

Volume 156
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-SEML 2025 Symposium: Intefrating AI into Software Engineering
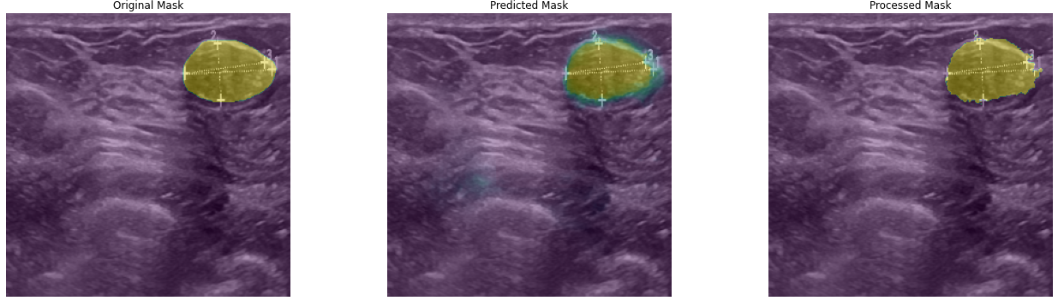
The segmentation of ultrasound image for breast cancer is an important task in the field of biomedical research. The traditional U-Net model, with its simple structure and remarkable performance, this approach has found extensive application in the segmentation of medical images. However, U-Net tends to be affected by background noise when handling images with complex backgrounds or blurry boundaries, which may impact the segmentation accuracy. To address this issue, the Attention U-Net model incorporates an attention mechanism, enabling the model to selectively focus on critical target areas within the image, thereby improving segmentation accuracy. This paper further optimizes the Attention U-Net architecture by increasing the depth of both the encoder and decoder sections, enhancing the model's capacity for feature extraction and image reconstruction. Consequently, both the accuracy and robustness of segmentation are enhanced. The experimental findings indicate that the proposed modified Attention U-Net model significantly outperforms traditional methods in breast ultrasound image segmentation tasks. It effectively handles various types of breast images, particularly those with complex backgrounds, blurred targets, or small sizes, maintaining high segmentation accuracy. This study offers an effective solution for the automated segmentation of breast ultrasound images, with substantial implications for enhancing both the automation and diagnostic efficiency in medical image analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


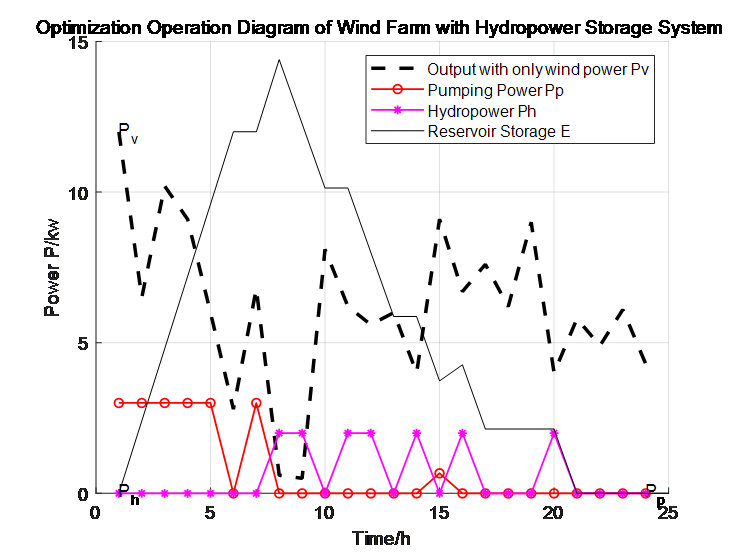
With the goal of maximizing the benefits of Contained Storage wind farm, a particle swarm algorithm based simulation analysis is proposed for the optimized operation of Contained Storage wind farm . The simulation results show that the optimized operation and power supply of Contained Storage Wind Farm not only improves the benefit of the wind farm, but also smoothes the power output of the wind farm, which will be helpful to increase the share of wind power in the power system.

 View pdf
View pdf


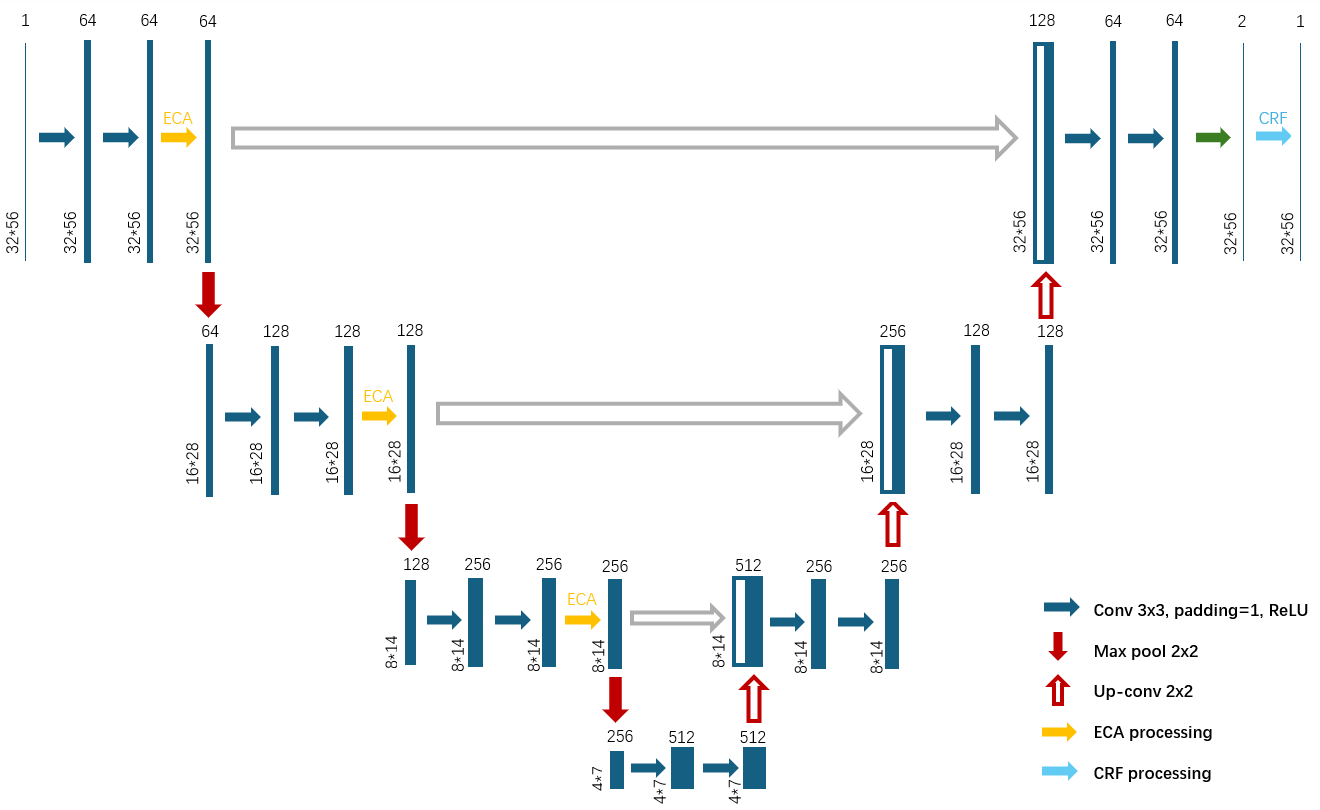
Pulmonary nodule segmentation plays a crucial role in the early detection and diagnosis of lung cancer, significantly impacting patient outcomes. The U-net model has emerged as a useful architecture in medical image processing like pulmonary nodule segmentation, gaining widespread popularity. However, U-net suffers from poor fine segmentation capabilities and the presence of noise in the segmentation results. In this study, we propose an Enhanced U-net model to improve segmentation results. The Enhanced U-net uses ECA and CRF modules. ECA module can make the model focus more on important features and improve the fine segmentation ability of the model. Meanwhile, CRF module allows the model to further refine the results, reduce the noise and boundary discontinuities. Utilizing the LIDC dataset, we evaluate the model’s performance through indicators such as recall, IoU, Dice score. Our findings show that Enhanced U-net can achieve the best performance among all U-net based models. And Enhanced U-net can significantly improve segmentation outcomes for small or blurred nodules.

 View pdf
View pdf


Blockchain technology has become a significant paradigm which has been utilized to transform various industries and applications. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature has led to widespread adoption in diverse fields such as finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and the Internet of Things (IoT). This paper presents a comprehensive survey of blockchain technology, focusing on three key aspects: consensus algorithms, data storage mechanisms, and blockchain architectures. We provide a detailed overview of various consensus algorithms, including Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Proof of Authentication (PoAh), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), discussing their mechanisms, advantages, limitations, and challenges. Furthermore, we explore different data storage mechanisms, such as on-chain, off-chain, and hybrid storage, analyzing their implications for scalability, security, and efficiency. We also delve into various blockchain architectures, including single, dual, and multi-blockchain architectures, examining their suitability for different applications. This survey provides a holistic understanding of blockchain technology, highlighting its potential, challenges, and future directions. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers, developers, and practitioners interested in exploring and leveraging the capabilities of blockchain.

 View pdf
View pdf


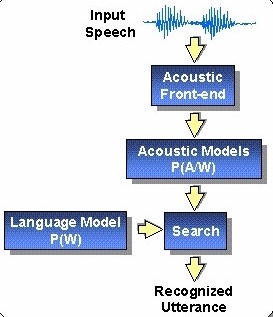
Speech recognition technology has developed from the 1950s to the present, evolving from template matching methods to Hidden Markov Model (HMM) statistical methods, then to machine learning techniques, and finally to the current use of Transformer technology for speech recognition tasks. However, the Transformer model has not yet been widely adopted in the field of speech recognition. This paper explores the characteristics of Transformer model, combines it with the characteristics of speech recognition tasks, analyzes the challenges associated with using Transformer model for these tasks, and provides suggestions for directions of future research, so as to facilitate the application of Transformer models in speech recognition. The paper finds that the reasons for the limited application of Transformer models in speech recognition tasks mainly include their numerous parameters, complex structure, and high computational costs, which have prevented their extensive use in this field. In the future, efforts should focus on enhancing model compression and lightweight design, and improving the attention mechanism to boost the applicability of Transformer models in speech recognition.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, AIGC has made significant progress in various fields, particularly in the generation of 2D images. However, in the 3D domain, traditional 2D model training methods have not achieved ideal results due to the lack of sufficient high-quality datasets. To address this issue, methods such as utilizing 2D diffusion models as priors and emerging 3D Gaussian Splatting have demonstrated the significant potential of AIGC in the 3D field. With the rapid development of AIGC 3D, the related evaluation metrics have not yet been unified. Although quantitative evaluation of 3D content is challenging, establishing a standardized evaluation system is crucial for future research. This article summarizes the technological progress and evaluation systems in the AIGC 3D field, focusing particularly on the potential applications of 3D Gaussian point set technology, and discusses future development directions and the challenges they face.

 View pdf
View pdf




