1. Introduction
This study examines the business risks associated with the Silicon Valley banking model, specifically focusing on the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank. The collapse of this major lending institution for technology startups has raised concerns about the broader implications of business risks within the financial industry. The study begins by outlining the investment strategy and balance sheet characteristics of Silicon Valley Bank. It highlights the bank's specialization in providing financial services to science and technology enterprises, its rapid asset growth during the pandemic, and its high proportion of financial investments. The paper emphasizes the contribution of deposits and the loose monetary policy of the Federal Reserve to the growth of total liabilities. It identifies interest rate risk and liquidity risk as the primary factors underlying the bank's unexpected bankruptcy. The study then delves into Silicon Valley Bank's exposure to interest rates, emphasizing its heavy investment in long-term bonds. This investment strategy creates a mismatch between assets and liabilities, exposing the bank to interest rate and liquidity risks. The paper explains how the aggressive rate hikes by the Federal Reserve led to a sharp decline in the market value of the bank's long-term portfolio investments, triggering depositor runs and market shorting.
Furthermore, the study examines the asset and liability structure of Silicon Valley Bank, highlighting the significant mismatch between short-term loans and long-term investments. This mismatch, combined with the Fed's interest rate hikes and tightening market liquidity, ultimately evolves into bank liquidity risk. The paper also points out deficiencies in managing interest rate risk and the underestimation of interest rate risk by not reflecting unrealized gains and losses in the net capital amount.
The study further discusses the quality of Silicon Valley Bank's management, addressing structural and institutional deficiencies in asset liability management. It highlights-issues related to stability, diversity, appropriateness, and initiative in managing debt quality. Additionally, the study explores the regulatory oversight of Silicon Valley Bank by the SEC, noting shortcomings in liquidity risk management and capital management. It emphasizes the importance of proactively managing risks and understanding market trends. The study then assesses the impacts of Silicon Valley Bank's bankruptcy on various aspects. It examines the repercussions for the Silicon Valley sector, the US financial market, and the global economy. The paper highlights potential consequences such as project terminations, increased unemployment, and reduced investment confidence.
Finally, the study provides insights and recommendations for the Bank of China, drawing lessons from Silicon Valley Bank's collapse. It underscores the importance of robust regulatory response, stable asset-liability structures, cautious monetary policies, and enhanced global cooperation. In conclusion, this study comprehensively analyzes the business risks associated with the Silicon Valley banking model using Silicon Valley Bank's bankruptcy as a case study. It explores the implications for the industry and offers guidance for risk management and development within the banking sector.
2. Literature review
In terms of the causes which triggered the collapse of SVB, IN FOCUS (2023) examines that there are many contributing factors to the bank failure, but the management of bank resources is the most trace back reason. If the bank’s capital situation is unwell, then it must take prompt corrective action, if it still fails to do so, it will be forced to close eventually. The article from the board of government of federal reserve system also believe that the failure on management of Silicon Valley bank would be one of the contributing factors to its bankruptcy. Apart from this point, it is argued that supervisors did not fully appreciate the extent of the vulnerabilities as Silicon Valley Bank grew and complexity.
Apart the internal reasons within the bank itself, there are also external influences CNN Business news (2023) regards that the interest rate grew leading the fall in bond price, so the jump in rates eroded the value of SVB’s bond portfolio. Meanwhile, the tech companies were forced to draw the deposits back to maintain a sustainable growth, which it led to a bank run and eventually formed the bankruptcy. From the Forbes news: “SVB realized more losses when it tried selling its securities, which had lost value due to high interest rate.” The main external reason would be the high interest rate leading to the fall of the value of its assets, and eventually the value of liabilities overweighted the value of assets.
The lessons and precautions should be noticed and take into action after such big bankruptcy, and this failure has brought security to the Fed’s hawkish interest rate approach. (Wharton Business Daily, 2023) And from board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, the banks should pay more attention on low probability/high severity events and rapid growth in size and complexity that might not be appropriately managed under existing prudential standards. Moreover, it will be important for regulators and policymakers to closely monitor the financial sector for signs of further instability and to take swift action to address any emerging risks. Also, it suggests that the collapse of SVB has highlighted the need for banks to have robust risk management practices in place and for regulators to maintain close oversight to prevent similar situations from occurring in the future. (April 2010) It is significant to making sure that the risk managements are well prepared.
To sum up, the articles and research mainly discussed the causes which are relevant to people’s life, and they should be the warning signs to the banks’ operations in the future.
3. Business risks associated with the Silicon Valley banking model
3.1. Silicon Valley Bank's investment strategy
Silicon Valley Bank's balance sheet presents the following characteristics: first, focusing on the field of science and innovation, Silicon Valley Bank provides comprehensive financial services such as loans, bond financing, investment banking, and venture capital for science and technology enterprises, and obtains low-interest or interest-free deposits; second, the rapid growth of assets, Silicon Valley Bank achieved rapid growth during the epidemic, and the asset scale expanded from US$71 billion to US$211.5 billion in two years, with an average annual growth rate of 73%; third, the proportion of financial investment is high, and bond investment (treasury bonds and MSB) is mainly increased during the asset expansion period; fourth, deposits contributed a lot, and the growth of total liabilities was basically the same as the growth of assets, mainly due to the loose monetary policy of the Federal Reserve and the financing boom of science and technology enterprises; fifth, the core indicators are good, under the advantages of high yield and low cost of assets and liabilities, Silicon Valley Bank maintains a trend of high growth, high return and high capital. In summary, "unexpected bankruptcy" directly stems from interest rate risk and liquidity risk caused by the serious mismatch of bank assets and liabilities under the rapid change of market environment. [1]
3.2. Silicon Valley Bank interest rate exposure
The primary reason for the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank was the mismanagement of interest rate risk due to its heavy position in long-term bonds. Figure 1 shows the US 10-year Treasury yield [2]. Silicon Valley Bank invested most of its new deposits in Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities (MBS). Silicon Valley Bank includes these investments in assets available for sale and assets at maturity in its accounting policy, which itself creates a maturity mismatch between assets and liabilities, introducing interest rate risk and liquidity risk. US financial market yields soared due to aggressive rate hikes by the Federal Reserve that began in 2022, with the 10-year Treasury note rising from 1.64% at the beginning of 2022 to 3.97% before the crisis erupted in 2023. As a result, the market value of Silicon Valley Bank's long-term portfolio investment fell sharply, far below the cost of investment, and then Silicon Valley Bank failed to seek to issue shares and increase capital, triggering a vicious circle of depositors' runs and market shorting.
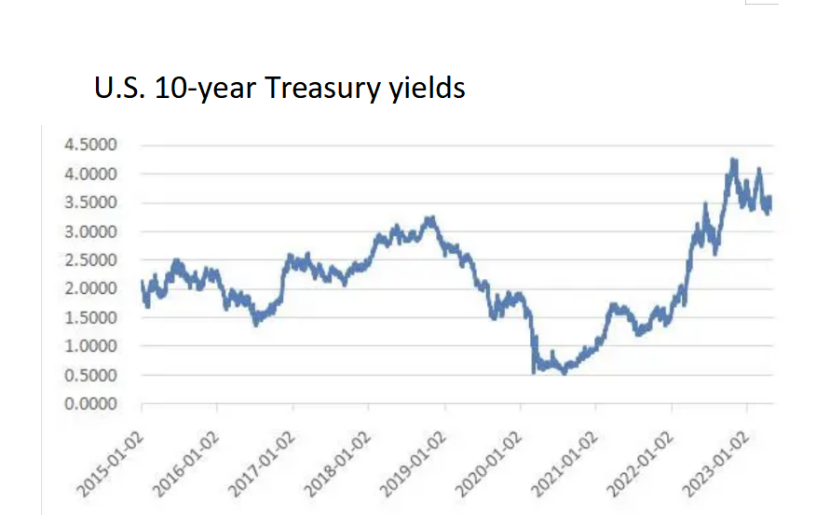
Figure 1: U.S. 10-year Treasury yields (Units in Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted). Resource: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US) [2].
3.3. Assets and liabilities of Silicon Valley Bank
Silicon Valley Bank's balance sheet structure failed to withstand the Fed's sharp rate hikes, resulting in operational failure. The asset-liability structure is seriously mismatched. Silicon Valley Bank has a serious maturity mismatch between short-term loans and long-term investments, which will bankrupt it in the event of a Fed rate hike. In the face of the Fed's interest rate hike and tightening market liquidity, the balance sheet mismatch problem of Silicon Valley banks eventually evolved into bank liquidity risk. Insufficient forward management of interest rate risk. According to the Federal Reserve's capital supervision rules and accounting standards, the unrealized gains and losses caused by Silicon Valley Bank's holding of bonds in financial investment accounts (AFS and HTM) are not reflected in the net capital amount daily, resulting in an "inflated" capital adequacy ratio of banks, which hides potential risks to a certain extent.
3.4. The quality of Silicon Valley Bank's management
Silicon Valley Bank has structural and institutional deficiencies in asset liability management. Silicon Valley debt quality management is inherently flawed.From the perspective of stability, in the environment of the Fed's interest rate hike, the stability of demand deposits has declined, volatility has increased, and Silicon Valley banks are facing the risk of a run. From the perspective of diversity, Silicon Valley Bank's customer structure focuses on start-ups in the technology sector, which is too single in the industry and has a high risk of deposit concentration. From the perspective of appropriateness, the large loss of deposits, the choice to increase short-term market financing to maintain their long-term assets, so that the debt structure of Silicon Valley banks continues to deteriorate. In anticipation of sustained Fed rate hikes, it has had to dispose of long-term assets at low prices. From the perspective of initiative, the proportion of active liabilities such as short-term and long-term debt of Silicon Valley Bank is low, far lower than the industry average.
3.5. Regulated by the SEC
Silicon Valley Bank is regulated by the SEC. Liquidity risk management is not in place. In the face of the drastically changing market environment, the source and use of funds of Silicon Valley banks are obviously mismatched, and there are major shortcomings in liquidity risk management. Floating losses on bonds and inadequate capital management. During periods of low interest rates and easy liquidity, deposits grew sharply, and Silicon Valley banks ramped up bond investments. After the Fed quickly raised interest rates to deal with the problem of high inflation, the bond investment strategy of Silicon Valley Bank has not changed significantly, and the interest rate risk is underestimated, and the means to respond are relatively limited.
4. Business risks led to the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank
The recent bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), a major lending institution for technology startups, has raised concerns about the wider implications of business risks in the financial industry. This essay explores the factors that contributed to SVB's downfall and highlights the risks faced by banks in a changing economic landscape.
4.1. Background of SVB and its Role in the Technology Startup Ecosystem
Silicon Valley Bank, as a key lender to early-stage companies, played a pivotal role in supporting the growth of the technology and healthcare sectors. Its partnership with nearly half of the risk-backed tech and healthcare firms listed in the stock market last year made it a significant player in the industry.
Financial Troubles and Stock Market Plunge
SVB's financial troubles came to the fore when it announced a record-breaking single-day drop in its stock price of over 60%. The plunge was prompted by its plan to sell $2.25 billion worth of stocks in an attempt to improve its financial situation. Following this announcement, the market value of the top four U.S. banks collectively declined by over $50 billion.
Losses and Asset Sale
SVB suffered substantial losses of approximately $1.8 billion after selling its asset portfolio, primarily consisting of U.S. government bonds. The decision to sell these assets at a loss added to the bank's financial woes and raised concerns about the profitability of its operations.
4.2. Implications for Startups and Venture Capitalists
The bankruptcy of SVB has left numerous startup companies, which had deposited funds with the bank, advised to withdraw their money. This situation has been described as "crazy" by Hannah Chelkowski, founder of investment fund Blank Ventures. She suggests that investment portfolios should be reevaluated, and funds should be moved out of SVB.
Wider Market Concerns and Bond Valuation
The decline in stock prices of banks globally has raised concerns about the value of bonds held by these institutions. Rising interest rates have caused a decrease in the value of these bonds. Central banks, including the Federal Reserve and the Bank of England, have significantly increased interest rates in an attempt to curb inflation. Banks, having large bond portfolios, face potential losses as the value of these bonds decreases. However, the situation becomes problematic when banks are forced to sell bonds at a loss, impacting their profitability.
The Unforeseen Consequences of Interest Rate Hikes
The unexpected duration of interest rate hikes caught many banks, including SVB, off-guard. Ray Wang, CEO of Silicon Valley consulting firm Constellation Research, believes that banks have been victims of these interest rate hikes. They misjudged the situation and made wrong bets. This underscores the need for financial institutions to have a comprehensive understanding of market trends and potential risks.
4.3. A Reflection of Systemic Vulnerabilities
The ripple effects of SVB's troubles indicate wider systemic vulnerabilities in the financial industry. SVB's decision to sell off its bond portfolio while simultaneously issuing stock raised concerns about the fixed-income investments held by many institutions. It serves as a reminder that fixed-income assets held by various organizations face significant unrealized losses due to the decrease in their value.
The bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank highlights the risks faced by financial institutions in today's dynamic economic landscape. The unexpected nature of interest rate hikes, coupled with the challenges in bond valuation, has put banks at risk. Furthermore, the implications for startup companies and venture capitalists highlight the interconnectedness of the financial ecosystem. As businesses navigate the evolving market conditions, it becomes imperative for banks and other stakeholders to adopt proactive risk management strategies to safeguard their operations and mitigate potential losses.
5. The impact of the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank
5.1. Impacts to the Silicon Valley
To begin with, the operations within the companies would be badly affect. More than 2,500 VC firms banked are in Silicon Valley. It fell in less than 48 hours Silicon Valley bank is the most important bank in the Silicon Valley technology sector [3]. Because the money in the bank is not able to be paid off, many projects would be ended, which it will be threatened to the long-term growth of the technology companies and therefor it might bring a massive loss of profit to them. Furthermore, the unemployment would be rose. To be more specific, many startups do not have sufficient capital since the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley bank disrupted the chain of capital in the companies. As a result, to reduce the cost, the firms might need to recruit less workers or cut down the spending on salary, so many workers might lose their jobs. Lastly, the confidence would be lessened. This collapse striking on the technology companies in the Silicon Valley may weaken their willingness to do the further investments, as they may be afraid of losing their money.
5.2. Impacts on the financial market in the US
First, the businesses may face the shortage of fund. Because the credits between bank in America are closely interacted, after the Silicon Valley bank collapsed, the deposits, lending and even stocks in it will all might face the risk of unsuccessful paying back which leads to a reduced trade between banks, and therefore the capital flow would decrease, and the economy would contrast. Moreover, the unemployment rate might be increased. As mentioned above, the insufficient fund in the firms would lead to a decrease in the budget on workers. Consequently, the job positions would be reduced which might also trigger the increase in the instability within the economy. On top of that, this unemployment would cause the long-term consequences. One of which is that the pressure. On the families would be increased as the income source might be reduced learning to the increase in the divorce rate. Another negative affect might be that the social instability might be risen.
5.3. Impacts on global economy
As a major player in the banking industry, SVB has relationships with many banks and financial institutions around the world. Figure 2 shows the timeline of regulatory activities. The bank has relationships with many companies and governments around the world, particularly in the technology sector. Silicon Valley bank has a significant role in the global financial system, and it has a close relationship with other banks, its bankruptcy will cause a series effect to the others. To be more specific, this practice would bring the instability and some fluctuations. Moreover, it might also negatively affect the development of global technology sector. Despite the fact that this collapse do bring bunch of physical and serious consequences to these sectors, whereas it does carry one positive influence which is that it put warming to the banks and governments around the globe. It's worth noting that the true impact of the Silicon Valley Bank's bankruptcy is twofold: The recurring occurrence of severe financial risks in Western countries, exemplified by the U.S, has a negative impact on global market expectations and the world's economic rebound. Additionally, it prompts reflection over the effectiveness of the current macroeconomic policies [4]. Through this painful lesson and cost, the managers in banks must be more aware of the management of risks, amid the duration. More specific enlightenments will be illustrated in the next section.
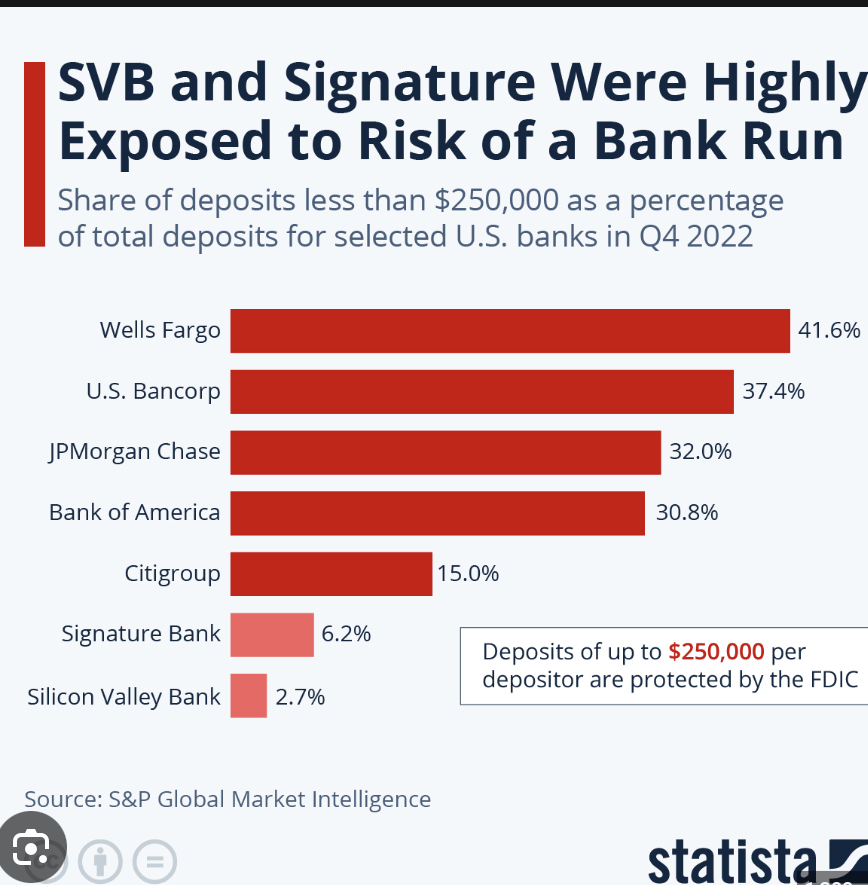
Figure 2: SVB and signiture were highly exposed to risk of a bank run Resouce: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System [5].
6. The enlightenment of the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank to the development of bank of China
6.1. The extremely fast and strong regulatory response is key to disposing of financial risks
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank highlights the importance of risk management in financial institutions. In Helyette Geman's (March 2023) "From Lehman to Silicon Valley Bank and Beyond. Why are U.S. Banking System Mistakes Repeating Themselves?" In the article, it is mentioned that in 2021, Silicon Valley Bank doubled its deposits; unfortunately, in 2022, there was a lack of risk management within the bank [6]. In 2018, the US decided to categorize financial institutions, and before its bankruptcy, Silicon Valley Bank belonged to the "Category 4" category, which was subject to less stringent standards of prudential supervision due to the transition arrangement and the biennial stress test. Silicon Valley Bank did not conduct a stress test until its bankruptcy due to transitional arrangements and a biennial stress test requirement. China must strengthen its regulation of financial institutions to ensure that they are proficient in assessing and controlling a variety of risks, including credit risk and market-related risks. Xu Tianqi, an assistant researcher at the Institute of Finance at the Renmin University of China, mentioned in his article that compared to China's actual situation, China is more likely to adhere to the Party's overall leadership of financial work and take the road of financial development with Chinese characteristics, and financial regulators should cooperate and work more closely together to hold the bottom line of no systematic financial risks and contribute financial power to the high-quality development of the economy.
6.2. Stability of banks' asset-liability structure should be concerned
On the liability side, Silicon Valley Bank's deposits are primarily from startups. This segment of customers shows a marked consistency, while the percentage of savings deposits is quite low. Surprisingly, more than 90% of the funds on deposit are not covered by deposit insurance, creating a situation where the vast majority of deposits lack such protective cover. This composition highlights the relative lack of stability in the liability structure. On the asset side, Silicon Valley Bank's loans account for only 35 percent of total assets, 57 percent of assets are invested in U.S. Treasuries and home mortgage-backed securities, and there is a lack of effective hedging arrangements against interest rate risk. Instability in the asset-liability structure ultimately leads to liquidity risk. Therefore, Bank of China should make good use of risk management tools such as stress tests, and actively respond to the situation in light of various types of risks, so as to match its risk management capability with its asset-liability structure.
6.3. Monetary policy should avoid large receipts and payments
As the Fed tightened its policies and interest rates rose, the price of bonds purchased by Silicon Valley banks fell, leading to book losses on revaluation at market value. According to the New Beijing News, during the epidemic, developed economies pursued quantitative easing, quickly implemented zero interest rates, and then rapidly raised and reduced interest rates due to high inflation, and the low-yielding assets allocated by commercial banks during the easing phase needed to be balanced with high-interest rate liabilities during the tightening phase, resulting in large losses. China adheres to a prudent monetary policy, actively maintains monetary stability, promotes the smooth operation of the national economy, and lays a solid foundation for financial stability.
6.4. China should strengthen cooperation with the world
On March 18, 2023, the Global Wealth Management Forum opened in Shanghai. Lou Jiwei, Chairman of the Forum and former Minister of Finance of China delivered the keynote speech. The speech mentioned that the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank reflects the complex forms and challenges currently facing international financial markets [7]. During the epidemic, governments adopted unconventional monetary and fiscal policies to support economic growth. Today's world is full of uncertainties and risks, and countries should strengthen cooperation and communication to jointly maintain global financial stability and prosperity. China has played an important role in the global fight against the epidemic, stabilizing the economy and safeguarding people's livelihoods. On the way forward, it will continue to promote the internationalization of the renminbi, expand the scope and scale of its cross-border application, raise its global status, continue to expand the opening of its financial markets to the outside world and work hand in hand with other countries to jointly address risks and challenges based on mutual respect, equality, and mutual benefit, and cooperation for win-win results, to promote the stable growth of the world economy.
7. Conclusion
Silicon Valley Bank, a subsidiary of Silicon Valley Bank Financial Group, provides lending services to venture capital and startup companies. The bankruptcy sparked global concern. In summary, the Silicon Valley Bank insolvency provides valuable lessons for other banks, emphasizing the importance of risk management, asset-liability management, and international cooperation to meet the challenges posed by the changing financial market environment.
This article is organized into four parts. Part I explores the business risks inherent in the Silicon Valley banking model in five key areas: investment strategy, interest rate volatility sensitivity, asset-liability dynamics, management quality, and SEC regulation. Part II delves into the specific business risks that led to Silicon Valley Bank's failure. This includes an exploration of Silicon Valley Bank's background and its key role in the tech startup ecosystem, its impact on startups and venture capitalists, and a broader examination of systemic vulnerabilities.
Moving into Part III, the focus shifts to the far-reaching implications of Silicon Valley bank failures. This impact will be scrutinized from three perspectives: the effect on the industry landscape, the ripple effect in the U.S. financial markets, and the repercussions on the global economy.
The fourth and final part draws lessons from the Silicon Valley bank's failure to provide insights into the development of Chinese banks. These insights are presented from four different perspectives: improving regulatory efficiency, ensuring the stability of banks' asset-liability frameworks, refining monetary policy approaches, and promoting international cooperation. These lessons can serve as rationalization recommendations for the future development of finance in China.
The recent failures of Silicon Valley banks have led to a cascade of contemplation. The crucial significance of effectively managing risks has been underscored, emphasizing that a robust risk management framework forms the foundation for maintaining stable bank activities and adapting to shifts in the market. The significance of balancing assets and liabilities has been brought to the forefront to mitigate the dangers of over-reliance on any single asset class, consequently lowering overall risk exposure. This situation has also underscored the necessity for well-designed financial regulations that proactively anticipate potential risks. The anticipation is that nations will enhance their collaborative efforts in the future, proactively addressing a spectrum of challenges and fostering sustainable development.
References
[1]. He, J. (2023) Reflections on Bankruptcy and Asset Liability Management of SVB. Banker, 2023(04): 40-43.
[2]. Li Yang. (2023). Implications of the Silicon Valley Bank Incident on financial risk management. China Finance (8), 73-74.
[3]. Al-Sowaidi, A. S. S., & Faour, A. M. (2023). Causes and Consequences of the Silicon Valley Bank Collapse: Examining the Interplay Between Management Missteps and the Federal Reserve's Floundering Decisions. Journal of World Economic Research, 12(1), 38-46.
[4]. Van Vo, L., & Le, H. T. T. (2023). From Hero to Zero: The case of Silicon Valley Bank. Journal of Economics and Business, 127, 106138.
[5]. Felix Richter, (March 13, 2023). "SVB and signiture were highly exposed to risk of a bank run". https://www.statista.com/chart/29478/share-of-fdic-protected-deposits-at-selected-banks/
[6]. Geman, H, (2023, March 23). From Lehman to Silicon Valley Bank and beyond : Why are mistakes repeated in the US banking system?. https://www.policycenter.ma/publications/lehman-silicon-valley-bank-and-beyond-why-are-mistakes-repeated-us-banking-system
[7]. Lu, J. (2023, November). Research on the Causes and Suggestions of Silicon Valley Bank's Bankruptcy Based on the Dual Perspective of the Information Age, Interest Rate Impact. In 2023 International Conference on Finance, Trade and Business Management (FTBM 2023) (pp. 193-201). Atlantis Press.
Cite this article
Xia,Y.;Zhang,Z. (2024). The Collapse of Silicon Valley Banks Improves Risk Management for Other Commercial Banks. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,82,163-172.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. He, J. (2023) Reflections on Bankruptcy and Asset Liability Management of SVB. Banker, 2023(04): 40-43.
[2]. Li Yang. (2023). Implications of the Silicon Valley Bank Incident on financial risk management. China Finance (8), 73-74.
[3]. Al-Sowaidi, A. S. S., & Faour, A. M. (2023). Causes and Consequences of the Silicon Valley Bank Collapse: Examining the Interplay Between Management Missteps and the Federal Reserve's Floundering Decisions. Journal of World Economic Research, 12(1), 38-46.
[4]. Van Vo, L., & Le, H. T. T. (2023). From Hero to Zero: The case of Silicon Valley Bank. Journal of Economics and Business, 127, 106138.
[5]. Felix Richter, (March 13, 2023). "SVB and signiture were highly exposed to risk of a bank run". https://www.statista.com/chart/29478/share-of-fdic-protected-deposits-at-selected-banks/
[6]. Geman, H, (2023, March 23). From Lehman to Silicon Valley Bank and beyond : Why are mistakes repeated in the US banking system?. https://www.policycenter.ma/publications/lehman-silicon-valley-bank-and-beyond-why-are-mistakes-repeated-us-banking-system
[7]. Lu, J. (2023, November). Research on the Causes and Suggestions of Silicon Valley Bank's Bankruptcy Based on the Dual Perspective of the Information Age, Interest Rate Impact. In 2023 International Conference on Finance, Trade and Business Management (FTBM 2023) (pp. 193-201). Atlantis Press.









