1. Introduction
Topological sorting describes the relationship between the vertices of the graph G or DAG by providing a linearized sequence of the vertices [1]. First introduced by Kahn, the algorithm can be applied to arrange activities such that each group of activities can relate to the previous activities in large networks [2]. Topological sorting plays an essential role in various applications like semantic analysis in compiler design, management tool Gantt charts, and calculation models determining exchanged power paths in integrated and sustainable power systems [1, 3].
C++ and Python are two widely used programming languages. In 1980, Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Laboratories contributed to the first revolutionary step in moving from C to C++ with improvements on the imperative features and added constructions to support object-oriented programming [4]. At the beginning of the 1990s, the Python project was first begun by Guido Van Rossum, entitled BDFL. Since then, Van Rossum and the Python community have led to the further development of Python by reviewing and commenting on the Python Enhancement Proposal (PEP) [5]. As a compiled language, C++ directly converts the source code into machine code, whereas interpreter-based Python needs to translate the source code into bytecode through an interpreter and then into machine code. Thus, C++ theoretically has higher execution efficiency [6]. Nowadays, the execution efficiency of an algorithm is super essential, especially when the algorithm is dealing with a large data set of a billion or larger magnitude. To better understand the difference in efficiency between C++ and Python and to test the potential special situation in which C++ does not run faster, this study specifically compares the efficiency of the C++ and Python algorithms through Topological sorting. Both programs are compared by their execution time spent on each randomly generated DAG. This research provides a good suggestion as to which language is superior when execution efficiency is seriously considered in some projects.
2. Literature review
One of the previous studies focusing on program energy efficiency studied the influence of the languages, compiler, and implementation choices on three programs: Fast Fourier Transform, Linked List Insertion/Deletion, and Quicksort. The results showed that a carefully selected language, optimization flag and data structure are significant for conserving energy [7].
If an appropriate language is selected carefully, it will also save a lot of execution time. Previous research used many sorting algorithms including Quicksort, Mergesort, Bubble Sort, Insertion Sort, and Selection Sort to compare C++ and Python execution efficiency [8, 9]. One researcher implemented the Selection sort in C/C++, Python, and Rust and collected the execution time. The data displayed that since the Python language has fewer lines of code, it runs faster and consumes less storage compared to other two languages [8]. This research introduced a negative relationship between the number of lines of code and execution efficiency. Another study compared the efficiency of the bubble sort algorithm and insertion sort algorithm in Rust and Python. It is observed that Python is less efficient than Rust in both algorithms [10]. So far, comparing C++ and Python efficiency through Topological sorting has not been found in the preceding study. In this research, the execution efficiency of running Topological sorting in C++ and Python will be unveiled.
3. Methodology
3.1. Topological sorting algorithm
In order to compare the time efficiency of C++ and Python, two programs are controlled by using the same Topological Sorting algorithm based on the method as shown in Figure 1: 1. Create a deque dq and a list (or a vector) L. 2. Insert all vertices with 0 indegree at the back of dq. 3. If dq is empty, return L. Otherwise, continue. 4. Add the first element k in dq to L. 5. Delete k from dq. 6. Iterate through vertices. 7. If there is an edge directed from k to the vertices i, subtract 1 from the integer of i. 8. If the indgree of i is 0, insert i at the back of dq. 9. After the iteration is done, go back to step 3.
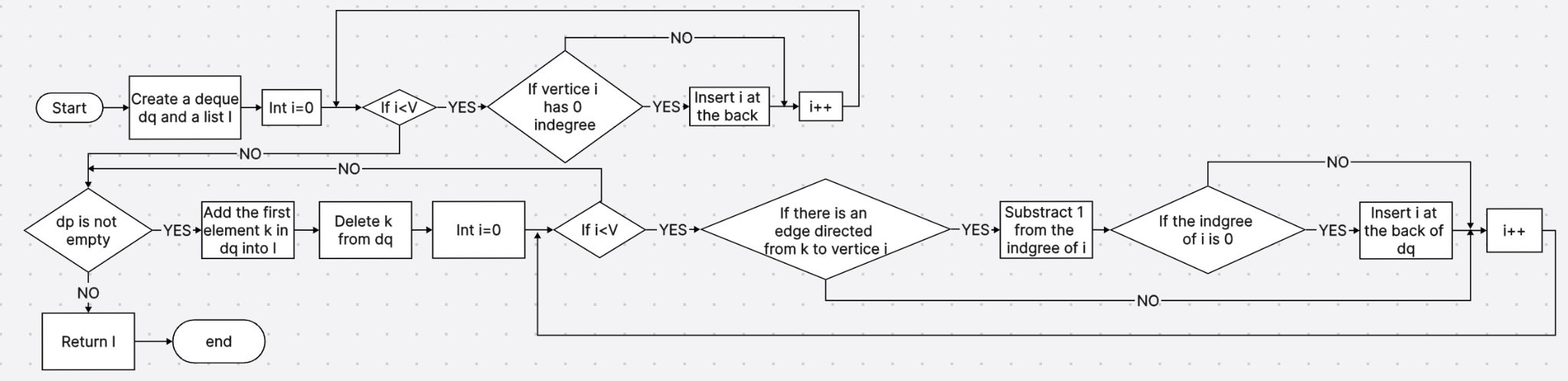
Figure 1. Flow chart of topological sorting algorithm.
vector <int> topoSort(vector<vector<int>> matrix, int n){
deque <int> dq;
vector <int> results;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if (indegree[i]==0) dq.push_back(i);
}
while (!dq.empty()){
int k=dq.front();
results.push_back (k);
dq.pop_front();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(matrix[k][i]==1){
indegree[i]--;
if (indegree[i]==0) dq.push_back(i);
}
}
}
return results;
}
3.1.1. Python program: def topological_sort(n,graph)
dq = deque()
result = []
for i in range (n):
if in_degree[i] == 0:
dq.append(i)
while len(dq)>0:
k = dq.popleft()
result.append(k)
for i in range (n):
if graph[k][i]>0:
in_degree[i] -= 1
if in_degree[i] == 0:
dq.append(i)
return result
3.2. Testing sample
To measure the execution time, the clock( ) function is utilized in C++. By subtracting the start time of the Topological Sorting from the end time and using CLOCKS_PER_SEC to convert the result into a number in seconds, the time elapsed by C++ algorithm is obtained. Similarly, time( ) is imported in Python in order to gain the elapsed time in the Python algorithm by calculating the time in seconds since epoch (the point where time starts). The following Python program is used to randomly generate a n*n matrix that represents a DAG with n vertices. This program generates 3 100*100 matrixes and 2 5000*5000 matrixes. For each matrix, both C++ and Python programs are runed for 50 times, and the average execution time and Standard Deviation are calculated.
def generate_adjacency_matrix(n):
matrix = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
for i in tqdm(range(n)):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if not has_path(matrix, j, i):
matrix[i][j] = random.choice([0, 1])
return matrix
def has_path(matrix, start, end):
stack = [start]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node == end:
return True
for neighbor in range(len(matrix)):
if matrix[node][neighbor] == 1:
stack.append(neighbor)
return False
4. Findings
Table 1. Execution time of C++ and Python for M1, M2, and M3 DAG with 100 vertices.
C++ | Python | C++ | Python | C++ | Python | |
Average (s) | 0.000781 | 0.005687 | 0.000767 | 0.003768 | 0.000951 | 0.001850 |
STD (s) | 0.000049 | 0.007429 | 0.000006 | 0.001570 | 0.000189 | 0.000514 |
Number of Vertices V | 100_M1 | 100_M1 | 100_M2 | 100_M2 | 100_M3 | 100_M3 |
Table 2. Execution time of C++ and Python for M4 and M5 DAG with 5000 vertices.
C++ | Python | C++ | Python | |
Average (s) | 0.825765 | 5.280759 | 0.801024 | 3.289814 |
STD (s) | 0.014798 | 0.933097 | 0.032283 | 0.476987 |
Number of Vertices V | 5000_M4 | 5000_M4 | 5000_M5 | 5000_M5 |
As the V is greater, the average execution time and the Standard Deviation for C++ and Python are also greater. For a DAG with 100 vertices, the C++ algorithm runs faster than Python (See Table 2). The execution time of the Python algorithm is much longer than that of C++ for a DAG with 5000 vertices (See Table 3). Hence, it can be concluded that although the C++ algorithm has 4 more lines of code than Python, it is still more efficient than Python. This is probably because the time Python wastes on the procedure of converting the source code into bytecode exceeds the time Python saves from its smaller lines of code. In addition, the execution time of Python is more unstable due to its larger Standard Deviation (See Table 2 and Table 3). Indeed, during the testing process, Python sometimes runs for a long time, even exceeding 7s when V is 5000, while sometimes it runs as quickly as C++ when V is 100. However, execution times in each run are close to each other in C++ code.
5. Conclusion
In this passage, two different coding languages, C++ and Python, are compared in their time efficiency to run the Topological Sorting algorithm. For each randomly generated DAG, the results of execution time are collected. By comparing the average execution time C++ and Python need to run a 100 or 5000 vertices DAG and the average Standard Deviation, it is observed that the efficiency of C++ is greater than that of Python. However, there are flaws in this paper. First, the tested DAGs are not enough to reveal that the C++ algorithm is more efficient than Python universally. In other words, more DAGs with different vertices should be generated and tested. Additionally, in C++ program, a vector is used to store the sorted vertices, while a list is used in Python. Though the possibly existing difference between a vector and a list during execution does not probably have a critical impact on the total execution time, the error of this difference should still be considered.
References
[1]. Mohana Lakshmi, J., Suresh, H. N., & Pai, V. K. (2018). Nonlinear Speed Estimator and Fuzzy Control for Sensorless IM Drive. In Proceedings of First International Conference on Smart System, Innovations and Computing: SSIC 2017, Jaipur, India (pp. 307-318). Springer Singapore.
[2]. Kahn, A. B. (1962). Topological Sorting of Large Networks. Communications of the ACM, 5(11), 558-562.
[3]. M. Soyah, "Exchanged electricity paths calculation in integrated and sustainable power systems using topological sort," 2021 12th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), Hammamet, Tunisia, 2021, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/IREC52758.2021.9624764.
[4]. Sebesta, R. W. (2012). Concepts of Programming Languages - 10th Edition. Pearson Addison Wesley.
[5]. Nosrati, M. (2011). Python: An Appropriate Language for Real World Programming. World Applied Programming, 1(2), 110-117.
[6]. Zehra, F., Javed, M., Khan, D., & Pasha, M. (2020). Comparative Analysis of C++ and Python in Terms of Memory and Time. Preprints.org. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202012.0516.v1.
[7]. S. Abdulsalam, D. Lakomski, Q. Gu, T. Jin and Z. Zong, "Program energy efficiency: The impact of language, compiler and implementation choices," International Green Computing Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 2014, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/IGCC.2014.7039169.
[8]. Naz, A., Nawaz, H., Maitlo, A., & Hassan, S. M. (2021). Implementation of Selection Sort Algorithm in Various Programming Languages. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2021/1071032021.
[9]. Tait, J., Ripke, T., Roger, L., & Matsuo, T. (2018, December). Comparing Python and C++ Efficiency Through Sorting. In 2018 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI) (pp. 864-871). IEEE.
[10]. Agha, F. A., & Nawaz, H. (2021). Comparison of Bubble and Insertion Sort in Rust and Python Language. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2021/761022021.
Cite this article
Zhang,Y. (2024). Comparative study of the execution efficiency of Python and C++——Based on topological sorting. Applied and Computational Engineering,34,13-17.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Mohana Lakshmi, J., Suresh, H. N., & Pai, V. K. (2018). Nonlinear Speed Estimator and Fuzzy Control for Sensorless IM Drive. In Proceedings of First International Conference on Smart System, Innovations and Computing: SSIC 2017, Jaipur, India (pp. 307-318). Springer Singapore.
[2]. Kahn, A. B. (1962). Topological Sorting of Large Networks. Communications of the ACM, 5(11), 558-562.
[3]. M. Soyah, "Exchanged electricity paths calculation in integrated and sustainable power systems using topological sort," 2021 12th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), Hammamet, Tunisia, 2021, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/IREC52758.2021.9624764.
[4]. Sebesta, R. W. (2012). Concepts of Programming Languages - 10th Edition. Pearson Addison Wesley.
[5]. Nosrati, M. (2011). Python: An Appropriate Language for Real World Programming. World Applied Programming, 1(2), 110-117.
[6]. Zehra, F., Javed, M., Khan, D., & Pasha, M. (2020). Comparative Analysis of C++ and Python in Terms of Memory and Time. Preprints.org. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202012.0516.v1.
[7]. S. Abdulsalam, D. Lakomski, Q. Gu, T. Jin and Z. Zong, "Program energy efficiency: The impact of language, compiler and implementation choices," International Green Computing Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 2014, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/IGCC.2014.7039169.
[8]. Naz, A., Nawaz, H., Maitlo, A., & Hassan, S. M. (2021). Implementation of Selection Sort Algorithm in Various Programming Languages. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2021/1071032021.
[9]. Tait, J., Ripke, T., Roger, L., & Matsuo, T. (2018, December). Comparing Python and C++ Efficiency Through Sorting. In 2018 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI) (pp. 864-871). IEEE.
[10]. Agha, F. A., & Nawaz, H. (2021). Comparison of Bubble and Insertion Sort in Rust and Python Language. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2021/761022021.









