1. Introduction
The global fashion market is highly dynamic and competitive, with fast-paced change manifest in the environment. In this cluttered market, brand recognition plays an instrumental role in determining success and positioning in the market [1]. Brand recognition will help it stand out from the sea of competitors, this will build loyalty and trust, the two ingredients that mean guaranteed long-term success. Fabric modification is one of the most efficient methods for getting brand identification and can be described as altering the physical and aesthetic qualities of textiles to achieve some specific branding goals.
Fabric modification is not a mere functional process, but a strategic tool for creating distinctive and memorable brand identities [2]. Advanced techniques of dyeing, texturing, and combining sustainable materials have revolutionized how brands portray their values and aesthetics. Such modifications allow brands to create unique visual and tactile experiences, therefore standing out in a saturated market. Thus, it has become synonymous with Chanel's unerring classicism, the same way Nike Flyknit technology speaks of innovativeness and performance.
This study attempts to discuss the assertion that techniques for fabric modification have a role to play in brand recognition within the fashion industry. It researches the relation of changes in fabric with the perception of consumers, placed under the effect that sensory and emotional experiences have on brand recall and customer loyalty. This research uses qualitative research methodology in order to give an in-depth case examination of popular brands and interviews with industry specialists concerning the meaning of fabric alteration in branding [3]. This study also looks at the growing importance of sustainability within the innovation of fabrics by underlining ways in which environmentally friendly practices can improve brand perception and, as a result thereof, capture consumers awareness of ecological problems. The results of this study provide strong recommendations for fashion marketers and designers, pointing out the top priority that should be given to fabric modification in branding strategy. It would therefore help these companies to harmonize their fabric choices with more generic approaches to branding as a way of increasing their presence in the market and building a competitive edge [4]. This study also highlights the fact that new fabric technologies have to be investigated further and possible branding impacts in a time of fast technological and environmental changes [5].
2. Types of Fabric Modifications and Their Aesthetic Impact
The fabric modification techniques span a wide array of possibilities for brands to create impactful and unique identities. Some of them, such as advanced dyeing and texturing, are bridges between the aesthetic goals of a brand and practical needs.
2.1. Advanced Dyeing Techniques
Dyeing has been the fundamental element in textile manipulation for ages, but modern technology has transformed the traditional process into a powerful tool in the arsenal of branding [6]. Among the few, ombre dyeing, digital printing, and natural dyeing have become the go-to methods for designers working with unique patterns and palettes [7]. More specifically, ombre dyeing allows seamless gradations of color, giving this method a soft, sumptuous look that is particularly popular with evening wear and haute couture. Luxury brands like Versace and Valentino usually follow the same tactics for targeting their consumers in the name of exclusivity and glamorousness [1]. Natural dyeing, adopted by companies such as Stella McCartney, is adopted in the attainment of being “green” while at the same time improving aesthetic values [4].
Moreover, digital printing enables the creation of intricate patterns with high precision, thereby allowing brands to explore bold and innovative design possibilities. Besides, digital printing has made fabric customization possible on a larger scale, thanks to which smaller, young brands can compete with bigger counterparts in the industry by offering unique and personalized collections. A trend that is in great harmony with modern consumers' tendency of standing out and expressing themselves through their fashion.
In addition, natural dyeing techniques using pigments from plants or minerals have been gaining popularity for their environmentally friendly characteristics. Companies like Eileen Fisher and Stella McCartney have incorporated this practice into their work, demonstrating commitment to sustainability but at the same time maintaining aesthetics of high quality. Natural dyes reduce ecological damage and also imbue specific profoundness and brightness of color that is often not found with synthetic dyes, adding to the product's appeal.
2.2. Texturing and Material Innovation
Texture is an important element in fabric design and reflects both the visual and tactile senses of garments. The texturing techniques of pleating, quilting, and embossing give fabrics depth and dimension by rendering visual interest and improving the texture experience. For example, Chanel's tweed expresses the ability of texture to become synonymous with the identity of a brand: in this case, sophistication and classic chic [2].
One of the more prominent emerging trends in texturing has to be three-dimensional printing technology; through this, designers are able to create complex, sculptural textiles that would have been impossible before. Apart from pushing the design boundaries, textiles made by 3D printing enjoy high popularity among progressive consumers who appreciate novelty and creativity. Iris van Herpen has been called a pioneer in this field and is well recognized around the globe for her visionary works that combine technology with traditional craft.
In influencing contemporary fashion, the advancement of materials has played a significant role. The development of functional textiles, such as moisture-wicking and temperature-regulating fabrics, has made clothing more useful for the consumer who values comfort and function. Companies such as Lululemon and Uniqlo have succeeded in making use of such fabrics in their product range and therefore have gained growing consumer interest in athletic and functional wear.
2.3. Sustainable Material Choices
Sustainability has become less of a specialty and more of a mainstream expectation by consumers, who now expect that brands will adopt environmentally responsible practices. Choosing sustainable fabrics, such as organic cotton, recycled polyester, and biodegradable materials, has turned into one of the main profiles of modern fashion branding. In this regard, Patagonia is known for its keen interest in using recycled and upcycled fabrics, placing the brand at the forefront of sustainable outdoor fashion [8].
Emerging materials, such as bio-fabricated leather and textiles, made from algae or mushroom mycelium are coming to the fore. These alternatives not only offer sustainability opposite mainstream leather and synthetic textiles but also reduce the ecological footprint of manufacturing while adding unique textures and aesthetic qualities to a product. It creates an opportunity for brands to attract environmentally conscious consumers and to stand out in a crowded market.
Table 1: Comparison of Fabric Modification Techniques in Sustainability and Brand Recognition
Technique | Environment Impact | Brand Recognition Contribution | Cost Level |
Natural Dyeing | Low | High | Medium |
Digital Printing | Medium | High | Low |
3D-Printed Textures | Medium | Very High | High |
Sustainable Materials | Very Low | Very High | High |
This section is on sustainable fabrics and how they align with brand differentiation. Table 1 covers the environmental impact, contribution to brand recognition, and cost of the different fabric modification techniques in an effective manner, hence making the discussion more concrete and easier to follow.
3. Consumer Perception and Brand Recall
Consumer perception is at the core of any successful branding strategy; fabric innovations play a critical role in shaping consumer attitudes and brand recall. Changes in fabric establish sensory and emotional connections that enhance customer experiences, which fosters brand loyalty and continued interaction.
3.1. Sensory and Tactile Engagement
The tactile properties of textiles are among the first attributes consumers perceive when experiencing a garment. For example, soft fabrics in cashmere portray luxury, whereas fabrics with spring, like denim, portray durability [9]. Companies, such as Hermès, use these sensory details to reinforce their image of exclusiveness. All these sensory associations are vital consumer perceptions that help influence purchase decisions. Studies have found that tactile sensations last longer, and therefore, consumers are more likely to remember brands that create unique sensory experiences [7]. For example, the soft, buttery feel of Loro Piana's cashmere acts as a core part of its brand identity, further solidifying its relationship with luxury and exclusivity.
3.2. Visual Impact
Equal ranking with consumer perception is the aesthetic dimension. Striking colors, elaborate patterns, and distinctive textures attract attention and convey the essence of a brand's identity. Innovations in fabric technology allow designers to explore non-traditional aesthetics, resulting in clothing that distinguishes itself in a saturated market [7]. Alexander McQueen, with his bold and often theatrical designs, has confirmed the brand position as well known for its creativity and originality, making it one that consumers can instantly recognize.
3.3. Emotional Connections
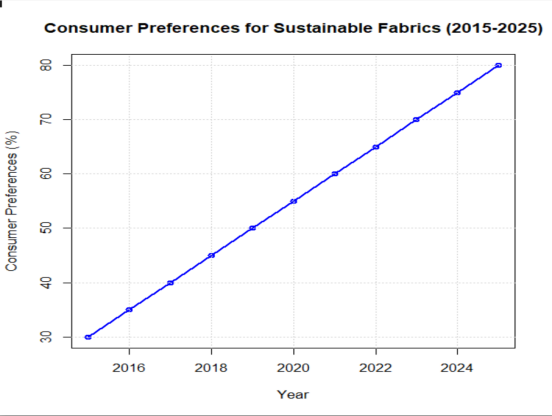
Figure 1: Consumer Preferences for Sustainable Fabrics by Percentage
Figure 1 illustrates consumer preferences have undergone significant changes over time, clearly demonstrating the point that innovations in fabric, particularly those that prioritize sustainability, establish strong emotional and ethical bonds with consumers. This shift in consumer behavior underscores the growing importance of sustainability, which has become a central factor in their purchasing decisions. The graph provided here serves to visually highlight and emphasize this trend, showcasing the noticeable movement among consumers toward prioritizing sustainability in their choices
Fabrics can evoke feelings and memories, therefore creating strong bonds between consumers and brands. Among the ways in which such emotions are elicited, colors play a paramount role. Warm colors like red and orange yield feelings of energy and passion; at the same time, cool colors like blue and green show tranquility and trustworthiness. From the careful selection of color to texture, brands can design clothes that resonate emotionally with their target market.
Burberry's iconic plaid, for instance, evokes sentiments of heritage and tradition, relevantly attracting consumers who value timelessness and authenticity [5]. Equally, the use of sustainable materials by brands such as Stella McCartney fosters positive associations with sustainability and ethical responsibility, yielding increased customer loyalty. The textiles used, for example, the very famous Burberry plaid, make the user feel a sense of heritage and authenticity, thus fostering relationships with consumers [5]. The emotional appeal is even stronger because of the sustainable practices of the brands that attract consumers with ethical concerns [10].
3.4. Impact on Brand Recall
Fabric innovation not only shapes consumer perception but also enhances brand recall by creating distinctive and memorable designs. Levi’s, for example, has built its identity around denim innovation, ensuring that its products are immediately recognizable to consumers. Research indicates that brands with unique fabric modifications are more likely to be remembered and recommended by consumers, highlighting the importance of innovation in branding [1].
4. Case Studies of Brand Differentiation through Fabric Modification
The real-life examples clearly demonstrate the successful implementation of fabric modification strategies in the fashion industry. These examples provide concrete evidence of how such strategies are being effectively utilized to drive innovation and sustainability. In the following section, we will explore in greater detail the new and emerging approaches at well-known brands such as Burberry, Nike, Stella McCartney, and other rising sustainable brands. These brands are at the forefront of integrating sustainability into their fabric modification strategies, and their efforts will be closely examined to highlight the ways in which they are leading the charge in this field.
4.1. Burberry: Tradition Meets Innovation
Burberry gabardine trench coats have, over time, become synonymous with the brand itself, representing an epitome of functionality and style combined in perfect harmony. The closely woven aspect of gabardine fabric makes it weatherproof and robust, hence highly suited for outerwear. Such innovation in textile technology did not only revolutionize the fashion industry but also established Burberry at its leading edge [2].
In addition to its functional textiles, Burberry's adoption of the signature plaid pattern has further cemented it. Since the introduction of the plaid design in the 1920s, it has become an iconic representation of British heritage and craftsmanship, hence making Burberry easily recognizable on a global scale. With a combination of leading-edge materials and timeless aesthetics, Burberry has maintained its relevance in the ever-changing market.
4.2. Nike: Performance and Innovation
Nike's Flyknit technology epitomizes how fabric innovation can enhance both performance and branding. Flyknit is a light, airy material engineered to provide a second skin fit for athletes looking for comfort and functionality. This not only enhances the performance of the athlete but also reinforces the identity of Nike as an innovator in sportswear [5].
The aesthetic appeal of Flyknit designs with their intricate patterns and bright colors plays a substantial role in the brand awareness created by Nike. By successfully fusing together fabric innovation with its core tenets of performance and fashion, Nike has truly captured the loyalty of its target audience.
4.3. Stella McCartney: Sustainability at the Core
Stella McCartney has emerged as a leader in the realm of sustainable fashion, advocating for the adoption of environmentally friendly materials and ethical production methods [3]. The brand's dedication to sustainability is manifested in its utilization of organic cotton, recycled polyester, and groundbreaking materials such as bio-fabricated leather. Such selections not only mitigate environmental effects but also resonate with consumers who are environmentally aware [8]. McCartney's designs are characterized by minimalism and timeless appeal, which ensure that they remain in style in a fast-moving industry. In this way, Stella McCartney has become one of the leaders in the field of ethical fashion by combining sustainability with style.
4.4. Emerging Sustainable Brands
Brands like Pangaia are taking sustainability to the next level with seaweed-based fabrics, proving that environmental innovation is no hindrance to high fashion [4]. In this case, Pangaia uses materials like seaweed fiber and recycled plastic bottles while creating up-to-date and eco-friendly products. On the other hand, Reformation focuses on transparency by availing full information relating to the environmental impact of its products. These companies prove that sustainability and innovation are not only compatible but indeed synergistic, providing a framework for the future trajectory of the fashion industry.
5. Conclusion
This research has focused on how fabric modification helps in creating brand recognition within the fashion industry. Now, advanced dyeing processes, texturing, and sustainable material development all make up a big part of constructing strong brand identities with resonance among consumers. The added aesthetic value to a product through modification not only does justice to its looks but also creates brand recall and loyalty by forging sensory and emotional connections with the consumer base. That will be even better with the sustainable materials, as they fall in with consumer demand for environmental responsibility.
Although there are many advantages to using thematic analysis, it is important to also acknowledge the disadvantages of this method. Therefore, a study can be carried out with wider support by the finding within a comprehensive framework. In addition, future research could concentrate on emerging fabric technologies, including smart textiles and 3D printing, which may redefine branding strategies within the fashion industry.
In a nutshell, fabric modification is one of the effective ways of competitive differentiation that is only going to increase in importance as new technologies and sustainability trends further shape the fashion landscape. The adaptation of such novel practices is very important for any brand that would like to stay put and be able to foster long-term consumer loyalty.
References
[1]. Wilson, P., Green, K., Brown, T. (2021) Advanced dyeing techniques and brand differentiation. Color Science in Design, 22(1): 15–32.
[2]. Greenwood, A., Parker, J., White, H. (2020) Texturing trends in modern fashion branding. Journal of Fashion Aesthetics, 18(3): 101–115.
[3]. Green, P., Brown, T., Taylor, L. (2022) The role of sustainability in fashion branding. Environmental Design Journal, 14(3): 23–37.
[4]. Nguyen, T., Brown, T., Taylor, L. (2022) Consumer behavior and sustainable fabrics. Journal of Eco-Fashion, 11(1): 12–29.
[5]. Davis, R., Smith, J., Brown, T. (2017) Case studies in fabric innovation: Lessons from Burberry and Nike. Fashion Studies Review, 10(2): 78–91.
[6]. Carter, R., McDonald, J., Lee, S. (2019) The evolution of textile innovation. Textile Research Journal, 25(6): 67–84.
[7]. Jones, K., Smith, A., Taylor, R. (2021) The sensory impact of fabric innovation on consumer perception. Consumer Behavior Quarterly, 19(4): 89–103.
[8]. Taylor, L., Davis, R., Green, P. (2018) Consumer recall and fabric modification. Journal of Brand Management, 13(1): 45–58.
[9]. Smith, J., Brown, T., Davis, R. (2020) The aesthetic appeal of fabric modifications in fashion branding. Journal of Textile Innovation, 15(3): 56–67.
[10]. Brown, T., Green, P., Taylor, L. (2019) Sustainable materials and brand differentiation. Fashion and Sustainability, 12(2): 34–45.
Cite this article
Dai,Y. (2025). The Role of Fabric Modification in Enhancing Brand Recognition in Fashion. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,162,55-61.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wilson, P., Green, K., Brown, T. (2021) Advanced dyeing techniques and brand differentiation. Color Science in Design, 22(1): 15–32.
[2]. Greenwood, A., Parker, J., White, H. (2020) Texturing trends in modern fashion branding. Journal of Fashion Aesthetics, 18(3): 101–115.
[3]. Green, P., Brown, T., Taylor, L. (2022) The role of sustainability in fashion branding. Environmental Design Journal, 14(3): 23–37.
[4]. Nguyen, T., Brown, T., Taylor, L. (2022) Consumer behavior and sustainable fabrics. Journal of Eco-Fashion, 11(1): 12–29.
[5]. Davis, R., Smith, J., Brown, T. (2017) Case studies in fabric innovation: Lessons from Burberry and Nike. Fashion Studies Review, 10(2): 78–91.
[6]. Carter, R., McDonald, J., Lee, S. (2019) The evolution of textile innovation. Textile Research Journal, 25(6): 67–84.
[7]. Jones, K., Smith, A., Taylor, R. (2021) The sensory impact of fabric innovation on consumer perception. Consumer Behavior Quarterly, 19(4): 89–103.
[8]. Taylor, L., Davis, R., Green, P. (2018) Consumer recall and fabric modification. Journal of Brand Management, 13(1): 45–58.
[9]. Smith, J., Brown, T., Davis, R. (2020) The aesthetic appeal of fabric modifications in fashion branding. Journal of Textile Innovation, 15(3): 56–67.
[10]. Brown, T., Green, P., Taylor, L. (2019) Sustainable materials and brand differentiation. Fashion and Sustainability, 12(2): 34–45.









