

Volume 211
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: Resilient Business Strategies in Global Markets
Based on data from the 2019 China Household Finance Survey (CHFS), this paper systematically investigates the impact of social interaction on household consumption upgrading and its underlying mechanisms. The findings reveal that social interaction not only significantly increases total household consumption expenditure but also promotes a higher proportion of hedonic consumption. These conclusions remain robust across a series of robustness checks. Mechanism analysis suggests that social interaction operates primarily through two channels: first, the financial literacy accumulation effect, wherein information sharing and cognitive improvement lead to optimized household financial decisions; and second, the risk-sharing effect, which alleviates future uncertainties and unleashes consumption potential by encouraging participation in commercial insurance. Heterogeneity analysis further shows that the positive impact of social interaction is more pronounced in eastern regions and among rural households. This research contributes to the understanding of how informal institutions affect microeconomic behavior and offers policy insights into enhancing financial literacy, expanding the coverage of risk management tools such as insurance, and promoting household consumption upgrading and domestic demand expansion.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper investigates central-local policy deviation in China’s electric vehicle car (EV car) industry through a case study of Hefei, Anhui Province. The study classifies policy deviation into three aspects: objectives, execution, and resource allocation. It reveals significant misalignment between national, provincial, and municipal policies. The study finds that these deviations reflected in over concentration of resources, excessive subsidies, and protectionist practices, have distorted market competition, weakened technological innovation, and created risks of overproduction. Using literature review, policy text analysis, and case comparisons, the paper discovered that the extent of deviation is getting larger and larger as is passed to lower levels with more detailed measures taken. This article also concludes with recommendations for improving coordination, including enhanced central supervision and mechanisms for cross-regional collaboration. By revealing the economic consequences of policy deviation, this research contributes to understanding the governance challenges in China’s green transition and offers insights for aligning local development with national strategic objectives.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, the number of backdoor listings in the film and television industry has increased, and audit risk issues have become increasingly prominent. This paper takes the case of H&R Century Pictures’ backdoor listing to examine the characteristics of audit risks specific to the industry. The study finds that audit risks in the film and television sector are mainly concentrated in areas such as revenue recognition, related-party transactions, accounts receivable, and inventory valuation. H&R Century Pictures inflated its profits and assets by prematurely recognizing revenue and fabricating accounts receivable. At the same time, it concealed related-party relationships through complex related-party transactions and multi-layered nested company structures, thereby increasing the difficulty of audit procedures. Additionally, overvaluation of inventory and insufficient provision for impairment are also significant audit risks in the industry. In response to these issues, auditors must strengthen their understanding of the film and television industry's complex business models, conduct penetrating reviews of related-party transactions, and carefully assess inventory valuations. Regulatory authorities should also improve accounting standards and auditing guidelines, enhance regulatory oversight, and promote the standardized development of capital operations within the film and television sector.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the acceleration of globalization and digitalization, companies are facing increasingly complex supply chain challenges. Zara, a globally renowned fashion retail brand, has become a key subject of academic and practical research due to its unique supply chain management model. This study aims to explore Zara’s supply chain management strategies in the global market, analyzing key factors such as its fast response capability, inventory management, information flow, and supplier collaboration, to uncover the reasons behind its success. Using a mixed-method approach that combines qualitative and quantitative techniques, including literature review, case studies, and relevant data, the research analyzes the key elements of Zara’s supply chain and its implementation outcomes. The research indicates that Zara's success in supply chain management is due to its swift market response mechanism, accurate inventory control, and well integrated information technology system. Zara encounters obstacles in market expansion, sustainability, and reliance on technology. Future study may concentrate on sustainable supply networks, technological advancements, and the effects of globalization on supply chain reconfiguration.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper treats the entry of ride-hailing services into cities as a quasi-natural experiment and systematically examines the causal effect of the sharing economy on urban carbon emissions based on panel data from Chinese cities spanning 2014 to 2017. The study finds that the market entry of ride-hailing services significantly reduces per capita carbon dioxide emissions in cities. This conclusion holds robust across a series of sensitivity tests. Mechanism analysis reveals that ride-hailing contributes to emission reduction primarily through two channels: optimizing industrial structure and strengthening the digital technology infrastructure. Further heterogeneity analysis indicates that this carbon-reducing effect is significantly moderated by cities’ geographic and economic characteristics: its low-carbon advantage is more pronounced in large cities with dense populations and industrial agglomeration, while in smaller cities with limited market capacity and economic activity, the marginal benefits tend to diminish. This study provides micro-level empirical evidence for the green value of the sharing economy and offers valuable policy implications for how cities can leverage the sharing economy to promote sustainable development.

 View pdf
View pdf


In today's era of data-driven decision making, Business Intelligence (BI) tools have evolved significantly, revolutionizing the way businesses process, analyze, and visualize data. This article explores the evolution of BI tools from traditional spreadsheets to advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven systems. The study found that, initially, Excel provided basic functionality for data entry, calculations, and basic visualization, enabling businesses to manage small data sets. However, as businesses faced larger and more complex data environments, Excel's limitations became increasingly apparent. The emergence of mid-level visualization tools such as Tableau and Power BI brought significant innovation, providing interactive dashboards, user-friendly interfaces, and enhanced visual storytelling capabilities. Despite these advances, using these tools still requires a certain level of skill. In recent years, AI-driven BI tools have revolutionized the industry landscape by incorporating natural language processing and machine learning. These technologies enable users to work and analyze these tools even without professional training. However, challenges remain, such as ensuring data security, maintaining analytical transparency, and avoiding over-reliance on automated insights that can undermine business acumen. This study systematically traces the historical trajectory of the development of business intelligence tools, analyzes technical milestones and functional characteristics, and explores their practical significance for enterprise decision-making. It is hoped that it can provide a comprehensive perspective for researchers and practitioners.

 View pdf
View pdf


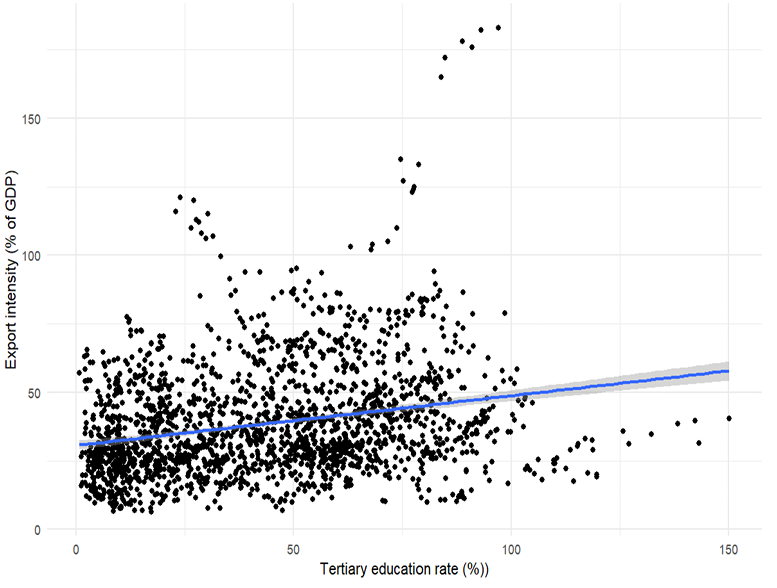
This study examines the socioeconomic determinants of trade performance, with a particular focus on tertiary education, export structure, export intensity, and GDP. The research intention is to figure out whether a country's advantage in higher education translates into stronger export outcomes through a mediating mechanism, and to what extent this effect is observed. To address this question, this research employs mediation analysis using the causal steps regression approach, and the results are reviewed with robustness test using the bootstrap method. Research data come from public open databases. The empirical findings suggest that tertiary education serves as a significant secondary drive of exports. Notably, a substantial portion of this influence operates indirectly and primarily through enhancing the complexity of the export structure. These results imply that the diversity and specialization of university programs underpin the educational edge in export performance, highlighting the critical role of human capital composition in shaping a nation's comparative advantage in international trade.

 View pdf
View pdf


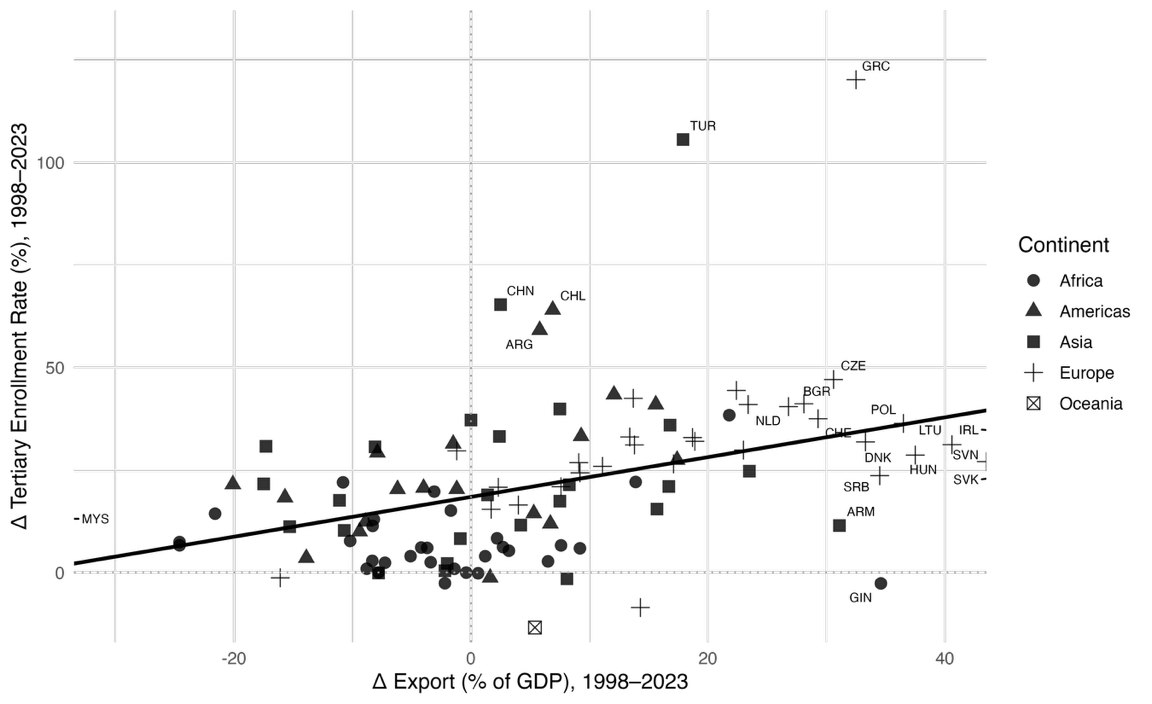
This study examines the bidirectional relationship between export intensity and tertiary education enrollment across 109 countries from 1998 to 2023, with a focus on the moderating role of economic complexity. Using fixed-effects panel models, interaction terms, and system GMM estimation, the analysis reveals an asymmetric pattern: while both directions are statistically significant, the influence of education on exports is more robust and contingent on structural sophistication. The Economic Complexity Index (ECI) significantly strengthens the education-to-export link but has limited moderating effect in the reverse direction. The study highlights the importance of aligning human capital development with structural transformation to support inclusive, export-led growth. Context-specific strategies are recommended for countries at different levels of economic complexity. The robustness of findings is confirmed through alternative specifications and transformations. Overall, the study offers new insights into how trade and education co-evolve and underscores the role of productive capabilities in shaping development pathways amid shifting global dynamics.

 View pdf
View pdf




