1. Introduction
The PlayStation, a revolutionary brand owned by Sony Interactive Entertainment (also referred as Sony Computer Entertainment Inc.), has not only succeeded in technical aspects but also became a dominance power in game console market for its marketing tactics monopolizing different hierarchy of consumers. Since its debut in 1994, the PlayStation brand has emerged as a transformative force, leveraging innovative hardware and a robust library of games to establish a formidable presence. The original PlayStation disrupted the cartridge-dominated market with its CD-ROM technology, while the PlayStation 2 (PS2), released in 2000, became the best-selling console of all time, with over 160 million units sold. Despite a challenging launch in 2006, the PlayStation 3 (PS3) regained momentum through strategic adjustments, setting the stage for the PlayStation 4 (PS4). Launched in 2013, the PS4 marked a turning point, solidifying Sony’s global dominance with over 117 million units sold by 2022 [1].
In recent years, Microsoft’s Xbox has struggled to maintain its competitive footing against PlayStation. The Xbox Series X|S, released alongside the PS5 in 2020, has sold approximately 25 million units by 2024—less than half of the PS5’s total [2]. Industry observers, including bigsocrates [3], argue that Xbox’s console business may be on the brink of decline, with speculation that Microsoft could exit the hardware market entirely. A Giant Bomb blog highlights Xbox’s shift toward cloud gaming and subscription services like Xbox Game Pass, which boasts over 34 million subscribers [4]. This strategic pivot, combined with weaker hardware sales, suggests a potential reconfiguration of the console market, leaving PlayStation and Nintendo as the primary hardware competitors.
This paper aims to analyze PlayStation’s current market position and propose marketing strategies to address the implications of Xbox’s potential withdrawal from the console market. By employing a SWOT analysis focused on the PlayStation product line and a comparative STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning) framework against Xbox, this study offers actionable recommendations to reinforce PlayStation’s dominance and adapt to an evolving competitive landscape.
2. SWOT analysis
For the purposes of this analysis, PlayStation is treated as a standalone entity, distinct from Sony’s wider operations, to focus exclusively on its gaming ecosystem.
2.1. Strength
2.1.1. Exclusive games and popular intellectual property (IP)
Exclusive games are titles created, released, and restricted to playing on a particular gaming console, PC platform, or digital distribution service. As the gaming console industry has evolved, exclusivity has become a strategic advantage for companies like Sony, Xbox and Nintendo. For PlayStation itself, Bloodborne which developed by Hidetaka Miyazaki is the best example of exclusive game [5].
“What else is there to say about Bloodborne, the sole reason I purchased a PlayStation 4? It’s given me more than I ever bargained for”.
PlayStation’s portfolio of exclusive titles, such as “God of War”, “The Last of Us”, and “Spider-Man”, serves as flagship offerings that differentiate the platform from its rivals. Porter [6] posits that differentiation is a critical strategy for achieving competitive advantage in saturated markets, a principal PlayStation exemplifies through its curated library of high-profile exclusives. These games, often developed by Sony’s first-party studios like Naughty Dog and Santa Monica Studio, are tailored to showcase the PS5’s technical capabilities, reinforcing the platform premium positioning.
Academic research by Yee [7] underscores the role of narrative-driven games in cultivating emotional attachment among players, a dynamic PlayStation exploits to foster loyalty. Additionally, media analyses, such as IGN’s coverage of PS5 sales spikes tied to exclusives like “Horizon Forbidden West”, affirm that these titles are not merely games but brand ambassadors that enhance consumer allegiance.
2.1.2. Innovative technology: the portal
The PlayStation Portal, a handheld device enabling remote play of PS5 games, exemplifies Sony’s technological innovation. This console-exclusive technology enhances user experience by offering portability without sacrificing graphical fidelity, a feature unavailable on rival platforms. Schilling [8] argues that technological differentiation is a key driver of competitive advantage in tech-driven industries, an approach PlayStation leverages effectively.
2.1.3. Brand equity
PlayStation benefits from strong brand equity, familiarity, and positive consumer perception. Aaker [9] defines brand equity as a set of assets linked to a brand name and symbol that add value to a product.
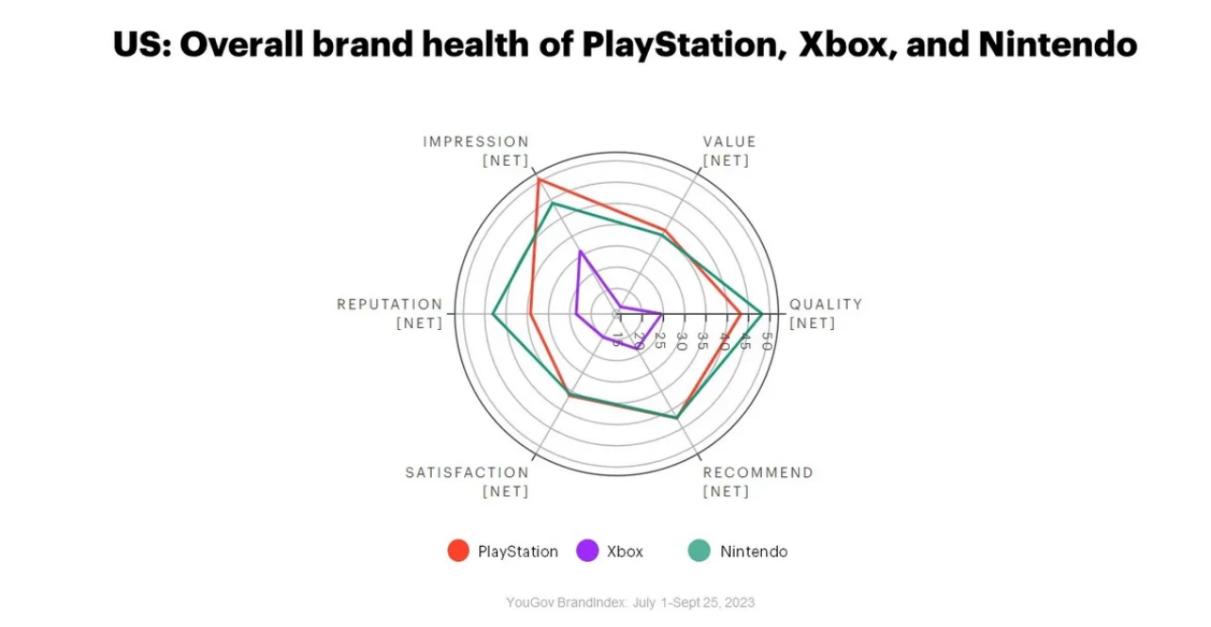
Figure 1: Overall brand health of PlayStation, Xbox and Nintendo
As it is shown in Figure 1, Surveys conducted by Kineree Shah in 2023 reveal that PlayStation ranks highest among console brands in consumer trust and preference, reinforcing its market dominance [10].
2.2. Weakness
2.2.1. High price of games
A notable weakness is the high cost of PlayStation games, which are often priced at $70 USD, significantly higher than PC equivalents on platforms like Steam, where frequent discounts make gaming more affordable. Tschang [11] highlights how pricing strategies impact market accessibility, suggesting that PlayStation’s premium model may alienate price-sensitive gamers. Criticism from gaming communities, particularly on Microsoft platforms, argues that this pricing risks losing market share to PC gaming, especially as hardware costs rise.
2.2.2. Limited game type diversity and controller constraints
While PlayStation’s controller is optimized for action and adventure games, it is less suited to genres like real-time strategy (RTS) and sandbox games, which thrive on PC with mouse-and-keyboard precision. Adams and Rollings [12] note that input device compatibility shapes genre viability, limiting PlayStation’s appeal to certain player demographics. Compared to the versatility of PC gaming, where customization and diverse input options are readily available, this constraint reduces PlayStation’s ability to attract broader gaming audiences.
2.2.3. Over-reliance on exclusives and studio performance
PlayStation’s heavy dependence on exclusive titles and first-party studios presents vulnerability. The 2024 failure of Concord, a multiplayer shooter from Firewalk Studios, exemplifies this risk, with sales underperforming and the game shutting down within months. Zhu and Zhang [13] caution that over-reliance on specific product lines can destabilize brand influence if releases falter, a scenario PlayStation must navigate carefully.
Furthermore, Sony’s decision-making missteps in assessing player preferences contributed to Concord’s downfall. The game was widely criticized for its emphasis on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) themes, which some players perceived as forced, leading to backlash within gaming communities. This backfired release resulted in PlayStation's brand reputation being tarnished by the game alone, and it quickly became fodder for rivals to hype it up.
2.3. Opportunities
2.3.1. Expansion of cloud gaming
Advancements in cloud infrastructure enable PlayStation to enhance its PlayStation Plus cloud gaming service, attracting users seeking flexibility. By 2025, Sony has expanded streaming capabilities, reducing hardware barriers for new players. Ahmad Tabeh Khalilian [14] notes that cloud gaming democratizes access to high-end gaming experiences, positioning PlayStation to capitalize on this growing trend.
2.3.2. Emerging markets
Regions such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America represent untapped potential for console gaming. Rising disposable incomes and expanding digital infrastructure make these markets increasingly viable for console gaming. The popularity of postmodernist cultural ideas and video game culture, or better known as the "Ninth Art", through the widespread spread of social media, has created an excellent potential market for PlayStation, the "Coca-Cola", which symbolizes the game console industry.
2.4. Threats
2.4.1. Economic factors
Global economic conditions, including inflation and recessions, impact consumer spending on luxury goods like gaming consoles. A 2024 report notes a 10% decline in high-end electronics purchases amid economic uncertainty. Apparently, economic downturns disproportionately affect discretionary industries like gaming. The global shock of the COVID-19 epidemic in 2020 highlighted these vulnerabilities when the PS5 launch faced severe challenges due to supply chain disruptions, logistics stagnation, and widespread scalping. This turbulent release underscores the risks associated with launching expensive next-generation consoles during periods of economic uncertainty.
2.4.2. Shifting industry trends
The gaming landscape is shifting toward free-to-play models (e.g., Fortnite) and subscription services (e.g., Xbox Game Pass), challenging PlayStation’s traditional sales model. A large number of discounts and low price offers began to hit the market with the downturn in the gaming industry, and PlayStation, which relied on high-end prices to make profits, began to diverge in cooperation with well-known game companies such as EA and Ubisoft. However, the company must navigate these shifts carefully to maintain profitability while adapting to evolving consumer expectations.
3. STP analysis
3.1. Segmentation
The console gaming market can be segmented into three distinct consumer groups:
3.1.1. Mid-age white-collar workers
Mid-age white-collar workers, typically aged 30-50, represent a significant portion of PlayStation’s casual gaming audience. These individuals face high-pressure environments, particularly in East Asian countries like Japan, where workplace stress is well-documented. For this segment, PlayStation serves as an escapist tool, offering an "unreality" to alleviate emotional strain. Games such as Astro’s Playroom (a parkour-style casual title) and single-player narrative experiences like The Last of Us appeal to their preference for low-commitment, immersive entertainment.
Economically, this group is price-sensitive yet financially stable, which drives their interest in second-hand PlayStation game discs. A 2023 Statista report highlights Japan’s robust second-hand gaming market, where physical disc sales outpacing digital downloads in the region [15]. This behavior underscores their pragmatic approach to gaming as a stress-relief mechanism rather than a lifestyle commitment.
3.1.2. Internet-addicted teenagers from wealthy families
Teenagers from affluent households in developed countries and regions such as the United States and Europe form a second key segment. Typically aged 13-19,, these players leverage PlayStation as a social tool, aligning with findings that gaming fosters peer connectivity among youth. As experienced players, they gravitate toward high-intensity genres like first-person shooters (Call of Duty) and AAA titles (Cyberpunk 2077), reflecting their familiarity with gaming mechanics.
This segment’s preference for digital downloads and subscription services like PlayStation Plus stems from their access to disposable income and demand for convenience. Their reliance on PlayStation’s online ecosystem positions this group as a lucrative target for Sony’s digital strategy.
3.1.3. PlayStation loyal players
The third segment comprises older, loyal players who have followed PlayStation since the PS3 or PS4 eras, typically aged 25–40. These individuals exhibit strong brand affinity, often drawn to exclusive titles like God of War and Horizon Zero Dawn. Despite varying personal backgrounds—from college students to self-identified "geeks"—their long-term engagement with PlayStation unites them. Subcultures such as "two-dimensional players" (those immersed in anime-inspired games) further diversify this group.
Loyalty to PlayStation reflects a psychological attachment to the brand, a phenomenon explored by Fournier [16] in her study of consumer-brand relationships. Media data from IGN indicates that PS5 exclusive titles consistently rank among the top sellers, underscoring this segment’s dedication to Sony’s ecosystem.
3.2. Targeting
3.2.1. Primary market: home game console market
PlayStation’s primary market is the home game console sector, where it competes with Xbox and Nintendo. Unlike PCs, which cater to professional gamers requiring customizable hardware, PlayStation targets players who prioritize high-quality graphics and interactivity. As the first choice for gamers and amateurs alike, the seamless integration of PlayStation's hardware and software is an important factor in gaining traction in the home console market. This is largely attributed to PlayStation engineers' optimized use and simplification of the console's design structure, making the PS5 easier to repair and more accessible to casual players.
3.2.2. Secondary market: multipurpose media devices and non-gamers
Beyond gaming, PlayStation appeals to non-gamers through its multimedia capabilities, such as 4K Blu-ray playback and streaming apps (e.g., Netflix). This secondary market positions the console as a household entertainment hub, broadening its appeal. While PlayStation has traditionally been associated with gaming, strategic investments from Sony’s U.S. and international shareholders since 2000 have transformed it into a more versatile entertainment device. Compared to PCs, PlayStation has the advantage of being more enjoyable and portable, and the introduction of streaming platforms such as HBO and Netflix has made this console for gaming shine compared to TV set-top boxes in the same price range, and has won favor from the non-console market.
3.3. Positioning
3.3.1. Product characteristics
PlayStation positions itself as a premium, innovative gaming platform, emphasizing superior image quality, exclusive content, and an immersive experience. This contrasts with Xbox, which focuses more on affordability and services like Game Pass. A comparative analysis by Entertainment Software Association reveals that PlayStation’s exclusive titles generate higher critical acclaim and sales than Xbox’s, reinforcing its leadership in content-driven positioning [17].
3.3.2. Sub-conclusion
Across segmentation, pricing, and targeting, PlayStation holds a competitive edge. Its ability to cater to diverse needs—casual escapism, social gaming, and brand loyalty—distinguishes it from rivals.
3.4. Repositioning
3.4.1. Differentiated market strategy
To sustain its competitive advantage, PlayStation employs a differentiated market strategy by launching varied console models, including the PS5, PS5 Slim, and PS5 Pro. The PS5 Slim targets price-sensitive consumers, while the PS5 Pro appeals to performance-driven senior players. As a multinational gaming giant, PlayStation has reached a near-monopoly position in the share of consoles in several regions and countries. Like Apple, PlayStation needs to differentiate its products to meet the needs of a large consumer base.
However, this differentiation has also drawn criticism from the player base. Each generation of PlayStation consoles has a sales life of about 5-10 years, yet updated versions are often introduced within three years of the original release. This practice has frustrated early adopters, and some media outlets claim that PlayStation’s approach aims to maximize the commercial lifespan of each console generation rather than focusing on genuine innovation.
3.4.2. Product strategy
PlayStation’s exclusive games, such as God of War and Spider-Man, cater to both hardcore and casual players, fostering inclusivity. Compared to Xbox’s reliance on Game Pass, PlayStation differentiates itself through a robust gaming ecosystem, including PlayStation Plus, which offers multiplayer access and monthly free titles. This ecological, exclusive gaming service has allowed PlayStation to gain a loyal following, and players are willing to pay several times the price of other rival gaming services for a smooth and highly innovative service like PlayStation.
However, PlayStation’s growing reliance on its exclusive services and game ecosystem has led to strategic missteps. While all bets and investments are being placed on exclusive services and PlayStation studios, the PlayStation console, which is the carrier of exclusive game services, is being ignored by Sony's decision-makers. Although they are in a leading position in the console game industry, they are unable to cope with PC gaming platforms with lower prices and higher hardware adaptability.
3.4.3. Promotion and advertising
PlayStation leverages advertising, social media, and events like E3 (or its successors) to reinforce its image as the premier gaming platform. Marketing campaigns highlighting exclusive titles and graphical fidelity resonate with enthusiasts, while influencer partnerships on platforms like Twitch amplify reach among younger demographics.
4. Conclusion
PlayStation’s success in the gaming industry is rooted in its nuanced market segmentation, precise targeting, and strategic positioning. By catering to the needs of mid-age white-collar workers, affluent teenagers, and loyal gamers, Sony has established a versatile market presence. PlayStation’s market dominance is underpinned by its exclusive game titles, innovative technological advancements, and a dedicated brand community. A SWOT analysis reveals the following:
Strengths: PlayStation enjoys the acclaim of critically acclaimed exclusive titles, such as God of War, and cutting-edge hardware, as exemplified by the PlayStation Portal.
Weaknesses: Challenges include the high cost of games, a limited diversity in game genres, and an overreliance on exclusive content.
Opportunities: Potential growth avenues include the expansion of cloud gaming services and increased penetration into emerging markets.
Threats: External risks comprise economic recessions and the industry’s shift towards free-to-play and subscription-based models.
The STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning) analysis indicates that PlayStation strategically targets mid-age white-collar professionals, affluent adolescents, and loyal gamers, positioning itself through a premium, content-rich gaming ecosystem. In the event of Xbox’s withdrawal from the hardware market, PlayStation would need to address its weaknesses—such as implementing flexible pricing strategies—and capitalize on opportunities like cloud gaming. This strategic approach would enable PlayStation to balance innovation with accessibility, thereby solidifying its leadership within the global gaming industry.
References
[1]. Business Data and Sales (2022), Sony Interactive Entertainment. Retrieved from [https://sonyinteractive.com/en/our-company/business-data-sales/].
[2]. von Nandelstadh, O. (2024). The implications of library subscriptions on video game marketing: featuring case study of Xbox Game Pass.
[3]. Amos, E. (2021). The game console 2.0: A photographic history from Atari to Xbox. No Starch Press.
[4]. Warren, T. (2024). Microsoft’s Xbox Game Pass service grows to 34 million subscribers. The Verge. Erişim adresi: https://www. theverge. com/2024/2/15/23570040/microsoft-xbox-game-pass-subscriber-numbers-34-million. Son Erişim Tarihi, 25, 2024.
[5]. Deckert, C., & Phan Ngoc, D. A. (2023). PlayStation 4 vs. Xbox One: Competitive Analysis of the Video Game Industry.
[6]. Belton, P. (2017). An Analysis of Michael E. Porter's Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors. Macat Library.
[7]. Yee, N. (2006). Motivations for play in online games. CyberPsychology & behavior, 9(6), 772-775.
[8]. Schilling, M. A. (2017). Strategic management of technological innovation. McGraw-Hill.
[9]. Aaker, D. A. (2012). Building strong brands. Simon and schuster.
[10]. Cecchetto, M. (2024). When innovation outruns customers' interest: practical cases from the video game industries.
[11]. Tschang, F. T. (2007). Balancing the tensions between rationalization and creativity in the video games industry. Organization science, 18(6), 989-1005.
[12]. Rollings, A. (2010). Fundamentals of game design.
[13]. Zhu, F., & Zhang, X. (2010). Impact of online consumer reviews on sales: The moderating role of product and consumer characteristics. Journal of marketing, 74(2), 133-148.
[14]. Khalilian, A. T., Ibrahim, O., & Nilashi, M. (2017). Integrated feedback control reporting for improving quality of technical service reporting in IT service management. Telematics and Informatics, 34(8), 1736-1771.
[15]. Granados, N., Zwagerman, A., & Oliver, D. (2025). The MEDIA Report: Media & Entertainment Data In America 2019 to 2025.
[16]. Fournier, S. (1998). Consumers and their brands: Developing relationship theory in consumer research. Journal of consumer research, 24(4), 343-373.
[17]. Messina, K. E. (2024). Why the Truth is Essential in a Democracy: Pivoting Toward Evidence. In A Psychoanalytic Study of Political Leadership in the United States and Russia (pp. 7-28). Routledge.
Cite this article
Wang,H. (2025). PlayStation’s Market Dominance: A New Era of Console War. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,178,26-33.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Business Data and Sales (2022), Sony Interactive Entertainment. Retrieved from [https://sonyinteractive.com/en/our-company/business-data-sales/].
[2]. von Nandelstadh, O. (2024). The implications of library subscriptions on video game marketing: featuring case study of Xbox Game Pass.
[3]. Amos, E. (2021). The game console 2.0: A photographic history from Atari to Xbox. No Starch Press.
[4]. Warren, T. (2024). Microsoft’s Xbox Game Pass service grows to 34 million subscribers. The Verge. Erişim adresi: https://www. theverge. com/2024/2/15/23570040/microsoft-xbox-game-pass-subscriber-numbers-34-million. Son Erişim Tarihi, 25, 2024.
[5]. Deckert, C., & Phan Ngoc, D. A. (2023). PlayStation 4 vs. Xbox One: Competitive Analysis of the Video Game Industry.
[6]. Belton, P. (2017). An Analysis of Michael E. Porter's Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors. Macat Library.
[7]. Yee, N. (2006). Motivations for play in online games. CyberPsychology & behavior, 9(6), 772-775.
[8]. Schilling, M. A. (2017). Strategic management of technological innovation. McGraw-Hill.
[9]. Aaker, D. A. (2012). Building strong brands. Simon and schuster.
[10]. Cecchetto, M. (2024). When innovation outruns customers' interest: practical cases from the video game industries.
[11]. Tschang, F. T. (2007). Balancing the tensions between rationalization and creativity in the video games industry. Organization science, 18(6), 989-1005.
[12]. Rollings, A. (2010). Fundamentals of game design.
[13]. Zhu, F., & Zhang, X. (2010). Impact of online consumer reviews on sales: The moderating role of product and consumer characteristics. Journal of marketing, 74(2), 133-148.
[14]. Khalilian, A. T., Ibrahim, O., & Nilashi, M. (2017). Integrated feedback control reporting for improving quality of technical service reporting in IT service management. Telematics and Informatics, 34(8), 1736-1771.
[15]. Granados, N., Zwagerman, A., & Oliver, D. (2025). The MEDIA Report: Media & Entertainment Data In America 2019 to 2025.
[16]. Fournier, S. (1998). Consumers and their brands: Developing relationship theory in consumer research. Journal of consumer research, 24(4), 343-373.
[17]. Messina, K. E. (2024). Why the Truth is Essential in a Democracy: Pivoting Toward Evidence. In A Psychoanalytic Study of Political Leadership in the United States and Russia (pp. 7-28). Routledge.









