1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the economy and science and technology, the supply chain operation process has become more complicated. Supply chain logistics is key in daily enterprise work and has gradually attracted more attention. However, for the existing supply chain logistics patterns, there are still problems like information barriers, high difficulty, a long time to integrate information and lack of trust. In recent years, under the context of big data, some enterprises have achieved the goal of reducing costs and increasing efficiency through artificial intelligence or blockchain technology, and certain results have been achieved. This paper will take the existing mode of supply chain logistics of JD and Alibaba as an example, introduce the advantages of the application of AI technology and blockchain technology in the field of supply chain logistics, respectively, and then discuss the application practice of the combination of AI and blockchain in the site selection of logistics warehouses, intelligent warehouse management and intelligent logistics path management.
As one of the largest users, developers and promoters of logistics systems in China, JD Logistics adheres to the core concept “people and enterprises have no room for each other, goods have no boundaries, and scenes have no boundaries”, realizing intelligent logistics parks and building highly efficient and coordinated international supply chain networks, with the help of AI and big data technologies to make accurate forecasts of unit volumes and intelligent site selection of warehouses. They research and develop a variety of intelligent equipment independently, such as the Wolf Goods-to-People System, the Wolf Intelligent Handling and Picking Robot, the Automated Distribution Wall, the Unmanned Forklift Trucks, Packing Machines, and Transportation Machines. These facilities have participated in the cooperation of major e-commerce, medicine, industrial electronics and other fields of enterprises so that each link of logistics has the ability of self-awareness, self-learning and self-decision-making, forming a technical service capability covering the entire supply chain scene, greatly reducing the hidden costs and invariably improve the efficiency of each link.
As a logistics platform under Alibaba, Cainiao Network uses Alibaba’s powerful e-commerce resources to promote the deep combination of intelligent logistics and e-commerce actively, establishes its express delivery team through big data, AI and other technologies, and also possesses a different degree of digital intelligence in various aspects such as automotive, fast-consumption, and other industries, which makes the Cainiao Network's digital intelligence logistics have a wider extension power. Cainiao Network has established electronic waybill, supply chain digitization, unmanned logistics, realized automated distribution and integrated face list, used RFID to realize bulk data collection, and vigorously developed “seamless” cross-border logistics so that the whole chain of participants, merchants and consumers can realize visual control. Through intelligent express cabinets and other end distribution methods, Cainiao Network solves the distribution of the "last kilometer" problem to ensure the safety of the parcels and improve the timeliness of consumers sending and picking up the parcels.
Blockchain is a decentralized, non-codifiable distributed bookkeeping technology with transparency and security. JD launched “Zhizhen Life” to the public in 2018, an aggregated small program for traceable commodities through blockchain technology, which can be compatible with various underlying chains, cloud services, etc., and has the function of one-key deployment. It is used in the supply chain, finance, government affairs, commodity anti-counterfeiting traceability and other fields. Ant Gold Service under Alibaba has also developed “Ant Blockchain” on blockchain technology and combined it with e-commerce to trace the whole chain of information to prevent counterfeiting, as well as mutual insurance, housing leasing, cross-border remittance, copyright and supply chain finance to a certain degree of innovation in the direction. Nevertheless, the application of blockchain in logistics has yet to be developed. The innovative combination of AI technology can effectively simplify the process of supply chain logistics, reduce management costs, promote the synergy of various links in supply chain logistics, improve the efficiency of real-time updating of inventory and speed of response, and break down the information barriers to solve the problem of asymmetric information.
2. Case Description
2.1. Alibaba Application Status
Alibaba is enhancing supply chain logistics in various innovative ways by integrating artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. By integrating AI and blockchain, Alibaba is not only streamlining supply chain operations but also improving reliability and efficiency to manage complexity in logistics better and increase customer satisfaction.
Real-time monitoring and optimization: Alibaba’s AI Supply Chain solution, offered through Alibaba Cloud, utilizes artificial intelligence and machine learning to provide real-time monitoring and intelligent troubleshooting for the entire supply chain operation. This includes diagnosing inventory issues, recommending optimization strategies and forecasting demand accurately [1].
Transparency and efficiency. Alibaba is utilizing blockchain to improve supply chain transparency and traceability. The technology helps create a more direct relationship between stakeholders such as wholesalers, logistics providers and consumers, automating processes and reducing the likelihood of errors and delays. Blockchain enhances accountability and connectivity across the supply chain, leading to faster and more accurate operations [2].
Control towers for decision-making. Alibaba uses AI-powered “control towers” to predict risk and provide decision support for supply chain management through data mining. These systems use machine learning algorithms to handle anomalies and optimize supply chain decisions based on various performance metrics.
Enhance product integrity. Alibaba is exploring blockchain to ensure product integrity and combat fraud, especially in the food industry. The technology keeps a digital record of each product and tracks its movement through the supply chain, thereby enhancing inventory management and reducing costs associated with delays and fraudulent activity [3].
2.2. JD Application Status
JD likewise adopts artificial intelligence and blockchain technology in its supply chain logistics to improve efficiency and transparency. It is committed to improving its supply chain logistics by utilizing cutting-edge technologies to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer trust and satisfaction. Here’s how JD is integrating these technologies.
Intelligent logistics and automation. JD has developed an intelligent logistics system that includes a fully automated warehouse and uses robots and drones for deliveries, especially in remote areas. This automation extends to their transportation system, using artificial intelligence to improve the efficiency of operations and delivery processes [4].
It enables traceability and efficiency. JD has launched a blockchain platform that allows its enterprise customers to track shipments. The platform supports creating and managing smart contracts to automate and rationalize supply chain operations. This innovation helps to ensure transparency and increase trust among consumers and business partners [5].
IoT and 5G innovations. JD pioneered using 5G and IoT in its logistics operations, creating efficient, connected logistics parks. These technologies enable real-time communication between machines and humans, greatly improving operational efficiency and response times [6].
JD Blockchain Open Platform. The platform is designed to help other businesses utilize JD’s blockchain technology to improve transparency and operational efficiency. It allows for the tracking and verifying of products throughout the supply chain, thus ensuring authenticity and quality. In addition to this, JD also utilizes blockchain technology to promote sustainable development, ensure transparency in all supply chain activities, and support better environmental, social and governance (ESG) practices.
3. Case Analysis
3.1. The Application of AI on the Supply Chain Logistics
AI makes machines imitate human thinking, with human-like judgment and resilience of intelligent technology. Its deep learning has a better ability to parse unstructured data such as images, audio and video, so it can greatly improve efficiency, reduce human resource costs and increase corporate profits in various aspects, like warehouse location, inventory management, logistics control and tracking. AI can also collect real-time customer evaluation and feedback for future demand prediction and adjustment of supply-demand balance to improve customer satisfaction, which is conducive to developing and extending supply chain logistics platform services. In terms of inventory optimization, AI helps enterprises predict and analyze the optimal inventory interval by analyzing suppliers' effective response and delivery to reduce holding costs and improve inventory turnover rate. With transportation flow and weather monitoring of distribution paths, AI also helps reduce traffic congestion and the cost per unit of distance consumed [7].
In traditional supply chain management, multiple participants are involved, and many contract documents, logistics and payment processes must be handled manually. These processes typically require significant time and labor costs and are prone to errors and delays. We can combine AI and blockchain technology to optimize supply chain management processes and create smart contracts.
For some large enterprises, combining AI and blockchain can improve the efficiency and transparency of supply chain management. Combining sensor data and AI algorithms with blockchain technology enables real-time monitoring and analysis of logistics status, warehouse inventory and production processes in the supply chain. The system can help reduce inventory costs, minimize delays and waste, and improve supply chain traceability. Using AI technology to analyze large amounts of transaction data and combining it with the blockchain’s immutability and transparency can be established to help large corporations such as Ali and JD create smart marketplaces and trading platforms more effectively. This combination can be applied not only to stock trading and digital asset trading but also to auctions, bidding and other fields, thus improving transaction efficiency and reducing transaction costs.
A decentralized AI application platform can be constructed using blockchain technology to enable developers and users to share and trade AI models and data, facilitating the sharing and trading of AI models and data, lowering the threshold and cost of AI application development, and increasing the credibility and transparency of models. In technology integration, compatibility of new technologies with existing supply chain systems may face technical and operational difficulties.
As a new digital technology, Blockchain needs more professionals to develop and maintain it for small and medium-sized enterprises. If the development and maintenance of digital technology are left to an outsourcing company (Ali Cloud), there may be a risk of leaking sensitive data. Therefore, when using blockchain technology, there is often the problem of protecting the privacy and security of data, which can be effectively solved by artificial intelligence.
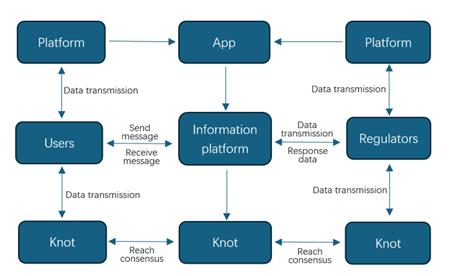
Figure 1: Design diagram of storage traceability based on blockchain technology
As shown in Figure 1, AI can be used for data privacy protection and authentication on the blockchain, using machine learning algorithms to encrypt and anonymize personal data, which is then stored on the blockchain to ensure data security. This combination can be applied to healthcare, finance, and other sectors to improve data security and compliance with privacy regulations, reducing the cost of intermediaries.
In addition, smart contracts on the blockchain can be automated and executed using AI technology. Embedding AI algorithms into smart contracts enables more complex logic and decision-making processes. It can automate supply chain management, insurance claims processing, and contract enforcement, reducing human intervention and management costs. In the Ali and JD platforms, AI and blockchain can automate contract execution, customer payment and data recording in the supply chain logistics process, reducing human errors and delays.
3.2. Risk Management
Both Alibaba and JD implement sophisticated risk management strategies in their supply chain operations, and both companies are constantly innovating and adopting new technologies to enhance their risk management frameworks and ensure the robustness and resilience of their large and complex supply chains. Combined, these technologies not only strengthen their risk management capabilities but also streamline operational processes, improve regulatory compliance, and increase the overall efficiency of the supply chain. The strategic integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence enables Alibaba to address better the complexities and challenges of modern global trade logistics.
3.2.1. Alibaba's Risk Management Approach
Traceability. Alibaba utilizes blockchain to create a transparent, immutable ledger for all transactions throughout the supply chain. This level of traceability ensures that each product can be verified throughout its journey from origin to consumer, which is critical to confirming authenticity and effectively managing recalls. This reduces the risks associated with counterfeit goods and compliance violations.
Predictive analytics. By integrating AI with data stored on the blockchain, Alibaba can use predictive analytics to anticipate and manage potential disruptions before they occur. AI algorithms analyze patterns and trends in blockchain data to predict potential supply chain disruptions, enabling Alibaba to proactively manage inventory, adjust supply routes, and modify production schedules to mitigate these risks.
Smart Contracts. Smart contracts automate the execution of transactions on the blockchain when predefined conditions are met, thereby reducing the risk of manual error and improving compliance with trade regulations. AI supports these contracts by analyzing past performance and external conditions to optimize contract terms and conditions, ensuring that operations are efficient and compliant with international laws and standards [8].
Risk Detection. AI algorithms continuously monitor blockchain data to detect anomalies or unusual patterns that could signal risks such as fraud, supply bottlenecks, or operational inefficiencies. This enables Alibaba to quickly resolve potential issues before they escalate, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the supply chain.
3.2.2. JD's Risk Management Approach
Traceability and Transparency. JD uses blockchain to maintain a transparent and immutable record of its supply chain from the origin of goods to delivery. This level of traceability is essential for verifying authenticity, effectively managing recalls and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. It significantly reduces the risks associated with counterfeit products and fraudulent activity.
AI-Driven Decision Making. AI algorithms are applied to the vast amounts of data captured on the blockchain. These algorithms analyze trends and patterns to provide predictive insights into potential disruptions or inefficiencies in the supply chain. For example, AI can predict demand surges, supply shortages, or potential logistics delays, enabling JD to take preemptive action to mitigate these risks [9].
Smart Contracts. JD utilizes smart contracts on its blockchain platform to automate compliance and operational processes. When conditions are met, these contracts are automatically executed based on pre-defined rules, minimizing human error and increasing efficiency. AI supports these processes by optimizing contract terms based on historical data and predictive analytics, ensuring operations are efficient and compliant with relevant laws and regulations [10].
Fraud Detection. Combining blockchain and AI also strengthens JD's ability to secure its supply chain. Blockchain's inherent security features protect data integrity and prevent tampering, while AI can monitor and detect anomalous or suspicious activity in real-time. This dual approach helps prevent data breaches and reduces the risk of cyber threat infiltration.
4. Conclusion
Artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies offer great possibilities and potential benefits for optimizing JD and Alibaba's supply chain logistics model. By combining these two technologies, automation, intelligence and efficiency in supply chain logistics can be realized, thereby reducing costs, improving efficiency and enhancing overall competitiveness. The application of AI in supply chain logistics, such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization and transport route planning, can provide accurate data analysis and decision-making support, which can help to reduce inventory costs, decrease transport time and optimize resource allocation throughout the supply chain. At the same time, AI can also improve the efficiency and reliability of equipment and vehicles through predictive maintenance and troubleshooting. Blockchain technology provides data traceability, security and transparency in supply chain logistics. Through blockchain's distributed ledger and smart contracts, trusted transactions and information sharing between supply chain participants can be realized, reducing information asymmetry and trust issues. It helps to enhance collaboration and communication between partners in the supply chain and improve the efficiency and sustainability of the overall supply chain.
However, several challenges still need to be overcome to take full advantage of AI and blockchain. For example, the issues of data privacy and security need to be properly addressed; the challenges of technology costs and standardization need to be resolved; and the challenges of organizational change and staff training need to be addressed. Further research and practice are therefore essential. Through continued research and practice, the application of AI and blockchain in JD and Alibaba's supply chain logistics will be continually improved and optimized to achieve cost reductions further and increase efficiency, thereby driving innovation and development in supply chain logistics. At the same time, technical, privacy and organizational challenges will be actively addressed to realize the maximum potential of AI and blockchain to bring sustainable competitive advantage and business value to JD, Alibaba and the industry.
Authors Contribution
All the authors contributed equally, and their names were listed alphabetically.
References
[1]. Falcone, E., Kent, J., & Fugate, B. (2020). Supply chain technologies, inter-organizational network and firm performance: A case study of Alibaba Group and Cainiao. International journal of physical distribution & logistics management, 50(3), 333-354.
[2]. Long, D. (2018). Alibaba launches blockchain technology to improve supply chain integrity and enhance trust in the platform—the Drum.
[3]. Bindi, T. (2017). Alibaba and AusPost team up to tackle food fraud with blockchain. 20th May. http://www. ZDNet. Com/article/alibaba-and-auspost-team-up-to-tackle-foodfraud-withblockchain.
[4]. Li, Z., Shu, Z., & Wang, X. (2024). Exploring competitive advantages in enterprise supply chains: A case study of JD’s predictive and logistics links. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 181, p. 03014). EDP Sciences.
[5]. Wang, Y. Y., Tao, F., & Wang, J. (2022). Information disclosure and blockchain technology adoption strategy for competing platforms. Information & Management, 59(7), 103506.
[6]. Zheng, K., Zhang, Z., & Song, B. (2020). E-commerce logistics distribution mode in big-data context: A case analysis of JD. COM. Industrial Marketing Management, 86(1), 154-162.
[7]. H. Shen, J. Ling & S. B. Jiao. (2023). Research on the security application of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology in smart supply chains. Confidential Science and Technology (10), 39-45.
[8]. Lahkani, M. J., Wang, S., Urbański, M., & Egorova, M. (2020). Sustainable B2B E-commerce and blockchain-based supply chain finance. Sustainability, 12(10), 3968.
[9]. Shen, Z. M., & Sun, Y. (2023). Strengthening supply chain resilience during COVID‐19: A case study of JD. com. Journal of Operations Management, 69(3), 359-383.
[10]. Li, M., Shao, S., Ye, Q., Xu, G., & Huang, G. Q. (2020). Blockchain-enabled logistics finance execution platform for capital-constrained E-commerce retail. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 65, 101962.
Cite this article
Chen,H.;Wang,Z.;Zhang,M. (2024). Mechanism Study on Innovative Influences of AI and Blockchain on Supply Chain Logistics: Case Study of JD and Alibaba. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,109,94-100.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2024 Workshop: Innovative Strategies in Microeconomic Business Management
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Falcone, E., Kent, J., & Fugate, B. (2020). Supply chain technologies, inter-organizational network and firm performance: A case study of Alibaba Group and Cainiao. International journal of physical distribution & logistics management, 50(3), 333-354.
[2]. Long, D. (2018). Alibaba launches blockchain technology to improve supply chain integrity and enhance trust in the platform—the Drum.
[3]. Bindi, T. (2017). Alibaba and AusPost team up to tackle food fraud with blockchain. 20th May. http://www. ZDNet. Com/article/alibaba-and-auspost-team-up-to-tackle-foodfraud-withblockchain.
[4]. Li, Z., Shu, Z., & Wang, X. (2024). Exploring competitive advantages in enterprise supply chains: A case study of JD’s predictive and logistics links. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 181, p. 03014). EDP Sciences.
[5]. Wang, Y. Y., Tao, F., & Wang, J. (2022). Information disclosure and blockchain technology adoption strategy for competing platforms. Information & Management, 59(7), 103506.
[6]. Zheng, K., Zhang, Z., & Song, B. (2020). E-commerce logistics distribution mode in big-data context: A case analysis of JD. COM. Industrial Marketing Management, 86(1), 154-162.
[7]. H. Shen, J. Ling & S. B. Jiao. (2023). Research on the security application of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology in smart supply chains. Confidential Science and Technology (10), 39-45.
[8]. Lahkani, M. J., Wang, S., Urbański, M., & Egorova, M. (2020). Sustainable B2B E-commerce and blockchain-based supply chain finance. Sustainability, 12(10), 3968.
[9]. Shen, Z. M., & Sun, Y. (2023). Strengthening supply chain resilience during COVID‐19: A case study of JD. com. Journal of Operations Management, 69(3), 359-383.
[10]. Li, M., Shao, S., Ye, Q., Xu, G., & Huang, G. Q. (2020). Blockchain-enabled logistics finance execution platform for capital-constrained E-commerce retail. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 65, 101962.









