1. Introduction
After entering the 21st century, advanced technology has made vigorous progress and rapid development, and artificial intelligence has gradually become an emerging discipline and has been widely used in many fields, such as healthcare, transportation, education, finance, and manufacturing. Among them, the auditing industry is also deeply affected by artificial intelligence [1]. The traditional mode of audit is time-consuming and laborious, and is prone to supervisory errors, while the introduction of artificial intelligence technology can increase the accuracy of the auditing process, automate complex and cumbersome tasks, and reduce the risks that are likely to occur in the auditing process, and the realization of the auditing industry has become the consensus of the community [2]. Governments and organizations attach great importance to the development of AI auditing and have introduced relevant policies to support the innovation and application of AI. Governments and organizations attach great importance to the development of AI auditing and have introduced relevant policies to support the innovation and application of AI [3]. Ye pointed out that AI auditing has extremely high requirements for data accuracy, and every link from data selection to model setting may affect the accuracy of data. If there are errors in the original data or defects in the model design, the authenticity and reliability of the data will be difficult to ensure [4].
Up to now, there is no very clear theoretical basis and behavioral norms for this new technology of convergence of AI and auditing, and there has little research in this area. Up to now, there is no very clear theoretical basis and behavioral norms for this new technology of convergence of AI and auditing, and there is a lack of academic research in this area [5].
This paper will select PwC as an example, it studies the specific process and strategy of its application of AI auditing, analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of this application mode, and puts forward the methods and suggestions that can be improved. Through the collection of existing literature related to the study of AI auditing, as well as the use of big data information technology to search and query the current development status and application of AI auditing, to integrate and analyze. On this basis, the study analyzes the current situation of AI auditing in accounting firms, analyzes the problems, and proposes corresponding strategies.
2. Case study of PwC accounting firm
2.1. Overview of PwC accounting firm
PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) is one of the world's leading professional services firms. Founded in 1998 as a result of the merger of PriceWaterhouse and Coopers & Lybrand, PwC is headquartered in London, UK. Its core services include audit and assurance, tax consulting, management consulting and legal services, covering a wide range of industries including finance, technology, healthcare and energy. Meanwhile, the firm actively fulfills its social responsibilities, promotes sustainable development and digital transformation, and applies cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data through its global innovation centers.
2.2. The current status of artificial intelligence audit applications in PwC accounting firm
As one of the four major international accounting firms, PwC has seized the digital audit trend with a forward-looking vision and started researching intelligent financial robots as early as 2017. Robotic Process Automation, also known as RPA, is a combination of related technologies such as autonomous systems, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and robotics. These emerging technologies have shaped the structure of RPA solutions and become the framework for RPA [6]. PwC's RPA services are an important component of its digital transformation solutions, combining technologies such as artificial intelligence and natural language processing to provide end-to-end automation and intelligent services for enterprises. PwC designed a complete RPA process during the development of digital auditing, The complete framework for implementing RPA projects includes key steps such as requirement collection, operational model design, team training, pilot verification, process evaluation optimization, cross-departmental collaboration, performance indicator development, and continuous promotion, ensuring that automation is aligned with business strategy and improving efficiency.
2.3. Specific application of PwC intelligent audit
The first is the iBAS intelligent bank flow analysis solution. On November 9, 2023, PwC launched its innovative digital tool: intelligent bank flow analysis solution at the Sixth China International Import Expo. It aims to solve the complex problem of bank flow analysis through artificial intelligence and big data technology, provide intelligent special solutions for users in the fields of enterprise asset management, financial audit and IPO intermediary services of listed companies, and help them efficiently cope with the massive and complex needs of bank flow data analysis in the era of digital economy. As shown in Table 1, it is the application scenarios and cases of PWC iBAS technology. In the Financial Sharing Project of Zhonghua International, RPA realizes the automation of bank reconciliation, VAT invoice verification and other processes [7]. It also improves the reconciliation efficiency of enterprise banks by 90%, and handles the reconciliation tasks of 80 accounts of 15 banks every day; Manual intervention time is reduced by 60%, and the financial team can focus on high-value-added analysis.
Table 1: PwC iBAS application scenarios and cases
Scenarios | Functionality Implementation |
IPO Audit | Automatically verifies the full volume of enterprise water flow, identifies related transactions and abnormal fund exchanges, and generates audit drafts |
Anti-money laundering monitoring | based on the rule engine, screens suspicious transactions (e.g., high-level small amount of money transfers), generates a risk report, and pushes it to the supervisory system |
Enterprise Funds Management | analyzes the trend of cash flow, optimizes the allocation of working capital, and reduces the cost of financing |
Second is the digital transformation of internal audit. As shown in Figure 1, PwC proposes a “positioning-value-technology” trinity transformation framework, which covers the following key elements: Positioning transformation refers to the shift from traditional compliance checking to strategic consulting and risk management, covering corporate strategy, social hotspots, and emerging technology areas. Value transformation is to provide decision support to management through data insights, such as risk early warning and process optimization suggestions. Technology transformation refers to the application of big data, AI, blockchain, and other technologies to reconfigure the audit process, such as full-volume data analysis and intelligent report generation [8].
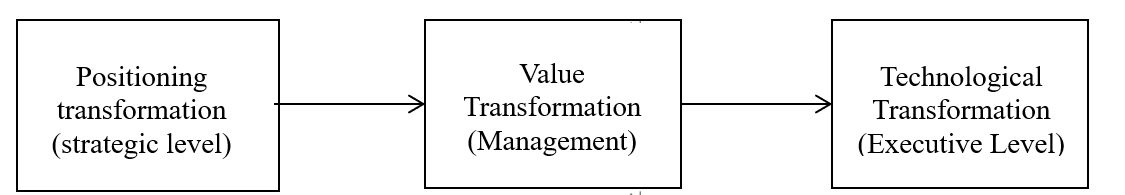
Figure 1: Trinity transformation framework
Under this framework, PwC has partnered with Open AI to introduce GPT-4 technology in 2023, which is used to analyze unstructured data such as corporate contracts and notes to financial reports to automatically flag potential legal risk points. Tests have shown a 25.1% increase in compliance review efficiency and a 43% increase in task quality for low-performing employees. Based on the DeepSeek-R1 model developed independently in 2025, audit summaries and adjustment recommendations are automatically generated, and manual writing time is reduced by more than 50% [9].
2.4. PwC AI audit implementation effectiveness and industry impact
First is the increase in audit efficiency. As shown in Table 2, according to the PwC 2024 report, AI utilized audit projects with high productivity increase five times that of inefficient projects. The speed of audit task completion increased by 25.1% relative to traditional auditing, the error rate was reduced by 5.9% relative to manual auditing, and labor costs were reduced by 32%.AI Audit of PwC reduced data processing time by 62.5%, increased risk identification accuracy from 65% to 91%, and reduced audit costs by 25%. In the case of regional banks, full-volume data analysis increased the risk detection rate by 35% and shortened the audit cycle by 40%.
Table 2: Comparison of traditional audit and AI audit indicators
Metrics | Traditional Audit | AI-Assisted Audit | Improvement |
Speed of Task Completion | 100% | 125.1% | +25.1% |
Error Rate | 8.2% | 2.3% | -72% |
Labor Costs | 100% | 68% | -32% |
The second is to improve the quality of the audit. At the same time, PwC uses gl.ai tools and machine learning-based audit robots to analyze billions of data points in milliseconds and identify abnormal transactions (such as misstatements or fraud) in the general ledger, which have been verified in audit projects in Canada, Germany, and other countries. And integrate enterprise ERP and financial system data, and use AI to build a real-time risk early warning platform. For example, in a financial audit, an AI model can dynamically monitor abnormal cash flow, and the response speed of triggering early warning is 80% higher than that of manual operation.
Finally, we should promote the transformation of the audit talent structure. With the introduction of AI audits, auditors can only gradually shift from basic operations to strategic analysis [8]. PwC pointed out that the number of jobs requiring artificial intelligence skills has increased 3.6 times as fast as all positions, and the salaries of employees with AI skills are 14%—49% [9]. PwC has transformed 30% of its auditors into "Ai+audit" compound talents through internal training programs. From "compliance inspection" to "risk forecasting+business insight". For example, through AI analysis of supply chain data to generate market trend reports, the added value of services increased by 30%. Forcing the transformation of audit talent training requires mastering Python, SQL, and other technical tools, and establishing "technology+business" compound capabilities. As shown in Figure 2, the transformation of internal audit talents at PwC tends to be digital audit.
Figure 2: PwC audit talent transformation number
3. PWC's application of artificial intelligence audit faces problems
3.1. Algorithm bias and discrimination risk
In PwC's business scenarios, such as auditing and consulting, artificial intelligence may be used to analyze large amounts of data to provide decision support. However, if there are biases in training data, such as historical biases against certain customer groups or industries, artificial intelligence systems may replicate these biases, resulting in unfair treatment of specific customers or industries [10]. In audit risk assessment, artificial intelligence may overestimate or underestimate the risk level of some customers due to historical data bias.
3.2. Model opacity and explanatory risk
When PwC uses complex artificial intelligence models, such as deep learning models, these models are often seen as "black boxes" whose decision-making process is difficult to explain. That presents challenges for customers, regulators, and internal teams, who struggle to understand how A.I. concludes. When providing consulting services to customers, if artificial intelligence models give advice based on complex algorithms, but can not clearly explain the basis of decision-making, it may affect customers' trust in advice.
3.3. Data privacy and security risks
PwC is required to strictly comply with data protection and privacy regulations when handling client data. However, the application of artificial intelligence systems may increase the risk of data leakage [11]. If security measures are not in place during data collection, storage, and processing, hackers may attack the AI system and steal sensitive client data. In addition, the AI system itself may become a channel for data leakage. If the system is utilized maliciously, it may leak a large amount of client data, posing serious legal and reputational risks to PwC.
3.4. Risk of system loss of control and misoperation
When PwC deploys an AI system, it needs to ensure the stability and reliability of the system. However, due to the complexity of AI systems, system loss of control or misuse may occur. A malfunction or miscalculation of the AI system during the automated audit process may result in inaccurate audit results or even lead to client disputes [12]. In addition, if the AI system is modified or misused without authorization, it may also cause serious business disruption and loss to PwC.
4. Suggestion
Against the risk of algorithm bias and discrimination, PwC should strengthen data cleaning and preprocessing, ensure the diversity and fairness of training data, and eliminate historical bias. PwC should regularly detect model bias, use fairness indicators to evaluate the treatment of different customer groups and industries, and timely adjust and optimize the model [13]. In addition, PwC should improve audit transparency, explain the decision-making logic of the model to customers and stakeholders, and how to avoid bias and enhance trust.
In view of the opacity and explanatory risk of the model, PwC should give priority to the model with strong explainability to facilitate customers and internal teams to understand the decision-making process of the model and use model interpretation tools and technologies, such as feature importance analysis and visual interpretation, to improve the interpretability of the model. PwC also needs to strengthen communication with customers, explain the decision-making basis and logic of the model in detail, and enhance customers' acceptance and trust in suggestions.
In response to data privacy and security risks, PwC should implement strict data encryption and access control measures to ensure the security of data during collection, storage, and processing. PwC needs to conduct regular security audits and vulnerability scans to identify and repair potential security vulnerabilities promptly and strengthen security awareness training for employees to ensure that employees comply with data protection and privacy regulations and prevent data leakage and abuse [14].
For the risk of system runaway and misoperation, PwC should conduct adequate testing and verification before deploying artificial intelligence systems to ensure the stability and reliability of the system. A failure detection and recovery mechanism should be established to detect and deal with system failures promptly to ensure business continuity. Rights management and access controls should be strengthened to prevent unauthorized personnel from modifying or abusing the system. Emergency response plans need to be formulated to clarify the processes and measures to deal with runaway or misoperation of the system and reduce business disruptions and losses.
5. Conclusion
This paper takes the PwC accounting firm as the research object, uses the case analysis method and literature research method to study the specific application of artificial intelligence audit in accounting firms, and takes the PwC artificial intelligence audit as an example to draw the following conclusions: Artificial intelligence can significantly improve audit efficiency and decision-making quality, but its success depends on the collaborative optimization of technology, data, and talents. First, countries and other organizations have not yet developed a relatively complete bill for AI audits; Secondly, advanced artificial intelligence technology may lead to the abuse of AI, excessive dependence, old system adaptation, and other problems; Finally, the audit industry personnel are accustomed to the traditional audit mode, and have not yet adapted well to the AI audit mode. Given these potential problems, PwC should actively improve its technology, train the internal auditors on the firm's ability to operate and finance intelligent audit software and reduce the potential risks of intelligent audit while bringing convenience. This paper studies the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence audit, which is conducive to filling the current vacancy in the theoretical framework and supplementing the application research of different case enterprises. In the future, artificial intelligence audits can also carry out blockchain integration, vertical domain model development, multimodal AI integration, and achieve full dimensional audit, which is conducive to the more efficient and safe development of the audit industry in the future.
References
[1]. Vilma, M. (2018). Artificial intelligence and its scope in different fields, particularly in the field of education. Online submission, 3 (1), 5-10.
[2]. Celestin, M., & Vanitha, N. (2019). Artificial intelligence in fraud detection: Are traditional auditing methods outdated. In 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Arts, Science, Engineering & Technology (Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 180-186).
[3]. Oriri, DE (1995). AI in accounting, finance, and management. Intelligent systems in accounting, finance, and management,4,149-153.https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1099-1174.1995.tb00088.x
[4]. Ye Jiani. (2025) New Trends in Auditing: Big Data+Artificial Intelligence. Cloud, (02): 139-141
[5]. Fang Qiaoling, Prince Chen&Gao Sifan Construction of Audit Informatization and National Audit Quality Accounting and Economic Research, 1-27.
[6]. Kaya,C.T.,Erkilmaz,M.andBirol,Türkiye,B.(2019).TheimpactofRPAtechnologyonaccountingsystems. Muhasebe ve Finansman Dergisi (82).
[7]. Ke Wang. (2023) PwC releases iBAS intelligent banking transaction analysis solution. https://www.cs.com.cn/cj2020/202311/t20231109_6375151.html
[8]. Otia, J. E., & Bracci, E. (2022). Digital transformation and the public sector auditing: The SAI's perspective. Financial Accountability & Management, 38(2), 252-280.
[9]. PwC. (2024) The industry with the highest AI utilization has seen a surge in productivity and wages. https://www.163.com/dy/article/J2R05BT60514BIC1.html#:~:text=
[10]. Landers, R. N., & Behrend, T. S. (2023). Auditing the AI auditors: A framework for evaluating fairness and bias in high stakes AI predictive models. American Psychologist, 78(1), 36.
[11]. da Rosa, F. M. G. S. (2023). A Study of the Emerging Artificial Intelligence Risks: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies in the Context of a Financial Audit (Master's thesis, ISCTE-Instituto Universitario de Lisboa (Portugal)).
[12]. Fedyk, A., Hodson, J., Khimich, N., & Fedyk, T. (2022). Is artificial intelligence improving the audit process?. Review of Accounting Studies, 27(3), 938-985.
[13]. Murikah, W., Nthenge, J. K., & Musyoka, F. M. (2024). Bias and ethics of AI systems applied in auditing-A systematic review. Scientific African, e02281.
[14]. Huang, Y. H., & Brubaker, S. A. (2006). Safety auditing: Applying research methodology to validate a safety audit tool. Professional Safety, 51(1), 36.
Cite this article
Li,X. (2025). Research on the Application of Artificial Intelligence Auditing--Taking PricewaterhouseCoopers as an Example. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,184,13-19.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICMRED 2025 Symposium: Effective Communication as a Powerful Management Tool
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Vilma, M. (2018). Artificial intelligence and its scope in different fields, particularly in the field of education. Online submission, 3 (1), 5-10.
[2]. Celestin, M., & Vanitha, N. (2019). Artificial intelligence in fraud detection: Are traditional auditing methods outdated. In 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Arts, Science, Engineering & Technology (Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 180-186).
[3]. Oriri, DE (1995). AI in accounting, finance, and management. Intelligent systems in accounting, finance, and management,4,149-153.https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1099-1174.1995.tb00088.x
[4]. Ye Jiani. (2025) New Trends in Auditing: Big Data+Artificial Intelligence. Cloud, (02): 139-141
[5]. Fang Qiaoling, Prince Chen&Gao Sifan Construction of Audit Informatization and National Audit Quality Accounting and Economic Research, 1-27.
[6]. Kaya,C.T.,Erkilmaz,M.andBirol,Türkiye,B.(2019).TheimpactofRPAtechnologyonaccountingsystems. Muhasebe ve Finansman Dergisi (82).
[7]. Ke Wang. (2023) PwC releases iBAS intelligent banking transaction analysis solution. https://www.cs.com.cn/cj2020/202311/t20231109_6375151.html
[8]. Otia, J. E., & Bracci, E. (2022). Digital transformation and the public sector auditing: The SAI's perspective. Financial Accountability & Management, 38(2), 252-280.
[9]. PwC. (2024) The industry with the highest AI utilization has seen a surge in productivity and wages. https://www.163.com/dy/article/J2R05BT60514BIC1.html#:~:text=
[10]. Landers, R. N., & Behrend, T. S. (2023). Auditing the AI auditors: A framework for evaluating fairness and bias in high stakes AI predictive models. American Psychologist, 78(1), 36.
[11]. da Rosa, F. M. G. S. (2023). A Study of the Emerging Artificial Intelligence Risks: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies in the Context of a Financial Audit (Master's thesis, ISCTE-Instituto Universitario de Lisboa (Portugal)).
[12]. Fedyk, A., Hodson, J., Khimich, N., & Fedyk, T. (2022). Is artificial intelligence improving the audit process?. Review of Accounting Studies, 27(3), 938-985.
[13]. Murikah, W., Nthenge, J. K., & Musyoka, F. M. (2024). Bias and ethics of AI systems applied in auditing-A systematic review. Scientific African, e02281.
[14]. Huang, Y. H., & Brubaker, S. A. (2006). Safety auditing: Applying research methodology to validate a safety audit tool. Professional Safety, 51(1), 36.









