1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Significance
The rapid growth of e-commerce and the expansion of global trade have presented significant opportunities and challenges for the logistics industry. Emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics are being widely utilized in logistics to enhance operational efficiency and drive cost savings [1]. Simultaneously, heightened environmental consciousness has propelled the logistics sector towards a more sustainable trajectory. The global logistics market is fiercely competitive, with major international players and local service providers continuously striving to innovate and elevate service standards in the current intricate and competitive business environment, the traditional logistics sector is facing substantial obstacles. This study aims to enhance comprehension among relevant enterprises and the industry regarding how to manage the competitive pressures of the global logistics market by comparing the unique advantages and developmental stages of traditional and modern logistics. Additionally, it seeks to offer practical recommendations for improving and upgrading logistics systems. Furthermore, this research endeavors to address specific knowledge gaps in the field of logistics, optimize its evolutionary path, and clarify the impact of relevant technological advancements on the sector. Ultimately, these findings can offer valuable guidance for industry professionals in decision-making roles to optimize the diverse applications of logistics systems and enhance their public service capabilities.
1.2. Literature Review
Ma Jinli focused on discussing the potential and obstacles brought about by digital transformation in the logistics industry [2]. By emphasizing the significance of the logistics process, he illustrated how digital transformation has the capability to improve operational efficiency and enhance customer satisfaction for a wide range of logistics enterprises. Additionally, it is clear that during digital transformation, logistics companies need to prioritize technological advancements and data security measures to ensure their successful future development. Qu Yuhan's research on the impact of COVID-19 on logistics costs specifically examines Amazon Logistics as a case study, analyzing the company's strategies for managing supply chain disruptions and other operational challenges during the pandemic and similar public health crises [3]. The findings highlight the significant benefits of advanced supply chain management practices in modern logistics firms like Amazon, which leverage state-of-the-art technologies such as machine learning and big data to achieve seamless resource integration and enhance global logistics efficiency. This approach leads to substantial reductions in transportation expenses during various emergency scenarios. Additionally, it provides valuable insights for global logistics enterprises navigating public health emergencies or other critical situations, thereby influencing their optimization and transformation. Shi Yangyang and Zhang Quanran conducted a detailed examination of the internal logic and practical strategies for integrating and advancing the digital economy alongside the logistics industry [1]. The paper thoroughly explored the status and obstacles related to this integration, providing an in-depth analysis of its internal logic. Through integration with the digital economy, it is possible for the logistics industry to achieve visualization, transparency, and intelligent transformation across all stages from production to consumption, thereby improving efficiency and reducing costs. Additionally, it underscores the necessity of implementing policies for digital transformation within the logistics sector to enhance service quality, optimize operational efficiency, and promote environmentally sustainable development.
According to the literature, digital logistics transportation has emerged as an inevitable new trend for the future. While digital transformation holds significant potential for the logistics industry, it also presents substantial challenges. Prioritizing technological advancements, data security, and integration with the digital economy is essential for achieving operational efficiencies, reducing transportation costs, enhancing customer satisfaction, and improving flexibility and efficiency in responding to emergencies. These studies offer valuable guidance and practical insights for logistics enterprises, exerting a positive impact on optimizing and transforming the entire logistics industry.
1.3. Research Contents
The present study utilizes two distinct methodologies, namely case analysis and comparative analysis, to investigate the issue at hand. The primary focus is on analyzing the developmental trends and financial fluctuations of two representative logistics enterprises over the past four years with the objective of elucidating disparities between traditional and contemporary logistics firms in a competitive landscape. The ultimate goal is to enhance the advancement and progression of the logistics industry.
2. Case Description
2.1. Traditional Company of FedEX
2.1.1. Introduction of Company
FedEx, founded in 1973 by CEO and Chairman Frederick Smith. A part of the United States FedEx Corporation., serves as the cornerstone of the group's express transportation business. It is recognized as the world's largest express transportation company, offering swift and dependable delivery services to over 220 countries and territories [4]. With a global air and land network, FedEx ensures expedited delivery of time-sensitive shipments within one to two business days, guaranteeing punctual arrival. As an integral component of the FedEx Group, FedEx Express covers 90% of the world's gross national product and delivers door-to-door international express services with customs clearance in 24 to 48 hours. Leveraging unparalleled route rights and infrastructure, FedEx stands as the foremost express delivery company worldwide, delivering prompt, reliable shipping services to 220 countries and territories. The company handles over 3.2 million packages daily with a workforce exceeding 138,000 employees along with a fleet comprising 671 aircraft and 41,000 vehicles across the globe. Furthermore, it maintains seamless electronic communication with more than one million customers globally through its platforms FedEx Ship Manager at and FedEx Ship Manager Software.
2.1.2. Introduction of Business
FedEx is a global express delivery conglomerate with an extensive business scope, providing the following services.
Package delivery: Specializing in worldwide package delivery, including domestic and international services, FedEx ensures efficient and reliable transportation of customers' packages via land, air, and sea.
Cargo shipping: Operating a comprehensive shipping network for the handling and transport of cargo of various sizes and weights, FedEx collaborates with airlines to offer bulk cargo air services.
Supply chain management: Leveraging integrated logistics and transportation resources, FedEx's supply chain management services optimize processes, improve transportation efficiency, and reduce costs in areas such as logistics planning, inventory management, warehousing, and order fulfillment [5].
Logistics consulting: Offering tailored consulting services by professional logistics consultants to address intricate challenges in supply chain design and network optimization.
2.2. Modern Company of Amazon Logistics
2.2.1. Introduction of Company
The basic overview of Amazon logistics is: efficient, fast, automated global distribution network, with advanced technology and huge infrastructure, to achieve the full optimization from the receipt of orders to goods delivered to consumers.
Amazon Logistics is a highly integrated logistics system built by Amazon to support its global e-commerce business. It includes not only the storage and transportation of goods, but also a series of links such as order processing, inventory management, distribution and return processing. The core goal of Amazon Logistics is to ensure that customers receive their ordered goods quickly and accurately, anywhere and at any time, at the lowest cost and highest efficiency [6].
Overall, Amazon Logistics is a highly integrated, technology-driven and continuously optimized system that successfully supports Amazon's position as the world's largest e-commerce company and provides customers with a superior shopping experience.
2.2.2. Introduction of Business
The business scope of Fulfillment By Amazon (FBA) encompasses the following key areas:
Storage services: Sellers ship items in bulk to Amazon's operations centers for storage.
Order fulfillment: Upon sale, Amazon handles sorting, packaging, and delivery of the order.
Customer service: Providing buyer consultation and return services.
First leg Logistics: Sellers can opt for Amazon Global Logistics (AGL) or third-party logistics carriers to transport goods to Amazon warehouses overseas.
End delivery: After a product is sold, Amazon Logistics (FBA) delivers it to the buyer and offers after-sales support.
Additionally, Amazon Logistics not only manages its own website's order delivery but also provides logistics services for non-Amazon platform enterprises through its two business units - "Fulfillment by Amazon" and "Amazon Multi-Channel Fulfillment," thereby bolstering its e-commerce network. Specifically, "Amazon Logistics" focuses on its own website's order distribution while the "multi-channel logistics department" caters to other sales channels beyond the Amazon platform [7].
3. Data Analysis
3.1. Analysis of FedEX's Profitability
Upon analyzing the financial reports of FedEx submitted to NASDAQ during the period from 2020 to 2023, along with the relevant data in Figure 1, it is evident that despite encountering challenges such as the impact of COVID-19, decline in stock market performance, and decrease in freight unit prices, the company has managed to sustain a consistent level of profitability. Nevertheless, an examination of the information presented in Figure 2 indicates that there has been limited progress. The company's profit margin has consistently remained at approximately 60%, suggesting potential saturation within traditional logistics and highlighting the need for exploration of new opportunities to optimize return on investment.
3.2. Analysis of Amazon Logistics' Profitability
Upon examination of the financial report submitted by Amazon Logistics to NASDAQ from 2020-2023 and Figure 1, it is evident that there has been a significant increase in profitability over the four-year period, with an annual growth rate surpassing 7 percentage points. Despite various challenges including the COVID-19 pandemic, Amazon Logistics has effectively managed order acceptance and delivery through an efficient intelligent supply chain layout, ensuring seamless global logistics operations [3]. Additionally, the advancements in Amazon's electronic logistics business and its expanding multi-scenario applications depicted in Figure 2 indicate accelerated development compared to traditional companies such as FedEx. This underscores the company's evolving profitability and reinforces Amazon Logistics' position as a leading global entity.
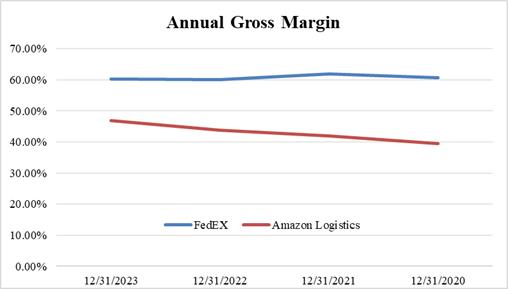
Figure 1: The Annual Gross Margin of Two Companies
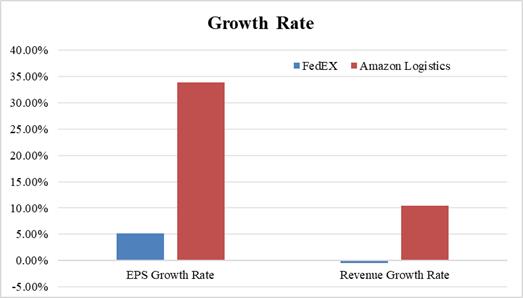
Figure 2: The EPS/Revenue Gross Rate of Two Companies
3.3. Data Comparison
3.3.1. Comparison of Parcel Traffic
According to internal Amazon documents, as of the end of 2023, Amazon has successfully delivered over 4.8 billion packages in the United States, with an internal forecast projecting approximately 5.9 billion packages by year-end. In comparison, FedEx handled around 3.05 billion domestic Express and Ground packages in the fiscal year ending on May 31, 2023. It is important to note that Amazon's data only encompasses packages shipped directly by Amazon from origin to destination, while FedEx's data includes packages it collects and then transfers to the postal service for final delivery.
3.3.2. Comparison of Core Advantages
Compared to Amazon Logistics, FedEx offers the following advantages.
Specialized global delivery services: As a professional express delivery company, FedEx provides services covering over 220 countries and regions worldwide, with a dedicated service team offering diverse logistics transportation and distribution solutions for various customers [8].
Competitive delivery costs: FedEx generally offers lower prices than mainstream express companies for shipments of similar weight and distance, along with flexible pricing options and discounts for larger shipments, effectively reducing transportation costs for customers.
Secure and reliable logistics assurance: Utilizing the Ship Manager system to track the entire transportation process in real time, FedEx delivers goods through direct flight express mode to minimize transit times and reduce loss rates, establishing itself as a globally recognized logistics company with high security standards.
Compared to FedEx, Amazon Logistics offers the following advantages.
Vertically integrated and efficient delivery: Amazon's seamless integration of its global logistics network and distribution centers with its online retail business allows for rapid delivery across various regions. Prime members also receive free next-day shipping, significantly boosting Amazon's logistics sales growth rate and customer loyalty.
Technology-driven logistics management: Through the use of big data analysis and technology integration, Amazon optimizes distribution routes and planning, continuously develops technologies such as drone delivery, smart express cabinets, and the Internet of Things in the field of logistics to greatly enhance distribution efficiency and punctuality [9].
Impeccable and dependable after-sales service: Amazon provides all customers with professional 24/7 customer service to address transportation-related issues, effectively reducing time and operating costs while offering reliable logistics services without any worries or hassles.
4. Suggestion
Faced with the gradual proliferation of electronic logistics information and the increasingly intertwined relationship between e-commerce and logistics transportation, traditional logistics enterprises are finding themselves gradually marginalized in the market. In order to ensure the future development of both traditional and new logistics industries, it is imperative for traditional logistics enterprises to expedite their digital transformation. By implementing strategic management, conducting real-time analysis of data, and fostering collaboration across multiple platforms, logistics enterprises can effectively manage all facets of operations, optimize the allocation of resources, enhance client satisfaction, minimize expenses, and pave the way for sustainable development in anticipation of future needs [2]. This includes promoting the adoption of electronic data interchange (EDI) and other digital tools to enhance logistics information exchange and traceability, thereby bolstering transportation safety. Furthermore, traditional logistics enterprises should leverage technologies such as Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and big data analysis to achieve intelligent and automated operations, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency. On the other hand, while new logistics enterprises possess certain electronic information logistic capabilities, their relatively short development history has resulted in a lack of brand recognition. Therefore, these companies must allocate more resources towards brand promotion efforts. Additionally, while electronic information logistic procedures offer convenience and speed advantages, they also present potential data security and privacy concerns for customers [10]. Only through implementing robust data security measures can new logistics enterprises instill confidence in their customers' minds and establish a solid foundation for future growth.
5. Conclusion
Through the analysis of the case, the rapid development of e-commerce network scale is exerting pressure on traditional logistics enterprises such as FedEx. Meanwhile, new logistics enterprises like Amazon Logistics are continuously encroaching on the market share of traditional logistics enterprises in the transportation market. With their rapid development through electronic logistics platforms and global e-commerce networks, new logistics enterprises are gradually surpassing traditional leaders in terms of profit growth rate and company value. It is evident that traditional logistics enterprises cannot meet current and future transportation market needs and objectives solely based on their reputation and long-term experience established over the past decade. However, despite achieving a high level of compatibility between logistics and electronic information networks, new logistics companies led by Amazon still need to improve data security, transportation stability, and pricing. If these issues are not addressed in a timely manner, traditional logistics companies may successfully transform and regain dominance in the market. Therefore, it is imperative for new logistic companies to continuously enhance their capabilities to maintain a leading position in this highly competitive industry.
During the study, the research results may be limited due to a small number of case studies. Additionally, as a researcher, personal subjective consciousness and bias could influence the analysis of the case, potentially leading to a lack of objectivity in the research conclusion. Moreover, insufficient real-time performance of logistics-related information data in comparative analysis might lead to inaccurate conclusions. However, it is anticipated that this paper can offer effective recommendations for the modernization of traditional logistics firms and the enhanced growth of new logistics companies, contributing to the collective advancement of the global logistics and transportation industry.
References
[1]. Shi, Y., & Zhang, J. (2024). The Intrinsic Logic and Practical Path of Digital Economy and Logistics Industry Integration Development. Logistics Technology, (08), 17-19.
[2]. Ma Jinli.(2024). Application and challenge of digital transformation in logistics field. Market modernization (02), 37, 39.
[3]. Qu, Y. (2021). Study on Logistics Costs Based on the Perspective of International Supply Chains Under the Epidemic: A Case Study of Amazon Logistics. China Storage and Transportation, (02), 115-117.
[4]. Gomez, L. (2022). Strategic Audit of FedEx. (Undergraduate Honors Thesis). University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
[5]. Gregory, A. (2022). Case 2: FedEx–Innovation Through Sustained Adaptability. In Business Innovation (pp. 195-203). Routledge.
[6]. Hassel, A., & Sieker, F. (2022). The platform effect: How Amazon changed work in logistics in Germany, the United States and the United Kingdom. European Journal of Industrial Relations, 28(3),
[7]. Andreoli-Versbach, P., & Gans, J. (2024). Interplay between Amazon store and logistics. European Competition Journal, 1-38.
[8]. Birla, M. (2013). FedEx Delivers: How the World's Leading Shipping Company Keeps Innovating and Outperforming the Competition. John Wiley & Sons.
[9]. Singireddy, S. R. R., & Daim, T. U. (2018). Technology roadmap: Drone delivery–amazon prime air. Infrastructure and Technology Management: Contributions from the Energy, Healthcare and Transportation Sectors, 387-412.
[10]. Tao, J. (2023). Research on the Development of E-commerce Logistics under the Background of Big Data. Logistics Engineering and Management, (12), 56-58.
Cite this article
Zhang,Q. (2024). Comparison of Business Investment Value Between Traditional and New Logistics Companies. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,98,22-28.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2024 Workshop: Finance in the Age of Environmental Risks and Sustainability
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Shi, Y., & Zhang, J. (2024). The Intrinsic Logic and Practical Path of Digital Economy and Logistics Industry Integration Development. Logistics Technology, (08), 17-19.
[2]. Ma Jinli.(2024). Application and challenge of digital transformation in logistics field. Market modernization (02), 37, 39.
[3]. Qu, Y. (2021). Study on Logistics Costs Based on the Perspective of International Supply Chains Under the Epidemic: A Case Study of Amazon Logistics. China Storage and Transportation, (02), 115-117.
[4]. Gomez, L. (2022). Strategic Audit of FedEx. (Undergraduate Honors Thesis). University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
[5]. Gregory, A. (2022). Case 2: FedEx–Innovation Through Sustained Adaptability. In Business Innovation (pp. 195-203). Routledge.
[6]. Hassel, A., & Sieker, F. (2022). The platform effect: How Amazon changed work in logistics in Germany, the United States and the United Kingdom. European Journal of Industrial Relations, 28(3),
[7]. Andreoli-Versbach, P., & Gans, J. (2024). Interplay between Amazon store and logistics. European Competition Journal, 1-38.
[8]. Birla, M. (2013). FedEx Delivers: How the World's Leading Shipping Company Keeps Innovating and Outperforming the Competition. John Wiley & Sons.
[9]. Singireddy, S. R. R., & Daim, T. U. (2018). Technology roadmap: Drone delivery–amazon prime air. Infrastructure and Technology Management: Contributions from the Energy, Healthcare and Transportation Sectors, 387-412.
[10]. Tao, J. (2023). Research on the Development of E-commerce Logistics under the Background of Big Data. Logistics Engineering and Management, (12), 56-58.









