1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the global economy, causing unprecedented disruptions across various industries. Businesses worldwide faced challenges such as plummeting market demand, disrupted supply chains, and restricted access to financial resources. The tech industry, while initially resilient, was not immune to these effects. As consumer spending habits shifted and uncertainties loomed, companies had to innovate and adapt to sustain their growth.
Studying sustainable business growth in the post-pandemic era is crucial as it offers insights into how companies can build resilience and adapt to future crises. Sustainable growth strategies ensure that businesses can maintain their market positions, continue to innovate and contribute positively to the economy, even in times of adversity. This paper focuses on the smartphone industry developments of two major technology companies, Apple and Huawei. While Apple, a global leader in technology, decided to cancel its car project amidst the pandemic, Huawei successfully developed and launched its AITO cars. Huawei's venture into the automobile market marks a significant diversification of its business, contrasting sharply with Apple's decision to retract its automotive ambitions[1].
It is interesting to understand the reasons behind these divergent scenarios for Apple and Huawei. The purpose of this paper is to identify the differences in Apple and Huawei's approaches to the automotive industry and, by extension, their broader business strategies post-pandemic. This analysis will provide insights into how governments and the automotive industry can support market recovery and address the economic downturn following the pandemic. By understanding the strategic decisions of these leading companies, this paper can draw lessons on how to foster sustainable business practices in a post-pandemic world.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Business Sustainability in Downturns
Existing research on business sustainability during economic downturns highlights the critical challenges that companies face, such as decreased market demand, cash flow constraints, and difficulties in accessing loans. Studies have shown that businesses that adopt flexible and adaptive strategies are more likely to survive and thrive during economic crises[2]. The literature emphasizes the importance of innovation, diversification, and strategic resource management as key factors in maintaining business sustainability during periods of economic instability[3].
2.2. Theoretical Frameworks: Market, Cash Flow, Loans
Theoretical frameworks provide a foundation for understanding how market demand, cash flow, and loan accessibility influence business sustainability. The demand-supply theory suggests that fluctuations in market demand directly impact a company's revenue and profitability[4]. Cash flow management theories emphasize the importance of maintaining liquidity to ensure operational continuity during downturns[5]. Additionally, theories on financial accessibility underscore the role of banking institutions and credit availability in supporting business operations during economic crises[6].
2.3. Corporate Strategies Post-COVID-19
Studies on corporate strategies in response to economic crises, particularly the COVID-19 pandemic, reveal various approaches that companies have employed to maintain sustainability. Research indicates that businesses have focused on digital transformation, supply chain resilience, and strategic cost management to navigate the challenges posed by the pandemic[7]. Specific case studies of companies like Apple and Huawei provide insights into how leading firms have adapted their business models and strategies to sustain growth post-COVID-19. For instance, Apple has focused on enhancing its digital services and expanding its ecosystem, while Huawei has diversified into the automotive sector. These strategic responses have helped Apple strengthen its core product lines and maintain a robust digital presence, while Huawei's diversification has opened new revenue streams and mitigated risks associated with its traditional markets. Such approaches have enabled both companies to maintain their competitive edge and ensure long-term sustainability in the post-pandemic era[8]. Additionally, strategies for maintaining business continuity, such as those discussed by Dehghani[9], and the impact of innovation on business sustainability during crises, further underscore the importance of adaptive and forward-thinking strategies in navigating economic disruptions.
3. Methodology
This study employs a comparative case study approach to analyze the sustainable business strategies of Apple and Huawei in the post-pandemic era. The case study method allows for an in-depth examination of each company's strategic responses to the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. By comparing two leading technology companies with distinct strategies, this approach provides valuable insights into the effectiveness and implications of different business practices in sustaining growth during economic downturns.
The analysis relies on a variety of data sources to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the strategies employed by Apple and Huawei. The primary sources of data include financial reports, market analysis, and industry reports. Annual and quarterly financial statements from Apple and Huawei are used to assess their financial performance during and after the pandemic. Industry reports and market analysis from reputable sources such as Gartner and International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Quarterly Mobile Phone Tracker, are utilized to understand market trends and the competitive landscape. Additionally, reports from industry associations and research firms provide insights into the automotive sector and the broader technology market.
Apple and Huawei were selected as case studies based on several criteria. Firstly, both companies are leaders in the technology industry, with significant market influence and innovation capabilities. Secondly, Apple and Huawei adopted different strategies in response to the pandemic, with Apple canceling its car project and Huawei successfully launching its AITO cars. This contrast in approaches provides a rich basis for comparison. Thirdly, both companies have a global presence, making their strategies and outcomes relevant to a wide range of markets and economic conditions. Lastly, there is sufficient publicly available data on their financial performance, strategic decisions, and market activities, facilitating a thorough analysis.
The comparative analysis involves several analytical methods. Financial analysis is conducted to evaluate key financial metrics such as revenue, profit margins, and cash flow, comparing the financial performance of Apple and Huawei during and after the pandemic. Then, trend analysis is used to analyze market trends and pricing strategies over the pandemic period, understanding the impact of their business decisions on market positioning.
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of the Pandemic's Impact on Apple's Business Operations
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on Apple's business operations. With global supply chain disruptions, Apple faced delays in the production and delivery of its products. Temporary closures of Apple Stores worldwide also affected sales, particularly in the early months of the pandemic. Despite these challenges, Apple managed to pivot by enhancing its online sales channels and focusing on its digital ecosystem. The launch of the iPhone 12 with 5G technology, for instance, saw robust demand and helped offset the initial decline in sales. Additionally, the company's services segment, including the App Store, Apple Music, and iCloud, experienced significant growth as more consumers turned to digital solutions during lockdowns.
4.2. Analysis of the Pandemic's Impact on Huawei's Business Operations
Huawei's business operations were doubly impacted by the pandemic and geopolitical tensions, particularly the US sanctions that restricted its access to essential technologies. Supply chain disruptions and restrictions on semiconductor supplies posed significant challenges. Despite these hurdles, Huawei demonstrated resilience by pivoting towards the domestic market in China and focusing on new business areas. The company accelerated its development in the consumer electronics segment, particularly in wearables and smart home devices. Moreover, Huawei's strategic move into the automotive sector with the launch of AITO cars showcased its ability to diversify and adapt to changing market conditions, mitigating some of the adverse impacts on its core telecommunications business.
4.3. Comparative Financial Performance of Apple and Huawei During the Pandemic
A comparative analysis of Apple and Huawei's financial performance during the pandemic reveals contrasting outcomes. Apple's revenue initially experienced a drop due to supply chain issues and store closures, but it quickly rebounded with strong sales of the iPhone 12 and a significant increase in service revenue. In fiscal year 2020, Apple reported a revenue growth of 6% year-over-year, driven by its diversified product portfolio and robust digital ecosystem. Conversely, Huawei faced a more turbulent financial performance. The company's international sales were particularly hit by sanctions, resulting in a slowdown in overall revenue growth. However, Huawei's focus on the domestic market and its entry into the automobile industry provided new revenue streams, partially offsetting the decline in its traditional business segments.
4.4. Key Strategic Responses to the Pandemic from Apple and Huawei
The first strategy was Apple's decision to cancel car plans. In response to the pandemic and changing market conditions, Apple decided to cancel its ambitious car project. Instead, the company redirected resources towards strengthening its core product lines, such as iPhones, iPads, and Macs, and expanding its digital services. This strategic shift allows Apple to streamline operations and focus on areas with proven demand and profitability, ensuring sustained growth during the pandemic.
At the same time, Huawei has successfully entered the automobile market. Huawei's strategic pivot into the automobile market marks a significant diversification of its business. By launching AITO cars, Huawei tapped into the growing demand for electric vehicles and leveraged its technological expertise in telecommunications and consumer electronics. This move not only provided a new revenue stream but also showcased Huawei's ability to innovate and adapt to new market opportunities, reinforcing its resilience amid geopolitical and pandemic-related challenges.
The financial performances of the two companies in recent years, in the form of figures and charts, reflect the effectiveness of the strategic response, represent the market adaptability of the two companies, and highlight the different paths taken by the two companies to achieve sustainable growth during the pandemic.
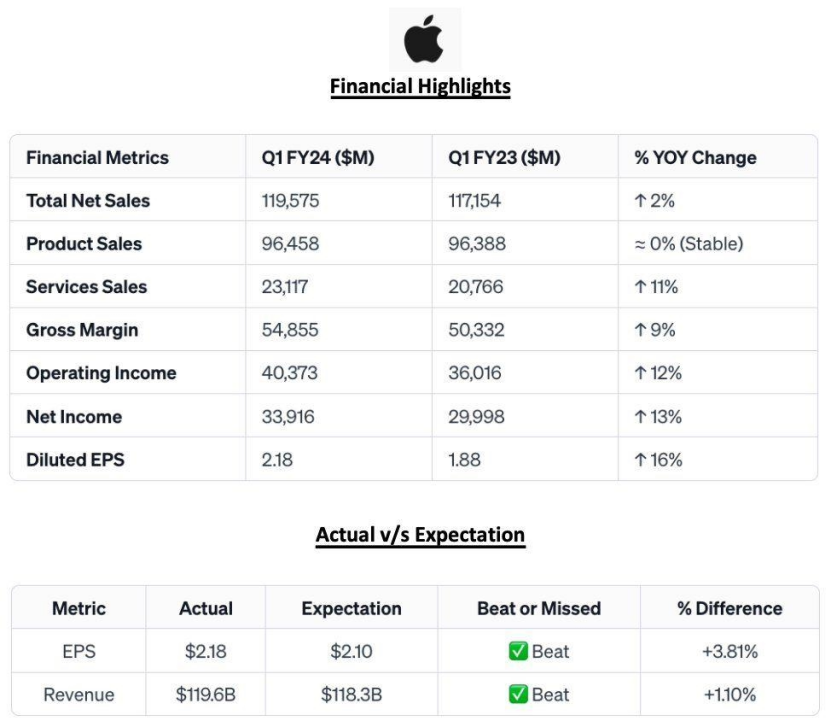
Figure 1: Apple’s 2024 Q1 financial highlights (matching financial performance of Oct./Nov./Dec. 2023)[10]
Table 1: Key financial indexes from Huawei annual report in 2023[11]
FY2023 | FY2022 | FY2021 | FY2020 | FY2019 | ||
($million) | (RMB million) | (RMB million) | ||||
Sales revenue | 99,448 | 704,174 | 642,338 | 636,807 | 891,368 | 858,833 |
Operating profit | 14,744 | 104,401 | 42,216 | 121,412 | 72,501 | 77,835 |
Operating profit margin | 14.80% | 14.80% | 6.60% | 19.10% | 8.10% | 9.10% |
Cash flow from operating activities | 9,859 | 69,807 | 17,797 | 59,670 | 35,218 | 91,384 |
Cash and short-term investments | 67,128 | 475,317 | 373,452 | 416,334 | 357,366 | 371,040 |
Operating capital | 59,550 | 421,662 | 344,938 | 376,923 | 299,062 | 257,638 |
Net profit | 12,280 | 86,950 | 35,562 | 113,718 | 64,649 | 62,656 |
Debt-to-asset ratio | 59.80% | 59.80% | 58.90% | 57.80% | 62.30% | 65.60% |
Note: The U.S. dollar amount is converted using the exchange rate at the end of 2023, which is 1 U.S. dollar to 7.0808 RMB. | ||||||
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of the Results
Apple's strategic response to the pandemic, particularly its decision to cancel the car project and focus on its core product lines and digital services, significantly strengthened its market position. By mainstreaming its flagship products and enhancing its digital ecosystem, Apple ensured a steady revenue stream despite the economic downturn. This focus on core competencies and high-demand products allowed Apple to maintain its premium brand image and sustain growth, highlighting the effectiveness of strategic focus and innovation in achieving long-term sustainability.
Huawei's strategy of diversifying into the automotive sector and focusing on the domestic market demonstrated its adaptability and resilience. The successful launch of AITO cars provides Huawei with a new stream of cash flow and helps to mitigate the impact of sanctions and supply chain disruptions on its traditional telecommunications business. This diversification not only stabilizes Huawei's financial performance but also positions it as a significant player in the emerging electric vehicle market. Huawei's ability to pivot and innovate under pressure underscores the importance of flexibility and strategic diversification in sustaining business operations during a crisis.
5.2. Changes in Business Models and Channels for Both Companies
Both Apple and Huawei changed their business models and channels to navigate the challenges posed by the pandemic. Apple enhanced its online sales channels and digital services, ensuring continued consumer engagement despite physical store closures. This shift towards a more digital-centric business model not only increased sales but also expanded Apple's service ecosystem. On the other hand, Huawei's entry into the automotive market marked a significant change in its business model. By leveraging its technological expertise in telecommunications and consumer electronics, Huawei successfully integrated into the automotive industry, creating new synergies and revenue opportunities.
During the pandemic, Apple adjusted its product pricing strategies to reflect changing consumer behavior and economic conditions. While some products, particularly new releases, maintained premium pricing, Apple also introduced more affordable options to attract price-sensitive consumers. This balanced approach helped Apple maintain its brand image while expanding its customer base. With this price adjustment, Apple captured the edge of the smartphone industry in 2023 with a huge market share[12].
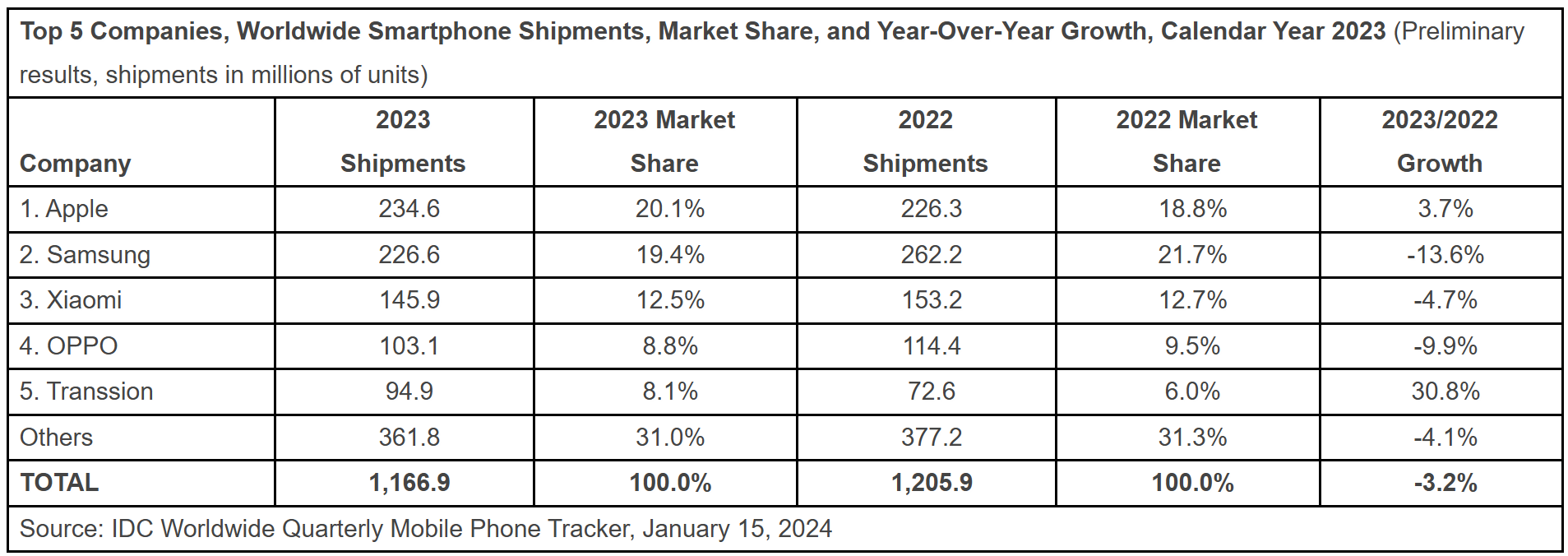
Figure 2: Financial comparison of the world's top five mobile phone companies[12]
In contrast, Huawei's pricing trends showed an upward trajectory, especially in its new ventures such as tablets, computers, and automobiles. By positioning its products at a higher price point, Huawei aimed to capitalize on its brand strength and technological advancements. This strategy not only reinforces its market positioning but also supports revenue growth in new segments.
5.3. Implications for Business Sustainability in a Post-Pandemic World
The comparative analysis of Apple and Huawei's strategies reveals critical implications for business sustainability in a post-pandemic world. One key takeaway is the necessity for companies to focus on core competencies and adapt their business models to meet evolving market conditions[13]. This adaptability is crucial for mitigating risks and capitalizing on new opportunities that may arise in a rapidly changing environment. Diversification and innovation emerge as crucial strategies for businesses post-pandemic. Diversifying into new markets or product lines can help reduce reliance on a single revenue stream and increase resilience to economic shocks. Innovation, whether in products, services, or business models, is essential for maintaining competitiveness and meeting the changing needs of consumers.
Meanwhile, maintaining a strong digital presence and leveraging technological advancements are also vital for sustainable growth. The pandemic has accelerated the shift towards digitalization, and businesses that invest in technology to improve operational efficiency and customer engagement are likely to fare better in the post-pandemic world.
Government support is critical for businesses post-pandemic. Providing financial assistance, such as grants and low-interest loans, can help businesses overcome liquidity challenges and invest in growth initiatives[14]. Additionally, investing in infrastructure and technology can foster innovation and improve the overall competitiveness of businesses.
Industry associations and leaders can also play a significant role in guiding the development of enterprises post-pandemic. By promoting best practices, facilitating knowledge sharing, and supporting research and development, they can help businesses adapt to new challenges and seize emerging opportunities. Collaboration between different industries can drive innovation and growth while establishing standards and regulations that encourage sustainability and technological advancement, which will be crucial for ensuring long-term viability.
5.4. Recommendations for Other Businesses Based on These Case Studies
Based on the practical experiences shared by Apple and Huawei during the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses can draw several key recommendations for navigating the post-pandemic era and achieving sustainable growth. Firstly, businesses must focus on their core competencies. Strengthening and innovating within these areas can help maintain a competitive advantage and resilience in the face of uncertainty. Additionally, diversifying into new markets or product lines can mitigate risks and open up new revenue streams. Secondly, leveraging technology is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and customer engagement. Investing in digital transformation can improve business processes and enable businesses to adapt to changing consumer behaviors and market trends.
Meanwhile, businesses should be prepared to be flexible and adapt their strategies in response to changing market conditions. This strategic flexibility can help businesses stay agile and responsive to emerging opportunities and threats. Moreover, collaboration and partnerships can be beneficial for businesses looking to drive innovation and expand their capabilities[15]. By collaborating with other businesses or industry partners, companies can access new markets, technologies, and resources that may not be available internally.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, the comparative analysis of Apple and Huawei's business strategies in the post-pandemic era, particularly in the context of the automotive industry, reveals significant differences in their approaches and outcomes.
The analysis highlighted that Apple's decision to cancel its car plans and focus on core products, coupled with its strong digital ecosystem, enabled the company to maintain its market position and sustainability. On the other hand, Huawei's successful entry into the automotive sector with the launch of AITO cars showcased its ability to diversify and adapt to new market opportunities, mitigating the impact of sanctions and supply chain disruptions on its core business. The key findings from the comparative analysis underscore the importance of strategic focus, innovation, and adaptability in sustaining business operations during crises. Both companies demonstrated resilience and strategic agility in responding to the challenges posed by the pandemic and geopolitical tensions, providing valuable lessons for other businesses facing similar challenges.
Broad lessons learned from this case study include the significance of focusing on core competencies, diversifying into new markets, leveraging technology, maintaining strategic flexibility, and fostering collaborations. These strategies can help businesses navigate uncertainties and build resilience for sustainable growth in the post-pandemic era. In terms of government intervention, providing financial assistance, investing in infrastructure and technology, and implementing policies that promote market stability and consumer confidence are essential for supporting market recovery and business sustainability. For the automotive industry, industry guidance should focus on promoting collaboration between technology and automotive companies, implementing conducts and establishing ways that inspire new corporations and participation, and fostering innovation in response to changing consumer preferences and market trends.
Recommendations for other businesses based on these case studies emphasize the importance of focusing on core competencies, diversifying into new markets, leveraging technology, maintaining strategic flexibility, and fostering collaborations. By incorporating these strategies into their business models, businesses can enhance their resilience and competitiveness in the post-pandemic era, contributing to overall industry development and sustainability.
References
[1]. Herbane B. The evolution of business continuity management: A historical review of practices and drivers. Business history. 2010 Oct 1;52(6):978-1002.
[2]. Shino Y, Utami F, Sukmaningsih S. Economic Preneur's Innovative Strategy in Facing the Economic Crisis. IAIC Transactions on Sustainable Digital Innovation (ITSDI). 2024 Feb 9;5(2):117-26.
[3]. Huang, J. (2024) ‘Resources, innovation, globalization, and Green Growth: The BRICS financial development strategy’, Geoscience Frontiers, 15(2), p. 101741. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101741.
[4]. Rezazada M, Nassir N, Tanin E, Ceder A. Bus bunching: a comprehensive review from demand, supply, and decision-making perspectives. Transport Reviews. 2024 Feb 8:1-25.
[5]. El Baz J, Ruel S. Investigating the role of business continuity during COVID-19: an empirical examination. InSupply Chain Forum: An International Journal 2024 Apr 2 (Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 134-147). Taylor & Francis.
[6]. Verreynne ML, Ford J, Steen J. Strategic factors conferring organizational resilience in SMEs during economic crises: a measurement scale. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research. 2023 Jun 13;29(6):1338-75.
[7]. Kariv D, Cisneros L, Guiliani F, Chouchane R. Family businesses navigating the COVID-19 pandemic through a gender perspective: the role of external and internal factors in stimulating dynamic capability development. Journal of Family Business Management. 2023 Mar 2;13(1):26-45.
[8]. Margherita A, Nasiri M, Papadopoulos T. The application of digital technologies in company responses to COVID-19: An integrative framework. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management. 2023 Aug 3;35(8):979-92.
[9]. Dehghani Sadrabadi MH, Makui A, Ghousi R, Jabbarzadeh A. An integrated optimization model for planning supply chains' resilience and business continuity under interrelated disruptions: a case study. Kybernetes. 2023 Sep 12.
[10]. Gu, Y. Apple 2023Q4 earnings report: Revenue of $119.6 billion, up 2%; Greater China was $20.8 billion, down 13%, IT Home. (2024) Available at: https://www.ithome.com/0/748/514.htm.
[11]. Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. 2023 Annual Report https://www.huawei.com/en/annual-report/2023
[12]. NEEDHAM, M. Apple grabs the top spot in the smartphone market in 2023 along with record high market share despite the overall market dropping 3.2%, according to IDC tracker, Business Wire (2024). Available at: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240115096425/en/Apple-Grabs-the-Top-Spot-in-the-Smartphone-Market-in-2023-along-with-Record-High-Market-Share-Despite-the-Overall-Market-Dropping-3.2-According-to-IDC-Tracker.
[13]. Shi Y. A Corpus-based Multi-dimensional Analysis on Chinese and US Corporate Responsibility Reports: A Case Study of HUAWEI and Apple. International Journal of English Literature and Social Sciences (IJELS). 2023;8(2).
[14]. Kumar, S., & Mishra, A. Corporate Governance and Business Strategies for Climate Change and Sustainability. Journal of Business Strategy, 2021, 42(3), 55-72. Retrieved from [ResearchGate] i. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352694751_Corporate_Governance_and_Business_Strategies_for_Climate_Change_and_Sustainability
[15]. Viardot E, Brem A, Nylund PA. Post-pandemic implications for crisis innovation: A technological innovation view. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 2023 Sep 1;194:122680.
Cite this article
Liu,S. (2024). Sustainable Business Growth in Post-Pandemic Era: A Comparative Analysis of Strategies Between Apple and Huawei. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,124,155-163.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Herbane B. The evolution of business continuity management: A historical review of practices and drivers. Business history. 2010 Oct 1;52(6):978-1002.
[2]. Shino Y, Utami F, Sukmaningsih S. Economic Preneur's Innovative Strategy in Facing the Economic Crisis. IAIC Transactions on Sustainable Digital Innovation (ITSDI). 2024 Feb 9;5(2):117-26.
[3]. Huang, J. (2024) ‘Resources, innovation, globalization, and Green Growth: The BRICS financial development strategy’, Geoscience Frontiers, 15(2), p. 101741. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101741.
[4]. Rezazada M, Nassir N, Tanin E, Ceder A. Bus bunching: a comprehensive review from demand, supply, and decision-making perspectives. Transport Reviews. 2024 Feb 8:1-25.
[5]. El Baz J, Ruel S. Investigating the role of business continuity during COVID-19: an empirical examination. InSupply Chain Forum: An International Journal 2024 Apr 2 (Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 134-147). Taylor & Francis.
[6]. Verreynne ML, Ford J, Steen J. Strategic factors conferring organizational resilience in SMEs during economic crises: a measurement scale. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research. 2023 Jun 13;29(6):1338-75.
[7]. Kariv D, Cisneros L, Guiliani F, Chouchane R. Family businesses navigating the COVID-19 pandemic through a gender perspective: the role of external and internal factors in stimulating dynamic capability development. Journal of Family Business Management. 2023 Mar 2;13(1):26-45.
[8]. Margherita A, Nasiri M, Papadopoulos T. The application of digital technologies in company responses to COVID-19: An integrative framework. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management. 2023 Aug 3;35(8):979-92.
[9]. Dehghani Sadrabadi MH, Makui A, Ghousi R, Jabbarzadeh A. An integrated optimization model for planning supply chains' resilience and business continuity under interrelated disruptions: a case study. Kybernetes. 2023 Sep 12.
[10]. Gu, Y. Apple 2023Q4 earnings report: Revenue of $119.6 billion, up 2%; Greater China was $20.8 billion, down 13%, IT Home. (2024) Available at: https://www.ithome.com/0/748/514.htm.
[11]. Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. 2023 Annual Report https://www.huawei.com/en/annual-report/2023
[12]. NEEDHAM, M. Apple grabs the top spot in the smartphone market in 2023 along with record high market share despite the overall market dropping 3.2%, according to IDC tracker, Business Wire (2024). Available at: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20240115096425/en/Apple-Grabs-the-Top-Spot-in-the-Smartphone-Market-in-2023-along-with-Record-High-Market-Share-Despite-the-Overall-Market-Dropping-3.2-According-to-IDC-Tracker.
[13]. Shi Y. A Corpus-based Multi-dimensional Analysis on Chinese and US Corporate Responsibility Reports: A Case Study of HUAWEI and Apple. International Journal of English Literature and Social Sciences (IJELS). 2023;8(2).
[14]. Kumar, S., & Mishra, A. Corporate Governance and Business Strategies for Climate Change and Sustainability. Journal of Business Strategy, 2021, 42(3), 55-72. Retrieved from [ResearchGate] i. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352694751_Corporate_Governance_and_Business_Strategies_for_Climate_Change_and_Sustainability
[15]. Viardot E, Brem A, Nylund PA. Post-pandemic implications for crisis innovation: A technological innovation view. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 2023 Sep 1;194:122680.









