1. Introduction
In the first half of 2022, against the backdrop of a more complex and severe international situation, frequent outbreaks of COVID-19 in China and increasing downward pressure on the economy, the default situation in China's bond market eased somewhat, but the scale of rollover reached a new high. Specifically, in the first half of 2022, there were 7 newly defaulted issuers in the Chinese bond market, involving a total of 32 maturing defaulted bonds, and the total amount of maturing defaulted bonds was about 192.78 billion yuan. The number of newly defaulted issuers, the number of maturing defaulted bonds and the amount of maturing defaulted bonds all decreased significantly year-on-year, but increased compared with the second half of 2021. The industry of defaulting enterprises is concentrated in the real estate industry. Under the pressure of declining sales and worsening financing differentiation, the credit risk of private housing enterprises continues to be exposed. The financing of urban investment enterprises continues to be under strict supervision, and credit risk events continue to occur. In this essay, based on some literature related to bond market and how it deals with occurred or potential default as follows, deep researches on bonds market and related risk management are applied and some further information and results are concluded. Shi and Liu [1], Shi and Xu [2], and Fan [3] pointed out some fundamental concepts of bond market, especially that numbers of advantages can be gained from a mature bond market, which benefit to both the economic structure and even the national or global economy, and all of these will help investors to make good decisions so that they may gain more from their investment in bond markets. Besides, Li [4], Liu [5], and Shi [6] introduced several methods on dealing with the risk may occur in the bond market. Finally, some effects that bond market can offer on risk management are stated from the learning on articles of Bao [7], An empirical test of China's inflation rate and stock returns by Yang [8], Hen [9], Chen [10], and Niu [11]. Through this paper, some deeper and more detailed advantages, strategies and roles of bond market will be demonstrated, which will help investors or other groups to have a clear cognition in this field.
2. Advantages of Bond Market
2.1. High Safety
Inflation risk applies to almost all securities, and it is most pronounced in bonds with fixed interest rates [2]. When there is severe inflation, the expected interest income and principal of bond investors will depreciate. The longer inflation persists, the worse it will be for holders of long-term bonds.
Although investors in bonds face all these risks, they are relatively safe compared with other investment instruments, especially stocks. Just as what illustrated in Fig. 1 below, in the period between September 2018 and September 2022, the opening return rates of national treasury bond stayed in a range between 2.655% and 3.651% with a quite low difference. At the same time, the closing rates of return ranged from 2.663% and 3.155%, which also referred to a stable tendency. Therefore, investors who choose bonds as their investment will often enjoy a safer environment even if the economic environment may fluctuate with changes in the society.
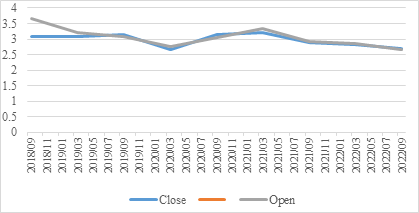
Figure 1: National debt treasury bonds return rate.
The security of a bond is based on: First of all, the principal of the bond will be repaid at the coupon amount on the agreed maturity date, and the fixed interest rate will be paid in installments or one time on the agreed coupon payment date, which is not affected by the market interest rate change after the issue [8]. Countries have also enacted relevant laws to guarantee the repayment of the principal and interest of bonds, so that investors have a sense of security. Even floating-rate bonds generally have a minimum interest rate to protect bondholders from losses if market rates fall too far.
Secondly, the issuers of bonds are mainly national and local governments, public organizations, special legal persons related to the government, first-class large companies and big banks, etc., with strong financial strength and high credit. In addition, the issuance of bonds has certain legal approval procedures, the relevant authorities must strictly examine the issuer's capital and financial situation, so that there is a legal guarantee.
Thirdly, the bond is a contractual debt. The binding force of the contract makes the issuer of the bond pay attention to its own credibility and avoid the potential ability of raising funds in the market in the future due to the default. Especially for the issuer of corporate bonds, generally take some measures to ensure the security of debt repayment. The main measures include: mortgaged issue of movable or immovable property; Set up sinking fund with a portion of annual profits [3].
In general, important institutions that are connected to businesses and government organizations but have minimal influence over their operations and are comparatively stable issue bonds directly to the public.
2.2. Good Liquidity
The frequency with which a security exchanges hands in the market over a certain amount of time is referred to as "turnover rate." It is one of the measurements employed to gauge how good the liquidity of the stock market is. Depending on the characteristics of the sample population, various types of indicators may be used, such as the amount of turnover rate of each listed stock in the exchange, the turnover rate given out based on the number of a sole stock issued, as well as the turnover rate according to the portfolio owned by an institution. In this section, the turnover rates of two corporations, Poly Development and West China Energy, are collected, which show that bonds, especially some business companies have relative high turnover rates that refer to good liquidity. Just as what shown in the figure below, from September 2018 to September 2022, the turnover rate of Poly Development maintained at an average around 16%, while the turnover rate of West China Energy maintained at an average around 60%. Even though the turnover rates of Poly Development were much lower than that of West China Energy (as that shown in Fig. 2), relatively high turnover rates still can be witnessed in this 4-year period, which refer to a good liquidity in the bond market.
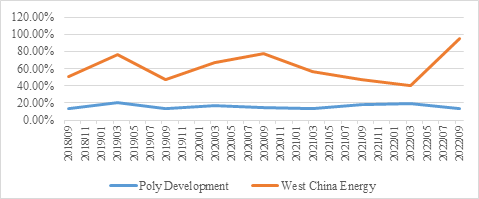
Figure 2: Turnover rate of Poly Development & West China Energy.
2.3. Revenue Is Guaranteed
Bond rates are greater than bank deposits but lower than stock investments, making them the perfect choice for conservative investors. In addition to earning a steady interest income from their bond investments, investors may take advantage of variations in bond prices to buy and sell bonds and profit from price discrepancies.
Current income, which makes up the majority of the income generated by corporate bonds, is specifically defined as the revenue generated by interest income, which is typically paid twice a year. It only considers the money made by purchasing particular bonds over time, not any capital gains or losses from bond investments [7].
In addition, the yield to maturity refers to the yield obtained by holding the bond until the repayment date, including all interest due. It is equivalent to what investors would get if they bought at the current market price and held until maturity. Finally, the early-call yield refers to the return that investors receive when the bond issuer redeems the bond before its prescribed maturity date.
3. How to Make Risk Management
3.1. Steps of Risk Management
The first phase in the basic risk management process is to thoroughly and continually gather internal and external initial information about the enterprise's risk and risk management, including past data and future projections. The preliminary data must be gathered in accordance with the categories of risks examined, such as the examination of strategic, financial, market, operational, and legal risks.
Then, risk assessment should be done. Risk identification, risk analysis, and risk assessment are the three phases that make up risk assessment. The identification, analysis, and assessment of risks should integrate qualitative and quantitative methodologies. Businesses must manage risk information dynamically and frequently or irregularly conduct risk identification, analysis, and assessment in order to assess both new risks and changes to existing risks.
Planned risk management is the third thing that has to be done. In accordance with its own circumstances and the external environment, an organization creates the guidelines for allocating human resources as part of its development plan and selects the right risk management methods, such as risk taking, risk aversion, risk transfer, risk conversion, risk hedging, risk compensation, and risk control. A risk management approach is what this is.
Additionally, measures for risk management are proposed and implemented. Explicit objectives for risk resolution, necessary organizational leadership, engaged management and business processes, necessary conditions, means, and other resources, precise reaction actions carried out before, during, and after the occurrence of risk events, and risk management tools should all normally be included in the plan (such as key risk index management, loss event management, etc.) [5].
Finally, risk management oversight and development must be accomplished. The business should concentrate on significant risks, significant occurrences, significant choices, significant management and business procedures, and oversee the application of initial risk management data, risk assessment, risk management strategies, significant control initiatives, and risk management solutions. Stress tests, return tests, walk-through tests, and risk control self-assessments are used to evaluate the efficacy of risk management, and timely modifications are made in response to changes and existing flaws [4].
3.2. Several Strategies
Risk Avoidance Strategy. Any economic office in the globe will prioritize avoiding risk when developing a risk management plan. Avoiding significant vulnerability is the most practical and straightforward solution when the loss brought on by the risk is not compensated by the possible benefit of the project that is commencing it. For instance, operational risk might mitigate the risk associated with an investment if one is not undertaken. However, the algorithm to avoid risk has great limitations. First, reducing system risk only works when it is possible to do so. Second, certain hazards cannot be avoided [5]; Third, although some risks can be minimized, the cost is too high; The fourth is that the company will merely tolerate system risk, be comfortable with the present state of affairs, and refrain from aggressively seeking out improvement.
Risk control strategy. The first thing an economic unit considers is how to control the occurrence of risks, reduce the occurrence of risks, or how to reduce the loss caused by the occurrence of risks, which is risk control, when it cannot eliminate systematic risks or is required to face certain risks in a certain economic activity. Risk control has two major definitions: the first is to manage risk causes and lessen risk occurrence; the second is to manage risk occurrence and lessen the severity of risk harm. Accurate forecasting is required to limit the frequency of risk occurrence, and effective and prompt action is required to lessen the severity of risk harm. Several factors provide restrictions on the ability to control market risks [6]. Although human knowledge and technology have advanced significantly, there are still numerous obstacles that cannot be overcome, making it impossible to totally control risks and reduce losses. In order to reduce the risk that investors may experience, risk diversification can be applied, which largely relates to the diversification of risks by economic units through diverse operations, investments, financing methods, and foreign exchange asset sources, as well as the enticing of several suppliers and the pursuit of numerous clients. Risk neutralization primarily relates to risk protection choices made in foreign exchange risk management, such as lowering foreign exchange positions, futures hedging, forward foreign exchange trading, and other risk-neutralizing actions [9].
Risk Transfer Strategy. Economic units can use several methods of risk distribution, such as insurance or non-insurance transfer, to avoid injury and disadvantage to their economic activity after accepting risks. The best method to transfer risk is through early stage insurance. As an illustration, the unit manages property, health insurance, and other factors while shifting the risk of vulnerability to the insurance provider [17]. Additionally, under Chapter III rules, the company's policies may potentially transfer some of the risk elements to the third party.
One of these strategies is the portfolio, a diversified investing approach in which investors place a percentage of their funds in several kinds of assets or different variations of the same kind of securities. Investors must diversify their capital among a variety of investment projects in order to adhere to the risk diversification concept. Diversifying the allocation of this asset is also important for some investment projects in order to achieve the ideal investment ratio. The most effective portfolio successfully diversifies risk.
4. Contributions of Bond Market to Risk Management
The full development of the bond market can effectively provide a financial platform with depth and breadth, enhance the resilience of the financial system against risks, and create a high-quality income realization platform for financial micro subjects.
4.1. Improve the Transmission Mechanism and Guard Against Inflation Risks
Issuing government bonds can solve both inflation and deflation. The issuance of national bonds can bring back funds and reduce the circulation of currency to curb inflation. When the domestic economy is depressed and domestic demand is insufficient, issuing national debt can concentrate funds for construction and promote economic growth to cope with deflation [18]. When the yield rate of the bond market excess the inflation or deflation rate, it illustrates that the bond market successfully defend the inflation or deflation risk [12], which just like Fig. 3 below. These contains the inflation rates and yield rates from 2017 to 2021, the five years period, which can be witnessed that the yield rate often greater than the inflation rate so that the bond market actually have balanced or even surpassed the fluctuation of the economic environment. Although the yield rate and the inflation rate tend to be quite close in 2020, that was mainly the result of the breakout of the COVID-19, many industries were influenced by the epidemic and their revenue reduced a lot, however, that was only a sudden and rare event. Generally, the bond market can be helpful to deal with the risks.
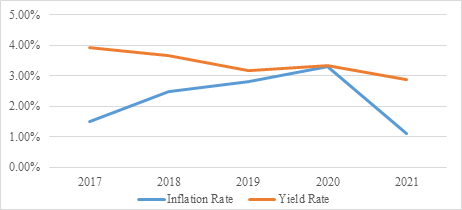
Figure 3: Inflation rate & yield rate.
4.2. Diversify Banking Risks and Prevent Systemic Risks
The indirect financing form of loan hides great risks in the existing financial structure. There is excessive concentration of financing risk in the banking system, and the banking industry has the characteristics of systemic risk, so if the risk is seriously exposed, there will be great harm [13]. The public status of the banking industry, once a run, will have a huge impact on the macro economy and various industries. In contrast, the securities industry is in an individual and relatively micro position, with more localized risks and less systemic impacts in a short time. A deep and sound bond market will effectively reduce corporate financing costs and improve the structure of the financial system [14]. Diversified investment channels in the bond market can help diversify the adverse effects of credit strains on the real economy when a banking crisis breaks out, thus preventing structural finance risks [15]. Basically, there can be three useful methods, which are investment in bonds with different maturities, portfolio management and determination of rate of return (as shown in Fig. 4).

Figure 4: Mechanism of risk diversification.
4.3. Ease Excess Liquidity and Optimize the Economic Structure
The problem caused by excess liquidity is that, a large amount of capital is invested in real estate, basic resources and various financial assets, which can easily lead to economic overheating, economic bubbles and even economic recession. At present, issuing central bank bills, raising benchmark deposit and lending rates and the reserve requirement ratio have become the central bank's regular means to shrink excess liquidity [15], and this is only a short-term solution. In the face of huge foreign trade surplus and foreign exchange reserve balance, other economic measures besides monetary policy are needed to solve the problem of excess liquidity. Among them, expanding domestic demand by increasing consumption and reducing savings rate is the fundamental solution to alleviate excess liquidity. To increase consumption, first of all, it should increase household consumption. The specific ways are as follows: to increase household income, especially the income of low-income people; Besides, people should push ahead with reforms in education and health care also the development of the social security system to keep household consumption expectations stable. In addition, increasing government consumption is also an important way to increase consumption, which also needs some macro-fiscal policy regulation and control [16].
In order to optimize the economic structure, the first method is to adhere to the market-oriented, strive to adapt social production to changes in domestic and foreign market demand, and meet the needs of multiple aspects [19]. To achieve the best possible resource allocation, the economy's structural changes must be driven by the market, intentionally adhere to the law of value, and fully exploit the fundamental functions of the market mechanism. The key to fully utilizing the fundamental function of market regulation is to respect the status of businesses and rural families as market participants and fully utilize their primary function in economic restructuring. Local governments in particular should appropriately position their own functions, play the role of service, demonstration, and advice, do their job but not err, and give full play to farmers' primary role in the structural adjustment of the agricultural structure and rural economic structure [20].
Secondly, the role of state macro-control should be fully played on the basis of market regulation and organically combine market regulation with state macro-control. Because market regulation still has its own defect, so adjust economic structure still must strengthen national macro-control. The main means of regulation are economic and legal means, supplemented by administrative means. To optimize the industrial structure and regional structure, we need the support of national finance, taxation and finance, the support of national policies, the supervision and guarantee of national laws, and the coordination and guidance of the government [19]. In addition, economic restructuring must be supported by scientific and technological progress, and economic restructuring must be combined with the implementation of the strategy of rejuvenating the country through science and education. Industrial structure adjustment is the core of economic structure adjustment, and the important work of industrial structure adjustment is to vigorously develop high-tech industries represented by information industry and transform traditional industries with high-tech industries [21].
The foundation of changing the economic structure is industrial structure optimization. The term "industrial structure optimization" describes the rationalization and progress of the process of attaining coordinated growth of numerous industries and addressing the increasing social demands through industrial adaptation. It is primarily based on the objectively proportional relationship of industrial, technical, and economic relations and adheres to the proportional demand of reproduction process in order to promote the coordinated growth of diverse industries within the national economy and make each industry's development adapt to the development of the entire national economy [22]. It is to follow the law of the evolution of industrial structure, via technological advancement, the overall quality and efficiency to a higher level of industrial structure trends and the development of the process, through the government's industrial policy adjustments [11], the effect of the industrial structure change of supply and demand structure, actualize the optimal allocation of resources, promote the rationalization of industrial structure and the high-level develop It is vital to alter the structure of the three major industries in the situation of the primary industry's shaky foundation, the secondary industry's inadequate development, and the tertiary industry's tardy start. The primary industry needs to be strengthened energetically, the secondary industry needs to be adjusted and improved, and the tertiary industry needs to be actively developed.
5. Conclusion
This paper mainly focused on the bond market and some relative factors. Through this process, it can be found that the advantages of the bond market are: high safety, good liquidity and guaranteed revenue. Besides, the strategies on risk management are also mentioned, which are risk avoidance, risk control and risk transfer strategies. Moreover, the contributions of bond market to risk management were also pointed out above, that are guarding against inflation risks, diversifying banking risks and optimizing the economic structure. Therefore, in this research, the public can basically know the advantages of bond market and its influence in risk management.
Generally, there are still some limitations exist in this research, for instance, the industries or the areas of companies are still not comprehensive enough, only data from a few corporations or bonds are mentioned in this essay. In order to get an improved and more accurate conclusion, relative data from various industries should be investigated and more effective values have to be considered, such as price earning ratio, inflation rate and even the fluctuation of the broad market, which needs further investigation in future studies.
References
[1]. Shi, Y., Liu X.: A comparative study of default rates in domestic and foreign bond markets. Bonds, (4), 6(2022).
[2]. Shi, D., Xu K.: Comparative advantages of corporate bonds and bank loan financing. 2013(11), 118-119 (2021).
[3]. Fan, Y. Discussion on the current situation and development of China's bond market. Investment and entrepreneurship, (2021).
[4]. Li, X.: Preliminary study on enterprise audit risk and avoidance strategy. Modern business, 7(3), 2022.
[5]. Liu, L.: Enterprise financial management internal control system construction and financial risk aversion under the background of the new period. China market, 6(2), 2022.
[6]. Shi, J.: Bond default and disposal mechanism of state-owned enterprises. Qinghai finance, 5(5), 2022.
[7]. Bao, J.: Problems in the development process of China's bond market and suggestions on preventing investment risks. Journal of Baoji College of Arts and Sciences: social science edition, 41(2), 6(2021).
[8]. Yang, Z.: An empirical test of China's inflation rate and stock returns. Journal of Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, (1), 12-15(2005).
[9]. He, M.: Suggestions on foreign investment in China's bond market. Entrepreneur information, (3), 2(2022).
[10]. Chen, H.: Convertible bonds help the high-quality development of China's economy. Bonds, (7), 6(2022).
[11]. Niu, Y.: Observation on the quality of China's bond market. Bonds, (2), 3(2020).
[12]. Li, C.: Current situation analysis and prospect of China's bond market. China circulation economy editorial department2013(11), 118-121(2021).
[13]. Wang, C.: Current situation and improvement proposals of medium-term bill financing in China. Times trade: late, 6(1), (2013).
[14]. Li, X., Zhu, L.: Research on the information mechanism of bond credit rating restraining bond default risk -- based on the perspective of bond default. Industrial economics review, (1), 171-184(2022).
[15]. Li, Z., Fang, P., Wang, J.: Research on default risk prevention of Chinese bond market, (2020).
[16]. Wang, K., Liu, J.: Research on decomposition of macro information implicit in bond yield. Tsinghua financial review, (2021).
[17]. Yuan, Y., Cao, X., Ma, L.: Research on credit default in Chinese bond market. 2018(3), 42-45(2021).
[18]. Yang C., Zhou, S., Ding, Z., et al.: Quantification of investors' risk preference in asset allocation -- also on the correlation between long and short termrisk preference. China management science, 30(6), 11(2022).
[19]. Wang, K., Bai, D.: Research on portfolio management based on deep reinforcement learning. Modern computer, (2021).
[20]. Hsu,H., Tsai, M., Yang, D.: A contingency model for long-term portfolio management. Journal of futures and options, 11(1), 75-114(2018).
[21]. Ji, C., Wang, Z.: Countermeasures for capital structure optimization of listed companies in China. Cooperative economy and science &technology,000(013), 100-101(2021).
[22]. Liu, W.: Current situation and countermeasures of Chinese listed companies capital structure analysis. (2021).
Cite this article
Zhou,Y. (2023). Research on the Bond Market and its Contributions to Risk Management. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,13,92-99.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Shi, Y., Liu X.: A comparative study of default rates in domestic and foreign bond markets. Bonds, (4), 6(2022).
[2]. Shi, D., Xu K.: Comparative advantages of corporate bonds and bank loan financing. 2013(11), 118-119 (2021).
[3]. Fan, Y. Discussion on the current situation and development of China's bond market. Investment and entrepreneurship, (2021).
[4]. Li, X.: Preliminary study on enterprise audit risk and avoidance strategy. Modern business, 7(3), 2022.
[5]. Liu, L.: Enterprise financial management internal control system construction and financial risk aversion under the background of the new period. China market, 6(2), 2022.
[6]. Shi, J.: Bond default and disposal mechanism of state-owned enterprises. Qinghai finance, 5(5), 2022.
[7]. Bao, J.: Problems in the development process of China's bond market and suggestions on preventing investment risks. Journal of Baoji College of Arts and Sciences: social science edition, 41(2), 6(2021).
[8]. Yang, Z.: An empirical test of China's inflation rate and stock returns. Journal of Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, (1), 12-15(2005).
[9]. He, M.: Suggestions on foreign investment in China's bond market. Entrepreneur information, (3), 2(2022).
[10]. Chen, H.: Convertible bonds help the high-quality development of China's economy. Bonds, (7), 6(2022).
[11]. Niu, Y.: Observation on the quality of China's bond market. Bonds, (2), 3(2020).
[12]. Li, C.: Current situation analysis and prospect of China's bond market. China circulation economy editorial department2013(11), 118-121(2021).
[13]. Wang, C.: Current situation and improvement proposals of medium-term bill financing in China. Times trade: late, 6(1), (2013).
[14]. Li, X., Zhu, L.: Research on the information mechanism of bond credit rating restraining bond default risk -- based on the perspective of bond default. Industrial economics review, (1), 171-184(2022).
[15]. Li, Z., Fang, P., Wang, J.: Research on default risk prevention of Chinese bond market, (2020).
[16]. Wang, K., Liu, J.: Research on decomposition of macro information implicit in bond yield. Tsinghua financial review, (2021).
[17]. Yuan, Y., Cao, X., Ma, L.: Research on credit default in Chinese bond market. 2018(3), 42-45(2021).
[18]. Yang C., Zhou, S., Ding, Z., et al.: Quantification of investors' risk preference in asset allocation -- also on the correlation between long and short termrisk preference. China management science, 30(6), 11(2022).
[19]. Wang, K., Bai, D.: Research on portfolio management based on deep reinforcement learning. Modern computer, (2021).
[20]. Hsu,H., Tsai, M., Yang, D.: A contingency model for long-term portfolio management. Journal of futures and options, 11(1), 75-114(2018).
[21]. Ji, C., Wang, Z.: Countermeasures for capital structure optimization of listed companies in China. Cooperative economy and science &technology,000(013), 100-101(2021).
[22]. Liu, W.: Current situation and countermeasures of Chinese listed companies capital structure analysis. (2021).









