1. Introduction
Malaysia is a multicultural and multiethnic country, and the Chinese community has a strong demand for education and cultural transmission. With the advancement of economic globalization, an increasing number of Malaysians of Chinese descent and their descendants are showing growing interest in Chinese language education, especially in areas such as business, cultural exchange, and academic research. Against the backdrop of the rise of digital education, the demand for online Chinese language education in Malaysia is also expanding. More and more Malaysian students are learning Chinese through online platforms, which requires educational institutions to provide high-quality online teaching content. As China's cultural soft power grows, the Malaysian public's interest in Chinese culture continues to rise, especially in areas such as film, music, and tourism. This has encouraged more Malaysians to learn Chinese to understand and engage in cultural exchange.
The implementation of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement has not only changed the economic landscape of Southeast Asia [1] but has also had a profound impact on the education market, particularly higher education and the development of Chinese language education. Within the trade alliance agreement, Chinese language education has become an important issue, and changes in its rules and implementation have affected cooperation and competition in the fields of educational content, teaching models, and educational services among various countries. The strengthening of Chinese language education under the RCEP framework provides new momentum for the cross-border flow of educational resources. After the RCEP agreement took effect, trade between China and ASEAN countries (including Malaysia) became more facilitated [2], especially with the new opportunities emerging in cross-border e-commerce. This means that more Malaysian businesses and consumers may need to engage in communication and collaboration with Chinese enterprises. Therefore, RCEP will offer Malaysian educational institutions opportunities to cooperate with other member countries, including online education, teacher exchange programs, and the sharing of educational resources. Moreover, the establishment of Confucius Institutes marks the promotion of China's educational model, resources, and language culture output. In addition, with China increasing its digital service exports to RCEP member countries, especially Malaysia, online education and digital language training products are likely to become an important field [3]. As the demand for Chinese language learning grows in the Malaysian market, online education platforms cooperating with China (such as online Chinese teaching, speech recognition, virtual classrooms, etc.) can enter the market and fill the digital education gap in Malaysia.
This paper analyzes the impact of the RCEP trade alliance policy on the Southeast Asian education market, particularly its role and strategic adjustments in Malaysia. It argues that, influenced by the RCEP trade alliance policy, the Chinese language education market in Malaysia is not confined to language teaching alone but can be enhanced through academic research, music exchange, cultural spirit communication, and other media support, thereby strengthening the exchange and dissemination of Chinese culture in Malaysia.
2. Literature Review
Currently, research on the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) mainly focuses on aspects such as service trade, agricultural product trade, and digital economy. These studies analyze the impact of RCEP on member countries from an economic perspective, based on trade analysis, but overlook its impact on the education sector.
In 2022, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) came into effect, marking the result of nearly a decade of negotiations and ushering in a new phase of economic integration in the Asia-Pacific region. The implementation of RCEP has had far-reaching effects not only in areas such as trade, investment, and tourism, but also has brought significant changes to education, especially in the language education market [4]. In fact, educational exchange between countries is one of the important channels for trade relations between nations. At the beginning of cultural exchanges between countries, academic exchanges or joint education collaborations are often used to strengthen educational interaction between nations. These exchanges between schools can promote the learning and communication of different cultures, thereby facilitating trade exchanges between countries, making them an indispensable part of economic trade analysis.
Apart from studies on the "Belt and Road Initiative" and the China-Japan-South Korea regional dynamics, many scholars have also focused on the ASEAN region. These scholars analyze the ASEAN region in terms of digital economy, cross-border e-commerce, and industrial cooperation. The signing of RCEP has not only promoted economic cooperation but also enhanced cultural exchanges within the region. As RCEP has strengthened free trade and personnel movement within the region, tourism has become an important economic sector between Malaysia and China [5]. Malaysia is one of the popular destinations for Chinese tourists, especially in major cities and tourist hotspots. In order to better serve these tourists, Malaysia’s tourism industry needs more employees with Chinese language proficiency, which directly impacts the Chinese language education market. Currently, only a small number of scholars have focused on the analysis of Chinese language education. Some scholars have examined the development of Chinese language education in ASEAN countries under the context of the "Belt and Road Initiative" and argued that the international influence of Chinese language education should be expanded. Other scholars have analyzed the state of Chinese language education in countries along the "Belt and Road" and suggested strengthening Sino-foreign cooperation, advancing teacher and textbook development, and promoting the joint development of economy and culture.
In summary, many scholars' research on RCEP is primarily based on digital economy, foreign trade of agricultural products, industrial chains, and cross-border e-commerce, but they overlook academic and educational exchanges between countries. As for the research on the ASEAN region, scholars tend to focus on the impact of the "Belt and Road Initiative" on ASEAN countries, but there is still a lack of analysis on the impact of the RCEP policy on ASEAN countries, especially the specific analysis of individual countries, such as Malaysia. Malaysia, as one of the important ASEAN countries, has been historically influenced by Chinese language education. Therefore, this paper takes Malaysia as a case study to analyze the impact of the RCEP policy on the Chinese language education market in Malaysia.
3. Methodology Design
After the implementation of the RCEP policy, China established three officially accredited Confucius Institutes in Malaysia: Shenzhai Confucius Institute, Sabah University Confucius Institute, and Limkokwing University Confucius Institute. This study collects online promotional content from these Confucius Institutes on platforms such as TikTok, Facebook, and Twitter, aiming to analyze the scientific impact of the RCEP trade cooperation policy on the Chinese language education market in Malaysia.
As an agreement promoting economic and cultural integration among member countries, RCEP indirectly influences educational policies, increases interest in Chinese language learning, especially in countries like Malaysia, where demand for Chinese education has been growing due to the expansion of economic exchanges and trade relations. Shenzhai Confucius Institute, Sabah University Confucius Institute, and Limkokwing University Confucius Institute play important roles in the dissemination of Chinese language and culture.
Confucius Institutes promote their activities through social platforms like TikTok, Facebook, and Twitter, providing a modern and dynamic way to connect with younger audiences and showcase Chinese language courses and cultural events. The influence of these platforms in attracting students and promoting cultural understanding contributes to evaluating the success of Confucius Institutes in international markets from a digital marketing perspective.

Figure 1: Word Cloud of Online Content from Confucius Institutes in Malaysia after the Implementation of RCEP Policy
As of December 2024, over 500 pieces of online content related to Shenzhai Confucius Institute, Sabah University Confucius Institute, and Limkokwing University Confucius Institute were collected. Figure 1 presents the results of text mining from the raw data. This paper uses keywords to measure the themes of online promotion and further explores key actions of Confucius Institutes in the Malaysian Chinese education market under the implementation of the RCEP policy through topic comparison analysis and word clustering analysis.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Text Coding Comparative Analysis
As shown in Figure 2, the results of the text coding comparative analysis reveal that the keywords in Confucius Institutes’ online promotions focus on four key areas: academic research, cultural spirit, music culture, and media promotion. These aspects reflect the multi-faceted impact and interactions of Chinese language education in Malaysia under the RCEP policy.
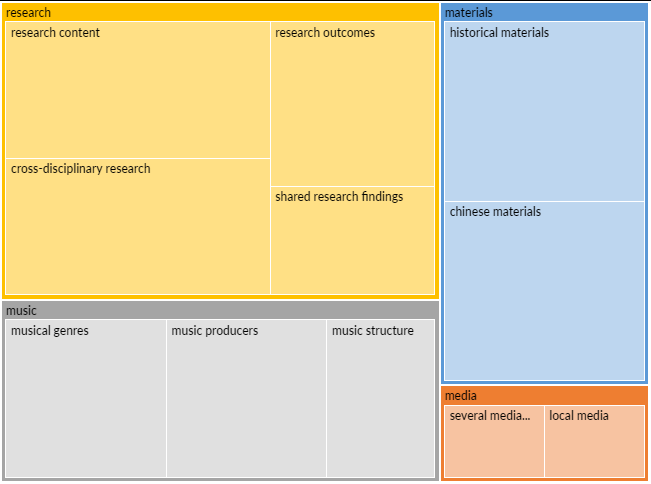
Figure 2: Results of the Text Coding Comparative Analysis
In the "Research" category, the topics include research content, research findings, interdisciplinary research, and sharing of research discoveries. The network media’s attention is primarily on academic research and its dissemination, especially research outcomes related to Chinese language education and interdisciplinary collaboration. The "Spirit" section emphasizes concepts related to historical and Chinese spirit, highlighting the inheritance and promotion of culture and values, particularly the influence of Chinese traditional cultural spirit in Chinese language education. The "Music" section addresses concepts such as music genres, music producers, and music structure, indicating the role of music as a tool for cultural transmission, particularly in relation to cultural display and language acquisition in Chinese language teaching. The "Media" section refers to multiple media organizations and local media, illustrating the role of media in promoting Chinese language education and how they spread information related to Chinese culture and language learning in local societies.
4.2. Word Clustering Analysis
To further analyze the interactions between academic research, cultural spirit, music culture, and media promotion, this study employs word clustering analysis to focus on the correlations between four core keywords. The word clustering results are shown in Figure 3.
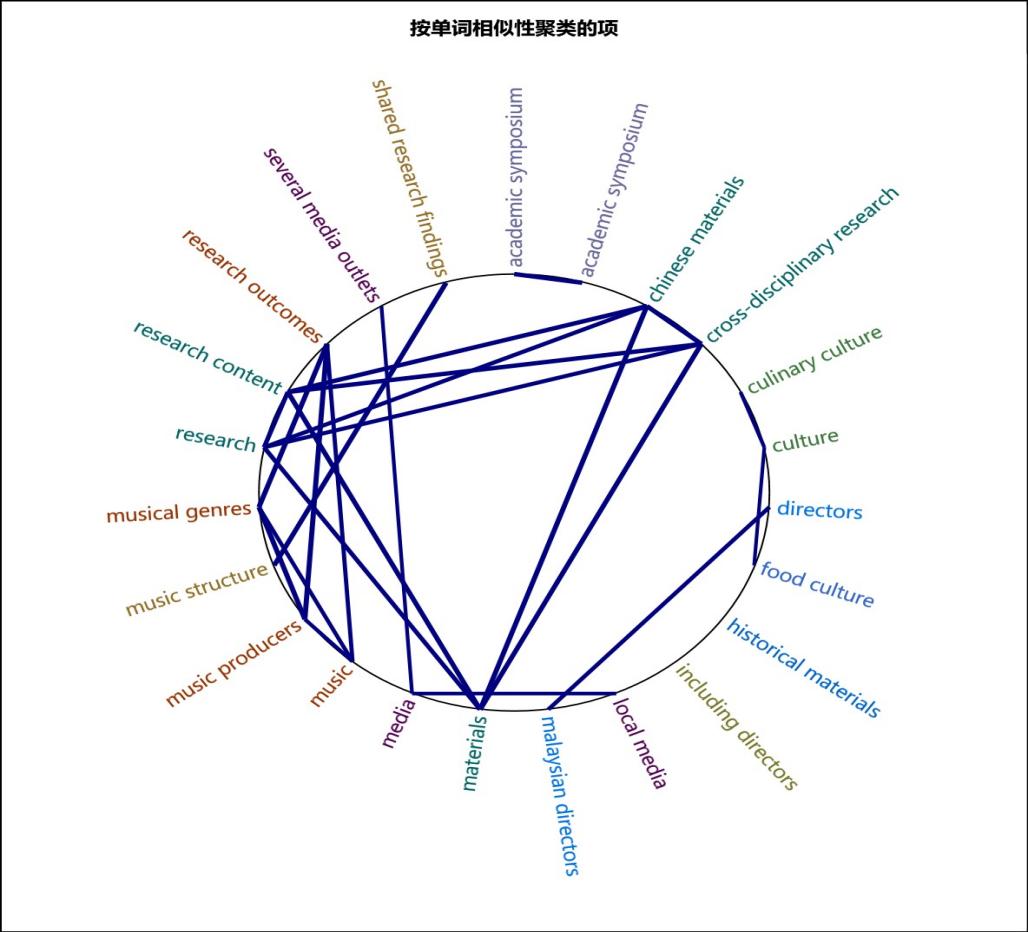
Figure 3: Results of Word Clustering Analysis Based on Word Similarity
As shown in Figure 3, the thickness of the lines between words represents the strength of the Pearson correlation coefficient. Pearson correlation coefficients greater than 0.85 are mainly observed between "research" and "music structure," "materials," and "Chinese materials." Through tracing the original data, this study found that the online content related to Shenzhai Confucius Institute, Sabah University Confucius Institute, and Limkokwing University Confucius Institute mainly focuses on the close integration of academic research and teaching materials in promoting Chinese language education and emphasizes the importance of music culture as a key component of Chinese language education. It also suggests that research on using music to promote language and culture could be an important direction for increasing engagement.
4.3. Discussion
The findings of this study suggest that the implementation of the RCEP trade alliance policy has had a profound impact on the Chinese language education market in Malaysia. The deepening of academic research, the dissemination of cultural spirit, the integration of music culture, and media promotion have all provided rich resources and platforms for the advancement of Chinese language education. These factors interact to drive the diversified development of Chinese language education and offer new directions for the future internationalization and localization of Chinese language education.
Based on the text coding comparative analysis in Figure 2, the core position of academic research in Confucius Institutes' online promotions, particularly in research outcomes and interdisciplinary collaboration related to the promotion of Chinese language education, suggests that the implementation of the RCEP policy may inject new vitality into Chinese language education. Under the RCEP framework, the deepening of economic and cultural cooperation between Malaysia and China has made Chinese language an important tool for economic and cultural exchange, making the development of academic research and teaching materials more crucial. From the word clustering analysis, the high correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient greater than 0.85) between academic research and "music structure," "materials," and "Chinese materials" indicates that the academic community recognizes that Chinese language education is not merely about language instruction but also involves multiple dimensions of cultural dissemination. Therefore, Confucius Institutes, by promoting the close integration of Chinese language education with academic research and teaching materials, have made the promotion of Chinese language education in Malaysia more systematic and efficient.
At the same time, the "Spirit" section highlights the inheritance of Chinese traditional culture and the Chinese spirit, emphasizing the promotion of historical and cultural values. This resonates with the deepening of cultural exchange under the RCEP policy. The RCEP has facilitated the flow of culture between member countries, particularly the spread of Chinese culture, further stimulating the growth of demand for Chinese language education. As a multicultural country, Malaysia’s promotion of Chinese language education is not only driven by the demand for language learning but also reflects cultural identity and the influence of cultural soft power. Through the efforts of Confucius Institutes and other institutions, Chinese language education should not be limited to language teaching but should further enhance Malaysian society's understanding and absorption of Chinese traditional cultural spirit.
Moreover, music culture plays a significant role in promoting Chinese language education, particularly in Confucius Institutes’ teaching. The RCEP has enhanced cultural exchange between China and Malaysia, and music, as a vital cultural transmission tool, can better engage Malaysian students and increase their motivation to learn Chinese. The introduction of concepts such as music structure, music producers, and music genres not only enriches the content of Chinese language education but also enhances the cultural experience of Chinese learners. Using music to promote language and culture helps learners better understand Chinese and enables them to appreciate the cultural connotations of China through music.
5. Conclusion and Recommendations
Under the framework of the RCEP policy, China has established three officially accredited Confucius Institutes in Malaysia: Shenzhai Confucius Institute, Sabah University Confucius Institute, and Limkokwing University Confucius Institute. These institutes have played an active role in promoting Chinese language education and cultural exchange. The text coding comparative analysis of the online promotional content of Confucius Institutes on TikTok, Facebook, and Twitter reveals that academic research, cultural spirit, music culture, and media promotion are the core areas of focus in Confucius Institutes' online outreach. The prominent emphasis on these areas reflects the diversified development of Chinese language education and the widespread dissemination of its cultural influence under the RCEP policy. The study further found that Confucius Institutes focus on the close integration of academic research and teaching materials in Chinese language education and actively promote music culture, highlighting educational innovation and the role of online traffic generation. Based on these conclusions, this paper provides the following recommendations to further promote the vibrant development of the Chinese language education market, particularly in Malaysia and other RCEP member countries, from the perspective of RCEP trade alliance policy participation:
(1) Encourage Confucius Institutes to deepen the integration of cultural and artistic content beyond traditional Chinese language teaching, such as strengthening the promotion of music culture, traditional arts (e.g., calligraphy, dance, drama), and other courses. These unique offerings can enhance the interest of international students in Chinese culture and increase the engagement and interactivity of language learning.
(2) Given the success of Confucius Institutes' promotion on social media platforms (such as TikTok, Facebook, and Twitter) under the RCEP policy, further strengthen the construction of educational resources on online platforms. More free or low-cost online Chinese language courses can be offered to attract a broader learner demographic.
(3) Promote academic cooperation between Chinese and Malaysian academic institutions, jointly developing Chinese language textbooks that meet the local needs of Malaysia, emphasizing the practical applicability and localization of these materials. Additionally, encourage the integration of academic research with practical teaching to continually update and optimize existing textbooks to meet the rapidly changing educational demands.
(4) Leverage the policy advantages within the RCEP framework to strengthen educational exchange and cooperation between China and Malaysia, especially through cultural and language education to deepen mutual understanding and friendship between the two peoples. Strengthen collaboration with Malaysia's Ministry of Education and major higher education institutions to expand the channels for Chinese language education.
(5) On the foundation of Confucius Institutes, further enhance the depth and breadth of cultural exchange between China and Malaysia. For example, joint events such as China-Malaysia cultural festivals, Chinese recitation competitions, and Chinese character calligraphy exhibitions can be organized to promote the spread of Chinese language and culture in Malaysia.
References
[1]. Yan Chen,Qiong Luo and Feipeng Zhang.(2024).Systemic risk and network effects in RCEP financial markets: Evidence from the TEDNQR model.North American Journal of Economics and Finance102317.
[2]. Netirith Narthsirinth and Ji Mingjun.(2024).Strategic enhancement infrastructure connectivity: a fuzzy exploratory factors analysis in Thailand’s regional ports within the RCEP framework.Maritime Business Review(4),369-390.
[3]. Xiaole Deng,Fang Zhang,Shuyi Lin and Wei Qiu.(2024).Research on the Structural Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Digital Service Trade Networks in RCEP Member States.Sustainability(23),10567-10567.
[4]. Sharon GM Koh,Grace HY Lee and Andrei OJ Kwok.(2024).Regional comprehensive economic partnership (RCEP) and tourism: Four research propositions.Tourism and Hospitality Research(4),630-635.
[5]. Mengyuan Liu,Hongzhong Xie and Tao Zhu.(2024).The Impetus for RCEP in Facilitating the High-Quality Development of the Tourism Service Trade in Yunnan Province, China.Journal of Resources and Ecology(4),966-976.
Cite this article
Tian,J. (2025). The Impact of the RCEP Trade Alliance Policy Implementation on the Chinese Language Education Market in Malaysia. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,172,16-22.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Yan Chen,Qiong Luo and Feipeng Zhang.(2024).Systemic risk and network effects in RCEP financial markets: Evidence from the TEDNQR model.North American Journal of Economics and Finance102317.
[2]. Netirith Narthsirinth and Ji Mingjun.(2024).Strategic enhancement infrastructure connectivity: a fuzzy exploratory factors analysis in Thailand’s regional ports within the RCEP framework.Maritime Business Review(4),369-390.
[3]. Xiaole Deng,Fang Zhang,Shuyi Lin and Wei Qiu.(2024).Research on the Structural Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Digital Service Trade Networks in RCEP Member States.Sustainability(23),10567-10567.
[4]. Sharon GM Koh,Grace HY Lee and Andrei OJ Kwok.(2024).Regional comprehensive economic partnership (RCEP) and tourism: Four research propositions.Tourism and Hospitality Research(4),630-635.
[5]. Mengyuan Liu,Hongzhong Xie and Tao Zhu.(2024).The Impetus for RCEP in Facilitating the High-Quality Development of the Tourism Service Trade in Yunnan Province, China.Journal of Resources and Ecology(4),966-976.









