1. Introduction
1.1. History of International Trade Between China and UK
As you can see, international trade between China and the UK has a long history, with around 400 years. starting from the point where the opium war started in the Mid 19th, When the Chinese military failed to defend against British Military forces, this led to a result of Hong Kong becoming a part of a British colony. Consequently, China was forced to pay a certain amount of fine to Britain; this had led to Chinese opening up more ports for foreign trade. Moreover, the outbreak of WW2 has brought more opportunities of trade taken place for e.g. ‘The hump’ the British empire in WW2 make a tremendous effort in the south Asia by replying to the Chinese war effort against Japan, and after that within the Chinese civil war the PRC has gained most control of the country and because of their change of ideology and the outbreak of cold war, the ‘close door policy’ has reduced their trade into a bare minimum amount.
The ‘open door policy’ in December 1978 by Deng Xiaoping had led to Chinese become more open with trade and foreign company from coming into the country, more ports for foreign trade, this not only allow more international trade to take place, it also opened their domestic market, which includes of about 1 billion people.
1.2. Key Statistics and Main Differentiation Between China and UK
As you can see after the open policy the exports increased by a significant amount (See Fig.1), import has also increased, UK is constantly in a trade deficit. Well, a trade deficit in this case it means that UK is constantly spending their foreign exchange reserves, in the past few years with the rise of the world Brexit and the outbreak of pandemic, Britain is now facing with multiple challenge, and in the recent year the trade war and also the conflict between Russia and Ukraine. The future of trade between China and the UK is unpredictable as the level of globalization increases and thus the stability of the political environment is very murky, it is hard to tell whether it is going to be good or not.
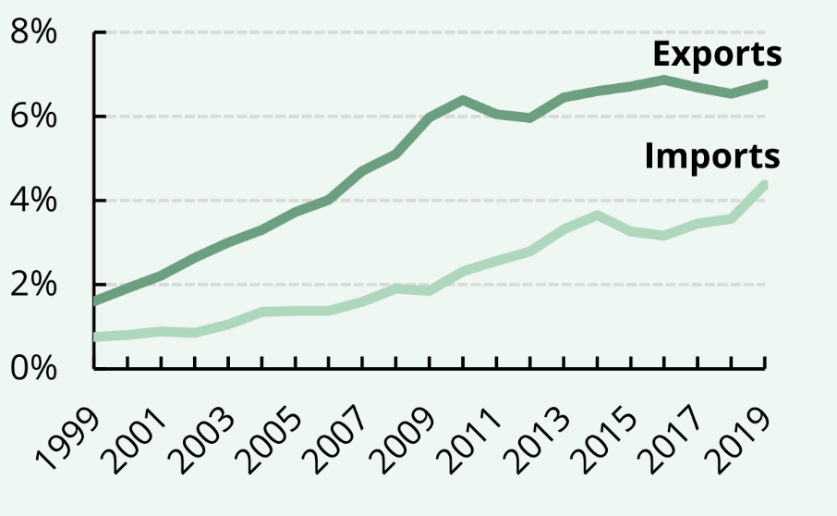
Figure 1: The comparison of China’s import and Export with UK [1].
As we can see on the data after the open policy China has a constant growth in their GDP (see figure 2); Whereas the UK has a very disruptive pattern (See Fig. 3), because both countries are very different in scales and have different political, economic, and population structures.
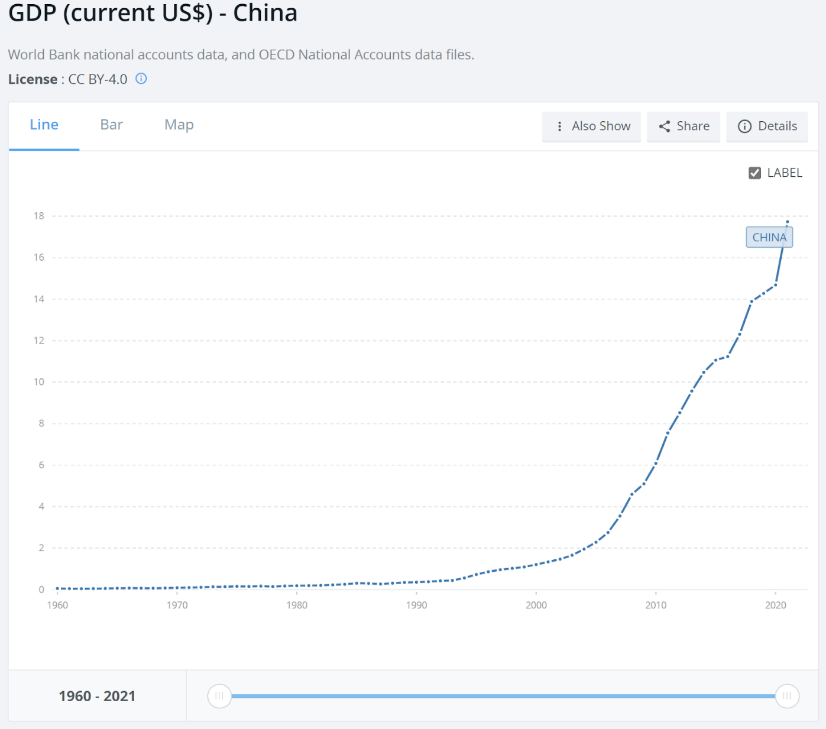
Figure 2: Gross Domestic Product of China [2].
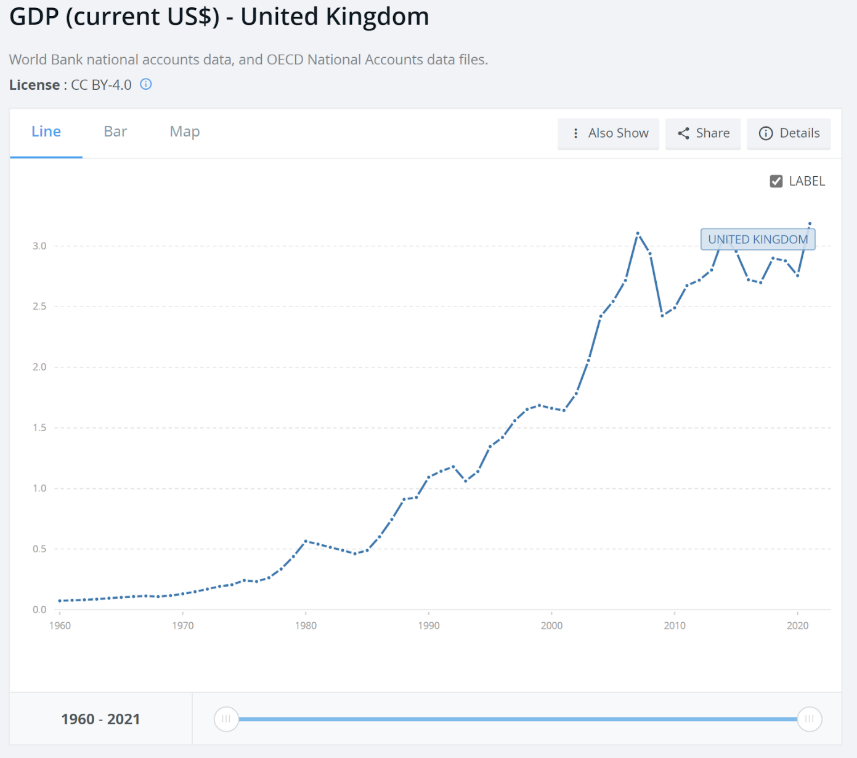
Figure 3: The comparison of China’s import and Export with UK [3].
China has a relatively higher inflation rate which is mainly due to their monetary policy from their government and rising wages as they are developing. Those are mainly ‘cost push’ inflation, but at the same time because of their economies of scale, they are willing to use it even though it may slow down their economic growth (See Fig. 4).
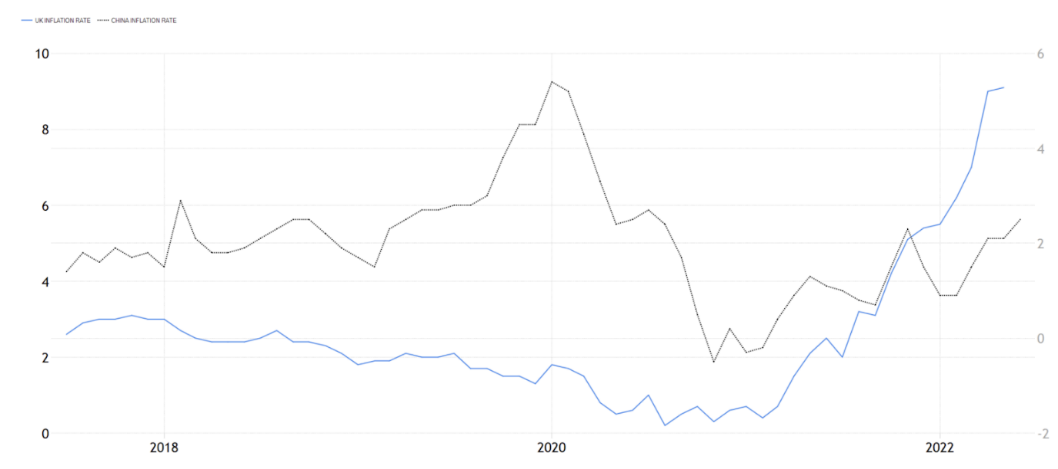
Figure 4: The comparison of China’s import and Export with UK [4].
Whereas UK’s inflation is mostly from price rises e.g. The rise in energy price, since the war between Russia and UK has started the global energy price has risen, this has a straightly effect on UK's transport cost and housing cost, as they are the main component which consumes the most energy. I think that we can call UK's inflation as passive inflation. I can’t conclude that the UK's current inflation is only a result of this energy crisis, there's multiple factors e.g., the covid lockdown, the unemployment, Brexit and many more, but what I can say is that I think the rise in energy cost are the most significant factors.
1.3. Current Statutes
As I mentioned before that UK are highly depend on importing goods as they can’t produce cheap produce due to their low employment efficiency and high labor cost, as the energy cost has increased; the cost of importing goods increases which means that all imported goods now has a rise in price, the leaving of EU triggered even more demand on China's market, therefore more trade between China and UK taken place which also indirectly increases the level of prices as two countries are very far apart from each other; After the lockdown people start to going out and shopping again, when there’s economic growth occurs there’s also going to be inflation occurs, we call that demand pull inflation, all those inflation add up in a result of this highest inflation rate of over 9% [5].
2. International Trade
2.1. What Can International Trade Between China Bring Us?
Trade with other countries can expand the UK's current market value, especially with a country which has over 1.3 billion population, it can reduce the level of competition of favourable goods/ and services within domestic market, e.g., private education, financial services (UK are the world’s financial centre) by doing so, it can largely increase their revenue and eventually achieve greater economic of scales. As i mentioned before , China has a totally different population structure, as a developing countries their labour cost is very low compared to UK, which means that for labour intensive production e.g. Agricultural Product and customize product China can produce it with much cheaper cost compare with UK’s domestic firm, therefore by importing those kinds of product UK can eventually achieve more efficient on the allocation of their resources, lower cost of good can push down the inflation rate which is a win-win situation.
The interaction between countries throughout international trade can reduce their misunderstanding of each other which could in a result of improving in relationship between UK and China, furthermore the interaction between China and UK can bring their local businesses better technology and way of management while UK is currently not in an efficient status, the disruption of domestic labour party causes UK has to overemploy people which is unnecessary. The UK can ‘copy’ Chinese’s company’s way of management and operation which increases their utilization of resources, production efficiency and product quality.
International trade enables countries to experience more economic growth, it increases people’s standard of living by accessing more physical capital and a much wider foreign profitable export market; it increases the Consumer surplus at the same time also increases the producer's surplus because now producers get access to a wider market [6].
2.2. Challenge of International Trade
The increase of international trade and investment now link countries closer to each other, countries are now more dependent on each other, we often call that globalization.
Nowadays, as cooperation and separation take into another level we can see now there’s increases level of conflict occurs within the world , major power are using anything they can to seizing their power thus to influence their surrounding and their opponents, financial sector are now more being used as a tool/weapon to ‘attack’ in a peaceful ways, international trade is very vulnerable to it, even though most of the time they are beneficial to both side they are still often been disrupted by their government's rules and regulations. For example, the ‘Trade war’ between China and US in 2018, government using restrictions and tax, also with media to ‘boycott’ other country's product.
3. Globalization
3.1. Geo-politicization
As we can see in the past 19th the British colony and the modern days United State they are both dominating economy throughout the world and as a leader of the international financial system, moreover the entering of information age now allows civilians to get access more information, the leaders around the world now has to take into account about public opinions, the regionally conflict and historical problems could become worsen depend on their leader’s view on it, now follow up with those developing countries they are also as much or less on the same path toward capitalism. As a result of that there will be an increase in inequalities.
Now we are moving back to China, as world’s biggest developing country, they are creating a new segment within the existing ‘global market’ and destroying ‘their’ (those developed capitalism countries for example UK, Germany, France, etc.)expected form of ‘globalization’, therefore, for sure there’ll be conflict taken place and in the near future there will be more and more conflict, it highly depends on their own perspective of their interest and in order to influence that the leader needs to consolidate their people and unite their whole country to do so.
As globalization continues, we can see now the US no longer has the ability and willingness of being the global leader, they are constantly suffering from the pandemic and safety issues domestically, while those traditional power (UK, France, German) don’t want to step up to take the responsibilities (partly because they are also dealing with their own problems e.g., Brexit, war crime, Health and safety issues). So, there’s a ‘missing’ of leader strength for globalization to take place, there's no clearly defined way to tell whether globalization is going to take place in the near future or not.
Well not only China are emerging and desperate to get political power and influences, change in power distribution is also a big part of it in the near future , countries like Russia, Turkey, India, Brazil are also developing and trying to gain power, well their interest, view of value are totally different from the western point of view, for example the ’the Belt and Road Initiative’ their aim is simply enhance connectivity and practical cooperation, well surely China is also seeking for political influence for it. Whereas the US in 1970 made the world has to trade oil in dollar, which in a result of bring huge political influence into middle east and throughout the world, their aim is to influence the world as a whole whereas nowadays most of those ‘project’ are very regional , Russia are now more and more urgent to get in touch with energy price (as their main exports are resources like gas and oil), Germany is taking over the control of Euros as well as China are trying to build a ‘Economic zone” in the Asia, those major power are trying to consolidate power at the same time leaving those small countries out of it ,which increases the hollowing of the peripherals’ and this may be there the world get separate from .(similar to what happened at the start of the cold war, countries start to take side and things starts to go bad) [7].
3.2. The ‘Use and for’ with International Trade Between China
For UK, globalization brings both advantage and disadvantages to British economies, the development of globalization now letting UK consumers now has greater choice of goods and wider range of product, the leaving of EU has triggered the problems of shortage with lorry drivers, which indirectly increased the cost of transport which also can be determined as a factor of inflation, increase in trade with China can reduce the price level of consumer goods at the same time stable the price down. To this extent I think that trade with China in the near future would be favourable for the UK's economies [8].
As part of the result of international trade, domestic business now can get access to the foreign market , which means that there’ll be greater competition with foreign business, it can lower down the price of the goods and also let the business maintain sufficient, China as world’s largest economies , due to their economic volume’s difference and their economic structure, UK are importing more than what they are exporting to China, as China’s export price are maintaining competitive UK are likely to increase their volume of import as their demand increases over year, and because of that UK government needs to be aware about the fact that China has a totally different inflation levels, even though the price level of current exported goods from China are relatively cheap compared to UK’s domestic good, but as China develop and apply more technology within the production, increasing their worker’s education levels, their cost of production increases overtime; UK as a big ‘importer’ in relate to China, with a continues growth in UK’s import from China, the future UK's import can potentially have big impact on UK’s inflation rate as Chinese goods increase in prices overtime. The UK government has to take more consideration on whether they should continue importing more from China or find other solutions. So, from this point of view, I think that it is good to have another consideration and maybe try to depend less on China's imports as we often hear ‘don't put all your eggs in the same basket’ [9].
3.3. Economies of Scales
As globalization continue, more and more trade between countries taken place for their both side benefits, countries are now can more working toward specialization and achieve toward their maximum, this means that they are more dependent on each other and in order for this to work they has to trade with each other's. As UK trade more with China, because the price of the imported goods from China are usually cheaper than their domestic product (because they are producing in a much larger scales and their labour are cheap), it can reduce the inflation figure at the same time stable their commercial price level, which means that UK can now prefer to stop or reduce those products that always has low productivity and high cost (e.g. Agricultural and Fabric industries) and allocate more of their resources to industries like tech firm and education; financial sector. As UK and China collaborate and trade with each other the cultural difference may causes many problems, as both side work with together they can also learn from each other it is good for UK firm to get better with their management so they can become more efficient.
The outbreak of pandemic in late 2019 into now has caused several problems worldwide, with inconsistent national lockdown, restrictions and government regulations nearly all industries has been effected, this has lead UK's economies into a short recession, with the effect of Brexit beforehand and the indirect influence from the trade war between China and us, the shortage of lorry driver with the step in of covid has enlarge of the problem and eventually causing a tremendous damage on Britain's supply chain, the cost of transportation increased due to the lack of driver already and now with more government restriction and currently the energy crises has made the problem even worsen, inconsistent demand from everywhere within the countries making the supply chain very chaotic. Meanwhile even though China was the first in which were hit by the pandemic firstly but due to their effective management and large scales in lockdown they had taken control of the spread of virus within the countries, but their production chain were also get hit with the use of ‘zero covid’ strategy, factories within China are frequently going back to lockdown and reopen, which wasted a lot of time and resources, the supply chain toward ‘Exporting UK’ are very intermittent and now it becomes even more challenging and difficult to do so. From this perspective i think that it is good to import the majority of goods from the surrounding countries rather than travel half of the world to get cheaper product from China [10].
4. Conclusion
The accelerated development of technology has now brought more changes in the modern days not only within technology, but also in communication, economy, politics, and culture. As we can see, the occurrence of more opportunities leads to more chance of interest by people, the selfish intends of people's mind creates cooperation as well as conflict. For UK, as the levels of globalization increases ,as far as i see that UK are more favourable to connect, collaborate and trade with countries rather than causing conflicts, UK don't has the capital compendial like USA to has the amount of influence and political power to use to maintain their interest; on another word by doing so, UK has to take more careful consideration, with the measure of their self-volumes, because UK has a much smaller scales of economies and populations, so that increase level of globalization is not gaining much interest for UK, So i think that the best way to solve that problem is to join like a trade union or like a reginal economic zone, but what we seen from now it that UK are currently doing the opposite by leaving the EU.
On another hand, from the economy's points of view, trading with other countries will mostly create positive side of effect to British economies which is corrigible, although the future inflation of China might bring side effect within long term, momently it only going to reduce inflation and stable the price down which is what they currently needed.
Although there's many challenges and opposite argument taken place, but i think that in the future UK should increase their trade volume with China at the same time also do the same with other countries, don't get too depended on one single product from one country because we don't want to see the same things happening like the energy resources imported from Russia. (As the war began the energy price increases by a significant amount and we can't do much within short term.
References
[1]. Matthew, W.: Statistics on UK trade with China. CBP-7379, 2-3(2020). From https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/cbp-7379/
[2]. The world bank. (2022). GDP (current US$) - China | Data. World development-indicators,1960-2021,GDP-China.https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.CD?contextual=&locations=CN.
[3]. The world bank. (2022). GDP (current US$) - UK | Data. World development indicators, 1960-2021, GDP-UK. from https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?contextual=default&locations=GB.
[4]. Trading Economics. (2022). United Kingdom Inflation Rate – June 2022 Data – 1989-2021 Historical – July Forecast. Retrieved 2022, from https://tradingeconomics.com/united-kingdom/inflation-cpi.
[5]. Hopson, E. (2022). Business insights and impact on the UK economy-office for National Statistics. Retrieved July2022fromhttps://www.ons.gov.uk/businessindustryandtrade/business/businessservices/bulletins/businessinsightAndimpactontheukukeconomy/latest.
[6]. Bye, S. (2022, February 14). International trade: benefits, barriers and business. University of Lincoln. Retrieved July 2022, from https://online.lincoln.ac.uk/international-trade-benefits-barriers-and-business/.
[7]. Leonard, M.(2015, January). Geo-economics: Seven Challenges to Globalization. World Economic Forum. Retrieved July 2022, from https://www.weforum.org/reports/geo-economics-seven-challenges-globalization.
[8]. TPS Global Logistic. (2021, August 12). How will the shortage of UK truck drivers impact businesses. TPS Global. Retrieved July 2022, from https://tps-global.com/how-will-the-shortage-of-uk-truck -drivers-impact-supply-chains/.
[9]. Ayres, S.(2014, April 15). The UK’s trade relationship with China. Https://Commonslibrary.Parliament.Uk/the-Uks-Trade-Relationship-with-China.
[10]. Stephens, M(2021,February12).Coronavirus and the impact on output in the-UK-economy-officefornationationalstatics.https://www.ons.gov.uk/grossdomesticproductgdp/articales/coronavirusandtheimpactOnoutputintheukeconomy/december2020.
Cite this article
Liu,X. (2023). The Effect of Globalization and International Trade Between UK and China on the UK's Economy and the Future of Trade Between China and the UK. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,8,1-7.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Matthew, W.: Statistics on UK trade with China. CBP-7379, 2-3(2020). From https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/cbp-7379/
[2]. The world bank. (2022). GDP (current US$) - China | Data. World development-indicators,1960-2021,GDP-China.https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.CD?contextual=&locations=CN.
[3]. The world bank. (2022). GDP (current US$) - UK | Data. World development indicators, 1960-2021, GDP-UK. from https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?contextual=default&locations=GB.
[4]. Trading Economics. (2022). United Kingdom Inflation Rate – June 2022 Data – 1989-2021 Historical – July Forecast. Retrieved 2022, from https://tradingeconomics.com/united-kingdom/inflation-cpi.
[5]. Hopson, E. (2022). Business insights and impact on the UK economy-office for National Statistics. Retrieved July2022fromhttps://www.ons.gov.uk/businessindustryandtrade/business/businessservices/bulletins/businessinsightAndimpactontheukukeconomy/latest.
[6]. Bye, S. (2022, February 14). International trade: benefits, barriers and business. University of Lincoln. Retrieved July 2022, from https://online.lincoln.ac.uk/international-trade-benefits-barriers-and-business/.
[7]. Leonard, M.(2015, January). Geo-economics: Seven Challenges to Globalization. World Economic Forum. Retrieved July 2022, from https://www.weforum.org/reports/geo-economics-seven-challenges-globalization.
[8]. TPS Global Logistic. (2021, August 12). How will the shortage of UK truck drivers impact businesses. TPS Global. Retrieved July 2022, from https://tps-global.com/how-will-the-shortage-of-uk-truck -drivers-impact-supply-chains/.
[9]. Ayres, S.(2014, April 15). The UK’s trade relationship with China. Https://Commonslibrary.Parliament.Uk/the-Uks-Trade-Relationship-with-China.
[10]. Stephens, M(2021,February12).Coronavirus and the impact on output in the-UK-economy-officefornationationalstatics.https://www.ons.gov.uk/grossdomesticproductgdp/articales/coronavirusandtheimpactOnoutputintheukeconomy/december2020.









