1. Introduction
Nowadays, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have become the most active force in China's economic life. It is becoming more and more important in economic growth, expanding employment, promoting technological progress and creating social wealth. However, according to public data, the average life span of Chinese smes is only 2.5 years, and the probability of enterprises going from start-up to listing is extremely small [1]. The oft-cited "valley of death" law of business is that most start-ups fail within the first three years. The main reason is that the financing of these private enterprises is difficult and expensive, making the development of these enterprises difficult. The main channel of financing is bank credit, but the risk of small and medium-sized private enterprises is high, so Chinese financial institutions prefer to lend money to state-owned enterprises, listed companies and other large enterprises. When these small and medium-sized enterprises cannot get the loan support of financial institutions, they are very likely to fail due to the fracture of capital chain and cannot develop. Therefore, for small and medium-sized enterprises, the expansion of financing mode is the most urgent matter to ensure their own development. At present, private equity financing has become the main channel for smes to raise development funds.
However, financing is also a double-edged sword, and the financing of smes through private equity will also bring some inevitable risks. For example, it is very speculative for investors, and the operation of enterprises is an important indicator of investors' investment and withdrawal of funds, as well as the signing of betting agreements between investors and enterprises. Therefore, risk assessment of private equity financing is particularly important for enterprises, and risk control is a necessary means for enterprises. This paper is based on the case of small and medium-sized enterprises for private equity financing risk assessment so as to effectively control the risk, which has a strong practical and empirical significance.
2. Financing Risks of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
2.1. Macro-influencing Factors
2.1.1. Financial Factors
Financial risk refers to the uncertainty of capital. The risk factors include the change in currency exchange rates, which directly affects the size of the company's assets and debts. It also includes the risk posed by financial institutions. If private equity funds do not obtain stable investment resources, they will stop investing in financing companies at any time, affecting the development of the enterprises.
2.1.2. Legal and Institutional Environmental Factors
In the development process of nearly 20 years, private equity funds have supported the development and expansion of a large number of small and medium-sized enterprises and made great contributions to the development of the whole social economy. The state also encourages the development of private equity investment funds, and has not formulated a strict legal system to regulate and supervise. Due to loopholes in the system, private equity funds have risks in attracting investment or investing.
2.1.3. Political Factors
In the current imperfect market mechanism, the resources of major listed companies are still under the control of the government. The formulation of relevant national financial policies will have various influences on various enterprise financing methods and may even cut off enterprise external financing methods. The promulgation and implementation of such state policies are compulsory and leave no room for consultation.
2.2. Micro Influencing Factor
2.2.1. From the Capital
The first factor is that the enterprise value is underestimated. Dilution of shares and loss of corporate control rights brought about by gambling agreements is another factor. Besides, Moral hazard is also an important influencing factor.
2.2.2. From Financing Enterprises
(1) Business model risk
For private equity investors, what matters more is a company's business model. Sometimes the innovation of business model is more important than the innovation of technology. The products produced by technology require enterprises to occupy the market with a certain business model to achieve profits. Business model innovation that does not meet the needs of the market cannot generate revenue and profit.
(2) Market risk
Market risk refers to the fact that when the financing project starts to operate, the enterprise's products are not accepted by the market and the value cannot be reflected, or the delivered products fail to be listed because they do not meet the national policy standards, so the profits brought by the enterprise to investors will be greatly reduced.
(3) Management risk of raised funds
After the target enterprise successfully raised funds, faced with a large amount of funds can not be effectively supervised, blind industrial expansion, rapid expansion of personnel, improve the treatment of management and other undesirable phenomena.
3. Risk Assessment Modeling of Private Equity Financing
On the basis of consulting domestic and foreign literature and expert interviews, the relevant indexes of private equity financing risk evaluation are selected. Through further interviews with professionals in financial institutions, bank managers and professionals engaged in financial research, the initial index system was deleted and all indicators that did not fit the research were removed. Then organize the experts, divide them into 6 groups, classify them according to the characteristics of the index system, and finally divide all the evaluation indexes into 6 major categories, and divide each specific evaluation index into corresponding categories respectively. According to the characteristics of each category, the final screening of indicators is carried out, so as to determine four indicators of each category, a total of 24 evaluation indicators as the index system of private equity financing risk evaluation.
It is difficult to describe the risk evaluation indicators of private equity investment by quantitative indicators, so the selection of evaluation indicators are mainly qualitative indicators. Qualitative indicators have strong fuzziness in quantitative description, and some errors will occur when the evaluation of fuzzy indicators is processed by AHP and factor analysis [2]. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method is more suitable for the processing of fuzzy data, so the principle of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation is used to evaluate the risk evaluation of private equity investment [3]. In the construction of a comprehensive fuzzy evaluation system, weight calculation is a very important aspect. In order to make the weight determination have scientific characteristics, this paper uses the method of combining subjective and objective to determine the weight of each index. Firstly, the weight of each index was calculated based on G1 method and coefficient of variation method, and then the combined weight of each index was determined.
3.1. Weight Determination by G1 Method
G1 weight determination method firstly sorts all evaluation indexes according to their importance, and then determines their comparison value according to the importance of comparison between two adjacent indexes. The advantage of this method is that there is no need to check the consistency between the importance of indicators, so that the degree of calculation can be simplified to a certain extent [4]. The specific steps are as follows:
Firstly, judge the ranking relationship of importance among all evaluation indicators.
If the evaluation index xi is important compared with the adjacent index xj according to the predetermined evaluation criteria, it is denoted as xi>xj. If a group of evaluation indicators x1,x2…xm have a ranking relationship of importance according to predetermined evaluation criteria 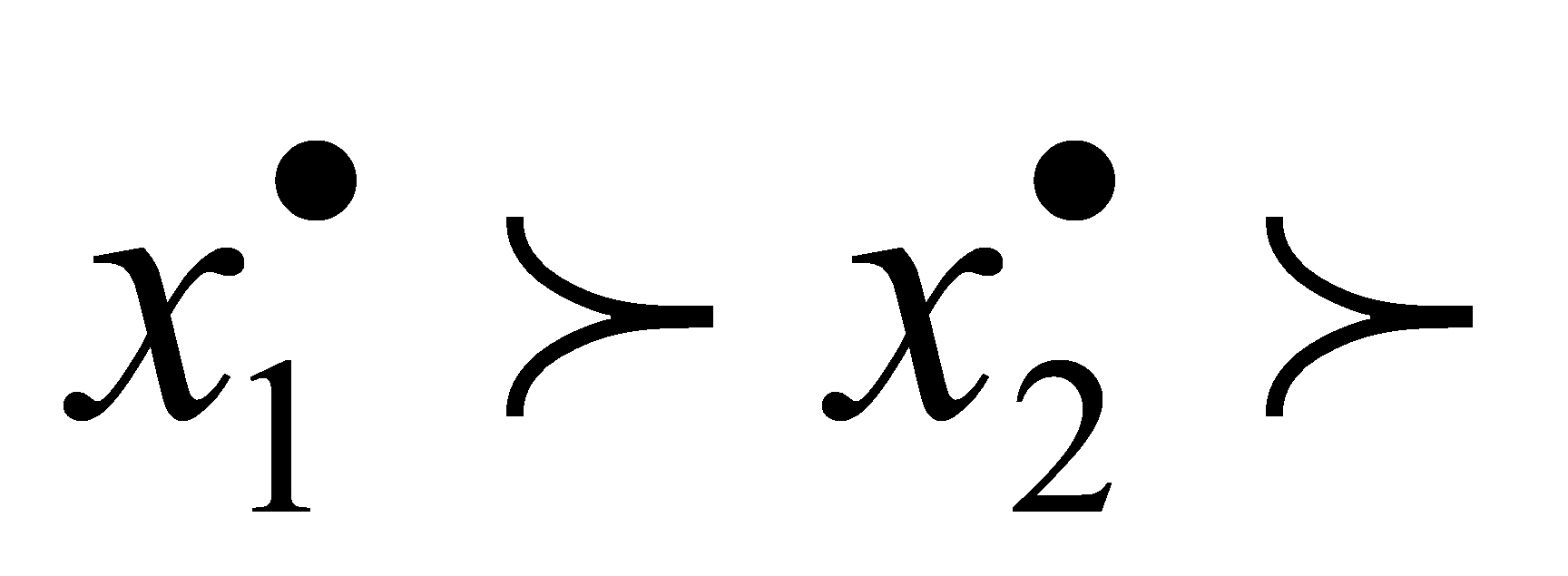 …
…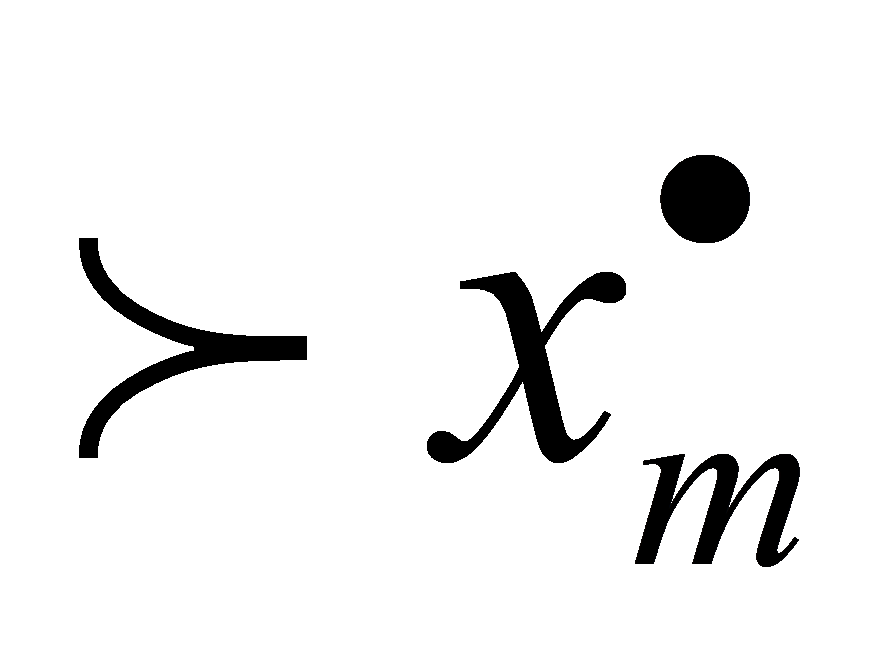 , it is said that the evaluation indicators x1,x2…xm determine the importance ranking relationship according to "
, it is said that the evaluation indicators x1,x2…xm determine the importance ranking relationship according to "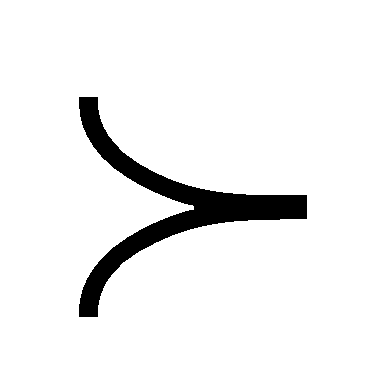 ".
".
Secondly, determine the importance degree of comparison between adjacent indicators.
For an index xk with pre-determined weight, the index adjacent to this index is xk-1. Experts confirm that rk=xk/xk+1 according to evaluation criteria and judgment criteria.
Thirdly, according to the comparative importance rk between adjacent indicators determined by experts, the weight value of the mth evaluation indicator is calculated as follows:
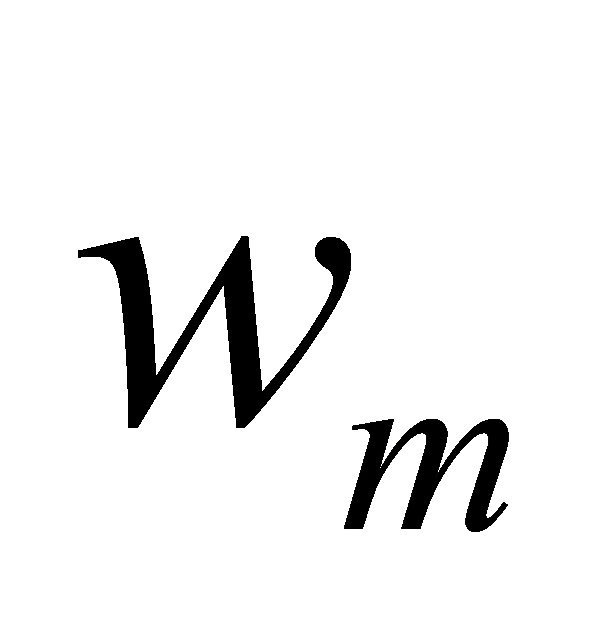 =(1+
=(1+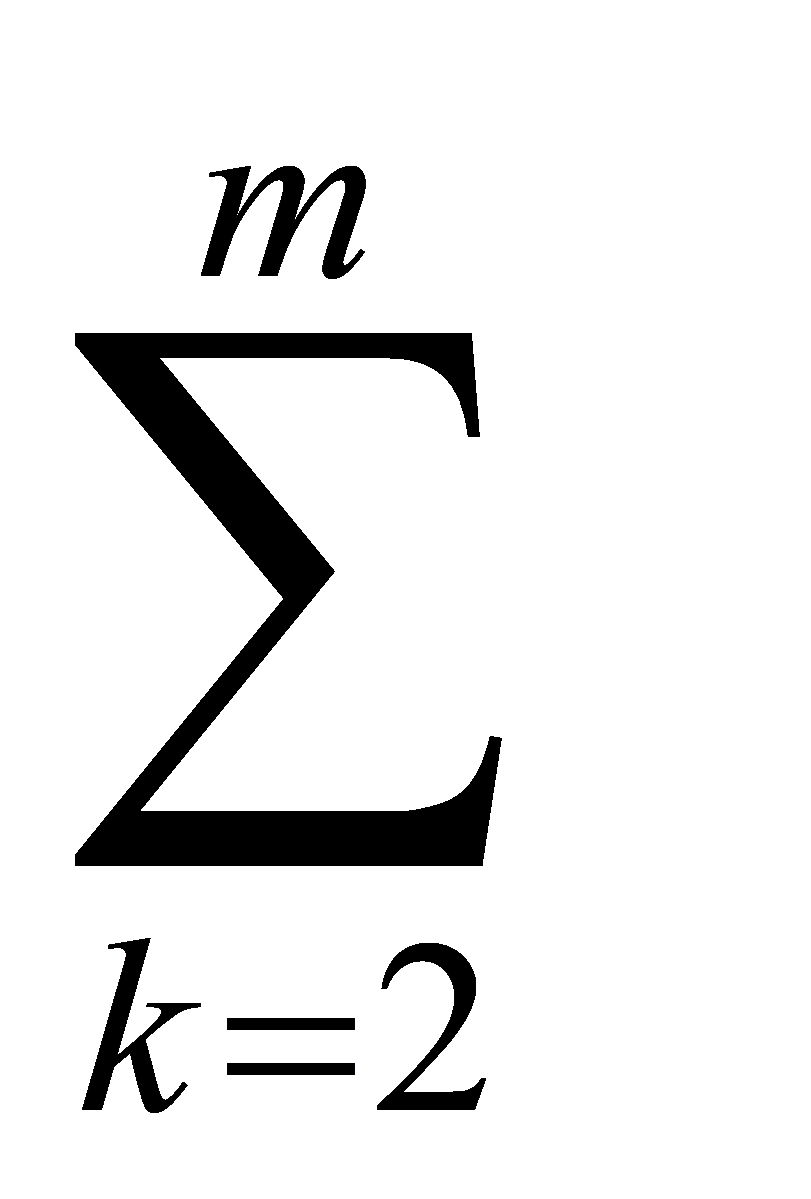
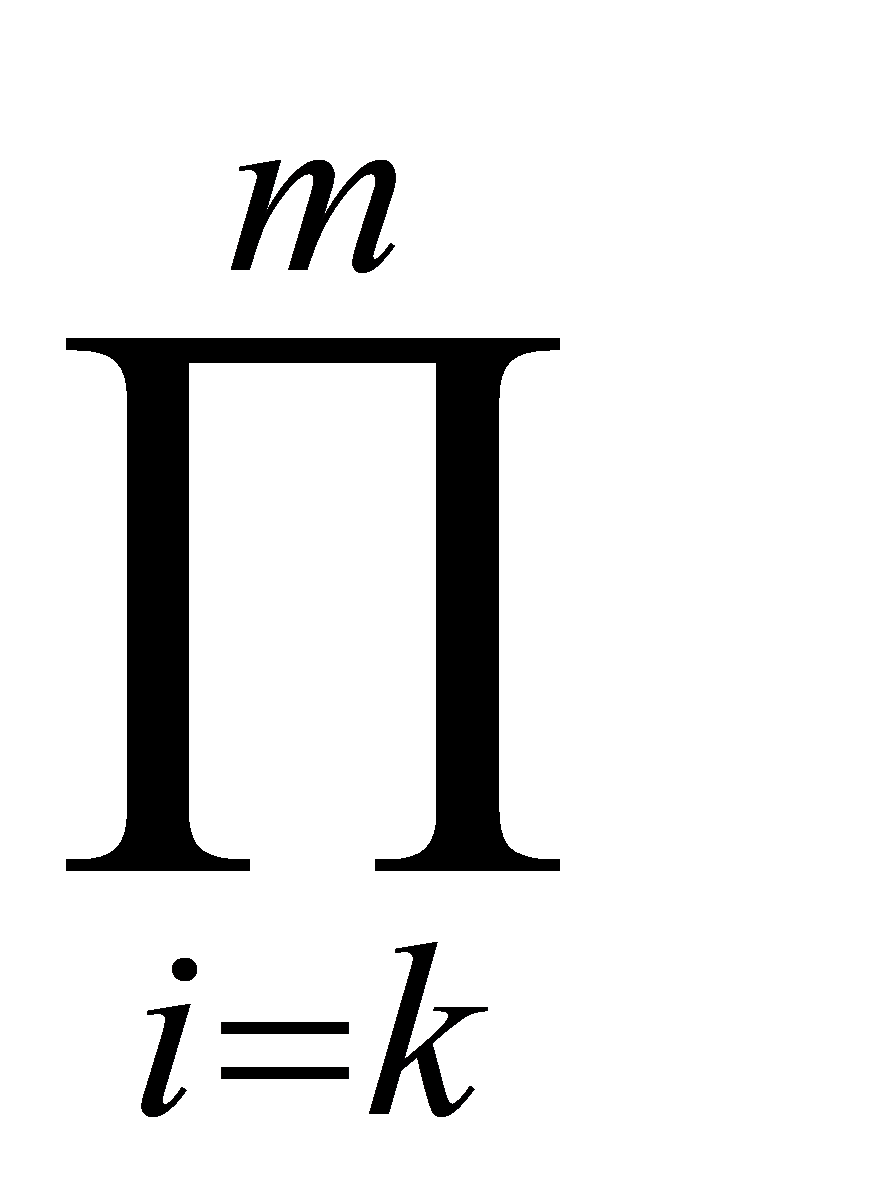 r
r )-1 (1)
)-1 (1)
Fourthly, the weight value of the m-1,m-2,……,3,2 index can be obtained from the weight wm:
 ,k=m,m-1,m-2,……,3,2
,k=m,m-1,m-2,……,3,2
Where, wk-1 is the weight calculation value of the k-1st evaluation index; rk is the relative importance of adjacent indicators determined by experts; wk is the G1 method weight of the kth evaluation index.
3.2. The Weight of Indicators Determination by Coefficient of Variation Method
Let uk be the weight of the kth index obtained by the coefficient of variation method, m be the number of evaluation indexes, and n be the number of evaluated objects. The formula for weight based on the coefficient of variation is:
\( {u_{k}} \) = \( \frac{\sqrt[]{\sum _{i=1}^{n}({V_{ki}}-{\overline{V}_{k}}{)^{2}}/n}}{{\overline{V}_{k}}} \) / \( \sum _{i=1}^{m}\frac{\sqrt[]{\sum _{i=1}^{n}({V_{ki}}-{\overline{V}_{k}}{)^{2}}/n}}{{\overline{V}_{k}}} \) (2)
Where, Vki is the value of the kth index of the ith evaluated object, and 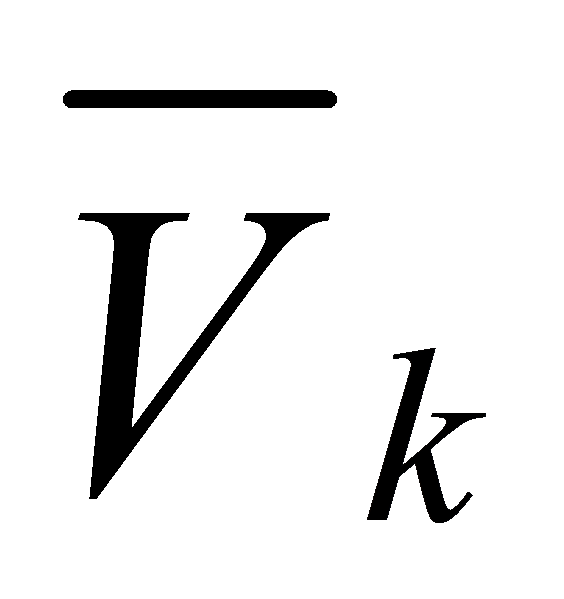 is the average value of all evaluated objects of the kth index.
is the average value of all evaluated objects of the kth index.
3.3. Determination of Comprehensive Weight
Suppose wk is the weight of the kth index after the combination of the two weighting methods. wk is expressed as a linear combination of subjective weight μk and objective weight ρk(k=1,2... , m), namely
\( {w_{k}}=α{μ_{k}}+(1-α){ρ_{k}} \) (3)
Where, α is the proportion of the weight of G1 method to the combined weight; μk is the G1 method weight of the kth index; (1-α) is the ratio of the weight of coefficient of variation method to the weight of combination; ρk is the coefficient of variation method weight of the kth index.
The objective is to minimize the sum of squares of the deviations between the combined weights and the weights of G1 method and the deviations between the combined weights and the weights of coefficient of variation method. The objective function is established as follows:
\( min{z}=\sum _{j=1}^{m}[({w_{k}}-{μ_{k}}{)^{2}}+({w_{k}}-{ρ_{k}}{)^{2}}] \) (4)
Substitute Equation (3) into Equation (4) to obtain:
\( \underset{α}{min}z=\sum _{j=1}^{m}\lbrace [α{μ_{k}}+(1-α){ρ_{k}}-{μ_{k}}{]^{2}}+[α{μ_{k}}+(1-α){ρ_{k}}-{ρ_{k}}{]^{2}}\rbrace \) (5)
Take the derivative of equation (5) with respect to α and set the first derivative to zero, and solve the equation α=0.5. Substitute this into equation (3) and get:
\( {w_{k}}=0.5{μ_{k}}+0.5{ρ_{k}} \) (6)
3.4. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model
The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model was constructed by Chad, an American cybernetics expert. It is a mathematical model that can effectively solve fuzzy problems. In the research, the "membership function" is used to objectively describe the evaluation level of the research object, and the specific application steps are as follows:
Firstly, the set of factors for the evaluation of financing risk of private equity funds is constructed U=Ui(i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5). Ui represents the first-level index of the evaluation of financing risk of private equity funds, and the first-level evaluation index Ui is composed of different second-level indexes, which can be expressed as U=Uij(j=1, 2, 3,……);
Second, the evaluation set V of financing risk evaluation is selected, and the fuzzy evaluation calculation matrix R is selected, where V=(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5)=(very low, low, average, high, very high).
The original evaluation data is collected in the form of a questionnaire survey, and the ratio between the number of people surveyed and the total number of respondents with the evaluation index Uij corresponding to the comment Vk is obtained through the processing of the survey data, and based on this, the financing risk of private equity funds is evaluated. All the index factors Uij in the index factor set U undergo an evaluation transformation, namely 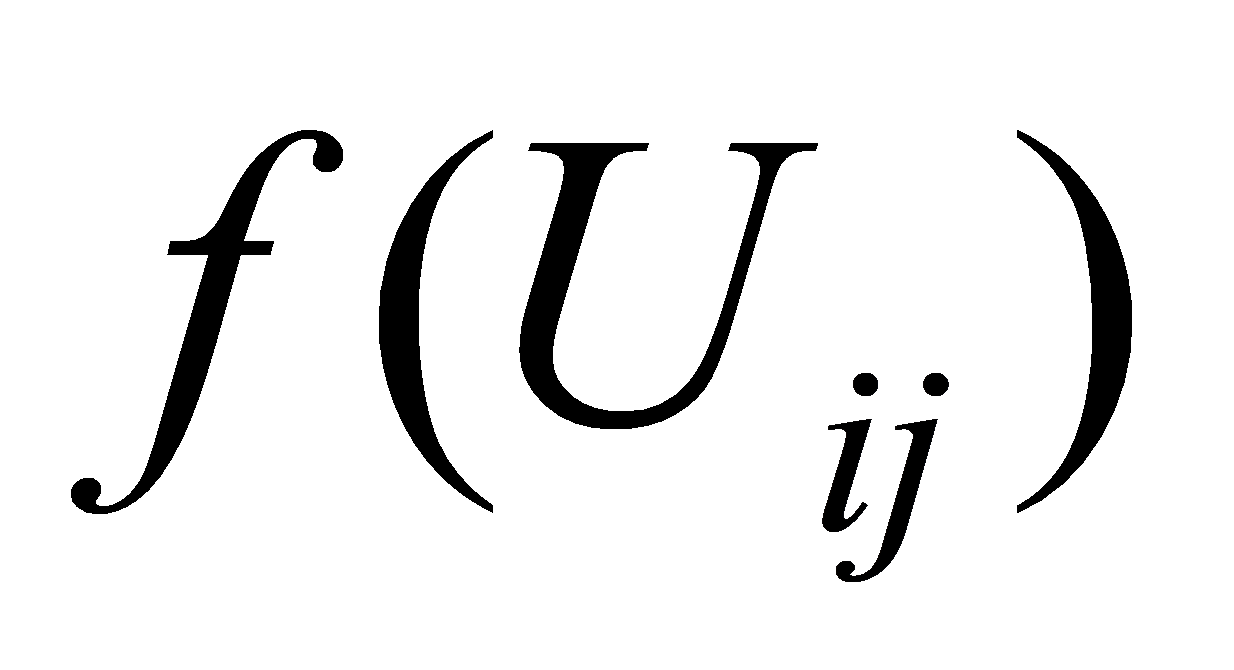 , so as to obtain a fuzzy conditional map
, so as to obtain a fuzzy conditional map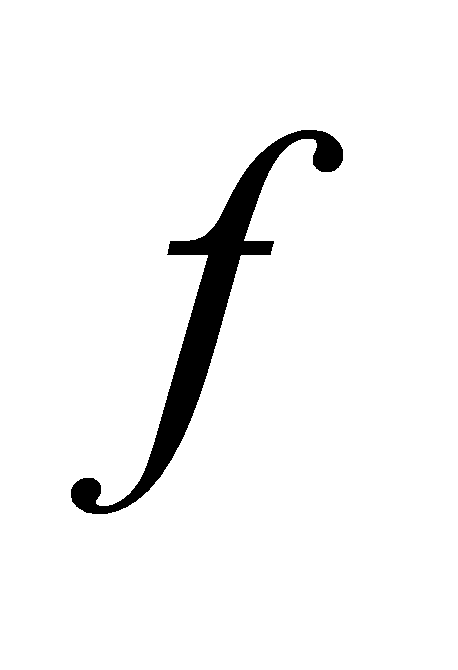 from U to V, namely:
from U to V, namely:
\( {u_{i}}→f({u_{i}})=({r_{i1}},{r_{i2}},\cdot \cdot \cdot ,{r_{if}})∈F(V) \) (7)
Where, F(V) represents the whole fuzzy data set on V. According to fuzzy mathematics principle and fuzzy transformation law, fuzzy mapping can construct a relative fuzzy relation R, namely fuzzy matrix of private equity fund financing risk evaluation:
\( {R_{j}}=[ \begin{array}{c} \begin{matrix}{r_{11}} & {r_{12}} & {r_{13}} & \begin{matrix}{r_{14}} & \cdot \cdot \cdot & {r_{1k}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}{r_{21}} & {r_{22}} & {r_{23}} & \begin{matrix}{r_{24}} & \cdot \cdot \cdot & {r_{2k}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}{r_{31}} & {r_{32}} & {r_{33}} & \begin{matrix}{r_{34}} & \cdot \cdot \cdot & {r_{3k}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}{r_{41}} & {r_{42}} & {r_{43}} & \begin{matrix}{r_{44}} & \cdot \cdot \cdot & {r_{4k}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}{r_{51}} & {r_{52}} & {r_{53}} & \begin{matrix}{r_{54}} & \cdot \cdot \cdot & {r_{5k}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}⋮ & ⋮ & ⋮ & \begin{matrix}⋮ & \cdot \cdot \cdot & ⋮ \\ \end{matrix} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}{r_{j1}} & {r_{j2}} & {r_{j3}} \\ \end{matrix} & {r_{j4}} & \cdot \cdot \cdot & {r_{jk}} \\ \end{matrix} \end{array} ] \) (8)
The weight result determined according to the combined weight is expressed as:
\( W=({w_{i}}) \) , \( {w_{i}}=({w_{ij}}) \) (i=1,2,3,4, 5, 6; j=1,2, 3,4) (9)
\( W=({w_{i}})=(X=({x_{ij}}{e_{j}})) \) :
\( {w_{1}}=({w_{11}},{w_{12}},{w_{13}},{w_{14}},{w_{15}},{w_{16}},{w_{17}}) \) ;
\( {w_{2}}=({w_{21,}}{w_{22}}) \) ;
\( {w_{3}}=({w_{31}},{w_{32}},{w_{33}},{w_{34}},{w_{35}},{w_{36}},{w_{37}}) \) ;
\( {w_{4}}=({w_{41}},{w_{42}},{w_{43}},{w_{44}},{w_{45}},{w_{46}}) \) ;
\( {w_{5}}=({w_{51}},{w_{52}},{w_{53}},{w_{54}},{w_{55}}) \) (10)
Combined with the weight changes, the fuzzy set of each index of private equity fund financing risk evaluation is calculated according to the survey data of each index. The set is divided into two levels of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation set, that is, the first level set corresponding to the first level index and the second level set corresponding to the second level index. The first level is calculated based on the second level, and the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation set of private equity fund financing risk at the second level can be expressed as:
\( {C_{i}}={w_{i}}×{R_{j}}={c_{ik}}=({c_{i1}},{c_{i2}},{c_{i3}},{c_{i4}},{c_{i5}}) \) (11)
Where i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6; k=1, 2, 3, 4, 5
The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation set of financing risk of private equity fund at the first level can be expressed as:
\( A=W×C=({w_{1}},{w_{2}},{w_{3}},{w_{4}},{w_{5}}) \) \( ×[ \begin{array}{c} \begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}{c_{11}} & {c_{12}} & {c_{13}} & {c_{14}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{15}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}{c_{21}} & {c_{22}} & {c_{23}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{24}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{25}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}{c_{31}} & {c_{32}} & {c_{33}} & {c_{34}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{35}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}{c_{41}} & {c_{42}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{43}} & {c_{44}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{45}} \\ \end{matrix} \\ \begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}\begin{matrix}{c_{51}} & {c_{52}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{53}} & {c_{54}} \\ \end{matrix} & {c_{55}} \\ \end{matrix} \end{array} ] \) (12)
This paper evaluates the financing risk of private equity funds according to likert 5-level scale, that is
,V=(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5)=(very low, low, average, high, very high)=(5,4,3,2,1)
The final evaluation value of private equity fund investment projects is:
\( {S_{z}}=5{c_{i1}}+4{c_{i2}}+3{c_{i3}}+2{c_{i4}}+1{c_{i5}} \) (13)
4. Risk Control of Private Equity Financing
Enterprises can carry out risk management before, during and after financing [5].
The first is called proactive control, which is to eliminate the risks that can be avoided before the action is taken. Enterprises should make preliminary preparations before introducing investors. For example, the state's knowledge of various laws and regulations related to private equity, relevant provisions of contracts, merger and acquisition regulations, investor screening, and investigation and analysis of third-party institutions employed, etc. The purpose of these preparations is to have a clear understanding of national regulations and oneself, and to prevent various uncertainties in the market when financing.
The second phase is called in-process control, where risks are dealt with in the course of action. After determining the investors to be introduced, the enterprise first needs to seriously evaluate whether it can meet the investment requirements and investment returns of investors. Secondly, enterprises should evaluate whether investors' valuation of enterprises is appropriate to prevent the value of target enterprises from being underestimated so that investors can obtain high returns. Third, the enterprise must determine the proportion of investors in the enterprise, which affects the profit of the enterprise dividend and ownership structure. Finally, enterprises need to consider whether the risk of the betting agreement is within the control range, so as to prevent enterprise managers from giving up control after the failure of the betting agreement.
The third phase is called post-action control, which is to follow up after the action is completed to further consolidate the results of the action. After the funds of private equity investment are in place, in order to achieve the expected profit target or listing target, enterprises and investors should jointly solve the problems in the process of enterprise development. Enterprises need to analyze and correct the financial indicators in each stage of investor disclosure to achieve the goal of reducing risks. And the enterprise should timely announce its revenue, cash flow, product market share and total assets to investors, so that investors know, if these major financial indicators are not good, these professional investors can help enterprises to analyze and correct, so as to minimize the risk.
We usually use the following means to control the risk.
Investors know how to exit before they decide to invest. Shareholders who are not willing to become financing enterprises permanently will sell their shares when the value is high, and their investment strategy is holding, increasing value and selling. Investment institutions choose promising companies, allowing investment capital to grow.
The introduction of private equity investment by enterprises needs to have a clear financing purpose and choose different types of investors. If the target enterprise does not have a clear financing purpose before financing, it will be in a passive position in the future.
The purpose of choosing target enterprises to be strategic investors is to make use of the advantages of strategic investment resources to achieve in-depth leapfrogging trial development. However, the selection of strategic investors also has its risks. In the process of development, the target enterprise cannot reach the conditions stipulated in the original betting agreement, and it is easy to be annexed or acquired by investors. In addition, it has great legal hidden trouble for companies that need to be listed in the future, because the equity structure of listed companies cannot be set as "one dominant share". Just because of this reason, target enterprises need to consider how to optimize the ownership structure when introducing strategic investors. Most companies choose multiple strategic investors at the same time to prevent equity from falling into the hands of one investor. Strategic investors are industry giants and potential competitors of target enterprises. In order to avoid disputes and brand loss, financing enterprises should sign some agreements with strategic investors on the commercial secrets of target enterprises [6].
Enterprises need to carefully determine the right investors according to their financing purposes and development stages, and should not blindly follow the trend and leave themselves in a dilemma in the future development.
The value of the target enterprise is of special concern to both investors and financiers. As investors hope the target enterprise value is as low as possible, they will later obtain more profits. However, as the financiers, they want to raise the value of their enterprises, which will raise more money and get a larger proportion of the company's shares. At present, cash discount method is widely used in the industry to carry out market valuation of financing enterprises compared with company law, which is more objective and fair.
The limitation of cash flow discount method is that the flow of future cash flow cannot be accurately obtained, and the discount rate is a judgment of potential risks. This approach, while perfect in theory, is unusable in practice. In practice, the comparable company law is used, which means that the price-earnings ratio is calculated based on the performance of the listed company or the peer non-listed company, and the enterprise valuation is the multiple of the price-earnings ratio multiplied by the target company's previous year's or future profit. As a result, the adoption of comparable company law can objectively evaluate the value of the company, whether before or after the enterprise's financing. Investors will not get super high returns and project enterprises will suffer losses due to low valuation.
In addition, financing enterprises should not value themselves too high, otherwise investors will be deterred, enterprises will miss the good development period.
In order to obtain investors' funds, financing enterprises must accept high betting standards. Although the betting agreement is not the primary cause of enterprise failure, it is usually worse for the failing party (especially financing enterprises).
Investors and target enterprises need to carefully consider the terms of the betting agreement, and lower expectations when appropriate, so as to strive for the satisfaction of both sides of the betting conditions, and finally achieve the goals of both sides and achieve a win-win situation. As for the target enterprise, if it accepts investment under acceptable betting conditions, it will also bring an incentive effect to to the target management and develop steadily in a good direction, so that investors can obtain ideal investment returns. If the standard of the betting agreement is too high, the management will pursue short-term interests excessively and finally go astray, so that the target company not only cannot bring profits to investors, but also needs to introduce new investors. Therefore, it is necessary to set up acceptable betting conditions for both investors and financing parties to control the risks brought by financing failure.
In addition, the target enterprise should be properly financed at each stage of development. When gu finance must play to consider whether the condition is in oneself bear range, do not blindly financing.
Investors' funds let the target enterprise get rid of the difficulty of financing. Once the target enterprise receives the funds from the investors, it must take advantage of this favorable condition to develop rapidly and occupy the market.
Enterprises should do something and do nothing. Project enterprises must have a strong sense of market competition, pay close attention to the trend of the industry, design products and services required by the market, and actively explore the market to become a player in the market competition. When enterprises are aggressive, sometimes they should adopt the strategy of risk avoidance, which can effectively avoid risks. If enterprises improve their supply chain and product quality after financing, they will not go down due to changes in the external environment. Enterprises in the rapid development of the time must be steady, to avoid rapid expansion after rapid collapse.
Financial risks may bring risks to corporate financing. If the interest rate of banks in the market or the exchange rate of foreign currency fluctuates, it will affect the value of corporate assets as well as the value of liabilities. Financing enterprises can use insurance to avoid financial losses caused by interest rates or exchange rates. Financing enterprises need to keep extra part of the capital, to resist the loss caused by financial risks.
Financing enterprises need to feedback the financial indicators to investors after financing. After the target enterprise gets the capital from the investor, the investor, as the shareholder of the company, needs to understand the financial indicators of the enterprise. If the target is not reached, the reasons must be analyzed and measures taken to reduce market risks. Generally speaking, the financial indicators concerned by both investors and financiers include the enterprise's revenue status, market position, sales status and property status.
Once the operation of financing enterprises deteriorates, it is necessary to discuss with investors the remedy method for default. In the case of continuous decline of financing enterprises, investors can remove the management or even accept the whole board of directors to reduce their investment risks.
5. Conclusion
Small and medium-sized enterprises (smes) are playing an increasingly important role in the development of our country, but financing difficulties and high financing costs have been plaguing the development of smes. Private equity financing can precisely solve the problem of difficult and expensive financing for enterprises. Private equity financing does not need to be mortgaged, guaranteed or repaid when due, which is the most ideal financing method for small and medium-sized enterprises. Starting with the current situation of financing difficulties for small and medium-sized enterprises, this paper introduces the concept of private equity, summarizes its characteristics, and draws a conclusion:
The introduction of private equity financing brings capital to enterprises at the same time also brings risks. According to its characteristics, the investor is one of the shareholders of the financing enterprise, and has a seat on the board of directors. In order to ensure its interest return, the investor will strictly control various economic activities of the enterprise, which may bring adverse side to the enterprise's operation and development. This paper divides the risks from the macro and micro aspects and comprehensively analyzes the risks in the process of enterprise financing.
In view of the identification of the risk of introducing private equity investment to enterprises, a risk assessment is carried out, and the risk control measures are put forward to provide constructive and operable risk control measures for enterprises in need of financing.
As the author is still in the learning stage, it is difficult to collect questionnaires from professionals for analysis, and it is not possible to evaluate a specific enterprise as an example. It is expected that in the next stage of the research, data collection will be carried out through the internship channel for a specific enterprise, and the method proposed in the paper will be adopted.
References
[1]. Zhou Shi. 2022(07). China Small and medium enterprises research report, 2021(11). Research on the trend, problem and supporting strategy of the development of small and medium-sized enterprises. macroeconomic study:165-177.
[2]. Cheng Juan, 2022(01).Research on the construction of private equity investment risk evaluation index system based on analytic hierarchy process. .Industry, finance and technology:118-126.
[3]. Teng Ying,He Xueshuang,Ni Debing,2017.Risk Assessment of private equity Investment Projects based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation -- Taking three private equity investment projects as examples. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (Social Sciences):67-73.
[4]. Ni Shaokai, 2002(06).Comparison of 7 methods to determine the weight of evaluation index.south china journal of preventive medicine:54-55+62
[5]. Bai Rui, 2014.Research on supply chain Finance and its risk control from the perspective of SME financing. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201501&filename=1014404428.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=sHon15EcmxRs_czke3QdOZKmjU42hWqxpLtfGNM_aoD909ejbHbYH1yrOrnjmVKI.
[6]. Song Caixia, 2007. The financial risk of enterprise merger and acquisition and its control strategy. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2011&filename=2009062872.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=NQhx5YMM4lnLZbQQXZxnqOS--imRpH-Ko8Ry6ME94Pu4suF7nYZN2iVWf_LRQH3M
Cite this article
Hou,X. (2023). Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Private Equity Risk Management. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,10,37-45.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhou Shi. 2022(07). China Small and medium enterprises research report, 2021(11). Research on the trend, problem and supporting strategy of the development of small and medium-sized enterprises. macroeconomic study:165-177.
[2]. Cheng Juan, 2022(01).Research on the construction of private equity investment risk evaluation index system based on analytic hierarchy process. .Industry, finance and technology:118-126.
[3]. Teng Ying,He Xueshuang,Ni Debing,2017.Risk Assessment of private equity Investment Projects based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation -- Taking three private equity investment projects as examples. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (Social Sciences):67-73.
[4]. Ni Shaokai, 2002(06).Comparison of 7 methods to determine the weight of evaluation index.south china journal of preventive medicine:54-55+62
[5]. Bai Rui, 2014.Research on supply chain Finance and its risk control from the perspective of SME financing. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201501&filename=1014404428.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=sHon15EcmxRs_czke3QdOZKmjU42hWqxpLtfGNM_aoD909ejbHbYH1yrOrnjmVKI.
[6]. Song Caixia, 2007. The financial risk of enterprise merger and acquisition and its control strategy. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2011&filename=2009062872.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=NQhx5YMM4lnLZbQQXZxnqOS--imRpH-Ko8Ry6ME94Pu4suF7nYZN2iVWf_LRQH3M









