1. Introduction
1.1 Research Background and Significance
Marine fouling, which refers to the colonization of Marine microorganisms on any underwater surface, is a long-standing global problem (Fig.1). Marine biological fouling is ubiquitous and has been a real problem since human navigation[1]. Biological fouling can increase hull drag, accelerate surface corrosion, and damage propellers, resulting in additional fuel consumption and excessive maintenance costs. The extra fuel consumption exacerbates the excess emissions of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and other gases, affecting the achievement of the carbon-neutral goal of governments worldwide. Marine biological pollution also harms a variety of underwater facilities such as cross-sea bridges, drilling platforms, aquaculture cages, and subsea pipelines. According to statistics, marine biological fouling causes more than $15 billion of losses to the global marine industry every year. It is a considerable challenge to control it without simultaneously causing unacceptable environmental impacts on non-target species. In 1981, the US Navy consumed 18 million barrels of fuel, with 3.3 million attributed to biofouling losses[2]. A biofilm 1 mm thick can increase the ship hull friction by 80 percent, which translates into a 15 percent loss in speed[3]. Furthermore, a 5 percent increase in biofouling increases ship fuel consumption by 17 percent, with a 14 percent increase in greenhouse gases CO2, NOx, and SO2 emissions.


Figure 1.Vessels fouled by marine organisms. Images show fouling by the green alga (seaweed) Ulva (image courtesy of Dr J. Lewis) and barnacles (image courtesy of Dr C.D. Anderson)[1].
Conventional antifouling coatings are designed to kill fouling organisms by releasing toxic substances such as copper oxide and tributyltin. However, studies have found that these toxins are also toxic to non-contaminating organisms and can affect more species, even humans, through the food chain. In order to protect the marine ecological environment, many countries have enacted laws to prohibit the use of these toxic antifouling coatings on ships. In 2001, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) passed a ban on the use of tributyltin coatings on ships starting in 2008. Therefore, the development of green, environmental protection, efficient antifouling coatings is an unmet, urgent need. In the long evolutionary process, different natural organisms have evolved their own antifouling strategies to reduce the survival pressure. Dolphins in the ocean, for example, can rely on their soft skin and high speed to swim, making it difficult for defilers to attach. Based on the study of antifouling surfaces evolved by organisms in nature, the researchers have developed six different methodologies to limit marine fouling. These includes natural antifoulants, mucus-like hydrogels, SLIPS, dynamic surfaces, zwitterionic coatings, micro/nano structured surfaces[4].
1.2 Biofouling Formation Mechanism
Biofouling is the accumulation of unwanted chemicals or organisms on surface. Biofouling can be further categorized by adhering agents into two types: microfouling, namely films secreted by organisms like barnacles or macroscale biofouling (macrofouling) which are composed of the organisms themselves[2].In some literature, microfouling can be divided into the formation of molecular films and primary microbial films[3]. Additionally, it is noteworthy the differences among "microfouling" (slime) produced by unicellular microorganisms inducing diatoms; “soft macro fouling” consisting of eye-observable algae and invertebrates such as sponges, soft corals, anemones, tunicates and hydroids; and ‘hard macrofouling’ from invertebrates with hard protective shell such as barnacles, mussels and tubeworms[1]. A linear ‘successional’ model proposes that bacterial biofilm formation is firstly formed, followed by spores of macroalgae (seaweeds), fungi and protozoa within a week[3-8]. At last came larvae of invertebrates, such as barnacles, which adhere to the surface after several weeks. However, it was then discovered spores of seaweeds settling in a few minutes and larvae of some species of barnacles, bryozoans and hydroids settling within a few hours of immersion[9,10]. Compared with the linear successional model, it is more reasonable to describe the biofouling formation process as "dynamic", in which the composition of whatever accumulates is based primarily upon the numbers of each kind of item available[11,12]. In addition, physical, molecular and behavioral interactions between and within the various fouling categories also strongly influenced the adhesion process[13]. For example, the attachment of spores and larvae can be influenced by other organisms. The result is confirmed by testing biofilms of specific bacteria against algal spores and larvae of invertebrates[14-16]. Colonization process has five stages, which includes initial attachment, irreversible attachment, initial growth, final growth, and dispersion. Initial attachment is controlled by a physical adhesion between the micro-organism and the substrate. The organisms first attach to a surface through weak, reversible van der Waals bonds. Initial attachment is reversible, but after the secretion of EPS, which are are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment,the sponge-like matrix structure holds microorganisms permanently to one another and to the surface. The biofilm covered surface then attracts other organisms that may have been previously deterred. This permanent attachment allows initial growth, final growth, and dispersion[17-20].
Biofouling growth rates depend on a number of factors, including the organism, substrate, nutrient, flow velocity, shear stress, and temperature, and so forth[21]. For example, the researches show that the availability of nutrients has a significant effect on the thickness of biofilm. For a given velocity of 1.2 m/s through a tube, raising the nutrient level (glucose based) from 4 mg/L to 10 mg/L gave an increase of biofilm thickness of more than 400%.[22]. In tubular heat exchangers, the optimal temperature for maximum growth is about 40℃, and the velocity is in excess of 1m/s, which can reduce the occurrence of biological fouling[21].
1.3 Determinants of Surface Wettability
The basic parameter used to describe the wettability of a surface is the Young equation contact angle, the angle measured through the liquid, where a liquid-vapor interface meets a solid surface. In the case of water and a solid surface, the surface is classified as hydrophilic if the contact angle is between 0 and 90°, in which case water will spread out on the solid surface; for hydrophobic surface, Ɵ is between 90° and 180°, and water will bead up on the surface. A surface is called superhydrophobic if 150°<Ɵ<180°(Fig.2) [23-25].
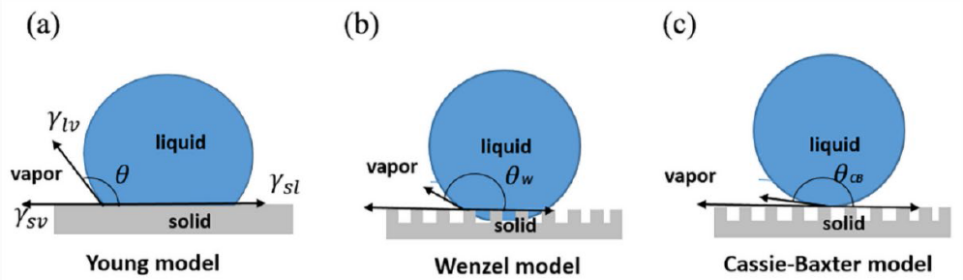
Figure 2.Various states of droplet on a solid surface. (a) Yong model, (b) Wenzel model, and (c) Cassie-Baxter model [26].
The Young equation assumes that surface is smooth and homogeneous. When a liquid droplet gets in contact with a smooth surface, the liquid and substrate come to equilibrium at a certain contact angle, which is expressed as: \( cosƟ =\frac{{γ_{sv}} -{γ_{sl}}}{{γ_{Lv}}} \) (equation 1.1). Here γsl, γsv, and γlv are the energy interaction between solid and liquid, the solid surface energy, and liquid surface tension. Based on the Young equation, a higher contact angle and thus higher repellency can be achieved with a solid with low surface energy and liquid with high surface tension.
However, perfectly smooth surface rarely exists in real world. The Wenzel equation takes into account the surface roughness, and is given as: \( {cos{Ɵ^{*}}=r cosƟ^{Y}} \) (equation 1.2), where r is the surface roughness parameter, which is the ratio of real surface area to projected surface area and is always greater than or equal to 1. Thus, in the Wenzel state, surface roughness in fact amplifies the hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of the surface [27].
In the Wenzel state, the water droplet is in full contact of the surface, i.e., it gets into the ‘valleys’ of the rough surface. Another type of wetting state is Cassie-Baxter state, in which air bubbles are entrapped in the grooves of the rough surface, and water droplet beads up. The apparent contact angle \( {Ɵ^{*}} \) given by the Cassie-Baxter equation is: \( cos{Ɵ^{*}}= {r_{f}}{Φ_{s}} cos{Ɵ^{Y}} + {Φ_{s}}-1 \) (equation 1.3), in which \( { r_{f}} \) is the roughness parameter of the wetted area, \( {Φ_{s}} \) is the fraction of liquid-solid area, and ƟY is the Young contact angle. In theory, if \( {Φ_{s}} \) approaches 0, the apparent angle under Cassie-Baxter state is close to 180° [28,29].
The Cassie-Baxter regime is preferred for superhydrophobic properties. However, the composite interface ideal for Cassie state may be fragile - destabilization mechanisms may transform it into Wenzel state (when \( {r_{f}}=r \) and \( {Φ_{s}}=1, \) the equation changes to Wenzel equation)[24,26,29,30]. For a simplified rough surface of vertical pillars, the equation for the critical contact angle Ɵc at which the transition between the Cassie-Baxter state and the Wenzel state happens is (r is the roughness factor, Φs the fraction of solid-liquid area) : \( cos{Ɵ_{c}}=-(1-{Φ_{s}})/( r-{Φ_{s}}) ( \) equation 1.4). Ɵc is actually dependent on surface roughness and morphology, and irrelevant of surface chemistry[24]. This sheds light on the surface design: a lower Ɵc can be achieved by controlling surface roughness, which could be obtained by increasing the height of the pillars. This will result in a greater chance of having Young contact angle > Ɵc, thus a greater chance of staying in Cassie state.
Contact angle hysteresis (CAH), the difference between advancing (maximum) contact angle ƟA and receding (minimum) contact angle ƟR, is another important factor to consider when designing anti-fouling surfaces[24,29,31]. Low CAH enables low adhesion and low liquid roll-off angle, while droplets on high CAH surface tend to stay and stick on the surface. Contact angle hysteresis is typically low for the Cassie state, but high for Wenzel state[23,32].
Conventional approaches for fabricating hydrophobic surface have focused on two aspects, using low surface energy material and acquiring surface structure and roughness to enable very low liquid solid interfacial fraction, with roughness being the more critical factor [24]. In practice, the method could be to add roughness to low surface energy material, or to coat a hydrophobic material upon a roughened surface. Materials like PDMS, Teflon, and fluorinated polymers are often considered; techniques applying roughness involve electrospinning, laser treatment, photolithography, layer-by-layer assembly[25].
1.4 Factors Preventing Soft and Hard Fouling
There are some examples of modifying surface texture and morphology to deter specific solid accretion. For instance, researchers have designed bioinspired topographies mimicking microstructure of shark skin to deter marine foulant such as the algae Ulva[33,34]; filling in lubricants such as oil into the micro texture of a rough surface of low surface energy material has proved effective in lowering adhesion of ice fouling, but the lubricants are susceptible to wear and loss. Research by Dhyani et al. showed that modifying surface texture is more applicable for bacteria. But for foulants like ice or some other marine foulants, the formation of solid fouling may start from a smaller scale than that of the surface structure, which increases the potential of surface interlocking and thus hinders fracture[33,35,36].
Surface design strategies for controlling solid fouling have been focused more on elastic modulus of the foulant, foulant length scale, and surface energy. Coating low surface energy materials upon the substrate is one approach to decrease solid adhesion. The work adhesion Wa between surface and foulant can be expressed as \( {W_{a}} = {γ_{s1v}} +{γ_{s2v}}-{γ_{s1s2}} \) , where \( {γ_{s1v}} \) \( {γ_{s2v}} \) and \( {γ_{s1s2}} \) are the interfacial free energy of the substrate, the foulant, and the substrate-foulant interaction[33,36,37,38]. Artificial materials with very low surface energy, like heavily fluorinated polymers, are often considered for solid anti-fouling. However, the range of surface energy between various smooth surfaces is narrow, so the effect of this method in decreasing adhesion bond may be limited. This method has proven useful for controlling soft biological and protein fouling[33,36,39].
Elastic modulus of the foulant and the foulant length scale are two other major considerations for surface design against solid fouling. Based on theory of Johnson et al[36,40-43], the total energy of the adhesion is both in positive relationship with its elastic strain energy, which is mainly determined by surface modulus, and its interfacial free energy, a function of surface chemistry. Thus, for large foulants with high modulus that adheres to elastic surface, minimizing the elastic modulus of the surface is an effective way to reduce the strength of adhesion bond[36,42]. As the span of modulus for different surfaces can be very large, it is possible to achieve a significant decrease in adhesion force by adopting this method. Halvey et al. demonstrated a guiding framework for low solid adhesion surface design in Figure 3. This mechanism takes fouling scale and foulant modulus together into consideration. For large and rigid foulant with high modulus, the effective strategy is to use a surface with much lower elastic modulus[33]. Dhyani et al. showed that minimizing surface modulus have proved effective in reducing adhesion of some algae and barnacle fouling[36,44,45].
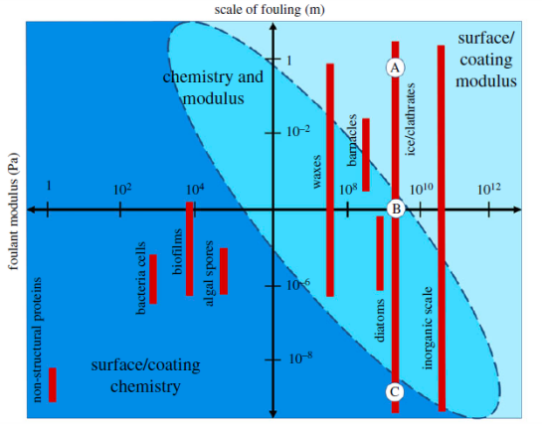
Figure 3. Low solid adhesion surface guide, which categorizes fouling materials according to their fouling scale[36].
2. Current Mainstream Bionic Marine Anti-fouling Technology
By studying six types of biological antifouling surfaces found in nature, the researchers created the following six antifouling methods (Fig.4).
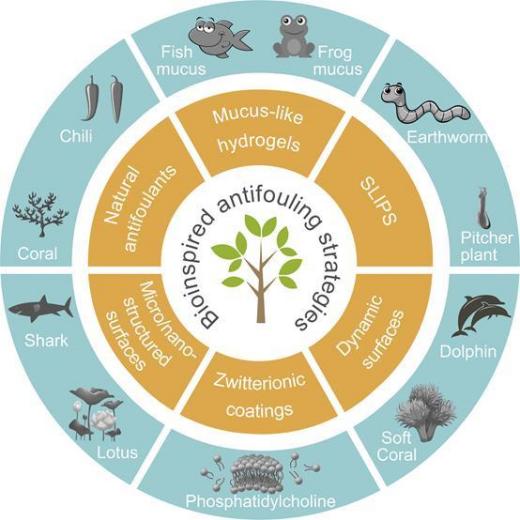
Figure 4. Six major biomimetic antifouling Strategies [4].
2.1 Micro/nano-structured Surfaces
The existence of micro-nano structure can reduce the adhesion between the fouling organism and the surface, and play the function of antifouling[4]. The current application challenge is the poor mechanical properties of the micro-nano structure. Even a minimal external force will cause excessive stress concentration on the micro-nano structure, resulting in the damage of the micro-nano structure, and eventually the loss of antifouling performance. Therefore, the development of robust micro/nano surface is an important development direction.
2.2 Natural Antifoulants
Corals, algae, peppers and the like secrete natural anti-pollutant substances that repel, poison, or inhibit the growth of bacteria and other organisms[4]. It is an effective antifouling strategy to extract these chemical substances or synthesize analogues for antifouling coatings. It is essential to note that the potential risks of these natural chemicals to the marine environment need to be fully assessed. Due to technical limitations, some coatings that contain low toxic antifouling agents are still used, copper being the most common low toxic antifouling element. Antifouling coatings usually use cuprous oxide as antifouling agent filler, and it is combined with organic reagents. Copper is a highly effective and widely used bactericidal element, but it has been proven that it only has an antifouling validity of about two years in the ocean, and heavy metal antifouling coatings cannot be degraded in seawater, so the technology should be developed in a more environmentally friendly direction. Researchers have extracted many natural antifouling agents, but they are still limited in practical use, such as not being able to be mass-produced and not able to cope with the complex marine environment.
2.3 Mucus-like Hydrogels
The main component of fish and amphibian epidermal mucus is a natural hydrogel, which is soft and hydrophilic[4]. Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions induce the formation of a hydration layer on the surface, which forms a physical barrier to contaminating organisms and thus acts as an anti-adhesion function. However, poor mechanical properties of hydrogels, low binding strength to substrates, and poor long-term use effect are obstacles to their application.
2.4 Slippery Liquid Infused Porous Surfaces (SLIPS)
The edge of the pitcher plant is always wet, and the wet edge of the pitcher plant is very smooth, and insects are easy to slip into the bottom and be digested and absorbed by it[4]. The key to the formation of this ultra-smooth surface is the porous micro-nano structure of the edge, which can lock the liquid lubrication layer and give the liquid lubrication layer the characteristics of flow in the porous structure. Earthworms secrete lubricants through their skin to move through the soil with low resistance while reducing the attachment of contaminants. Imitation of this ultra-smooth properties of the preparation of marine antifouling surface, can almost resist the attachment of any contaminating organisms. However, in fluid environments, the volatility of lubricants is a major challenge. It may be an effective way to solve this problem to develop new materials that can secrete lubricant by imitating the secretory function of earthworms.
2.5 Dynamic Surfaces
Some algae in the ocean molt to clean the surface of dirt[4]. Under the drag experienced from the surrounding water, the surface of organisms with soft surfaces, such as dolphins and soft corals, always deforms, forming an unstable surface, which increases the difficulty of settling the contaminate organisms. Even if the contaminate organisms are attached to the surface, they will detangle from the surface under the action of deformation. Therefore, the use of controlled degradation of the surface to mimic the effect of algae molting, or the use of soft materials to mimic the skin structure of dolphins, soft coral, can play a fouling function.
2.6 Zwitterionic Coatings
Phosphatidycholine is found in all cells of the human body and is an important component of the lipid bilayer of cells[4]. The head group of phosphatidylcholine is zwitterionic with the same amount of heterogeneous charge, which can reduce the adhesion of platelets and proteins and has the effect of anti-blood clotting. Since marine bacteria and diatoms promote adhesion by secreting extracellular polymers (mainly proteins, polysaccharides, etc.), mussels and barnacles rely on their secreted proteins to colonize solid surfaces, so zwitterionic polymers reduce the attachment of these foulants. The challenge for current applications is their poor long-term antifouling effect. Preliminary progress has been made in the development of this kind of long-acting antifouling coatings.
3. Anti-fouling Surfaces in Nature and Mechanism of Action
3.1 Coral
Corals are sessile in the marine environment, unable to reduce the attachment of dirt by swimming through the current like other organisms such as sharks. Coral, however, has a remarkably clean surface, thanks to its various anti-fouling strategies. Five main antifouling strategies have been developed for corals, including releasing natural antifouling components, releasing surface antifouling, molting antifouling, fluorescent antifouling, which they utilize fluorescent pigments to absorb harmful ultraviolet rays, and dynamic antifouling strategies (Fig.5)[46].
Figure 5. Schematic illustration of five anti-pollution strategies inspired by corals[46].
3.1.1 Bioactive Antifoulant
Antifouling paints have been used to reduce Marine pollution for a long time and with great success[47]. But the most efficient coatings utilize organotin that causes significant marine toxicity. Thus, researchers have now focused on natural active antifouling agents. Marine corals are one of the sources of natural antifouling products, and Cembranoids extracted from soft coral Sinularia rigida have high antifouling activity against barnacles. In fact, the active substances used by the coral to prevent pollution are not necessarily produced by the coral itself, but may also be released by the bacteria on its surface. These natural antifouling agents mainly include esters, terpenoids, polyphenols, indoles, steroids and nitrogenous compounds, etc. More than 100 marine natural products with antifouling function have been discovered. Studies showed that Marine bacteria or fungi with antifouling potential included Bacillus, Micrococcus, Paracoccus, Pseudobacter, Pseudovibrio, Psychrobacter, Staphylocuccus and Terribacillus. For example, nine lactones isolated and extracted by Xu et al. from Marine streptococcus species (UST040711-291) could effectively inhibit the growth and attachment of barnacle larvae, bryozoans and tubularworms(Fig.6) [48].
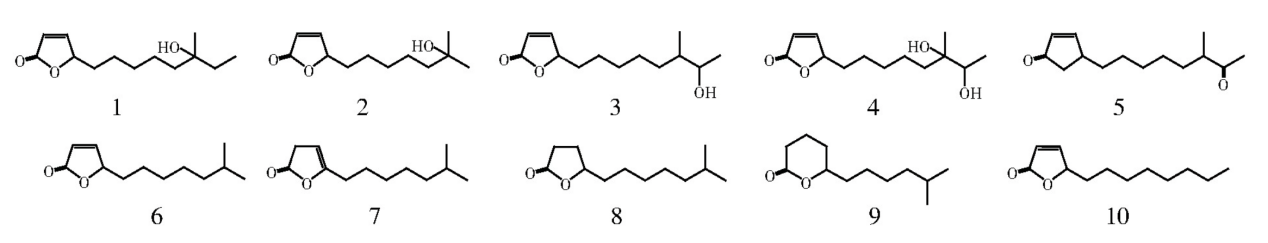
Figure 6. Chemical structures of compounds 1~9, which were isolated from the crude extracts of the bacterium and compounds 10, which was synthesized[47].
Thus, on the basis of summarizing the relationship between lactone structure and antifouling activity, Butenolide was synthesized, and it was found to be effective. Natural antifouling agents have given researchers an idea, but they don't just come from Marine life. They can also be produced by land life. Some terrestrial organisms in competition will release certain active substances, called allelochemicals, which have negative effects on other nearby organisms, mainly including alkaloids, flavonoids, lignins, terpenoids, phenolic acids and astragalus, etc.[48]. Such allelochemicals are rich in variety and large in quantity. It is an important way to develop natural antifouling agents to screen out the antifouling active substances with high efficiency, broad spectrum and low toxicity/non-toxicity from them. The researchers also found that the alkaloids and other terrestrial natural products based anti-fouling agent, such as tannic acid and its derivatives to barnacle larvae have an anesthetic effect[49]. Antifouling agents complexed with copper or zinc to form copper tannate or zinc tannate are also used in antifouling paints, but the bigger toxicity tannins, could harm to Marine ecological environment, so we must look for other active substances. Liu et al. isolated four cardonolides and eight analogues from Nerium Oleander L (Fig.7), four compounds were found to have significant inhibitory effects on barnacle attachment (EC50= 0.58-230.67 ng/mL), and toxic or low toxic to brine shrimp (LC50= 17.23-100 μg/mL)[50-52].
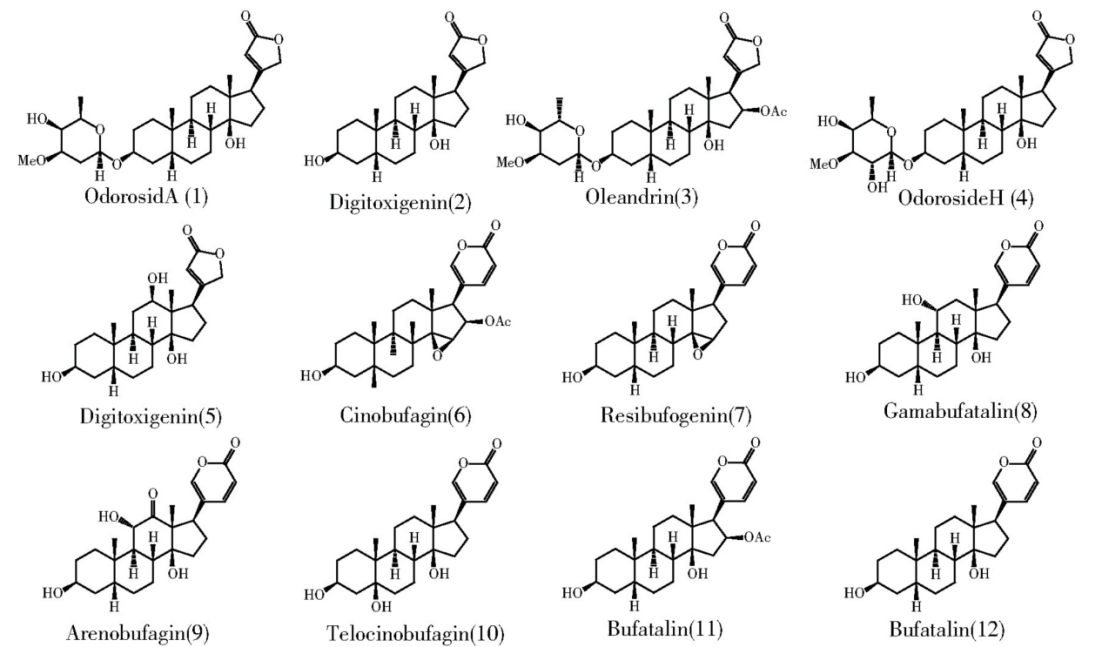
Figure 7. Chemical structures of four compounds (1~4) and eight analogues (5~12) isolated from Nerium oleander L[47].
3.1.2 Low Surface Energy
The surface energy of coral is low, which reduces the surface adhesion strength and prevents biological attachment.
3.1.3 Soft External Tentacles——Dynamic surfaces
The Soft External Tentacles of corals give researchers the inspiration to construct dynamic surfaces. Using Paraphylococcus SPP., which is common in the ocean, as the fouling bacteria, Wang conducted a comparative experiment on single, multiple rigid tentacle structures and single flexible tentacle structures in the flow rate range of 0-5m /s through flume test and simulation[53]. The experimental results showed that the rigid tentacle structure did not respond to the fluid excitation, and the flexible tentacle structure would not only bend along the flow direction, but also swing perpendicular to the flow direction. The bending angle, swing frequency and swing amplitude increased with the increase of the flow velocity. The experimental results also showed that the single flexible tentacle structure had the least amount of bacterial adhesion. Based on the experimental results and simulation, Wang found that the harmonic response of fluid media excitation and tentacle-like is the main mechanism to prevent bacterial adhesion.
3.2 Fish Mucus——Mucus-like Hydrogels
Glands in the skin of teleosts protect the fish from bacterial infections by secreting mucus. Typical teleost fishes have scales composed of very thin sheets of bone, usually so thin that they can be transparent. They are usually more or less rounded in appearance, with smooth margins of cycloid scales and spiky or serrated posterior margins of ctenoid scales. Scales grow in the dermis, the inner layer of skin, and are covered by a thin epidermis or outer layer of skin. The skin contains glands that secrete mucus, which keeps the scales smooth and flexible, and acts as a fungicide, protecting the fish from bacterial infections (Foy and Oxford Science Film 1982:86).
3.3 Pitcher Plant
SLIPS has self-cleaning and anti-fouling properties because of the capability of repelling immiscible liquids and even solids of varying surface tension. The droplets with both high and low surface tension are impossible to adhere, which allows that the droplets on SLIPS-based surfaces can quickly and automatically be shed under the effect of weight. In addition to resisting moisture and lessening the dirt accumulation, the frost also can be resisted by SLIPS-based coatings at temperature just below zero degree and icing in deep freezing conditions. They repair themselves almost instantaneously after scraping, as the injected liquid enters the impaired parts of the fundamental substrate through surface-energy-driven capillary action(Fig.8).
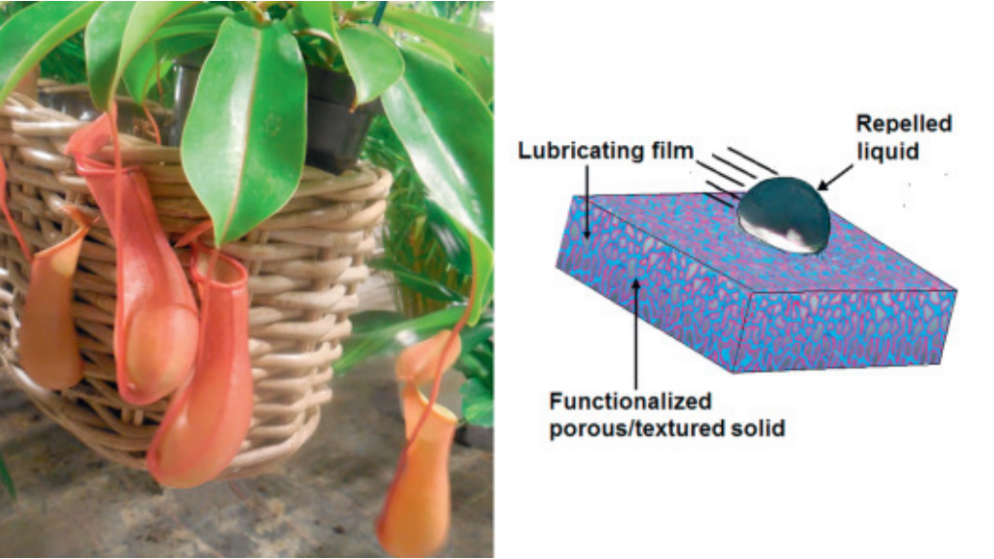
Figure 8. Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces mimicking the frictionless surface on the rim of the cupped leaf of the pitcher plant. Frank Moerman[54].
Pitcher plants grow in a wide range of habitats with harsh soil conditions, from pine forest badlands to coastal sandy marshes, and rely on meat for nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. The Nepenthes pitcher plant, are essentially carnivorous plants that can efficiently attract, trap, retain and ultimately digest insects or small frogs through the frictionless surfaces inside their cup-shaped leaves. Instead of using mechanisms behind the nanostructure surface like lotus leaf to shed liquid, the Nepenthes pitcher plant captures a layer of water, which is utilized as a smooth film. When insects step on it, they slip off the edge of the cup-like leaves into the digestive juices at the bottom, because the water-containing coating repels the oils that are attached on their feet [54]. The opening of these pitchers is lined with disc surfaces that are significant during trapping process through optical and olfactory inducements, as well as nectar given off at the inner rim. It is also significant for catching insects, which slip across their completely wettable anisotropic surfaces. The surface of the conductive area is also thought to be necessary to capture and retain prey because of its different downward orientation of lunate cells and its being covered by a dense tier of epicuticular waxen crystals. Despite these differing mechanisms, both surfaces are very smooth for insects and lead them to drop into the lower area of the pitcher plant. In this area, the specific glands excrete a digestive fluid in order to digest the trapped insects and obtain nutrients from them[55].
3.4 Lotus Leaf
Lotus leaf exhibits an outstanding example of superhydrophobic self-cleaning surface. Growing in muddy water, lotus leaf stays dirt free without being folded. Water droplet pops up on the surface and slight vibration of the leaf will cause it to roll off. In the process the water droplet takes away dust through adsorption and absorption, leaving a clean surface behind. The extreme water repellency and low adhesion feature of lotus leaf can be attributed to a very high water contact angle and low contact angle hysteresis – experiments reported value of water contact angle of lotus leaf is about 164°, and sliding angle (CAH) of 2°, characterizing a stable Cassie-Baxter state[24,29].
Lotus leaf’s surface morphology has made the dominant contribution to its self-cleaning property, compared to its surface chemistry. The epicuticular wax of the upper side lotus leaf is largely composed of hydrocarbon chain alcohols (nonacosanediols and nonacosan-10-ol), which contain polar OH-groups. In fact, research has shown that the wax material of lotus leaf is slightly hydrophilic[56,57]. However, in the layer structure the layers are curved to form tubules, OH-groups are hidden into the layers and only the hydrophobic CH3-groups present at the surface of the tubules(Fig.9) [58].

Figure 9. SEM micrographs (shown at three magnifications) of Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) leaf surface which consists of microstructure formed by papillose epidermal cells covered with 3-D epicuticular wax tubules on surface, which create nanostructure[24].
The hierarchical structure of lotus leaf is crucial for its anti-fouling property. The upper side of lotus leaf is composed of two layers of structure in different sizes - at micron scale, the leaf is covered with convex cells called papillae; at nanoscale, additional layer of wax clusters and wax tubules can be observed covering papillae. This hierarchical structure enables a high surface roughness contributed by both miro-pattern and nano-pattern; the high papillae density and the small space between adjacent papillae, together with wax tubules create a smaller space between papillae, compared to water droplet radius; small papillae diameters, varying height of the papillae, and nanoscale tubule effectively decrease the fraction of liquid-solid area ( \( {Φ_{s}} \) ). These features acting together result in a very high contact angle and low CAH, making possible the retention of Cassie-Baxter state and thus a stable superhydrophobicity the surface[24,58,59]. Lotus leaf effect has inspired development of various superhydrophobic surfaces. One approach is to use lotus leaf itself as a template, through pressing a negative replica of the lotus leaf template on an intrinsically hydrophobic soft polymer like PDMS. The other approach is to mimic and prepare lotus leaf like micro/nanostructures through different physical and chemical methods[30].
3.5 Springtail
Although lotus leaf shows superior water repellency and low adhesion properties, it is not so outstanding in preventing penetration of liquid with much lower surface tension than water – hexadecane with surface tension of 27.5mN/m is observed to spread out on lotus leaf. One of the few examples discovered in nature to exhibit superoleophobic property is a kind of arthropods called springtails. Because springtails breathe through their skin and live in soil, it is critical for them to prevent their skin from wetting and adhesion by water or organic oils. The oleophobic properties of their skin result from the hierarchical structure of the cuticle, which is composed of mushroom-shaped nanoscale interconnected granules (primary granules), and microscale grooves as secondary granules (Fig.10)[60-62].
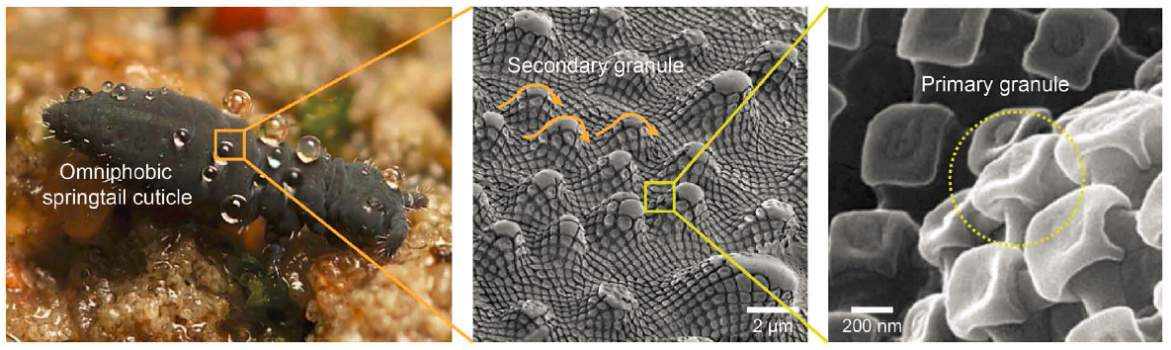
Figure 10. Photograph (courtesy of B. Valentine) of a springtail displaying liquid repellency and resistance to high-pressure raindrops in a flooded habitat (left). SEM images showing the hierarchical system in a springtail cuticle composed of primary and secondary granules (middle and right panels)[61].
The re-entrant curvature is a vital feature of the surface of sprintails to support their superoleophobic properties[60-62]. The re-entrant curvature makes it possible to find a certain point along the curvature where the texture angle is smaller than Young’s contact angle Ɵ (in the case of low surface tension liquid like methanol or octane, Ɵ is smaller than 900 even for solid with very low surface energy)[56]. At this certain point the three-phase energy interactions are balanced, and the liquid is pinned by entrapped air pockets within the nanocavities[62] - the low surface tension liquid wets the top of the structure but is strongly supported at a point underneath the overhanging structure – total wetting is prevented.This re-entrant nanostructure of the springtails surface has inspired development in omniphobic surfaces. The basic principle is to combine surface modified with materials of low surface energy and this re-entrant nanoscale structure. Tuteja et al. demonstrated that a micro-hoodoo surface can be fabricated to possess the re-entrant surface texture via lithography on SiO2 deposition. Then the micro-hoodooed surface was salinized to lower surface energy. Exceptional high contact angles with low surface tension liquids were observed for this salinized micro-hoodoo surface of SiO2, in comparison to a very low \( Ɵ \) (150) for water on a flat SiO2 surface[56].
3.6 Shark Skin——Physical Surface Structure
Shark skin is made up of microscopic scales, which are triangular in shape and generally 200-500 μm long. Along the axis of the body, the scales are arranged with finely spaced ridges (30-100 μm). Previous studies have demonstrated that the scales can alter the flow of water near the skin and may reduce resistance to the body. The same mechanism can help prevent biofouling, as fast-moving water near the surface of the skin can reduce the amount of time microbes can settle on the surface and help wash away any microbes that do. Another hypothesis is that the microscopic shape and surface topography of shark scales prevent microbial settlement. Schumacher et al. produced shark-like antifouling skin by changing the aspect ratio of PDMS surfaces to mimic the morphological features of shark skin[34]. It was found that with the increase of aspect ratio per unit area of shark antifouling skin surface, Ulva attachment density decreased by 42%[63]. Balanus Amphitrite had a 45% reduction in attachment. The experimental results showed that the shark-like surface also had a good effect on reducing bacterial adhesion.
4. Outlook
Inspired by the above antifouling surfaces in nature, novel research prospects in the field of antifouling include low surface energy coatings, synthetic bioactive antifouling agents, etc.
4.1 Low Surface Energy Coatings
Silicon-containing low surface energy anti-adhesion coating is a smooth functional coating based on silicon-modified polymer system[64]. The adhesion resistance of anti-adhesion coating to a variety of water/oil liquid and solid pollutants makes it can be used for a variety of surface self-cleaning, anti-graffiti, anti-corrosion and drag reduction, etc., which has broad application prospects. Because of its low surface energy, low elastic modulus, smooth surface and other characteristics, the organic silicon coating makes the fouling organisms not easy to adhere or adhere weakily, making the removal of foulants easy under the drag of water flow[65]. At the same time, the main chain of silicone is Si - O - Si repeating unit, which has good chemical stability and biocompatibility. What's more, it does not depend on the release of antifouling agents, so it is eco-friendly. Zeng et al. have prepared an organosilicon PDMS antifouling coating modified by surface self-enrichment amphiphilic trimer. Because fluorocarbon ester in the trimer is not compatible with organosilicon, and fluoropolymer surface energy is extremely low[66]. Therefore, in the process of film formation, the trimer is self-enriched on the coating surface to play the function of PEG fouling impedance. The above modification is based on highly compliant polydimethylsiloxane. Although the fouling impedance capacity is improved, the mechanical properties and adhesion are limited. In addition, the complex Marine environment and diversified application scenarios also put forward more requirements for the performance of antifouling coatings. For example, underwater equipment lenses need to be protected by highly transparent antifouling coatings, while high-speed propellers need to be protected by highly wear-resistant antifouling coatings.
To meet the above requirements, Zhang et al. proposed the following low surface energy coatings[64]. The first one is silicone - polyurethane/polyurea antifouling coating. By combining the desorption ability of PDMS, the mechanical strength of polyurethane material and the resistance of anti-fouling group, the Marine anti-fouling material with excellent comprehensive performance can be prepared. Xie et al. used low toxic 2,4, 6-trichlorophenylmaleimide (TCPM) as antifouling group, using PDMS as soft segment and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) as hard segment, silicone polyurethane grafted with antifouling group was synthesized by poly addition reaction (Fig.11). And by adjusting the antifouling group content to regulate the mechanical properties of the material and the resistance to fouling and other properties, the coating named PDMS-PU-x, x represents the mass fraction of TCPM in the polymer. In the process of film formation, due to the large difference in solubility parameters between PDMS and polar hard segments, and the ability of PDMS to migrate spontaneously to the surface, low surface energy surface enriched in PDMS can be formed, which can play a role in desorption of attached fouling organisms. At the same time, polyurethane side link organic antifouling agent TCPM group, can make the low surface energy of the material and antifouling properties of antifouling agent molecules combined, so as to achieve collaborative antifouling. The antifouling groups in the system are connected to PDMS through covalent bonds. On the one hand, it is beneficial to improve the long-term antifouling performance, and on the other hand, it does not release antifouling agents in the Marine environment. It is an environmentally friendly antifouling material. In addition, hydrogen bonds can be formed between the carbamate bonds and the base polar groups in the structure, which will effectively improve the mechanical properties and adhesion of the material. Laboratory experiments showed that the material had good resistance to bacteria, diatoms and barnacle larvae, and the results of 110 days of immersion in solid sea showed that the material had excellent antifouling performance in real sea (Fig.11).
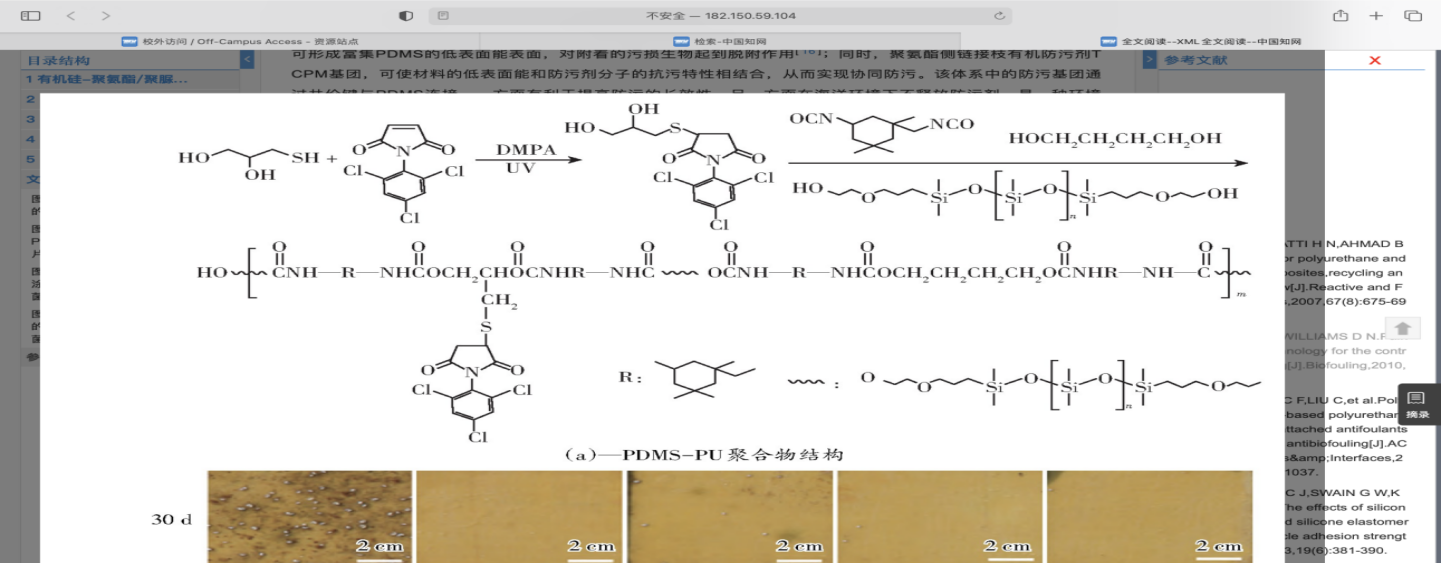

Figure 11. The structure and 110-day real sea immersion experiment results of PDMS-PU[64].
The second one is self-healing silicone Marine antifouling coating. Liu et al. first designed a kind of organosilicone-polyurea antifouling coating with self-stratification and self-healing ability. The self-healing coating was prepared by optimizing the ratio of hard and soft segments in the polymer. The principle is that after the material is damaged, the movement of the highly compliant silicone chain segments makes the urea-base units fully contact, forming dynamic reversible hydrogen bonds, and realizing the self-repair of the material. The present research shows that the nano-diamond modified silicone antifouling coating has the advantages of excellent mechanical properties, ecological friendliness, and excellent dynamic/static antifouling performance(Fig.12).
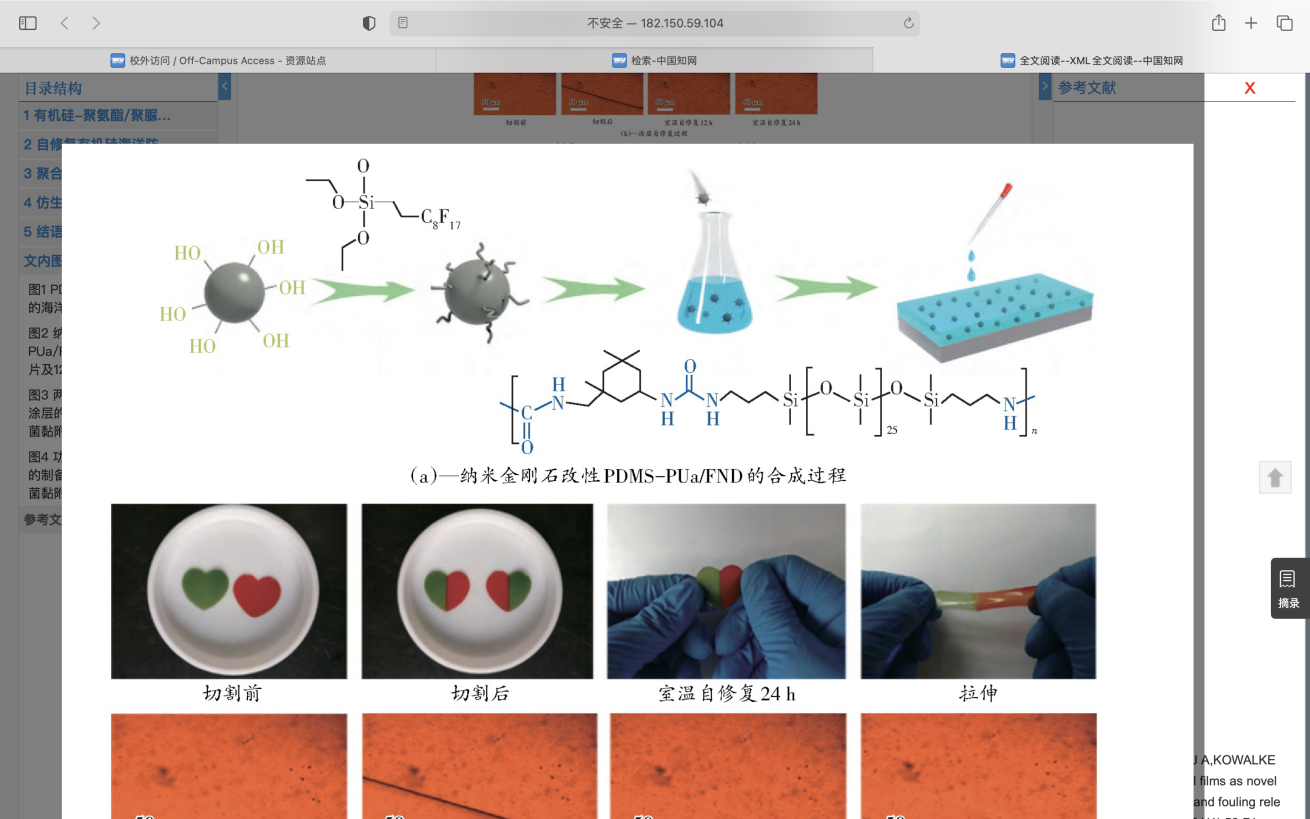
Figure 12. Synthesis of PDMs-PUa/FND modified by nano-diamond[64].
The third one is polymer ceramic antifouling coating. The development of hard silicone coatings by sol-gel method is another way to improve mechanical properties. Various fine linear, membranous and powdery materials can be prepared by sol-gel method. The organic-inorganic hybrid coatings with ultrathin, high stability, high mechanical properties and high smoothness can be prepared by SOL coating. This organic-inorganic hybrid coating can achieve uniformity at the molecular level, and the hybrid coating will have lower surface energy after the introduction of silicon-based structure. Therefore, using sol-gel method is expected to prepare high strength and toughness environmental protection antifouling materials.
4.2 Synthetic Bioactive Antifouling Agents
Many of the natural active antifouling agents mentioned above are not economical to produce on a large scale because of the difficulty in extracting them. So a better way is to synthesize bioactive antifouling agents. Although more than 1 000 potential antifouling compounds have been isolated from natural products, their application as effective antifouling agents in antifouling coatings is still progressing slowly[66]. By synthesizing structurally similar compounds, such as indole, furanones, isothiazolinones, etc., not only has the advantages of natural antifouling agents, but also can be mass produced.
4.3 Mucus-like Hydrogels——Biomimetic Silicone Antifouling Coating
Biomimetic silicone antifouling coating is mainly inspired by the natural ability of many organisms in nature to inhibit dirt, such as the behavior of mucus secretion by fish and other organisms. The silicone oil and other liquids are injected into the silicone antifouling coating, mimicking the secretion of mucus by fish. The silicone oil can migrate to the surface of the coating, forming an ultra-slippery surface that is conducive to the removal of stains. Galhenage et al. prepared a silicone polyurethane coating infused with silicone oil and studied its defilation removal ability. The results showed that the coating had good ability to remove macroalgae, barnacles and mussels.
4.4 Dynamic surfaces
As mentioned above, coral antennae can be deformed to produce dynamic surfaces, thus achieving antifouling effects. Inspired by biological surfaces that can be self-cleaned by deformation and movement, Shivapooja et al. designed a deformable silicone antifouling coating that responds to external stimuli. It is found that the external electric field can stimulate the surface deformation of the polymer, so that the attached biofilm can be effectively removed from the surface. The deformation of the polymer surface also significantly reduces the shear force required for barnacle separation. Therefore, the dynamic surface caused by this deformation makes the fouling organisms difficult to adhere to and easy to be removed, which has a certain application prospect.
5.Conclusion
As a huge economic problem, Marine pollution has been struggling to be solved. So far, researchers have taken a lot of inspiration from living things. Six types of anti-fouling strategies such as natural antifoulants, Mucus-like hydrogels and zwitterionic coatings are already widely used. However, with the increasing awareness of environmental protection, people are more and more aware of the importance of Marine ecological environment. Therefore, non-toxic and harmless to Marine environment and Marine organisms, and at the same time, cost-effective anti-fouling strategies are increasingly needed.
References
[1]. Callow, J. A.; Callow, M. E. Trends in the Development of Environmentally Friendly Fouling-Resistant Marine Coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2 (1), 244. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1251.
[2]. Bixler, G. D.; Theiss, A.; Bhushan, B.; Lee, S. C. Anti-Fouling Properties of Microstructured Surfaces Bio-Inspired by Rice Leaves and Butterfly Wings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 419, 114–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.12.019.
[3]. Wahl, M. Marine Epibiosis. I. Fouling and Antifouling: Some Basic Aspects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 175–189. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps058175.
[4]. Jin HC, Tian LM, Zhao J, Ren LQ. "Stealing from Nature" : Bionic Marine antipollution Technology. Chinese Science Bulletin 2022, 67 (1), 8--10.
[5]. Chambers, L. D.; Stokes, K. R.; Walsh, F. C.; Wood, R. J. K. Modern Approaches to Marine Antifouling Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201 (6), 3642–3652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.08.129.
[6]. Yebra, D. M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling Technology—Past, Present and Future Steps towards Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50 (2), 75–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2003.06.001.
[7]. Magin, C. M.; Cooper, S. P.; Brennan, A. B. Non-Toxic Antifouling Strategies. Mater. Today 2010, 13 (4), 36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(10)70058-4.
[8]. Rosenhahn, A.; Schilp, S.; Kreuzer, H. J.; Grunze, M. The Role of "Inert" Surface Chemistry in Marine Biofouling Prevention. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12 (17), 4275–4286. https://doi.org/10.1039/C001968M.
[9]. Callow, M. E.; Callow, J. A.; Pickett-Heaps, J. D.; Wetherbee, R. Primary Adhesion of Enteromorpha (Chlorophyta, Ulvales) Propagules: Quantitative Settlement Studies and Video Microscopy1. J. Phycol. 1997, 33 (6), 938–947. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3646.1997.00938.x.
[10]. Roberts, D.; Rittschof, D.; Holm, E.; Schmidt, A. R. Factors Influencing Initial Larval Settlement: Temporal, Spatial and Surface Molecular Components. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 150 (2), 203–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(91)90068-8.
[11]. CLARE, A. S.; RITTSCHOF, D.; GERHART, D. J.; MAKI, J. S. Molecular Approaches to Nontoxic Antifouling. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1992, 22 (1–3), 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/07924259.1992.9672258.
[12]. Rittschof, D. Research on Practical Environmentally Benign Antifouling Coatings. In Biofouling; Drr, S., Thomason, J. C., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp 396–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444315462.ch27.
[13]. Epibiosis of Marine Algae and Benthic Invertebrates: Natural Products Chemistry and Other Mechanisms Inhibiting Settlement and Overgrowth | SpringerLink. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-74560-7_4 (accessed 2022-10-24).
[14]. Dobretsov, S.; Abed, R. M. M.; Teplitski, M. Mini-Review: Inhibition of Biofouling by Marine Microorganisms. Biofouling 2013, 29 (4), 423–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.776042.
[15]. Huggett, M. J.; Williamson, J. E.; de Nys, R.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P. D. Larval Settlement of the Common Australian Sea Urchin Heliocidaris Erythrogramma in Response to Bacteria from the Surface of Coralline Algae. Oecologia 2006, 149 (4), 604–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0470-8.
[16]. Huang, S.; Hadfield, M. Composition and Density of Bacterial Biofilms Determine Larval Settlement of the Polychaete Hydroides Elegans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 260, 161–172. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps260161.
[17]. Molino, P. J.; Campbell, E.; Wetherbee, R. Development of the Initial Diatom Microfouling Layer on Antifouling and Fouling-Release Surfaces in Temperate and Tropical Australia. Biofouling 2009, 25 (8), 685–694. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010903089912.
[18]. Staudt, C.; Horn, H.; Hempel, D. C.; Neu, T. R. Volumetric Measurements of Bacterial Cells and Extracellular Polymeric Substance Glycoconjugates in Biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 88 (5), 585–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20241.
[19]. Stoodley, P.; Sauer, K.; Davies, D. G.; Costerton, J. W. Biofilms as Complex Differentiated Communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56 (1), 187–209. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160705.
[20]. Renner, L. D.; Weibel, D. B. Physicochemical Regulation of Biofilm Formation. MRS Bull. Mater. Res. Soc. 2011, 36 (5), 347–355. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2011.65.
[21]. Melo, L. F.; Bott, T. R. Biofouling in Water Systems. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1997, 14 (4), 375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-1777(96)00139-2.
[22]. Bott, T. R.; Miller, P. C. Mechanisms of Biofilm Formation on Aluminium Tubes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. 1983, 33 (3), 177–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.280330307.
[23]. Bixler, G. D.; Bhushan, B. Biofouling: Lessons from Nature. Philos. Transact. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370 (1967), 2381–2417. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2011.0502.
[24]. Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y. C. Natural and Biomimetic Artificial Surfaces for Superhydrophobicity, Self-Cleaning, Low Adhesion, and Drag Reduction. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56 (1), 1–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.04.003.
[25]. Webb, H. K.; Crawford, R. J.; Ivanova, E. P. Wettability of Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 210, 58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.01.020.
[26]. Wang, X.; Fu, C.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, B. A Comprehensive Review of Wetting Transition Mechanism on the Surfaces of Microstructures from Theory and Testing Methods. Materials 2022, 15 (14), 4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144747.
[27]. Wenzel, R. N. RESISTANCE OF SOLID SURFACES TO WETTING BY WATER. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28 (8), 988–994. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50320a024.
[28]. Cassie, A. B. D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546. https://doi.org/10.1039/tf9444000546.
[29]. Yan, Y. Y.; Gao, N.; Barthlott, W. Mimicking Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Grasping the Wetting Process: A Review on Recent Progress in Preparing Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169 (2), 80–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.08.005.
[30]. Latthe, S. S.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Developed by Mimicking Hierarchical Surface Morphology of Lotus Leaf. Molecules 2014, 19 (4), 4256–4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19044256.
[31]. Eral, H. B.; t Mannetje, D. J. C. M.; Oh, J. M. Contact Angle Hysteresis: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291 (2), 247–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2796-6.
[32]. Nosonovsky, M. & Bhushan, B. 2008 Multiscale dissipative mechanisms and hierarchical surfaces. New York, NY: Springer.
[33]. Dhyani, A.; Wang, J.; Halvey, A. K.; Macdonald, B.; Mehta, G.; Tuteja, A. Design and Applications of Surfaces That Control the Accretion of Matter. Science 2021, 373 (6552), eaba5010. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba5010.
[34]. Schumacher, J. F.; Carman, M. L.; Estes, T. G.; Feinberg, A. W.; Wilson, L. H.; Callow, M. E.; Callow, J. A.; Finlay, J. A.; Brennan, A. B. Engineered Antifouling Microtopographies – Effect of Feature Size, Geometry, and Roughness on Settlement of Zoospores of the Green Alga Ulva. Biofouling 2007, 23 (1), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010601136957.
[35]. Scardino, A. J.; de Nys, R. Mini Review: Biomimetic Models and Bioinspired Surfaces for Fouling Control. Biofouling 2011, 27 (1), 73–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2010.536837.
[36]. Halvey, A. K.; Macdonald, B.; Dhyani, A.; Tuteja, A. Design of Surfaces for Controlling Hard and Soft Fouling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377 (2138), 20180266. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2018.0266.
[37]. Chaudhury, M. K. Interfacial Interaction between Low-Energy Surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 1996, 16 (3), 97–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-796X(95)00185-9.
[38]. Packham, D. E. Surface Energy, Surface Topography and Adhesion. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2003, 23 (6), 437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7496(03)00068-X.
[39]. Baier, R. E. Surface Behaviour of Biomaterials: The Theta Surface for Biocompatibility. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17 (11), 1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0444-8.
[40]. Chaudhury, M. K.; Kim, K. H. Shear-Induced Adhesive Failure of a Rigid Slabin Contact with a Thin Confined Film. Eur. Phys. J. E 2007, 23 (2), 175–183. https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2007-10171-x.
[41]. Chung, J. Y.; Chaudhury, M. K. Soft and Hard Adhesion. J. Adhes. 2005, 81 (10–11), 1119–1145. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218460500310887.
[42]. Kendall, K. The Adhesion and Surface Energy of Elastic Solids. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 1971, 4 (8), 1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/4/8/320.
[43]. Ciavarella, M.; Joe, J.; Papangelo, A.; Barber, J. R. The Role of Adhesion in Contact Mechanics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16 (151), 20180738. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2018.0738.
[44]. Amini, S.; Kolle, S.; Petrone, L.; Ahanotu, O.; Sunny, S.; Sutanto, C. N.; Hoon, S.; Cohen, L.; Weaver, J. C.; Aizenberg, J.; Vogel, N.; Miserez, A. Preventing Mussel Adhesion Using Lubricant-Infused Materials. Science 2017, 357 (6352), 668–673. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aai8977.
[45]. Chaudhury, M. K.; Finlay, J. A.; Chung, J. Y.; Callow, M. E.; Callow, J. A. The Influence of Elastic Modulus and Thickness on the Release of the Soft-Fouling Green Alga Ulva Linza (Syn. Enteromorpha Linza ) from Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) Model Networks. Biofouling 2005, 21 (1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010500044377.
[46]. Yin Y. Research on bionic functional surface construction and antifouling mechanism based on harmonic dynamic antifouling strategy. Ph.D. Thesis, jilin university, 2021. https://doi.org/10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.000077.
[47]. Ai XQ Xie QY. Research progress of Marine antifouling coatings based on natural products. Coating industry 2019, 49 (6), 42, 48. https://doi.org/10.12020/j.issn.0253-4312.2019.6.42.
[48]. Xu, Y.; He, H.; Schulz, S.; Liu, X.; Fusetani, N.; Xiong, H.; Xiao, X.; Qian, P.-Y. Potent Antifouling Compounds Produced by Marine Streptomyces. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101 (4), 1331–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.046.
[49]. Clare, A. S. Towards Non Toxic Antifouling. Mar Botechnol 1998.
[50]. Achmad, A.; Kassim, J.; Ghafli, A. U.; Hamdan, H. Mangrove Tannin (Rhizophora Apiculata) Complexes with Copper (II) Ion as an Antifoulant in Antifouling Paint for Fish Net. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1043, 204–208. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1043.204.
[51]. Noor Idora, M. S.; Ferry, M.; Wan Nik, W. B.; Jasnizat, S. Evaluation of Tannin from Rhizophora Apiculata as Natural Antifouling Agents in Epoxy Paint for Marine Application. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 81, 125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2014.12.012.
[52]. Liu, H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Guo, J.-Y.; Su, P.; Qiu, Y.-K.; Ke, C.-H.; Feng, D.-Q. Effective Natural Antifouling Compounds from the Plant Nerium Oleander and Testing. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 127, 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.11.022.
[53]. Wang, J. Study on Antifouling Mechanism of Coral-like Tentacle Biomimetic Structure. https://doi.org/10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2022.000973.
[54]. Moerman, F.; Partington, E. Novel Materials of Construction in the Food Industry. In Handbook of Hygiene Control in the Food Industry; Elsevier, 2016; pp 395–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100155-4.00030-3.
[55]. Scholz, I.; Bückins, M.; Dolge, L.; Erlinghagen, T.; Weth, A.; Hischen, F.; Mayer, J.; Hoffmann, S.; Riederer, M.; Riedel, M.; Baumgartner, W. Slippery Surfaces of Pitcher Plants: Nepenthes Wax Crystals Minimize Insect Attachment via Microscopic Surface Roughness. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213 (7), 1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.035618.
[56]. Tuteja, A.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J. M.; McKinley, G. H.; Cohen, R. E. Robust Omniphobic Surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105 (47), 18200–18205. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804872105.
[57]. Cheng, Y.-T.; Rodak, D. E. Is the Lotus Leaf Superhydrophobic? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86 (14), 144101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1895487.
[58]. Ensikat, H. J.; Ditsche-Kuru, P.; Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Superhydrophobicity in Perfection: The Outstanding Properties of the Lotus Leaf. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 152–161. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.2.19.
[59]. Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14 (24), 1857–1860. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200290020.
[60]. Darmanin, T.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic Properties in Nature. Mater. Today 2015, 18 (5), 273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.01.001.
[61]. Yun, G.-T.; Jung, W.-B.; Oh, M. S.; Jang, G. M.; Baek, J.; Kim, N. I.; Im, S. G.; Jung, H.-T. Springtail-Inspired Superomniphobic Surface with Extreme Pressure Resistance. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4 (8), eaat4978. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aat4978.
[62]. Helbig, R.; Nickerl, J.; Neinhuis, C.; Werner, C. Smart Skin Patterns Protect Springtails. PLoS ONE 2011, 6 (9), e25105. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025105.
[63]. Yue, Y. Research on Bionic Functional Surface Construction and Antifouling Mechanism Based on Dynamic Antifouling Strategy.
[64]. Zhang, Y. Preparation and Application of Low Surface Energy Anti-Adhesion Coating Containing Silicon. https://doi.org/10.27040/d.cnki.ggzdu.2021.000581.
[65]. Zhang, Y. Research Progress of High-Performance Silicone Marine Antifouling Coatings. J Paint Coat. Ind.-83.
[66]. Ai, X. Research Progress of Natural Product-Based Marine Antifouling Coatings. Paint Coat. Ind.
Cite this article
Hu,J.;Huang,S.;Wang,Y.;Chen,X. (2023). Bio-inspired surfaces for resisting marine fouling. Applied and Computational Engineering,7,583-600.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering (CONF-MCEE 2023), Part II
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Callow, J. A.; Callow, M. E. Trends in the Development of Environmentally Friendly Fouling-Resistant Marine Coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2 (1), 244. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1251.
[2]. Bixler, G. D.; Theiss, A.; Bhushan, B.; Lee, S. C. Anti-Fouling Properties of Microstructured Surfaces Bio-Inspired by Rice Leaves and Butterfly Wings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 419, 114–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.12.019.
[3]. Wahl, M. Marine Epibiosis. I. Fouling and Antifouling: Some Basic Aspects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 175–189. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps058175.
[4]. Jin HC, Tian LM, Zhao J, Ren LQ. "Stealing from Nature" : Bionic Marine antipollution Technology. Chinese Science Bulletin 2022, 67 (1), 8--10.
[5]. Chambers, L. D.; Stokes, K. R.; Walsh, F. C.; Wood, R. J. K. Modern Approaches to Marine Antifouling Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201 (6), 3642–3652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.08.129.
[6]. Yebra, D. M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling Technology—Past, Present and Future Steps towards Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50 (2), 75–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2003.06.001.
[7]. Magin, C. M.; Cooper, S. P.; Brennan, A. B. Non-Toxic Antifouling Strategies. Mater. Today 2010, 13 (4), 36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(10)70058-4.
[8]. Rosenhahn, A.; Schilp, S.; Kreuzer, H. J.; Grunze, M. The Role of "Inert" Surface Chemistry in Marine Biofouling Prevention. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12 (17), 4275–4286. https://doi.org/10.1039/C001968M.
[9]. Callow, M. E.; Callow, J. A.; Pickett-Heaps, J. D.; Wetherbee, R. Primary Adhesion of Enteromorpha (Chlorophyta, Ulvales) Propagules: Quantitative Settlement Studies and Video Microscopy1. J. Phycol. 1997, 33 (6), 938–947. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3646.1997.00938.x.
[10]. Roberts, D.; Rittschof, D.; Holm, E.; Schmidt, A. R. Factors Influencing Initial Larval Settlement: Temporal, Spatial and Surface Molecular Components. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 150 (2), 203–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(91)90068-8.
[11]. CLARE, A. S.; RITTSCHOF, D.; GERHART, D. J.; MAKI, J. S. Molecular Approaches to Nontoxic Antifouling. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1992, 22 (1–3), 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/07924259.1992.9672258.
[12]. Rittschof, D. Research on Practical Environmentally Benign Antifouling Coatings. In Biofouling; Drr, S., Thomason, J. C., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp 396–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444315462.ch27.
[13]. Epibiosis of Marine Algae and Benthic Invertebrates: Natural Products Chemistry and Other Mechanisms Inhibiting Settlement and Overgrowth | SpringerLink. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-74560-7_4 (accessed 2022-10-24).
[14]. Dobretsov, S.; Abed, R. M. M.; Teplitski, M. Mini-Review: Inhibition of Biofouling by Marine Microorganisms. Biofouling 2013, 29 (4), 423–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.776042.
[15]. Huggett, M. J.; Williamson, J. E.; de Nys, R.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P. D. Larval Settlement of the Common Australian Sea Urchin Heliocidaris Erythrogramma in Response to Bacteria from the Surface of Coralline Algae. Oecologia 2006, 149 (4), 604–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0470-8.
[16]. Huang, S.; Hadfield, M. Composition and Density of Bacterial Biofilms Determine Larval Settlement of the Polychaete Hydroides Elegans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 260, 161–172. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps260161.
[17]. Molino, P. J.; Campbell, E.; Wetherbee, R. Development of the Initial Diatom Microfouling Layer on Antifouling and Fouling-Release Surfaces in Temperate and Tropical Australia. Biofouling 2009, 25 (8), 685–694. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010903089912.
[18]. Staudt, C.; Horn, H.; Hempel, D. C.; Neu, T. R. Volumetric Measurements of Bacterial Cells and Extracellular Polymeric Substance Glycoconjugates in Biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 88 (5), 585–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20241.
[19]. Stoodley, P.; Sauer, K.; Davies, D. G.; Costerton, J. W. Biofilms as Complex Differentiated Communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56 (1), 187–209. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160705.
[20]. Renner, L. D.; Weibel, D. B. Physicochemical Regulation of Biofilm Formation. MRS Bull. Mater. Res. Soc. 2011, 36 (5), 347–355. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2011.65.
[21]. Melo, L. F.; Bott, T. R. Biofouling in Water Systems. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1997, 14 (4), 375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-1777(96)00139-2.
[22]. Bott, T. R.; Miller, P. C. Mechanisms of Biofilm Formation on Aluminium Tubes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. 1983, 33 (3), 177–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.280330307.
[23]. Bixler, G. D.; Bhushan, B. Biofouling: Lessons from Nature. Philos. Transact. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370 (1967), 2381–2417. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2011.0502.
[24]. Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y. C. Natural and Biomimetic Artificial Surfaces for Superhydrophobicity, Self-Cleaning, Low Adhesion, and Drag Reduction. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56 (1), 1–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.04.003.
[25]. Webb, H. K.; Crawford, R. J.; Ivanova, E. P. Wettability of Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 210, 58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.01.020.
[26]. Wang, X.; Fu, C.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, B. A Comprehensive Review of Wetting Transition Mechanism on the Surfaces of Microstructures from Theory and Testing Methods. Materials 2022, 15 (14), 4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144747.
[27]. Wenzel, R. N. RESISTANCE OF SOLID SURFACES TO WETTING BY WATER. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28 (8), 988–994. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50320a024.
[28]. Cassie, A. B. D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546. https://doi.org/10.1039/tf9444000546.
[29]. Yan, Y. Y.; Gao, N.; Barthlott, W. Mimicking Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Grasping the Wetting Process: A Review on Recent Progress in Preparing Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169 (2), 80–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.08.005.
[30]. Latthe, S. S.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Developed by Mimicking Hierarchical Surface Morphology of Lotus Leaf. Molecules 2014, 19 (4), 4256–4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19044256.
[31]. Eral, H. B.; t Mannetje, D. J. C. M.; Oh, J. M. Contact Angle Hysteresis: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291 (2), 247–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2796-6.
[32]. Nosonovsky, M. & Bhushan, B. 2008 Multiscale dissipative mechanisms and hierarchical surfaces. New York, NY: Springer.
[33]. Dhyani, A.; Wang, J.; Halvey, A. K.; Macdonald, B.; Mehta, G.; Tuteja, A. Design and Applications of Surfaces That Control the Accretion of Matter. Science 2021, 373 (6552), eaba5010. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba5010.
[34]. Schumacher, J. F.; Carman, M. L.; Estes, T. G.; Feinberg, A. W.; Wilson, L. H.; Callow, M. E.; Callow, J. A.; Finlay, J. A.; Brennan, A. B. Engineered Antifouling Microtopographies – Effect of Feature Size, Geometry, and Roughness on Settlement of Zoospores of the Green Alga Ulva. Biofouling 2007, 23 (1), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010601136957.
[35]. Scardino, A. J.; de Nys, R. Mini Review: Biomimetic Models and Bioinspired Surfaces for Fouling Control. Biofouling 2011, 27 (1), 73–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2010.536837.
[36]. Halvey, A. K.; Macdonald, B.; Dhyani, A.; Tuteja, A. Design of Surfaces for Controlling Hard and Soft Fouling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377 (2138), 20180266. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2018.0266.
[37]. Chaudhury, M. K. Interfacial Interaction between Low-Energy Surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 1996, 16 (3), 97–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-796X(95)00185-9.
[38]. Packham, D. E. Surface Energy, Surface Topography and Adhesion. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2003, 23 (6), 437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7496(03)00068-X.
[39]. Baier, R. E. Surface Behaviour of Biomaterials: The Theta Surface for Biocompatibility. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17 (11), 1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-0444-8.
[40]. Chaudhury, M. K.; Kim, K. H. Shear-Induced Adhesive Failure of a Rigid Slabin Contact with a Thin Confined Film. Eur. Phys. J. E 2007, 23 (2), 175–183. https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2007-10171-x.
[41]. Chung, J. Y.; Chaudhury, M. K. Soft and Hard Adhesion. J. Adhes. 2005, 81 (10–11), 1119–1145. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218460500310887.
[42]. Kendall, K. The Adhesion and Surface Energy of Elastic Solids. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 1971, 4 (8), 1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/4/8/320.
[43]. Ciavarella, M.; Joe, J.; Papangelo, A.; Barber, J. R. The Role of Adhesion in Contact Mechanics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16 (151), 20180738. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2018.0738.
[44]. Amini, S.; Kolle, S.; Petrone, L.; Ahanotu, O.; Sunny, S.; Sutanto, C. N.; Hoon, S.; Cohen, L.; Weaver, J. C.; Aizenberg, J.; Vogel, N.; Miserez, A. Preventing Mussel Adhesion Using Lubricant-Infused Materials. Science 2017, 357 (6352), 668–673. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aai8977.
[45]. Chaudhury, M. K.; Finlay, J. A.; Chung, J. Y.; Callow, M. E.; Callow, J. A. The Influence of Elastic Modulus and Thickness on the Release of the Soft-Fouling Green Alga Ulva Linza (Syn. Enteromorpha Linza ) from Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) Model Networks. Biofouling 2005, 21 (1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010500044377.
[46]. Yin Y. Research on bionic functional surface construction and antifouling mechanism based on harmonic dynamic antifouling strategy. Ph.D. Thesis, jilin university, 2021. https://doi.org/10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.000077.
[47]. Ai XQ Xie QY. Research progress of Marine antifouling coatings based on natural products. Coating industry 2019, 49 (6), 42, 48. https://doi.org/10.12020/j.issn.0253-4312.2019.6.42.
[48]. Xu, Y.; He, H.; Schulz, S.; Liu, X.; Fusetani, N.; Xiong, H.; Xiao, X.; Qian, P.-Y. Potent Antifouling Compounds Produced by Marine Streptomyces. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101 (4), 1331–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.046.
[49]. Clare, A. S. Towards Non Toxic Antifouling. Mar Botechnol 1998.
[50]. Achmad, A.; Kassim, J.; Ghafli, A. U.; Hamdan, H. Mangrove Tannin (Rhizophora Apiculata) Complexes with Copper (II) Ion as an Antifoulant in Antifouling Paint for Fish Net. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1043, 204–208. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1043.204.
[51]. Noor Idora, M. S.; Ferry, M.; Wan Nik, W. B.; Jasnizat, S. Evaluation of Tannin from Rhizophora Apiculata as Natural Antifouling Agents in Epoxy Paint for Marine Application. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 81, 125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2014.12.012.
[52]. Liu, H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Guo, J.-Y.; Su, P.; Qiu, Y.-K.; Ke, C.-H.; Feng, D.-Q. Effective Natural Antifouling Compounds from the Plant Nerium Oleander and Testing. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 127, 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.11.022.
[53]. Wang, J. Study on Antifouling Mechanism of Coral-like Tentacle Biomimetic Structure. https://doi.org/10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2022.000973.
[54]. Moerman, F.; Partington, E. Novel Materials of Construction in the Food Industry. In Handbook of Hygiene Control in the Food Industry; Elsevier, 2016; pp 395–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100155-4.00030-3.
[55]. Scholz, I.; Bückins, M.; Dolge, L.; Erlinghagen, T.; Weth, A.; Hischen, F.; Mayer, J.; Hoffmann, S.; Riederer, M.; Riedel, M.; Baumgartner, W. Slippery Surfaces of Pitcher Plants: Nepenthes Wax Crystals Minimize Insect Attachment via Microscopic Surface Roughness. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213 (7), 1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.035618.
[56]. Tuteja, A.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J. M.; McKinley, G. H.; Cohen, R. E. Robust Omniphobic Surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105 (47), 18200–18205. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804872105.
[57]. Cheng, Y.-T.; Rodak, D. E. Is the Lotus Leaf Superhydrophobic? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86 (14), 144101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1895487.
[58]. Ensikat, H. J.; Ditsche-Kuru, P.; Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Superhydrophobicity in Perfection: The Outstanding Properties of the Lotus Leaf. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 152–161. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.2.19.
[59]. Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14 (24), 1857–1860. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200290020.
[60]. Darmanin, T.; Guittard, F. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic Properties in Nature. Mater. Today 2015, 18 (5), 273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.01.001.
[61]. Yun, G.-T.; Jung, W.-B.; Oh, M. S.; Jang, G. M.; Baek, J.; Kim, N. I.; Im, S. G.; Jung, H.-T. Springtail-Inspired Superomniphobic Surface with Extreme Pressure Resistance. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4 (8), eaat4978. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aat4978.
[62]. Helbig, R.; Nickerl, J.; Neinhuis, C.; Werner, C. Smart Skin Patterns Protect Springtails. PLoS ONE 2011, 6 (9), e25105. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025105.
[63]. Yue, Y. Research on Bionic Functional Surface Construction and Antifouling Mechanism Based on Dynamic Antifouling Strategy.
[64]. Zhang, Y. Preparation and Application of Low Surface Energy Anti-Adhesion Coating Containing Silicon. https://doi.org/10.27040/d.cnki.ggzdu.2021.000581.
[65]. Zhang, Y. Research Progress of High-Performance Silicone Marine Antifouling Coatings. J Paint Coat. Ind.-83.
[66]. Ai, X. Research Progress of Natural Product-Based Marine Antifouling Coatings. Paint Coat. Ind.









