1. Introduction
Digital currency is an alternative to electronic money. Digital currency includes digital gold coins and cryptocurrencies, which can be considered a virtual currency based on node networks and digital encryption algorithms, usually issued and managed by developers. China's central bank has been actively exploring and promoting the research and development and pilot of digital currency and has launched digital currency electronic payment [1]. The issuance policy emphasizes strict supervision of the digital currency market to ensure its legal and compliant operation, and the issuance of the digital yuan aims to improve the efficiency and security of the payment system, reduce reliance on traditional payment intermediaries, and promote financial service inclusion and fintech innovation. China has taken strict regulatory measures on cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, in particular cracking down on illegal financial activities, and has made it clear that some cryptocurrencies are not protected by law. At the same time, China's policy does not prohibit the sale and purchase of all virtual currencies but emphasizes that investors must bear their own risk. In the context of economic globalization, the demand for cross-border payments is growing, and traditional payment systems are facing challenges in efficiency, cost and convenience. Digital currencies provide new ideas for improving cross-border payments. The traditional monetary system has some limitations, such as the cost of currency issuance, and the precision of monetary regulation and control, and digital currency is expected to optimize the monetary system to a certain extent. This paper discusses the characteristics of digital currency, and shows the definition of digital currency[2].
2. Connotation Characteristics
At present, digital currency is considered to be a mechanism system that can realize decentralized payment transactions, wealth storage, accounting circulation and other functions through digital information technology [3].It relies on blockchain technology, has anonymity and cannot be modified. It is found that the origin of digital currency is not long, and the initial digital currency needs the credibility of the government to achieve stability and play the function of a currency, which will have a certain impact on the normally issued currency. China gradually discovered the important nature of digital currency and set up a national digital currency research and development team in 2014, launched the central bank's research on digital currency, and in January 2017, the central Bank officially established the Digital Currency Research Institute. In September 2018, the National Data Currency Institute established a trade finance blockchain platform. By August 2019, the central bank said it would accelerate the pace of research and development of fiat digital currencies. On April 22nd, 2020, the Reform and Development Bureau of the Xiongan New Area Management Committee organized a pilot promotion meeting for the legal digital renminbi, and on August 14th, 2020, the Ministry of Commerce issued the Overall Plan for Comprehensively Deepening the Innovative Development of Trade in Services [4]. Both the 2017 document and the 2021 document define virtual currencies as those that have not acquired the same legal status as fiat currencies and cannot be circulated as money. Digital currencies make the economic cycle more convenient and rapid, achieve transparent and efficient fund transfer and settlement, simplify complex procedures in supply chain finance, and reduce related costs. However, in many judicial cases in our country, different courts have a legal nature of virtual digital currency. According to the "flower of money" conceptual model proposed by the Bank for International Settlements in 2017, digital goods are distinguished into four aspects.
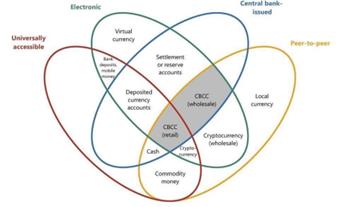
Figure 1: accessible class, digital form class, central bank-issued class, and token class [5]
As shown in Figure 1, it is classified into accessible class, digital form class, central bank-issued class, and token class. The shaded core represents a digital currency form: CB settlement account (universal), CB digital token (universal) and CB digital token (wholesale mode)[6].From the perspective of payment methods, the money tree is divided into four levels, and five types of money are obtained: bank money, electronic money, investment money, central bank money and cryptocurrency[7],If the above payment currency changes the centralized settlement to a decentralized settlement model based on the blockchain, it will get a series of currencies called "stablecoins". From the perspective of payment and clearing method, it is divided into four parts from the type of ownership, the form of asset value, the guarantor and the technical attribute. It traces back the monetary hierarchy and better explains the payment and settlement structure under the modern monetary system.
3. Development Status
In recent years, with the popularity of the digital economy, digital currency has also received a lot of research, forming a new trend of future development. However, as a newly formed monetary system, digital currency does not constitute a complete system.
3.1. Fiat Digital Currency
Legal digital currency is issued by the state, has a certain legal status, issued by the People's Bank of China and managed by the state, subject to state supervision, sovereign, digital financial innovation can improve the level of financial services, become an important part of our country's digital construction, has a great impact on the economic and social order [8].This kind of currency is decentralized management, which increases credibility, has traceability, is more convenient to track and capture illegal acts, almost avoids money laundering and other activities, and is more convenient and cheaper. The production process of paper currency is complex, the process is numerous, and the cost is lower. Therefore, it also improves stability and keeps the value of the currency stable in the long run. Centralized issuance and supervision mechanisms reduce potential risks, improve the security of the system, and provide the government with a new type of currency, policy tools and financial market supervision means to help promote financial innovation and economic development [9]. For the development of digital currency, money laundering methods emerge in an endless stream, and supervision is increasingly strict, but different courts have slightly different definitions of the legal nature of virtual digital currency, and by the end of 2020, China's central bank Digital currency Research Institute has applied for 84 patents for digital currency payment systems. At the same time, the People's Bank of China will also promote the cross-border project of "digital currency" with the Hong Kong Monetary Authority of China, and consider promoting cross-border transactions to achieve the integration of the global financial market and realize the development of the "token economy"[10], Digital currencies reduce issuance and circulation costs, making transactions more efficient. As a product of the rapid development of financial technology, the form of money has changed. Compared with paper money or WeChat Pay, it greatly saves the cost of issuance and circulation and does not need to use terminals and networks. The value of digital currency is stable for a long time and tends to be internationalized, and the value of the currency directly affects the exchange rate, national credit and international trade [11]. Therefore, the digital currency will also exist as an important factor in the market, and the legal digital currency will also be guaranteed by the national credit, which is legal and sovereign, and the value of the currency will be more stable. In the face of the reform of the international monetary system, the voice of China's legal digital currency will be increased.
3.2. Non-Legal Digital Currency
Non-fiat currencies, that is, cryptocurrencies, can also be called private digital currencies, private digital currencies, etc. This digital currency has no central issuance and regulatory authority, the currency adopts decentralized blockchain technology, and all transaction records are stored on the ledger, with anonymity but without monetary stability, and through special encryption algorithms, it can hide the identity information and transaction address of currency holders and traders, and transactions can be carried out in complete secrecy. Non-fiat digital currency transactions are global, have no geographical restrictions, and can be completed in the case of cross-border transfer payments, making payments more efficient [12], However, non-legal digital currencies are like storage items, like antiques, jewellery and other collectables, so in terms of pricing, they can only be used in the crypto ecosystem. At present, the highest acceptance of currency is Internet websites and their service providers. Private digital currencies are traded on a smaller scale and lack legal safeguards. In contrast, costs are high and the value of non-fiat digital currencies lacks universal recognition. As a collection item, non-fiat digital currency holders usually buy the collection and hold it for a long time, until the currency appreciates, which will lead to serious deflation. By 2017, China's regulatory attitude has changed to directly combat the hidden dangers of risk. By 2021, China's regulation of private digital currencies will extend to all types of token financing businesses at home and abroad [13].
4. The Opportunities and Challenges
4.1. Statutory Protection and Safety
The current digital currency policies and laws are not sound, and it is necessary to promote the legislative construction of legal digital currency, and its regulatory issues have become the focus of research in the industry. There are no clear guidance restrictions in the supervision and implementation of money laundering and other issues, but China's attitude toward financial supervision is increasingly strict, and private currency and legal currency are distinguished by the idea of distinguishing virtual currency and blockchain technology. And policy-based documents, so that many regulatory bodies cross responsibilities, power allocation is unclear [14].As a newly developed new monetary system, currency types need to be further explored, it is suggested to clarify the legal status and use rules of digital currency, and build a complete monetary system.
4.2. Regulatory Issue
There are many types of digital currencies, but the nature and function are not clearly defined, the supervision involves multiple fields, and it is easy to appear unclear responsibilities, etc., and because of the different regulatory frameworks and laws in different regions, the difficulty of coordinating supervision will be greatly increased, and the emergence of counterfeit currency may also disrupt the market order. According to the provisions of Article 19 of the Law of the People's Republic of China on the People's Bank of China, the circulation method of counterfeit currency also difficult to play an effective regulatory role for digital currency. As for the problem of money laundering supervision, the special form of legal digital currency makes it impossible to be included in the scope of regulation of the current law. A kind of transfer of currency ownership through peer-to-peer transactions, which does not pass the bank settlement system, makes the money laundering crime of digital currency completely avoid supervision. It is suggested to launch a complete anti-money laundering system, strengthen the responsible departments of specialized agencies to crack down on illegal money laundering activities, and combat tax evasion. In view of the regulatory problems in counterfeit currency, money laundering, tax evasion and other aspects, a comprehensive inspection can be carried out by expanding the subject of regulatory obligations, establishing an information-sharing mechanism, and strengthening international cooperation [15].
4.3. Technical Characteristics
The main challenge lies in transaction and security. Although it has encryption technology, it faces threats such as network security loopholes. The People's Bank of China should establish a sound system security management system and operational norms, monitor and evaluate the security of the digital RMB system, and take necessary measures to improve and update it. It not only needs to meet the protection of user privacy but also needs to have certain requirements for regulatory traceability, but also can design customized products according to the needs of different customer groups [16]. The Consensus algorithm is a distributed algorithm mainly used by blockchain technology, and the transaction performance and speed are mainly determined by the performance of each participating node in the network, requiring a large number of transactions [17]. At the same time, as technology continues to update, legal protection and regulation need to keep up with the pace of technological change.
4.4. Product Awareness
The awareness of digital currency is improving, but from the overall point of view, there are still some ordinary people's cognition of digital currency is extremely limited, and there are differences in public cognition in different regions, it is currently recommended that China's digital yuan be piloting at the wholesale end. Encouraging commercial banks to further promote digital RMB; The central bank's digital currency interest rate can be adjusted according to the needs of policy regulation, as an important supplement to the existing interest rate corridor, and even as a lower limit of the corridor to further optimize the transmission effect of monetary policy [18].
5. Conclusion
To sum up, digital currency has many advantages such as efficient transaction completion, decentralized management and low cost, but it should also pay more attention to regulatory issues. In contrast, having a complete financial system must be more helpful to the development of China's financial industry. This paper has extensively collected several domestic academic articles to explain the definition of legal digital currency and private digital currency and clarify the problems and challenges faced by digital currency. For the future research direction, the prediction includes but is not limited to the system, evaluation criteria, operation mode and other aspects of central bank digital currency. To develop China's financial industry, the digital technology industry should be improved. To determine the legal status and rules for the use of legal digital currency, technological progress will promote social change, and digital currency will be developed and disseminated [19], Product awareness will also increase. Driven by financial innovation, people continue to explore more efficient, safer and more convenient forms of payment and money. Make use of many advantages such as the high efficiency and low cost of digital currency, so that domestic digital currency can achieve greater development.
References
[1]. Guangmei Wan,Research on Financial Risks and Prevention Strategies of Digital Currency,Financial news journal,2024-01-23,page185
[2]. Gang Di,Digital Currency Analysis:,Financial technology,1994-2023,page52
[3]. Ming Zhang ,Zhe Wang, Yinmo Chen,Comparative analysis of three digital currencies: Bitcoin, Libra and digital Renminbi,International finance,2023-03-15,page54-55
[4]. Peijie Wang,On the Inevitability and Future Trend of Digital currency Issuance,Shanxi finance and Taxation,2024-01-01,page47
[5]. Salomé Bernhart,Applications of CBDCs and private stablecoins:,Comparative analysis,2020-08-21, page:29
[6]. Gang Di,Digital Currency Analysis,Financial technology,1994-2023,page52
[7]. Ziyu Ma ,Research on the Development path of new money under the Evolution of Monetary system classification,Prices in China ,2021-09-13,page10
[8]. Jingxuan Jiang,On the Regulatory Dilemma and Breakthrough of China's Legal Digital Currency,Northern Finance ,2024-01-15,page64-65
[9]. Guangmei Wan,Research on Financial Risks and Prevention Strategies of Digital Currency,Financial news journal,2024-01-23,page185
[10]. Ziyu Ma ,Research on the Development path of new money under the Evolution of Monetary system classification,Prices in China ,2021-09-13,page11-12
[11]. Jingxuan Jiang,On the Regulatory Dilemma and Breakthrough of China's Legal Digital Currency,Northern Finance ,2024-01-15,page67
[12]. Guangmei Wan,Research on Financial Risks and Prevention Strategies of Digital Currency,Financial news journal,2024-01-23,page187
[13]. Ziwei Dai, Hailong Guo ,Research on China's Digital Currency Development from the Perspective of Jingping Xi Economic Thought,Kunming, Yunnan Province 650000,Institute of Party History and Literature of the CPC Central Committee (Central Compilation and Translation Bureau), Beijing ,2014-03-15,page6
[14]. Yating Zhang,Fanqi Zhou,Regulatory reform of virtual digital currency,Investment and cooperation, 2024-02-15,page11
[15]. Jingxuan Jiang,On the Regulatory Dilemma and Breakthrough of China's Legal Digital Currency,Northern Finance,2024-01-15,page67-69
[16]. Zhihui Shi, Minfeng Lu,Study on the Influence Mechanism and Optimization Countermeasures of Digital RMB on the Development of Digital Financial Industry,Investment and cooperation ,2024-02-15,page109
[17]. Yingying Guan,Research on the Development of legal Digital Currency -- Taking Central Bank DCEP as an Example,Journal of HeiheCollege ,2024-02-25,page64
[18]. Xiaolei Liu,Changzhou Ma,Bowen Dong, Xiaolin Xiao,Research on Central Bank Digital Currency under the Interest Rate Corridor * -- A Discussion Based on the Theory of New Monetarism and the Reality of China,Manage world,2024-03-25
[19]. Gang Di,Digital Currency Analysis,Financial technology,1994-2023,page54-55
Cite this article
Zhang,Z. (2024). Central Bank Digital Currency Development Status and Future Challenges. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,105,157-162.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Guangmei Wan,Research on Financial Risks and Prevention Strategies of Digital Currency,Financial news journal,2024-01-23,page185
[2]. Gang Di,Digital Currency Analysis:,Financial technology,1994-2023,page52
[3]. Ming Zhang ,Zhe Wang, Yinmo Chen,Comparative analysis of three digital currencies: Bitcoin, Libra and digital Renminbi,International finance,2023-03-15,page54-55
[4]. Peijie Wang,On the Inevitability and Future Trend of Digital currency Issuance,Shanxi finance and Taxation,2024-01-01,page47
[5]. Salomé Bernhart,Applications of CBDCs and private stablecoins:,Comparative analysis,2020-08-21, page:29
[6]. Gang Di,Digital Currency Analysis,Financial technology,1994-2023,page52
[7]. Ziyu Ma ,Research on the Development path of new money under the Evolution of Monetary system classification,Prices in China ,2021-09-13,page10
[8]. Jingxuan Jiang,On the Regulatory Dilemma and Breakthrough of China's Legal Digital Currency,Northern Finance ,2024-01-15,page64-65
[9]. Guangmei Wan,Research on Financial Risks and Prevention Strategies of Digital Currency,Financial news journal,2024-01-23,page185
[10]. Ziyu Ma ,Research on the Development path of new money under the Evolution of Monetary system classification,Prices in China ,2021-09-13,page11-12
[11]. Jingxuan Jiang,On the Regulatory Dilemma and Breakthrough of China's Legal Digital Currency,Northern Finance ,2024-01-15,page67
[12]. Guangmei Wan,Research on Financial Risks and Prevention Strategies of Digital Currency,Financial news journal,2024-01-23,page187
[13]. Ziwei Dai, Hailong Guo ,Research on China's Digital Currency Development from the Perspective of Jingping Xi Economic Thought,Kunming, Yunnan Province 650000,Institute of Party History and Literature of the CPC Central Committee (Central Compilation and Translation Bureau), Beijing ,2014-03-15,page6
[14]. Yating Zhang,Fanqi Zhou,Regulatory reform of virtual digital currency,Investment and cooperation, 2024-02-15,page11
[15]. Jingxuan Jiang,On the Regulatory Dilemma and Breakthrough of China's Legal Digital Currency,Northern Finance,2024-01-15,page67-69
[16]. Zhihui Shi, Minfeng Lu,Study on the Influence Mechanism and Optimization Countermeasures of Digital RMB on the Development of Digital Financial Industry,Investment and cooperation ,2024-02-15,page109
[17]. Yingying Guan,Research on the Development of legal Digital Currency -- Taking Central Bank DCEP as an Example,Journal of HeiheCollege ,2024-02-25,page64
[18]. Xiaolei Liu,Changzhou Ma,Bowen Dong, Xiaolin Xiao,Research on Central Bank Digital Currency under the Interest Rate Corridor * -- A Discussion Based on the Theory of New Monetarism and the Reality of China,Manage world,2024-03-25
[19]. Gang Di,Digital Currency Analysis,Financial technology,1994-2023,page54-55









