1. Introduction
The Walt Disney Company (hereinafter referred to as Disney), founded in 1923, is a large multinational corporation headquartered in the United States of America, founded by Mr. Walt Disney together with his brother, Lloyd Disney, initially as Disney Brothers Studios, and later renamed as the Walt Disney Company. The company's main business at the beginning was the production and distribution of films, and in 1937 it succeeded in releasing its first animated film, Snow White, which became one of the most popular films of the time [1]. Subsequently, Disney made more and more progress in this field, releasing quality animated films such as Pinocchio, Fantasia, Dumbo, etc. [1]. In 1945, Disney hired live actors for the first time to play roles in the film ‘Song of the South’, and from then on, it also broadened the company's film genres and continued to release full-length live-action films. At the same time, the company also successfully built and opened the first Disneyland in California in 1955, which will make the name ‘Disney’ more and more familiar to more and more people. After that, Disney has been expanding its business market and successfully launched the Disney Channel on cable TV in the United States of America in 1983, on the other hand, it also endeavored to develop the Disneyland market in different regions such as Orlando Disneyland and Tokyo Disneyland, which enabled the company to achieve its major goals at the present stage. The establishment of Disneyland in different regions has not only brought lucrative benefits to Disney but is also slowly working towards making the company a leader amongst the entertainment companies in the global arena.
After entering the 21st century, Disney began to carry out a wide range of online media expansion, acquiring a number of companies such as Pixar, Fox, Marvel, etc., which has enabled Disney to achieve an important position in many fields and greatly expanded the company's business segments [2]. At the same time, Disney has also actively expanded other diversified businesses, such as gaming, consumer products, music, etc., which have brought Disney substantial revenues and increased its competitiveness in the global entertainment market [1]. In 2020, the company faced a major turning point during this period due to the outbreak of epidemic. As Disney's theme parks and cinema business are dependent on places where people congregate and thus operate, this has challenged Disney's traditional business model like never before. The Epidemic resulted in the limited or even forced closure of these venues, causing a significant drop in Disney's revenues, a financial shortfall that led directly to the official closure of Blue-Sky Studios. But as the epidemic gradually ended, Disney slowly got back on track. Last year was the 100th anniversary of Disney's founding, and in April the company released its 100th anniversary film, revisiting many of its classics with everyone. All in all, Disney has become a leading entertainment company in the world by virtue of its unique creativity, superior technology and excellent business strategy. It is believed that in the future, Disney will bring more excitement as well as unlimited possibilities to the audience.
2. Performance Evaluation
In the next part of this essay, three competing companies will be chosen to compare with Disney in three ways. As mentioned in the previous article, the scope of Disney's business has been expanding gradually. Therefore, the first competitor company, Netflix, has been selected from the film and television level. Netflix is a leading global streaming entertainment service company. As the main business of these two companies is inclined to film and television, there is competition in the target customers of film and television as well as the market flow of the corresponding placement. Secondly, the park aspect of Disney has been very popular in recent years, and if Disneyland is everyone's first choice, then the only one that can be mentioned alongside it is Universal Studios Park. Therefore, the second competing company is Comcast, which is the parent company of NBC Universal, the company that owns Universal Studios Park. It is an American multinational media and technology company, which is diversified due to its many different types of subsidiaries. One of these business areas is the park business, which has similarities with Disney in that they both build a different kind of fairytale park based on several animation or film IPs. Therefore, there is some competition between them in terms of attracting customers and growing revenues, as well as the right to develop certain areas is also an important factor in the competition between the two companies, which could affect the future growth of the company. The last competing company chosen was Mattel Inc. This is the world's largest toy company, which contains Barbie, Matchbox, American Girl and many other brands [3]. The two companies are in competition due to the fact that Disney, among others, is involved in the corresponding output of some toys or related items. These companies will be analyzed through the corresponding data (All data obtained from NASDAQ website on 2024/3/26).
2.1. Liquidity
Table 1: Liquidity ratios of Disney and its competitors.
Company | Current Ratio | Quick Ratio | Cash Ratio |
Walt Disney | 105.22% | 98.91% | 45.54% |
Netflix | 111.93% | 111.93% | 80.56% |
Comcast Corporation | 59.67% | 59.67% | 15.46% |
Mattel | 232.58% | 190.00% | 93.96% |
Data source: Nasdaq
Firstly, the liquidity of the four companies will be analyzed, in terms of the current ratio, except Mattel, the remaining three companies show a ratio of less than 2, which will mean that the ability to realize the assets of the company is weaker than other companies of the same type. The lowest of these is Comcast's current ratio, which is only 59.67%, which would imply that the company's ability to repay debt in the short term is weak. In terms of quick ratio, Disney has a good performance. His quick ratio is 98.91%, which is the closest to 1. This would reflect that he would have a stronger ability to use its most liquid assets to service its debt than other competing companies without relying on inventory sales or other additional financing. Regarding the cash ratio, generally the cash ratio is 20% to 30%. Table 1 shows that Netflix and Mattel have cash ratios of more than 50%, which suggests that the liquid assets of these two companies are not being used properly, which may ultimately lead to an increase in the opportunity cost of the company. Comcast, on the other hand, presents a cash ratio of less than 20%, which indicates that the business does not have enough cash flow to pay its short-term debts or meet its daily operational needs. It may be caused by the business over-investing in long-term projects or insufficient sales revenue. Above all, this paper concludes that the four compared to the other three competing companies, Disney exhibits good corporate liquidity, while the others all have not so good performance in a certain ratio respectively.
2.2. Solvency
Table 2: Solvency ratios of Disney and its competitors.
Company | Total Debt Ratio | Long-Term Debt Ratio | Times-Interest-Earned |
Walt Disney | 47.30% | 20.48% | 4.9446 |
Netflix | 57.75% | 29.02% | 9.8671 |
Comcast Corporation | 68.68% | 35.88% | 6.0105 |
Mattel | 66.61% | 36.20% | 4.7597 |
Data source: Nasdaq
Secondly, the repayment capacity of the four companies will be analyzed. In terms of long-term debt ratios, all four companies are at a similar level as shown in Table 2. The survey shows that the total gearing ratio of the company is generally in the range of 40%-60%. So Comcast and Mattel have higher ratios than the other two companies, which would not be good news for them. In terms of long-term debt, Disney shows a better value of 20.48%, while the other three companies have ratios of more than 25%. As long-term debt ratio mainly reflects the ability of a company to repay long-term debts, a high long-term debt ratio will increase the financial risk and financial cost of the whole company. In terms of earned interest multiples, both Disney and Mattel are close to 5, while both Netflix and Comcast show values over 5 or even close to 10. While the higher this indicator is, the better the company's ability to service its debt over the long term, internationally it is considered more appropriate when the indicator is 3. If it is too high, it will mean that the company needs more financing or investment to operate, which will increase the potential risk of the company. In conclusion, Disney also has a good performance in terms of repayment ability.
2.3. Profitability
Table 3: Profitability ratios of Disney and its competitors.
Company | Profit Margin | Operating Margin | Asset Turnover |
Walt Disney | 2.65% | 5.74% | 43.66% |
Netflix | 16.04% | 20.62% | 69.40% |
Comcast Corporation | 12.66% | 19.18% | 47.25% |
Mattel | 3.94% | 10.32% | 88.08% |
Data source: Nasdaq
The last thing is to analyze the profitability of the four companies, as shown in Table 3. In terms of profitability, in general, the profit margins of the four companies are low when looking at the market as a whole, probably due to industry constraints. However, in comparison, two companies, Disney and Mattel, have very low profit margins of 2.65% and 3.94% respectively. This implies that the profitability of these two companies is weak, which may be due to the fierce competition in the current market or certain problems in the marketing strategy. Similarly, the values from the operating margins of the four companies show the same situation. Disney remains in the position of the lowest operating margin of the four companies, a phenomenon that may be due to the fact that its streaming service is in a loss-making position at the current stage, requiring a certain amount of capital investment, which leads to the low profitability of its company. In terms of asset turnover, all three companies except Mattel have an asset turnover of less than 80%. The company's asset turnover ratio is generally at the more appropriate level of 80%-100%. These three companies are characterized as capital-intensive industries, and due to the diversity of their business, they may require large-scale capital investment from the company, which leads to a lower asset turnover ratio, and may result in a lower evaluation of the quality of the business operations as well as the efficiency of utilization. Therefore, for the future development of the three companies may need to adjust the corresponding operation mode, and thus improve this ratio. In conclusion, in terms of profitability, Disney still has this big problem that needs to be improved continuously.
In terms of liquidity, repayment ability and profitability, the overall performance of Disney has performed better than the other three companies. However, this is only based on the situation reflected in the data at the current stage. In the future, Disney should summarize its own shortcomings and the successful experience of other companies in the same industry, and adjust the company's strategic approach and mode of deployment to make it more in line with the needs of the current market and customers, so as to make the company more successful.
3. Valuation
3.1. Forecast
Table 4: Valuation of Disney and its competitors.
2024/3/26 | Walt Disney | Netflix | Comcast Corporation | Mattel |
Stock code | DIS | NFLX | CMCSA | MAT |
Stock price | 119.93 | 629.24 | 42.48 | 19.4 |
TTM EPS | 4 | 12.01 | 3.97 | 1.23 |
NTM EPS | 4.72 | 17.05 | 4.25 | 1.34 |
EPS growth rate % | 18.00% | 41.97% | 7.05% | 8.94% |
Revenue growth rate | 3.66% | 14.24% | 3.11% | 2.92% |
TTM P/E | 29.98 | 52.39 | 10.70 | 15.77 |
NTM P/E | 25.41 | 36.91 | 10.00 | 14.48 |
PEG | 1.67 | 1.25 | 1.52 | 1.76 |
GP/A (Last Fiscal year) | 14.45% | 28.74% | 32.03% | 40.15% |
The next step is to analyze and forecast the corresponding valuation of the shares of the four companies, and Table 4 is based on 26 March 2024 data as reported on the NASDAQ website. Firstly, regarding the EPS growth rate, Table 4 shows that NFLX has the best performance among the four companies with a value of 41.79%. This will mean that the company will earn higher earnings and also means that the company will have more profits that can be distributed to the respective shareholders. In contrast, CMCSA and MAT stocks have an EPS growth rate of no more than 10%, indicating that their companies are currently experiencing some difficulties and need to make some adjustments to their corporate strategies. Secondly, regarding the revenue growth rate, DIS, CMCSA, and MAT have similar values, but none of them exceed 5%. This indicates that all three companies are experiencing slow revenue growth, which could be due to a number of reasons, such as competitive pressure in the market or declining market share. Then there is about the P/E ratio, the TTM P/E ratio and NTM P/E ratio of each of the four companies are calculated in this paper, and NFLX reflects a very high result. This means that the companies are not only overvalued, but also may have a high degree of frothiness. The stock market may be inflated and exceeding its true value, which in turn poses some risk. CMCSA, on the other hand, reflects lower results and generally speaking, the appropriate range for P/E ratio is 14-20, which would imply that CMCSA may be undervalued. While DIS's TTM P/E ratio is also outside of a reasonable range, the NTM P/E ratio reflects a better result, and it is possible that the company may improve on this in the future, depending on the new quarterly data. In terms of PEG, all four companies have shown a similar picture. In terms of GP/A, DIS has the lowest value among the four companies with 14.45%. This corresponds to the profitability analyzed in the previous section, for which DIS has certain shortcomings, and which it is believed that DIS will be gradually resolved in the future as the various components are gradually improved and developed.
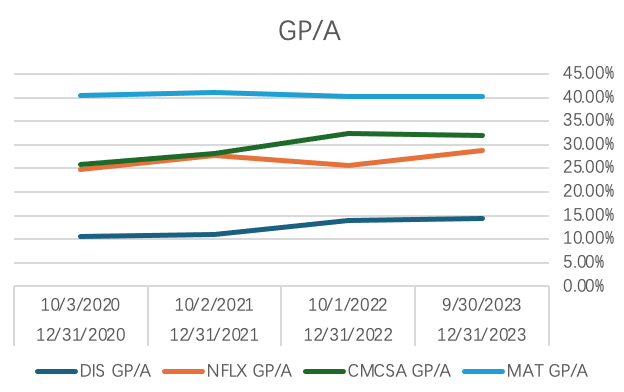
Figure 1: GP/A of Disney and its competitors (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Figure 1 shows the GP/A combination of the four companies for different time periods. And since DIS has a different fiscal year than the other three stocks, two different sets of dates are shown in the horizontal coordinate. One of them, MAT, has remained the highest among these four companies and has been changing very steadily in recent years, staying around 40%. And both DIS and CMCSA stocks are gradually trending upwards, which means that both companies are actively making improvements in response to some of the problems that existed at various stages. NFLX, on the other hand, is on a downward trend in 2022, which according to the corresponding data of that year may be due to the fact that Netflix has invested more in original TV content production and the corresponding streaming services, which leads to its GP/A being in a lower position at that stage [4]. But in any case, judging from the situation in the last year, the situation of all four companies are slowly getting better, for some problems are also gradually resolved, which will be a good trend towards the future.
3.2. Strategy Management
Next is the aspect of having an excellent marketing strategy regarding the Disney Company, this paper analyzes the main aspects of its corporate strategy from three different perspectives.
3.2.1. Brand Acquisitions and Corresponding IP Rights
Disney has been a leader in several industries compared to other companies due to its ownership of many popular IPs and animated characters that customers have come to love. The acquisitions of Pixar Animation, Marvel Entertainment, Lucasfilm, and 21st Century Fox in the 21st century increased the number of IPs owned by Disney at the time [5]. The acquisition of Marvel alone brought Disney up to 5,000 IP characters such as Spider-Man, Iron Man, Thor, and Captain America. The acquisition of 21st Century Fox also brought the X-Men, Fantastic Four, Deadpool and other IPs into the Disney fold, putting it directly at the forefront of the industry [5]. In recent years, Disney launched the "Duffy family" is loved by everyone, and Disney also quickly seize this selling point, in the corresponding product output launched parks, festivals, series of many different limited series of peripheral, so as to expand the profitability. From the beginning of Mickey Mouse, Donald Duck, Snow White, and then to the current Star Dale, Ling Na Beier, Shirley Mae and so on multiple cartoon images, Disney has always been to "family entertainment" as the core of the brand concept, in the future, Disney will also promote more high-quality diversified IP, so as to better meet the customer's expectations [6].
3.2.2. Globalization of Regions
In 1955, the first Disneyland successfully opened in California, the United States, which is the first theme park in the modern sense of the word, once the launch of the park is greatly loved by the people, in just six-month time attracted more than 3 million visitors to play [7]. And in the coming period of time, the income and the number of visitors rose sharply, even just one day's income can be up to millions, and add the cost of facilities in the park and various other, its income is even more substantial. Therefore, Disney quickly seized this market and spent five years to build a more luxurious Disneyland, and successfully opened to the public in 1971, which is the Orlando Disneyland, is also the second theme park in the United States. With the completion of the most luxurious Disneyland at the time, the company's revenue increased, and it began to gradually expand its parks to other countries. 1982 Tokyo Disneyland in Japan, 1992 Paris Disneyland in France, 2005 Hong Kong Disneyland in China, and 2016 Shanghai Disneyland in China, the successful construction of these parks shows that Disney is gradually focusing its strategy on the whole country. strategy to gradually focus on the country. However, at this stage, there is no clear information on which region the company will build a new Disneyland, so the main focus is on expanding the scope of the existing parks. Moreover, Disney has indicated that it will establish Disneyland in each region according to the culture of different countries and regions, whether it is the expansion of the current region or the location of the new park in the future, which will be a good selling point for customers and attract tourists from all over the world [8].
3.2.3. Digitalization and Corresponding Technological Expansion of Streaming Media
In November 2019, the Disney Company, in order to adapt to the trend of digitization and meet the needs of consumers, therefore went live with its streaming service Disney + (D+ for short), and made it the focus of the company at that time, investing a large amount of money, focusing on the film and television content of Disney and enriching it continuously, optimizing the distance between the customers and the company, and thus attracting a certain amount of users. Coincidentally, the following year, the world suffered a serious epidemic crisis, which caused serious damage to the economy of Disney's real industry. Therefore, the existence of Disney+ played a major role in providing a wealth of entertainment for people living in isolation at home. And as of March 2021, Disney+ has surpassed 100 million subscribers worldwide, a number that far exceeded the company's initial expectations [9]. Disney is investing heavily in originality to keep its streaming platform on track, retaining as many of its current subscribers as possible while expanding its subscriber base in other regions [9]. Disney is also continuing to invest in technological innovation, for example, the current popularity of virtual reality technology, augmented reality sense of the new technology and so on have gained significant results [9]. Technological innovation not only makes Disney in the content greatly improved, but also makes the customer to get a better sense of experience, and then enhance the customer stickiness [9]. Therefore, in terms of the current development strategy of Disney, it is gradually transforming into a technology company rather than being limited to a traditional media company [9].
3.3. Risk Assessment
According to Disney's annual report for the year 2023, in terms of the economic market of the business, Disney believes that the downturn in the economic conditions in the global regions is now having a greater negative impact on the profitability of its business [10]. Due to the recession in certain regions of the market and a certain level of inflation, it may result in Disney being forced to increase its costs in certain areas, which in turn will generate a certain amount of revenue loss [10]. In terms of public taste preferences, Disney sees this as an unpredictable risk, as the company is unable to accurately predict public tastes, there is a risk that the images or IPs introduced may not be accepted by the market [10]. At the same time, a similar problem is reflected in Disney+, where fatigue is observed in the growth of streaming services, especially the existence of a constant decline in the number of payers, which may affect the company's revenues. In addition, due to the decline in traditional forms of distribution, this may thus lead to an increase in the cost of its corresponding content for the streaming service, which may have a negative impact on profitability [10]. Therefore, in the future it may be necessary to make certain adjustments to its content and corresponding targets.
4. Conclusion
To summarize, this paper believes that the future development prospect of Disney Company is more considerable, according to the recent social status, the public's expectation and love for Disney is getting higher and higher. Especially in the 100th anniversary of the founding of Disney last year, the broadcast of the movie "Star's Wish" makes more people revisit the classic Disney, which evokes a lot of memories. The recent opening of the "Zootopia" park in Shanghai Disneyland in China has also attracted a large number of tourists, allowing more people to understand Disney and love Disney. But for investors, need to consider a number of factors, and this article also mentioned that Disney in some aspects of the same type of other companies compared to the existence of a certain disadvantage, at the same time there may be in the current stage of the situation is slightly overestimated, so need to be integrated with a variety of factors to accurately judge whether to invest. In the future, Disney will develop steadily, with the situation gradually adjust the company's strategy and center of gravity, and then for the children of big friends to create a richer Disney ‘utopia paradise’.
References
[1]. Zhu, W. (2024). Decoding Disney’s Marketing Mastery: A Strategic Analysis. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 188, p. 03011). EDP Sciences.
[2]. Britannica. (2023). The Editors of Encyclopaedia. "Disney Company summary". https://www.britannica.com/summary/Disney-Company. Accessed 18 April 2024.
[3]. Boellstorff, T., & Soderman, B. (2023). Toys, Video Games, Platforms, and Mattel Electronics’s Intellivision, The University of California, Irvine.
[4]. Lee, W. (2024). How Netflix won the streaming wars. Los Angeles Times. https://www.latimes.com/entertainment-arts/business/story/2024-03-06/how-netflix-held-onto-its-crown-as-king-of-streaming. Accessed 18 April 2024.
[5]. Zhao, X. (2020). Content and Marketing Strategies of Media Integration: A Case Study of Disney Group. Young Journalist (25), 60-61.
[6]. Yan, H. (2020). The Path to Successful Industrial Operation of Disney. Media (15), 48-50.
[7]. Rukstad, M. G., Collis, D. J., & Levine, T. (2001). The Walt Disney Company: The Entertainment King. Harvard Business School.
[8]. Li, Y. Q., & Hao, C. (2022). A Brief Discussion on the Expansion Motivation and Site Selection Characteristics of Disney Parks. Commercial Exhibition Economy (14), 41-43.
[9]. Zhang, J. Z. (2021). Turning to Streaming Media: Disney's Digital Transformation and Innovation. China Television (07), 101-104.
[10]. Walt Disney Company. (2023). Fiscal Year 2023 Annual Financial Report. Retrieved from https://www.thewaltdisneycompany.com/2023-Annual-Report. Accessed 18 April 2024.
Cite this article
Zhao,X. (2024). A Financial Analysis and Valuation on Disney. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,95,77-84.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhu, W. (2024). Decoding Disney’s Marketing Mastery: A Strategic Analysis. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 188, p. 03011). EDP Sciences.
[2]. Britannica. (2023). The Editors of Encyclopaedia. "Disney Company summary". https://www.britannica.com/summary/Disney-Company. Accessed 18 April 2024.
[3]. Boellstorff, T., & Soderman, B. (2023). Toys, Video Games, Platforms, and Mattel Electronics’s Intellivision, The University of California, Irvine.
[4]. Lee, W. (2024). How Netflix won the streaming wars. Los Angeles Times. https://www.latimes.com/entertainment-arts/business/story/2024-03-06/how-netflix-held-onto-its-crown-as-king-of-streaming. Accessed 18 April 2024.
[5]. Zhao, X. (2020). Content and Marketing Strategies of Media Integration: A Case Study of Disney Group. Young Journalist (25), 60-61.
[6]. Yan, H. (2020). The Path to Successful Industrial Operation of Disney. Media (15), 48-50.
[7]. Rukstad, M. G., Collis, D. J., & Levine, T. (2001). The Walt Disney Company: The Entertainment King. Harvard Business School.
[8]. Li, Y. Q., & Hao, C. (2022). A Brief Discussion on the Expansion Motivation and Site Selection Characteristics of Disney Parks. Commercial Exhibition Economy (14), 41-43.
[9]. Zhang, J. Z. (2021). Turning to Streaming Media: Disney's Digital Transformation and Innovation. China Television (07), 101-104.
[10]. Walt Disney Company. (2023). Fiscal Year 2023 Annual Financial Report. Retrieved from https://www.thewaltdisneycompany.com/2023-Annual-Report. Accessed 18 April 2024.









