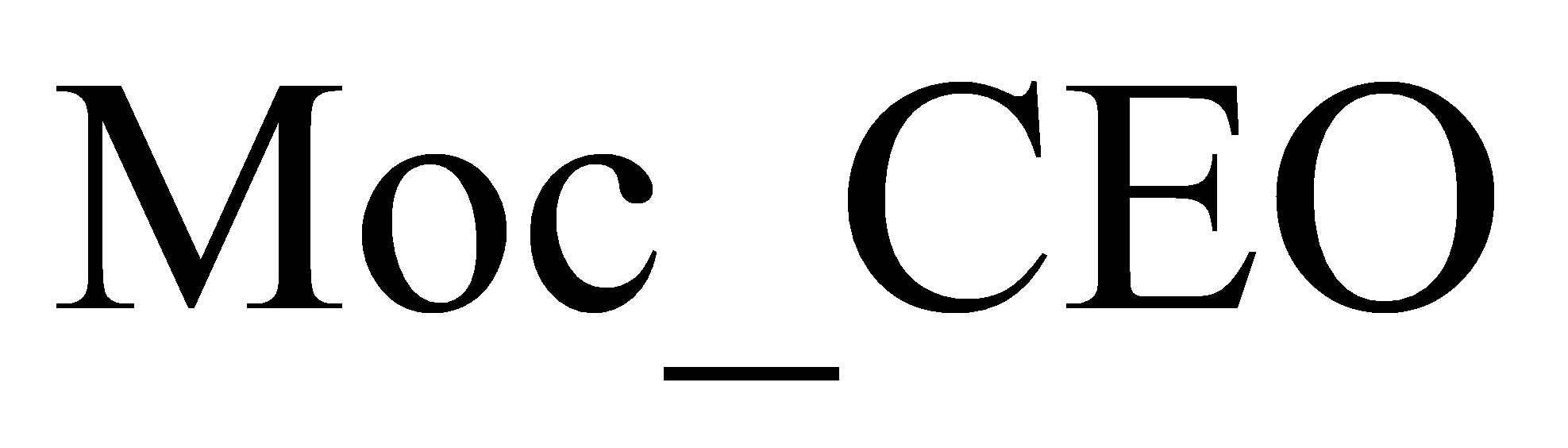1. Introduction
In today's complex, changing and highly competitive business environment, management, as the controller of the strategic direction of the enterprise and the maker of major decisions, plays a pivotal role in the success or failure of the enterprise. Overconfident management tends to overestimate its own ability and the correctness of its decisions, ignore negative information and risks, and lack due sensitivity and vigilance to potential risks, thus leading to a series of problems. In addition, overconfident management tends to overestimate the value of the target firm and its own integration ability during the M&A process, leading to excessive M&A premiums and increasing corporate risks [1] . These problems not only affect the short-term performance of the enterprise, but also may cause irreversible damage to the long-term development of the enterprise. In view of the many negative impacts that management overconfidence may bring to enterprises, it is particularly important and meaningful to study the phenomenon of management overconfidence in depth. Enterprises can optimise the selection and assessment mechanism of management based on the findings of the study, focusing on the assessment of the psychological quality and risk awareness of management, and selecting more rational and objective managers. At the same time, enterprises can effectively reduce the risks brought by management overconfidence, improve their own stability and sustainable development ability, so as to stand firmly in the market environment of white-hot competition, to achieve long-term steady development, and to stand invincible in the fierce market competition.
Against the backdrop of accelerating globalisation and deep transformation of the economic development model, the ESG performance of enterprises is becoming an increasingly important focus of attention in all walks of life. In terms of the environment, global climate change is intensifying and extreme weather is occurring frequently. The environmental performance of enterprises, as an important main body of resource consumption and pollutant emission, is directly related to the future of the earth's ecology. In order to pursue short-term economic benefits, some enterprises neglect environmental protection, resulting in waste of resources and serious pollution, and destroying the natural environment on which human beings depend for survival. At the social level, the constant labour disputes in enterprises and the lack of protection of employees' rights and interests, such as low pay, overtime work and lack of safety and security, have triggered social discontent and turmoil. At the corporate governance level, the phenomenon of insider control occurs from time to time. In order to seek their own interests, the management or controlling shareholders of an enterprise take advantage of their dominant position in the decision-making of the company to manipulate the company's operation and management activities, which makes the company's decision-making deviate from the overall interests of the enterprise and the long-term interests of shareholders, and influences the long-term and healthy development of the enterprise[2] . These problems in environmental, social and corporate governance fully highlight the urgency and importance of an in-depth study of corporate ESG performance. Only through a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the current situation and problems of enterprises in terms of ESG and the adoption of practical and effective measures to improve them can we guide enterprises to change their development concepts and operation modes, and encourage them to actively fulfil their social responsibilities and pay attention to environmental protection and the improvement of corporate governance while pursuing economic benefits.
In light of the various perspectives shaping corporate growth today, it is essential to delve into the connection between management overconfidence and a company's ESG performance. This relationship holds significant weight, influencing not only the quality of decision-making and operational effectiveness on an individual level but also contributing to the broader goal of sustainable societal development. From the environmental dimension, overconfident management tends to prioritise short-term financial performance and economic benefits when making corporate strategies and decisions [3]. They may have a one-sided view that investment in environmental protection is merely a cost burden and cannot bring direct economic benefits to the enterprise in the short term. As a result, they might overlook to invest in the research and development of environmental protection technology, the upgrading of environmental protection equipment and the green optimisation of production processes. At the social level, over-confident management may take a series of measures that are not conducive to the protection of employees' rights and interests in order to achieve the reduction of corporate costs and the maximisation of profits. They may over-compress labour costs, lower employees' remuneration packages, and reduce investment in employee training and career development opportunities. In terms of working time arrangement, they may unreasonably increase the working hours of employees, resulting in employees being under prolonged high-intensity work pressure and physical and mental exhaustion. As far as corporate governance is concerned, overconfident management tends to breed a dictatorial style. They think they possess excellent leadership ability and decision-making wisdom and are convinced of their own judgement, thus belittling or even ignoring the reasonable demands of shareholders and other stakeholders. In the process of major decision-making, the opinions of all parties may not be fully solicited, and comprehensive risk assessment and scientific evidence will not be conducted, but only based on the subjective will of individuals to make decisions [4] . This kind of decision-making method is easy to lead to the company's decision-making errors, making the company's strategy deviate from the market demand and the actual development of the enterprise. At the same time, in the absence of effective supervision and check-and-balance mechanism, the power of the management is not restrained, which may lead to internal corruption, transfer of benefits and other problems, which will seriously damage the governance structure of the company and the market reputation, and hinder the healthy development of the enterprise. However, there is a relative lack of research on the relationship between management overconfidence and corporate ESG performance in both academia and the corporate sector. Although there is a large amount of research in each of these two areas, there is not much literature that combines the two for an in-depth discussion. To a certain extent, this state of affairs limits our understanding of the complex interaction between internal decision-making mechanisms and external performance, and an in-depth study of this relationship is of great value from both a theoretical and a practical perspective.
The unique contribution of this study is evident in both its theoretical and practical dimensions. The literature review indicates that prior research predominantly concentrates on how management overconfidence influences corporate financial decisions and performance, along with exploring the connections between corporate ESG performance, value, and innovation. However, there is a notable gap in systematic and in-depth exploration of the interplay between management overconfidence and corporate ESG performance. This study will fill the research gap, enrich the relevant theoretical system, and provide new perspectives and theoretical foundations for subsequent studies. From a practical point of view, there is an urgent need to find effective solutions to the problems caused by management overconfidence and the negative social impacts of poor ESG performance. By elucidating this relationship, the study introduces a fresh perspective on corporate governance, suggesting that enhancing ESG performance can help mitigate managerial overconfidence. This, in turn, can lead to reduced corporate risks, improved public perception, and greater social acceptance, ultimately fostering sustainable business practices. Additionally, it offers a theoretical framework for policymakers, aiding in the formulation of regulations that support societal and economic stability.
The structure of this paper unfolds as follows: the second section encompasses the literature review, followed by the research hypotheses in the third section. The fourth section presents the research design, while the fifth focuses on empirical analysis. The sixth section discusses the mechanisms at play, concluding with the final section that encapsulates the conclusions and recommendations.
2. Literature review
Corporate ESG performance refers to the comprehensive performance of an enterprise in the three dimensions of environment, society and corporate governance, which reflects in an all-round way the degree of importance and practical results of the enterprise's attention to the ecological environment, social development and internal governance structure in its economic activities, and it is an important indicator of the enterprise's ability to sustainable development and fulfilment of its social responsibility. This indicator not only concerns the long-term survival and development of enterprises, but also has a profound impact on the sustainable progress of the whole society. When companies integrate ESG concepts into their strategic planning, it means that ESG is no longer an optional add-on, but is integrated into all aspects of corporate development and long-term goals. When making investment decisions, business expansion directions and product development plans, they will prioritise environmental impact, social needs and governance norms. The values of management, as the driving force behind corporate decision-making, play a crucial role in shaping a company's stance on ESG. If the management holds a strong sense of social responsibility and closely links the development of the enterprise with the well-being of the society, it will proactively invest resources in ESG-related matters[5] . In addition, a stable financial position allows enterprises to face ESG-related investments without excessive concern about risks such as broken capital chains, and even if ESG investments cannot bring obvious economic benefits in the short term, enterprises have sufficient capital reserves to maintain the advancement of related projects [6] . When a company's financial condition is poor, it may prioritise cutting back on ESG expenditures to ensure its survival and basic operations, thus affecting its ESG performance.
Management overconfidence refers to a psychological bias in the decision-making process in which management overestimates its own capabilities, judgements and future prospects and exceeds the objective reality. When there is overconfidence, they will subconsciously misjudge the boundaries of their own ability [7] . This is manifested in overestimating the probability of their own success, and when facing various projects and challenges, they are always sure that they can achieve their goals, while underestimating the potential difficulties and obstacles. They also underestimate risks and uncertainties, and selectively ignore factors that may cause adverse consequences when analysing market dynamics, industry competition and macroeconomic environment. At the same time, they are overly confident in their own knowledge and ability, convinced that the information they have is comprehensive and accurate, and make decisions easily based on past experience and personal knowledge, while ignoring the complexity and variability of the external environment. In M&A activities, overconfident management often overestimate the value of the target enterprise [8] . They may make hasty M&A decisions based only on the target's apparent market share, technological advantage or brand influence, without conducting in-depth and comprehensive due diligence on the target. Moreover, in the valuation process, due to overconfidence, they often give excessive M&A premiums, expecting to realise synergies and create great value through M&A. However, in practice, the integration process after M&A is far more complicated than imagined, resulting in a lot of contradictions during the integration process, low employee morale, and difficulty in realising business synergies. In the end, not only will the expected M&A goals not be achieved, but it may also lead to a decline in corporate performance and market competitiveness. In addition, overconfident management will put on an "optimistic filter" when reviewing investment projects. They tend to overestimate the returns of investment projects based on their one-sided understanding of the market and excessive trust in their own vision [9] . When assessing the expected return of a project, they will unconsciously over-amplify various favourable factors and downplay potential risks and disadvantages. This bias makes it easy for them to impulsively invest a large amount of the enterprise's capital in some projects with negative NPV when making decisions. These projects will not only fail to bring the expected profit for the enterprise, but also take up a large amount of human, material and financial resources, leading to a serious waste of enterprise resources. In the long run, the enterprise's return on investment will continue to decline, and the capital chain may also face a tight situation, seriously affecting the financial health and sustainable development of the enterprise.
The impact of management overconfidence on corporate ESG performance is a complex topic, with limited research focusing on their relationship. Most studies address ESG performance's influencing factors and its connection to corporate performance or investor decisions, but few explore how management overconfidence affects ESG outcomes. This paper examines that relationship, shedding light on how psychological factors influence corporate decisions and enriching management behavior theory.
3. Research hypotheses
Existing literature suggests that overconfident management tends to be overly optimistic about a firm's future prospects and may overlook the importance of ESG factors for long-term corporate growth, thereby reducing investment in ESG and leading to poor corporate ESG performance.
Management overconfidence affects corporate ESG performance in the following ways: firstly, overconfident management may overestimate its ability to cope with environmental risks and underestimate the risks of changes in environmental regulations and resource shortages, leading to insufficient investment in R&D of environmental protection technology, energy saving and emission reduction, and exposing the company to environmental regulatory penalties and reputational damage. Meanwhile, overconfident management may invest a large amount of resources in short-term profit-making projects and neglect investment in the construction and operation of environmental protection facilities, affecting the environmental performance of the enterprise[10] . Secondly, overconfident management may trust their own judgement too much and act arbitrarily, leading to imperfect corporate decision-making mechanism and lack of effective supervision and checks and balances. Moreover, overconfident management may selectively disclose information or even conceal or misrepresent the actual governance of the enterprise in order to safeguard the image of the enterprise and its own reputation, affecting the decision-making of investors and other stakeholders[11] . Thirdly, overconfident management may ignore the needs and rights of employees, such as providing unreasonable work intensity and remuneration packages, leading to a decline in employee satisfaction and serious brain drain. It may also overestimate the influence of the enterprise on the community, and in the process of project development and operation, it may not fully consider the interests and demands of the community residents, which may lead to community conflicts and contradictions.
H1: Management overconfidence can have a significant negative effect on firms' ESG performance.
In analysing the complex network of relationships between corporate operations and sustainability, the association between management overconfidence and corporate ESG performance has attracted much attention, and the significant negative mediating role played by media attention is a key entry point for understanding this relationship. The media, as an important force in information dissemination and social monitoring, will quickly and widely disseminate corporate information once it is captured[12] . That is, media attention can exacerbate the negative consequences of management overconfidence. Originally, ESG problems caused by management overconfidence may be relatively hidden, but after media exposure, the negative impact is rapidly magnified. This puts enormous external pressure on the company, such as consumer resistance, reduced trust from partners, and increased government regulation. However, overconfident management is often reluctant to change its decision-making mindset, and in the face of media pressure, it may adopt a tougher or more inappropriate response, further undermining the company's ESG performance.
H2:Media attention plays a significant negative mediating role in the effect of management overconfidence on firms' ESG performance.
4. Research design
4.1. Sample selection and data sources
To obtain a more precise assessment of the relationship among variables, this study utilizes A-share state-owned listed companies from 2017 to 2023 as its primary research subjects. The sample data was filtered based on specific criteria: (1) financial listed companies were excluded; (2) ST-type companies were not considered; and (3) companies with incomplete information were omitted. Ultimately, the research includes a total of 11,827 samples. Data regarding management overconfidence and corporate ESG performance was gathered through the meticulous collection and organization of annual reports, while additional financial information was sourced from the CSMAR and Wind databases. To mitigate the effect of outliers on the analysis, the variable values in the sample were trimmed at the 1% and 99% quantile shrinkage.
4.2. Variable selection
4.2.1. Explained Variables - Corporate ESG Performance
Corporate ESG performance (AvgESG), with reference to the research of Xie Hongjun [13] and other studies, selects Huazheng's ESG rating data as the core indicator for measuring corporate ESG performance, in which the key indicators are scored and weights are assigned, and each indicator is given the corresponding weight according to its degree of influence on the overall ESG performance of the enterprise, and the scoring process adopts standardised methods to ensure that different indicators are comparable to one another. The scores are standardized to ensure comparability, and the final ESG rating is derived from the total score. The data comes from Wind Information Financial Terminal, and the index has been recognised and used by the industry and academia. At the same time, we also consider the corporate ESG composite score provided by Wind as a robustness test.
4.2.2. Explanatory variable - management overconfidence
Management Overconfidence (Moc_CEO) is measured by a composite score based on the CEO's gender, age, education, and dual positions, with a higher score indicating greater overconfidence. This approach follows Wei Zhehai’s research[14].
4.2.3. control variable
Referring to the study of Xie Hongjun[13] et al. set control variables, namely, firm size (Size), gearing ratio (Lev), return on equity (ROE), cashflow ratio (Cashflow), board size (Board), growth rate of operating income (Growth), and the percentage of independent directors (Indep) Specific variables and their definitions are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Definition of variables
variant | variable name | variable code | Variable Definition |
explanatory variable | Corporate ESG performance | AvgESG | Huazheng ESG Rating Data |
explanatory variable | Management overconfidence |
| The composite score, based on the arithmetic mean of gender, age, education, and holding two jobs. |
control variable | Enterprise size | Size | Total assets at the end of the year are expressed in natural logarithms |
gearing | Lev | Total liabilities/total assets | |
return on net assets | ROE | Net profit/owners' equity | |
Cash flow ratio | Cashflow | Cash flows from operating activities/total assets | |
Board size | Board | The number of board members is taken as a natural logarithm | |
Growth rate of operating income | Growth | Current year's operating income/previous year's operating income - 1 | |
Percentage of independent directors | Indep | Number of independent directors/directors |
4.3. Modelling
In order to test whether management overconfidence has a negative impact on corporate ESG performance in various ways, this paper sets up the following regression model:
\( {AvgESG_{it}}={β_{0}}+{β_{1}}{Moc_{-}}{CEO_{it}}+{β_{n}}{Controls_{it}}+{μ_{i}}+{τ_{t}}+{ε_{it}}\ \ \ (1) \)
where the subscript 'i' refers to each firm, while the subscript 't' indicates the year. The explanatory variable \( {AvgESG_{it}} \) reflects firm i's ESG performance for year t; \( {Moc_{-}}{CEO_{it}} \) denotes management overconfidence, \( {Controls_{it}} \) denotes control variables; \( {μ_{i}} \) denotes individual fixed effects; \( {τ_{t}} \) denotes year fixed effects; and \( {ε_{it}} \) denotes a random disturbance term. The coefficient \( {β_{1}} \) estimates the effect of management overconfidence on ESG performance.
5. Empirical analysis
5.1. Descriptive statistical analyses
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics for the principal variables under study. The data reveals that the mean ESG performance rating across the sampled firms stands at 4.173, with a standard deviation of 0.898. The average level of management overconfidence is recorded at 0.673, indicating that, on average, management in these firms exhibits a 67.3% overconfidence level, with those demonstrating the highest overconfidence reaching an impressive 94.1%. Other variables display a favorable distribution that aligns with findings in existing literature and thus will not be elaborated upon further.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics
Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
AvgESG | 11827 | 4.173 | 0.898 | 1.500 | 6.000 |
Moc CEO | 11827 | 0.673 | 0.156 | 0.303 | 0.941 |
Size | 11827 | 22.110 | 1.163 | 20.069 | 26.014 |
Lev | 11827 | 0.390 | 0.190 | 0.062 | 00.862 |
ROE | 11827 | 0.060 | 0.143 | -0.703 | 0.351 |
Cashflow | 11827 | 0.052 | 0.067 | -0.134 | 0.244 |
Board | 11827 | 2.087 | 0.189 | 1.609 | 2.485 |
Growth | 11827 | 0.149 | 0.333 | -0.511 | 1.700 |
Indep | 11827 | 37.802 | 5.201 | 33.330 | 57.140 |
5.2. Management Overconfidence and Corporate ESG Performance - Benchmark Regression
The benchmark regression analysis presented in Table 3 indicates a robust negative correlation between management overconfidence and ESG performance at the 1% significance level, irrespective of the inclusion of control variables or fixed effects. After controlling for all relevant variables, every one-unit increase in management overconfidence decreases ESG performance by 0.298 units, supporting hypothesis H1.
Table 3: Benchmark regression
(1) | (2) | (3) | |
AvgESG | AvgESG | AvgESG | |
Moc_CEO | -0.255 *** | -0.270 *** | -0.298 *** |
(-2.58) | (-2.72) | (-3.02) | |
Controls | No | No | Yes |
N | 11827 | 11827 | 11827 |
r2 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.020 |
stkcd | Yes | Yes | Yes |
year | No | Yes | Yes |
t statistics in parentheses * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 00.01
5.3. Robustness test for benchmark regression
5.3.1. Substitution of explanatory variables
To deepen the investigation into how management overconfidence affects corporate ESG performance, this paper substitutes the ESG performance measure. Utilizing ESG-related data sourced from the WAND database, the research encompasses the pertinent timeframe and sample subjects, ensuring comprehensive and accurate data incorporation. The explanatory variable has been updated to include the WAND ESG composite score (ESG), with the resultant regression findings detailed in Table 4, Column (2).
5.3.2. Replacement of spanning years
In order to minimise the problem of endogeneity of reverse causation and foresight bias, this paper examines the stability of the findings across time by replacing the time span years, i.e. shortening the time window in order to test the stability of the findings over time. The findings displayed in column (3) of Table 4 illustrate the effect of management overconfidence on companies' ESG performance from 2017 to 2023. The coefficient for management overconfidence remains significant, aligning with previous results and reinforcing the hypotheses and conclusions drawn.
Table 4: Robustness test
(1) | (2) | (3) | |
AvgESG | ESG | AvgESG | |
Moc_CEO | -0.298*** | -0.345*** | -0.378 *** |
(-3.02) | (-4.03) | (-3.03) | |
Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes |
N | 11827 | 8925 | 8925 |
r2 | 0.020 | 0.059 | 0.027 |
stkcd | Yes | Yes | Yes |
year | Yes | Yes | Yes |
t statistics in parentheses * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 00.01
5.4. heterogeneity analysis
This paper further analyses the heterogeneity analysis to analyse the ways in which management overconfidence affects firms' ESG performance in different dimensions. The study poses two key questions: Does the influence of management overconfidence on corporate ESG performance vary significantly by the size of the firm? Additionally, is there a notable difference in how management overconfidence impacts ESG performance of companies situated in different regions?
5.4.1. Enterprise size
Enterprises are classified into two types, large-scale enterprises and small-medium-scale enterprises, based on the median enterprise size, and the dummy variable HighSize is set as a variable for judging the enterprise size. For the dummy variable HighSize, it takes the value of 1 if it is a large-scale firm, otherwise it takes the value of 0. From columns (1) and (2) of Table 5, it can be seen that when it is a large-scale firm, the coefficient of managerial overconfidence (Moc_CEO) is -0.468 and is significant at the 1 per cent level, which is more significant as compared to small and medium-sized firms. The possible explanation is that large-scale firms control a large amount of resources, and when management is overconfident, it is more likely to make high-risk, large-scale investments or strategic adjustments, which can have far-reaching impacts on all aspects of ESG. At the same time, the decision-making process of large-scale firms is complex and involves multiple departments and levels. Overconfident management may ignore or simplify key aspects of the decision-making process, leading to ESG-related decision-making errors. Moreover, large-scale enterprises have more hierarchical structures, and overconfident management may result in poor information transfer, hindering the effective implementation of ESG policies. Therefore, the impact of management overconfidence on ESG performance of large-scale enterprises is more significant.
5.4.2. Regional distribution of enterprises
The variable “Area” is used to categorize enterprises into three regions: East (2), Central (1), and West (0). It can be seen from columns (3) (4) (5) of Table 5 that when the enterprise is in the western region, the impact of management overconfidence on the enterprise's ESG performance is most significant, and the coefficient of management overconfidence (Moc_CEO) is -1.219 and is significant at the 1 per cent level. level. In the eastern region, the negative effect of management overconfidence on ESG performance is smaller, likely due to better market mechanisms, competition, and external supervision. In the western region, where market competition is relatively insufficient and external monitoring mechanisms are not perfect, overconfident management behaviour is more likely to affect firms' ESG decisions and performance.
Table 5: Heterogeneity test
(1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
HighSize=1 | HighSize=0 | Area=2 | Area=1 | Area=0 | |
AvgESG | AvgESG | AvgESG | AvgESG | AvgESG | |
Moc_CEO | -0.468*** | -0.220 | -0.195* | -0.325 | -1.219*** |
(-3.18) | (-1.57) | (-1.74) | (-1.25) | (-3.49) | |
Controls | Yes | Yes) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
N | 5913 | 5914 | 8976 | 1729 | 1122 |
r2 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.037 | 0.044 |
stkcd | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
t statistics in parentheses * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 00.01
6. Role channel analysis
The results table above suggests that overconfident management tends to underestimate risks and overestimate benefits, and may ignore potential environmental, social and governance risks when making ESG-related decisions, leading to firms' ESG problems. So what are the channels of action through which management overconfidence affects corporate ESG performance? It is found that media attention exacerbates the negative impact of management overconfidence on corporate ESG performance. On the one hand, media exposure can magnify the ESG problems of a company, attracting the attention of regulators, investors and the public, and bringing great pressure to the company. On the other hand, negative media coverage affects firms' reputation and image, which in turn affects their market value and operating performance, making their ESG performance worse.
6.1. Mediating effects of media attention
Overconfident management may tend to engage in large-scale investments, mergers and acquisitions, and other behaviours that are likely to attract media attention. At the same time, management may not pay enough attention to the disclosure of negative information, which may also increase the likelihood of media attention. When a company faces excessive media attention, it may create a "spotlight effect", leading to short-term and superficial ESG measures to maintain the company's image, while neglecting long-term and substantive ESG inputs. For example, firms with excessive media attention may increase environmental advertisements in the short term, but the actual investment in pollution control does not increase, and this kind of "greenwashing" behaviour will reduce the firm's ESG performance. The results of the mediation effect of media attention are shown in column (2) of Table 6, and media attention (Media_1) is significantly negatively related to firms' ESG performance. The regression results indicate that the coefficient of management overconfidence on firms' ESG performance is -0.302 and significantly negative at the 1% level, suggesting that media attention has a more serious negative impact on firms' ESG performance. A series of decisions and behaviours triggered by management overconfidence may only have an impact on corporate ESG performance to a certain extent, but due to media attention and dissemination, these problems are magnified and spread, further exacerbating the negative impact on corporate ESG performance. Initially, the hypothesis H2 of this paper is verified.
6.2. Variables replacing the mediating effect of media attention
Media attention is an important indicator of a company's external environment, reflecting the extent to which it receives public and media attention. The number of stories containing the company in online news content can provide a more comprehensive picture of the company's true attention, including not only mentions in the headlines, but also detailed reports in the content. This paper replaces the number of online media reports (Meida_1) with the number of reports containing the firm in online news content (Media_2) to further test the mediating effect of media attention in the impact of management overconfidence on firms' ESG performance. The coefficient of media attention (Media_2) in column (3) of Table 6 is -0.389 and significant at 1% level. Once again, the hypothesis H2 of this paper is verified.
Table 6: Intermediation effects
(1) | (2) | (3) | |
AvgESG | AvgESG | AvgESG | |
Moc_CEO | -0.298*** | -0.302*** | -0.389*** |
(-3.02) | (-3.06) | (-3.13) | |
Media_1 | -0.091*** | ||
(-6.02) | |||
Media_2 | -0.076*** | ||
(-4.42) | |||
Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes |
N | 11827 | 11827 | 8925 |
r2 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.031 |
stkcd | Yes | Yes | Yes |
year | Yes | Yes | Yes |
t statistics in parentheses, * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01
7. Conclusions and recommendations
7.1. Conclusions of the study
The study in this paper takes all A-share listed companies in 2017-2023 as a sample, and after theoretical derivation and experimental verification, it is concluded that management overconfidence has a significant negative impact on corporate ESG performance. Management overconfidence often leads to gaps in the environmental information disclosure of enterprises, resulting in a significant reduction in the quality of disclosure. In the field of environmental protection technology research and development, as they do not see the potential long-term benefits and strategic value, overconfident management will cut down the relevant investment, which will make the enterprise miss opportunities for development in green technology innovation, and make it difficult to form environmental protection competitive advantage in the market. Management overconfidence also This approach increases the likelihood of corporate decision-making error. When making major decisions, they often rely on their own subjective judgement and past experience, but neglect to conduct comprehensive and in-depth risk assessment and rational analysis of decision-making matters. This decision-making process significantly increases the likelihood of corporate errors, which may lead to serious mistakes in the selection of investment projects, market expansion strategy development, etc., and bring huge economic losses to the enterprise. Management overconfidence has a negative impact on all three key dimensions of ESG: environmental, social and governance, and prevents companies from achieving sustainable development goals. Therefore, enterprises need to pay attention to the psychological attributes of management and establish a sound risk assessment and decision-making monitoring mechanism to improve their ESG performance and enhance their overall competitiveness and sense of social responsibility.
7.2. Research recommendations
In order to solve the problems in the development of enterprises and establish modern high-quality enterprises adapted to the current market environment, this paper puts forward the following suggestions. First, improve the management selection and training mechanism. Training courses on risk management, decision-making theories and ESG concepts are regularly conducted. Second, strengthen the internal monitoring and check and balance system. Establish an internal reporting mechanism to encourage employees to report possible improper decisions by management that neglect ESG issues due to overconfidence, establishing a comprehensive internal monitoring network. Third, establish a scientific decision-making process: management is required to follow a strict decision-making process when making major decisions, especially those involving ESG-related matters.
References
[1]. SONG He,YU Jingjing,HE Dexu. Venture Capital, Management Overconfidence and M&A Premium[J]. Business Economics and Management,2022,(03):27-41.
[2]. Chen Kexi,Li Zhenzhen. Management Overconfidence, Board Governance and Firm Performance - Empirical Evidence from Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share Manufacturing Firms[J]. Finance and accounting newsletter,2017,(18):32-35.
[3]. Cen Wei,Tong Naqiong. Management overconfidence, diversification and firm performance[J]. Contemporary Economic Management,2015,37(09):14-19.
[4]. Hribar P ,Yang H .CEO Overconfidence and Management Forecasting[J].Contemporary Accounting Research,2016,33(1):204-227.
[5]. LI Hong,WANG Ruike,XU Ningning. The impact of management cognition on the decision to disclose internal control deficiencies-an analysis based on the conceptual model of management cognitive bias[J]. Enterprise Economy,2017,36(11):89-95.
[6]. Jingchang Xu,Xueyun Zeng. Financial asset size, fair value accounting and management overconfidence[J]. Economic Theory and Economic Management,2012,(07):5-16.
[7]. S. A A ,SCOTT D .Managerial Overconfidence and Accounting Conservatism:managerial overconfidence[J]. -30.
[8]. Lu Xiaozhe,Zhu Nanjun. High-premium M&A Characteristics and Timeliness of Goodwill Impairment - Based on the Perspective of Management Overconfidence at the Time of M&A[J]. Economic Theory and Economic Management,2022,42(08):73-87.
[9]. Ji Yafang. The impact of management overconfidence on corporate decision-making[J]. Journal of Management,2017,30(04):50-56.
[10]. HUANG Wensheng,ZHU Zhaohui,MENG Jun. The effect of overconfidence on behavioural decision-making:An example of financing decisions of listed companies[J]. Applied Psychology,2015,21(03):265-270.
[11]. LI Sifei,HOU Menghong,WANG Di. Management overconfidence and corporate social responsibility fulfilment[J]. Financial Review,2015,7(05):58-69+124.
[12]. Zhang Xiao,Xiao Zhichao. Does management overconfidence affect the comparability of accounting information? [J]. Journal of Central University of Finance and Economics,2018,(05):59-71.
[13]. Xie Hongjun,Lv Xue. Responsible international investment: ESG and China's OFDI[J]. Economic Research,2022,57(03):83-99.
[14]. Wei Zhehai. Managerial overconfidence, capital structure and firm performance[J]. Industrial Technology and Economics,2018,37(06):3-12.
Cite this article
Wu,Y. (2025). The Impact of Management Overconfidence and Corporate ESG Performance. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,173,1-12.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. SONG He,YU Jingjing,HE Dexu. Venture Capital, Management Overconfidence and M&A Premium[J]. Business Economics and Management,2022,(03):27-41.
[2]. Chen Kexi,Li Zhenzhen. Management Overconfidence, Board Governance and Firm Performance - Empirical Evidence from Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share Manufacturing Firms[J]. Finance and accounting newsletter,2017,(18):32-35.
[3]. Cen Wei,Tong Naqiong. Management overconfidence, diversification and firm performance[J]. Contemporary Economic Management,2015,37(09):14-19.
[4]. Hribar P ,Yang H .CEO Overconfidence and Management Forecasting[J].Contemporary Accounting Research,2016,33(1):204-227.
[5]. LI Hong,WANG Ruike,XU Ningning. The impact of management cognition on the decision to disclose internal control deficiencies-an analysis based on the conceptual model of management cognitive bias[J]. Enterprise Economy,2017,36(11):89-95.
[6]. Jingchang Xu,Xueyun Zeng. Financial asset size, fair value accounting and management overconfidence[J]. Economic Theory and Economic Management,2012,(07):5-16.
[7]. S. A A ,SCOTT D .Managerial Overconfidence and Accounting Conservatism:managerial overconfidence[J]. -30.
[8]. Lu Xiaozhe,Zhu Nanjun. High-premium M&A Characteristics and Timeliness of Goodwill Impairment - Based on the Perspective of Management Overconfidence at the Time of M&A[J]. Economic Theory and Economic Management,2022,42(08):73-87.
[9]. Ji Yafang. The impact of management overconfidence on corporate decision-making[J]. Journal of Management,2017,30(04):50-56.
[10]. HUANG Wensheng,ZHU Zhaohui,MENG Jun. The effect of overconfidence on behavioural decision-making:An example of financing decisions of listed companies[J]. Applied Psychology,2015,21(03):265-270.
[11]. LI Sifei,HOU Menghong,WANG Di. Management overconfidence and corporate social responsibility fulfilment[J]. Financial Review,2015,7(05):58-69+124.
[12]. Zhang Xiao,Xiao Zhichao. Does management overconfidence affect the comparability of accounting information? [J]. Journal of Central University of Finance and Economics,2018,(05):59-71.
[13]. Xie Hongjun,Lv Xue. Responsible international investment: ESG and China's OFDI[J]. Economic Research,2022,57(03):83-99.
[14]. Wei Zhehai. Managerial overconfidence, capital structure and firm performance[J]. Industrial Technology and Economics,2018,37(06):3-12.