with other aspects of artificial intelligence development is more mature, and has been able to replace the relevant work of the human eye.
Although graphics recognition is relatively mature compared to language understanding, the overall picture recognition technology is still in its early stages, and there are still problems when it comes to adapting to the real world. The biggest obstacle is instability, which also exists in other aspects of artificial intelligence. For example, an object is mixed into a background, which makes it difficult to recognize, or the object is blocked, only a small part of it is exposed, which causes the machine to fail to recognize, etc.
Thinking and Learning(man-machine game, Machine learning)
In March 2016, AlphaGo stunned the world with a 4-1 win in a human-computer game against Lee Se-dol, the world champion and a professional nine-dan Go, player. As one of the most difficult games in the world, Go has variations of 10 to the power of 170, which is more than 80 times the atomic number of 10 in the entire universe. Its complexity is unimaginable. It takes a lot of logical thinking and practice to play Go well, but even so, AlphaGo beat Lee by a wide margin. This makes people wonder, have machines already beaten people in thinking?
The original Alpha dog worked on deep learning. Through continuous training of artificial neural networks, learning to simulate human play go and constantly playing against themselves to increase actual combat experience. This is very similar to human learning to play Go.
Even so, the intelligence of the original AlphaGo was still very low, and it could not really understand Go. It was able to win the game by the powerful logical computation of the computer and practicing every day nonstop.
Whereas the original AlphaGo mimics human play Go game, the latest version of Alpha Zero shows autonomous learning exactly like a human. Unlike AlphaGo, Alpha Zero has no experience playing chess with humans and has no idea what Go is. Alpha Zero discovered the principles of Go simply by playing against himself and updating his neural network based on experience and quickly became the best player of all time. Alpha Zero taught itself three different board games, including Chess, Go, and Shogun, in three days without human intervention [11].
Later, in Go, Alpha Zero beat AlphaGo Zero [12]. Won 61% of the games. In chess, Alpha Zero beat Stockfish, winning 155 games and losing 6 games out of 1000. Alpha Zero beat Stockfish in every opening game [13].
Even more amazing, Alpha Zero doesn't rely on brute computation like other programs. Alpha Zero won by smarter thinking. It counted only 80,000 positions per second, compared with 70 million for the chess program Stockfish. It's obviously wiser and knows what to think and what to ignore.
There's no doubt that Alpha Zero is a major milestone in getting machines to think. But it still doesn't get rid of another problem with machine learning, which is its limitations. Alpha Zero is the best player in the world at Go or chess, but in other ways, he's just a retard.
3.4. The human brain's intelligence
The human brain is the most powerful, complex neural network model in the world. It's made up of about 100 billion neurons, with between 1,000 and 10,000 connections between each neuron. Each connection has about 5e17 switches. The world's strongest supercomputer can process 3 billion calculations per second, but it is still 500 times less complex than the human brain [14].
The neural networks in our brains are trained from birth. From the beginning of talking, and walking, to recognizing apples to recognizing everything. The neural network in the human brain becomes more and more perfect with the continuous enrichment of human experience.
Although artificial intelligence has great advantages in computing, and memory, the creativity correlation, conjecture, fuzzy reasoning, and abstract understanding ability of the human brain are not possessed by artificial intelligence at present. For example, for image recognition, the machine will be wrong or unable to recognize the object because it is blocked, while our human brain can infer the category or specific appearance of the object based on the exposed part of the object and the memory of the past. Of course, the category of the object needs to be the one that people have seen before. For example, a child who has never seen transportation would not know what a car is even if he saw one. But an adult, even if the car is obscured by only one wheel, can accurately infer that the object in front of him is a car. This is where the human brain's ability to conjecture and fuzzy reasoning comes in.
The other most important thing is that the human brain has independent consciousness and emotions. Human emotions can be expressed in everything from facial expressions, tone of voice, and even microexpressions that are extremely difficult to detect. Therefore, how recognizing human emotions through language and expression has always been a difficult point for artificial intelligence, let alone making it have the same emotional expression as human beings. Also, human beings do not have a clear definition of what consciousness is, which is also one of the reasons that artificial intelligence cannot completely surpass the human brain. Artificial intelligence relies on simulating the human brain to solve problems, but people have not fully solved the mysteries of the human brain.
Different from the limitation and singularity of artificial intelligence, human beings are a comprehensive intelligence that integrates listening, speaking, reading, thinking, and learning. A ten-year-old boy is not as good at Go as Alpha Zero, but he can find an apple hidden by his parents in his spare time when he is learning to play Go.
4. Conclusion
Today, artificial intelligence is usually divided into three stages, weak AI, strong AI, and Super AI, weak AI is Artificial intelligence that focuses on and can only solve problems in a specific domain. strong AI is Artificial intelligence capable of doing all human jobs. Super AI is an artificial intelligence that outsmarts the best human brain in every respect, including scientific creativity, intelligence, and social skills.
For now, AI has surpassed the human brain in memory, accurate calculation, and reasoning. No doubt some traditional industries will be replaced. But AI is still limited to solving specific problems and it’s do not have the emotions, consciousness, and ability to think and make decisions independently like human beings. So it is still in the weak AI stage. Therefore, whether it is a unilateral ability such as vision and language understanding, or centralized integration of various abilities such as vision, hearing, and thinking, it is still very difficult and long for artificial intelligence to completely surpass human beings.
References
[1]. Maruyama, Y. Quantum (2017) Pancomputationalism and Statistical Data Science: From Symbolic to Statistical AI, and to Quantum AI. Studies in Applied Philosophy Epistemology and Rational Ethics. 207-211.
[2]. Rahhal Errattahi, Asmaa El Hannani, Hassan Ouahmane(2018), Automatic Speech Recognition Errors Detection and Correction: A Review. Procedia Computer Science 128.32-37.
[3]. Swietojanski, P., Ghoshal, A., Renals, S (2014). Convolutional neural networks for distant speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 21, 1120–1124.
[4]. Bassil, Y., Semaan, P., (2012). Asr context-sensitive error correction based on microsoft n-gram dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:1203.5262.
[5]. Lindell Bromham, Russell Dinnage, Hedvig Skirgård, Andrew Ritchie, Marcel Cardillo, Felicity Meakins, Simon Greenhill and Xia Hua (2022). Global predictors of language endangerment and the future of linguistic diversity. Nature Ecology & Evolution volume 6, pages 163–173.
[6]. Hu Quanyi, Yang Jie, Qin Peng and Fong Simon(2020) Towards a context-free machine universal grammar (CF-MUG) in natural language processing, IEEE Access, Volume 8, Pages 165111-165129.
[7]. D. Jurafsky, J.H. Martin(2021).Chatbots & dialogue systems. Speech and Language Processing. Draft of December 29, 2021
[8]. Kapociute-Dzikiene, Jurgita(2020).A Domain-Specific Generative Chatbot Trained from Little Data. APPLIED SCIENCES-BASEL.2221,10.7.
[9]. Isabel Kathleen Fornell Haugeland, Asbjørn Følstad, Cameron Taylor, Cato Alexander Bjørklia(2022) International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, Volume 161.
[10]. Ivo Benke, Ulrich Gnewuch, Alexander Maedche(2022). Understanding the impact of control levels over emotion-aware chatbots. Computers in Human Behavior, Volume 129.
[11]. David Silver, Julian Schrittwieser, Karen Simonyan, Ioannis Antonoglou, Aja Huang, Arthur Guez, Thomas Hubert, Lucas Baker, Matthew Lai, Adrian Bolton, Yutian Chen, Timothy Lillicrap, Fan Hui, Laurent Sifre, George van den Driessche(2017), Thore Graepel & Demis Hassabis. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature volume 550, pages354–359
[12]. D. Silver, J. Schrittwieser, K. Simonyan, I. Antonoglou, A. Huang, A. Guez, T. Hubert, L. Baker, M. Lai, A. Bolton, Y. Chen, T. Lillicrap, F. Hui, L. Sifre, G. van den Driessche, T. Graepel, D. Hassabis (2017), Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature 550, 354–359.
[13]. David Silver, Thomas Hubert, et al (2018). A general reinforcement learning algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through self-play. SCIENCE, VOL. 362, NO. 6419 pp.
[14]. Sana Khanam, Safdar Tanweer, and Syed Khalid (2020). Artificial Intelligence Surpassing Human Intelligence: Factual or Hoax. The Computer Journal.
Cite this article
MU,C. (2023). Based on natural language processing, human-computer dialogue, image recognition, and machine learning analysis whether artificial intelligence will surpass the human brain. Applied and Computational Engineering,5,40-47.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Maruyama, Y. Quantum (2017) Pancomputationalism and Statistical Data Science: From Symbolic to Statistical AI, and to Quantum AI. Studies in Applied Philosophy Epistemology and Rational Ethics. 207-211.
[2]. Rahhal Errattahi, Asmaa El Hannani, Hassan Ouahmane(2018), Automatic Speech Recognition Errors Detection and Correction: A Review. Procedia Computer Science 128.32-37.
[3]. Swietojanski, P., Ghoshal, A., Renals, S (2014). Convolutional neural networks for distant speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 21, 1120–1124.
[4]. Bassil, Y., Semaan, P., (2012). Asr context-sensitive error correction based on microsoft n-gram dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:1203.5262.
[5]. Lindell Bromham, Russell Dinnage, Hedvig Skirgård, Andrew Ritchie, Marcel Cardillo, Felicity Meakins, Simon Greenhill and Xia Hua (2022). Global predictors of language endangerment and the future of linguistic diversity. Nature Ecology & Evolution volume 6, pages 163–173.
[6]. Hu Quanyi, Yang Jie, Qin Peng and Fong Simon(2020) Towards a context-free machine universal grammar (CF-MUG) in natural language processing, IEEE Access, Volume 8, Pages 165111-165129.
[7]. D. Jurafsky, J.H. Martin(2021).Chatbots & dialogue systems. Speech and Language Processing. Draft of December 29, 2021
[8]. Kapociute-Dzikiene, Jurgita(2020).A Domain-Specific Generative Chatbot Trained from Little Data. APPLIED SCIENCES-BASEL.2221,10.7.
[9]. Isabel Kathleen Fornell Haugeland, Asbjørn Følstad, Cameron Taylor, Cato Alexander Bjørklia(2022) International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, Volume 161.
[10]. Ivo Benke, Ulrich Gnewuch, Alexander Maedche(2022). Understanding the impact of control levels over emotion-aware chatbots. Computers in Human Behavior, Volume 129.
[11]. David Silver, Julian Schrittwieser, Karen Simonyan, Ioannis Antonoglou, Aja Huang, Arthur Guez, Thomas Hubert, Lucas Baker, Matthew Lai, Adrian Bolton, Yutian Chen, Timothy Lillicrap, Fan Hui, Laurent Sifre, George van den Driessche(2017), Thore Graepel & Demis Hassabis. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature volume 550, pages354–359
[12]. D. Silver, J. Schrittwieser, K. Simonyan, I. Antonoglou, A. Huang, A. Guez, T. Hubert, L. Baker, M. Lai, A. Bolton, Y. Chen, T. Lillicrap, F. Hui, L. Sifre, G. van den Driessche, T. Graepel, D. Hassabis (2017), Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature 550, 354–359.
[13]. David Silver, Thomas Hubert, et al (2018). A general reinforcement learning algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through self-play. SCIENCE, VOL. 362, NO. 6419 pp.
[14]. Sana Khanam, Safdar Tanweer, and Syed Khalid (2020). Artificial Intelligence Surpassing Human Intelligence: Factual or Hoax. The Computer Journal.









