1. Introduction
In 1989, the Berlin Wall collapsed, which nominally symbolic the re-unite of Germany. Until today, the debates and arguments about GDR and FRG are continuing, as these two Germanies represented two diverse political camps and two divergent economic systems, which is still meaningful to the politically ideological confrontation nowadays, the socialism versus capitalism or the market economy versus the planned economy didn’t flee with the end of the cold war. On the opposite, the direct confrontation transformed to integration of two economic systems, where the confliction is that whether market economy or planned economy should dominant the whole system with its opposite to play an assisting role. Considering the empirical fact of GDR and FRG, in 1989, the failure of GDR in economy seemed to be unstoppable. As the most economic successful country in socialism camp, with highly support by Soviet Union directly, the speed of development in economy of GDR was still far behind FRG. Furthermore, from 1980 onwards, there was a clear economic fatigue in East Germany, with a declining trend of individuals’ standards of living. Based on the fact, researchers conclude that market economy is more superior than planned economy. However, the conclusion is too subjective as the international background and economic basis of two countries are quite different, which are two decisive factors to impose impacts on the outcome. How to prove that market economy should be the dominant drive of the economy? What can we conclude and apply to the modern international relations? What progress might be achieved on the future economy? To address the research blanks, the study concentrates and compare the economy with the background in three dimensions. In respect of international relations, the study compared the policies of US to FRG and the policies of Soviet Union to GDR, as the confrontation of East and West Germany was essentially the confrontation of socialism camp versus capitalism camp. Some vital statistic about the economic foundations of two Germanies were also given in the study. Particularly, the study concentrates on the comparisons of economic systems, which is extended by revealing the fact that two economies are not purely single economic system. The ultimate objection of the study is to prove the unassailable superiority of market economy over planned economy currently, which could bring out some ideas and thoughts about the future economic system as an evolved integration of market economy and planned economy. Particularly, the outcome of the study reflects that the integrating economy is a combination, while the dominant part is still market economy.
2. Description of Planned Economy in GDR
2.1. International Relation
With the failure of Nazi in WWII, Germany was divided into two countries, representing two opposite ideological camps respectively. On October 7, 1949, German Democratic Republic was established on the occupation land of Soviet Union. As the Iron Curtain speech given by Churchill, the temporary cooperation between Soviet Union and western capitalist camps collapsed, with ideological confrontation replacing by. As a satellite country of Soviet Union and vanguard of cold war, East Germany was bond to the responsibility to construct a developed economy to prove the legitimacy and incontrovertible correctness of planned economy. Consequently, the international relation of GDR was restricted to only socialism camp, which leaded to the exhausting place of the GDR economy at the ending period of its regime. The trade with western capitalism camp was halted, with clear orders and supplies from Soviet Union and the socialism camp. Former flexibility of the industrial structure was blocked by the western world, which brought out the falling of technologies to some point.
However, the critical geographic position of GDR didn’t turn out as a bargaining chip for better treatment as a defeated country. Since Soviet Union was drastically damaged in WWII, the claim policy from it is correlative to the ethnic hatred correspondingly. It claimed a compensation of more than 10 billion dollars from Germany, (mostly from East Germany and partly from West Berlin). It is estimated that Russians removed about 1,300 industrial factors and more than 4,500 kilometers of railway, which considerably attacked the basis of industry and economy in GDR. It is stated that at the beginning of the cold war, individuals in GDR were imposed on debts about 2,500 marks per capita [1].
2.2. Important Statistics
The area of GDR is 41,828 mi², with a population from about 18.3 million in 1950 to 16.7 million in 1980 [2]. The personal income per capita of GDR is 6,000 dollars, with the rate of personal owned cars being less than 50%. It is given that in 1971, the average height of men in GDR went on 173 cm of female was 165 cm [3].
2.3. Planned Economy
Similar to the economic system of Soviet Union and the socialism camp, GDR had a command economy (planned economy), which means that decisions made on investments, production, distribution and pricing are from the order of government or an authority [4]. The establishment of planned economy sincerely contributed to the recovery of the economic structure in GDR. From 1950s to 1960s, the economy in East Germany maintained a stable increasing rate of 7% each year, which is not lasting as the authority neglected the significance of the Light industry and handicraft industry. After abolishing the rationing system, the economic development in GDR became slower. From 1950 to 1980, GDP per capita in East Germany increased from 2,500 dollars to 9,000 dollars, while it reached a plateau from 1980 onwards, at about 9,000 dollars.
3. Description of Market Economy in FRG
3.1. International Relation
As a response to the socialism camp, Federal Republic of Germany, on behalf of the capitalism camp, was established on May 23, 1949. It rose on the occupational land of France, UK and USA. As a result, it plays the role of the vanguard between socialism and capitalism. The original intension of America was to build a so-called high fence halting the potential ideological invasion from Soviet Union. But how is that possible in a defeated country with numerous debts to be paid? The most necessary affair is to recover the economy in west Germany in order that it is capable to play the political role and economic role, which is to defeat Soviet Union along with the socialism world by proving the correctness and the priority of market economy and capitalism. In a word, the restore of an economically developed FRG is the key to win the cold war.
Accordingly, Marshall Plan was promulgated by US, which considerably release the economic burden of FRG. It is estimated that FRG received about 1.5 billion dollars in total and precious technological aid through this plan and the economic trade with countries in the capitalism camp. The industrial foundation was recovered miraculously in a few years after the WWII. It is also claimed that at the beginning of the cold war, individuals in FRG obtained approximately 140 marks per capita [1].
3.2. Important Statistics
West Germany was integrated by the occupational lands from US, France and UK, accordingly the area of it went on 96,030 mi², the population was approximately from 50.9 million in 1950 to 61.4 million in 1980, which shown an upward trend. In 1983, the personal income per capita of FRG is 8,000 dollars. It is estimated that in 100 persons in FRG, the ratio of personal owned cars reached more than 90% [2]. Another research showed the biological standard of living in FRG [3]. In 1971, the average height of men was 175 cm, with female on 167 cm.
3.3. Market Economy
With aid from external trade and proper inner policies, FRG fulfilled Wirtschaftswunder (economic miracle) on the ashes of WWII by instituting its unique social market economy. The GDP per capita soared continuingly at 5,000 dollars in 1950 to 22,500 dollars in 1989 as a reflect. In particular, the social market economy must be distinguished with the traditional pure market economy. The broad definition of market economy is that the decisions on production, investment, and distribution are taken according to the market forces [4]. Compared to it, the social market economy in FRG mixed with ingredient of planned economy, which means that the capitalism in FRG has more direct regulations from government, along with the bigger proportion of stated-owned economy in the markets. With the regulation from the authority and the self-pushed market system, economy in West Germany is lasting till the reunification of Germany.
4. Comparison of GDR and FRG
GDR is radically opposite to FRG in almost every aspect delivered. Diverse international relations, distinct initial conditions, various kinds of economy and different agricultural strategies. Compared to GDR, FRG had a much better initial conditions in economy and industry. Soviet Union destroyed the industrial base in GDR while US and its allied countries aided FRG to restore its industry rapidly. GDR’s international trade was limited while FRG could freely have transactions with the most developed countries in the world. Also, when every citizen in GDR had to pay a debt for 2,500 marks per capita, individuals in FRG acquired a supplement of 140 marks per capita from the Marshall Plan.
The basic statistics of two Germanies are diverse. Compared to East Germany’s area of 41,828 mi², West Germany owned 96,030 mi² of land. From the comparison of the population quantity from 1950 to 1980 in each country, it is concluded that FRG was experiencing a period of moderate increasing in population, while in GDR, the population declined in 30 years. Also, from the research, it is clearly stated that the biological standard of living of FRG is better than GDR both in men and female as the figures of FRG’s average height is higher than in GDR.
GDR and FRG were established in different background with diverse economic system. GDR had a typical planned economy on the structure of Stalin’s mode, while a unique social market economy was promulgated in FRG, which correspondingly brought out comparative outcomes. At the very beginning, panned economy in GDR drew market economy in FRG as both two classifications of economy achieved a rapid economic development. Nevertheless, the increasing speed in GDR got slower and slower while the market economy in FRG continued to maintain a significant speed. The figure 1 and figure 2 show that from 1950 to 1980, the GDP per capita in FRG served as a leading role, being ahead of GDR about 2,500 dollars in 1950 to 13,500 dollars in 1980. In particular, both market economy in FRG and planned economy in GDR were integrated, as the economy in West Germany concluded a mare part of regulation from government instead of market itself. By contrast, East Germany also abolish the rationing system, which was a main part of planned economy.
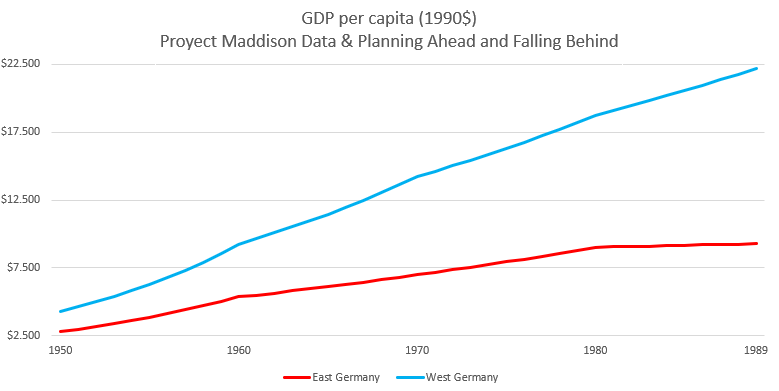
Figure 1: GDP per capita [5].
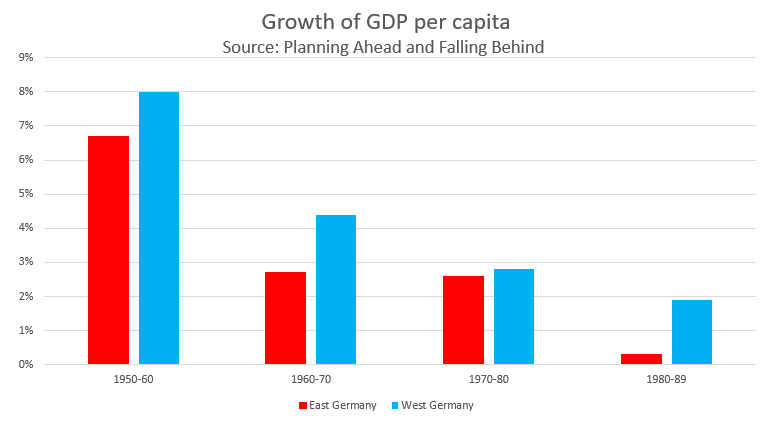
Figure 2: Growth of GDP per capita [6].
To sum up, in 1949, the initial conditions of FRG including industry, economy and external trade position in the world were much more superior than GDR, which is sincerely attributed to the completely divergent policies from the capitalism camp and socialism camp and their different roles in cold war. To prove the priority and correctness of the economic systems respectively, ideological confrontation pitted social market economy in FRG representing the ideology of capitalism versus command economy in GDR representing the ideology of socialism. Looking back to the competition these days, we can conclude that the social market economy defeated its opponent in every respect, as the economic road implemented in FRG is a sustainable way to drive the economy, with the improvement of the standards of living of individuals. It should be emphasized that the planned economy in GDR is far from useless as it also recovered economy in an extremely difficult situation, while the problem is that the fully controlled economy by government could hardly ever lead to the achievement of economic targets, as it would fail in deciding the consumer preference, surplus, and shortages in the market. As a consequence, the GDR’s government ignored the importance of the light industry and handicraft industry, being far behind of FRG in economy.
Such empirical example leads to a theoretical conclusion: Is it not persuasive to conclude that the mainly planned economy is less correct and less scientific compared to the mainly market economy since the initial condition of two countries were divergent? What is the enlightening significance and influence of the economic confrontation between East and West Germany? Is it possible to combine the strengths of the market economy with the strengths of the planned economy and merge and coexist to create a new economic system in the future?
The first question is posted since it seems not unassailable based on the fact of GDR and FRG as FGR had a more superior conditions to rebuild economy, which imposed a vital impact on the outcome. However, the resources at the binning could not the dominant factor in modern economy. As proofs, Singapore, Japan and South Korea achieved economic miracles respectively, with a fact that they are all small countries lacking raw materials and other economic basis. The starting conditions of these countries were similar to GDR, while the outcomes were completely different. At a more macroscopic level, market economy versus planned economy can be concluded as objective truth versus subjective willingness. The reason is that planned economy operates according to plans drawn in advance by the state or an authority, while market economy operates on the market forces, which is based on demand and supply. Then there is an obvious problem about planned economy, how to ensure the correctness of the so-called plans from the authority? In another words, the problem of planned economy is “planned” itself. Economy is not a game that can be foreseen the steps and the roads, only following the scientific objective truth can lead to the success of economy, which means that the planned economy could not be the dominant economic factor, or it would unavoidably lead to failure at last. To sum up, the mainly market economy is more superior to mainly planned economy in a scientific aspect through the comparison of GDR and FRG.
Of research two typical economic classifications is significant to modern economy and globalization nowadays. From the success of FRG and the failure of GDR, we can conclude that the economy dominated by market economy is the current best way to develop economy, with two main reasons to prove the thesis. First, the nature of market economy is open and comprehensive as market economy requires a free market. The wider scale of the market, the bigger interest would be generated by a dominant market economy, conforming to the trend of globalization. On the opposite, the planned economy naturally tends to be conservative and tends to have blocked internal economic circulation, which is worse in 2020s. For instance, North Korea blocked itself with external world with a highly backward planned economy, it subjectively missed the boat of development of economic globalization. With a free and open market, it would be common to have more opportunities to succeed. Consequently, there would be ample human resources to guarantee the productivity of the economy. It is stated that from 1949 to 1965, there were about 3 million immigrants from GDR to FRG [7]. Moreover, the open policies in West Germany also attracted more than 1 million workers from Western European countries. Particularly, the human resources sincerely affected the outcomes of two Germanies.
Second, market economy has a strength of protecting and promoting the equal chance of competition. At a macroscopic level, market economy strengthened the cooperation of countries and the benign competitions. It is emphasized by a research with statistic of a few countries in Western Europe that the productivity of FRG make considerable progress through the competition with its adjacent countries [8]. At a microscopic level, the establishment of a free market would also induce the competition of individuals, which would push the general economy in return. It is compared that in GDR [9], the dispersion of the wages of people was smaller than in FRG, most citizens share the same standards of living in GDR, lacking the competition on a free market. It is hard to find an extreme example of radical poverty, while it is also hard to obtain a high income in GDR. In FRG, the income dispersion is large, while it should be mentioned that with the general economic development, the lowest income in FRG was continuingly increasing from 1950 to 1989. In GDR, the propaganda of planned economy is to allocate the wealth equally, while it is hard to maintain a general economy without a free market, which could also reflect the downward trend of economy in GDR since 1980 and correspondingly the declining standards of living of citizens. In a word, there isn’t progress without competition, there isn’t wealth without a free market.
As mentioned, the market economy is better at chance of competition, the ability to create wealth and construct an open and comprehensive atmosphere in society, while it is worse in the aspect of allocate wealth. Compared to it, planned economy acted better at centralizing the state power to focus on single economic objection and has a more average allocation system, while it lacks the indispensable vigour of economy to maintain its sustainable development. Therefore, it is necessary to merge a new economic system, with the strength of both market economy and planned economy. The social market economy of FRG could be a form of the “new economy”. As mentioned, “The market economy's distribution via price, and social policy's distribution by means of state allocation, can be contrasted to each other as patterns of primary and secondary distribution” [10]. With a free market regulated by government in a restrained way, the wealth would be created, and the monopoly would be banned by the authority to prevent the inequivalence of the distribution of the social income. It is also mentioned that market economy is capable of continually producing and reproducing a surplus economy that concludes the entire economy, in the opposite, the planned economy is capable of continually producing and reproducing a shortage economy that concludes the entire economy [11]. These theories argue that both capitalism and socialism are essential in the drive of economy. Actually, they are complementary in economy. Nowadays, most countries in the world have a more or less economic form of combination of both two economy. Considering France, US and UK as entirely free market economies, they have relatively large numbers of state-owned enterprises, banks, and insurance companies. Social market economy with numerous private firms are existing in China, which is a socialism country. The tendency in the whole world is to combine market economy and planned economy to acquire the highest productivity and incomes. To sum up, the future new economy is predicted to be a combination of market economy and planned economy, while market economy would still be the dominant factor.
5. Conclusion
From the practical example of GDR and FRG, it is concluded that from a scientific and modern point of view, market economy has unassailable strengths compared to planned economy. First, market economy conform to the trend of globalization as the nature of market is the factor of openness and comprehension. Globalization is a entirely enhancement of market economy, while market economy is the essential condition of globalization. Market economy essentially is a form to obey the objective rule, which is the reason why it could boost the development of economy. By contrast, planned economy is more subjective as the nature of it is “plan”, which is often proved false and not lasting. The fact is, the reality is always changing, it is impossible to make proper plan or so-called command in advance. The history has proved many times (including GDR versus FRG), that economy dominated by plans couldn’t last to create wealth or promoting the productivity. Also, market economy entitles individuals to own various opportunities to compete and make fortune, which would incite and enlarge the scale of economy, increasing the standards of living of the entire society or country. In comparison, planned economy lacks the capability of competition, while it could address the problem of distribution in an equivalent way.
History is spiraling to upgrade and evolve. The experience of ideological confrontation in the past is likely to boost a new economy, which is dominated by a free market and assisted by regulations of plans from authority on the aspect of distribution.
The study addresses the research gaps on the controversies of the superiority of market economy and planned economy based on the empirical fact of GDR and FRG from a more comprehensive and more persuasive aspect. Moreover, the study focusses on the current enlightening significance of two economic systems and predicts the emergence of the new economy in future.
However, the study is defective as the argument of the future economy should be dominated by market economy lacks the practical and persuasive examples. There are still many successful countries with a economy dominated by plans from governments. In China, the social market economy is sincerely affected by the regulations and commands from the party, while it can still maintain the rapid economic growth for about 40 years. Therefore, future research in this topic should be based on the international outlines and use more specific and direct examples to prove and access the ultimate arguments.
References
[1]. Qi Jiang , Jiujiu Yu. On the economic differences between east and west Germany after the war. Eastern Europe and Central Asia today (03),1-6. doi:CNKI:SUN:ELSY.0.1995-03-000. (1995).
[2]. East Germany. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/East_Germany. last accessed 2022/10/27.
[3]. Komlos, J., & Kriwy, P. The biological standard of living in the two Germanies. German Economic Review, 4(4), 459-473. (2003).
[4]. Admin. (2015). Difference Between Planned Economy and Market Economy https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-planned-economy-and-vs-market-economy/
[5]. GDP per capita. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b7/GDP_per_capita_East_Germany.png. last accessed 2022/10/27.
[6]. By Midofe - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=93665423 Growth of GDP per capita. last accessed 2022/10/27.( 1996)
[7]. Yan Fang.(1987). Some Problems on the Comparison between East and West Germany. Today's Soviet Union and Eastern Europe (01),39-41. doi:CNKI:SUN:ELSY.0.1987-01-010.
[8]. Boguszewski, J. Growth and Productivity in Industry and Its Principal Sectors in the FRG, Austria, Poland, and Hungary, 1960-72. Eastern European Economics, 18(2), 3-75. (1979).
[9]. SZYDLIK. Incomes in Planned and a Market Economy: The Case of the German Democratic Republic and the “Former” Federal Republic of Germany. European Sociological Review, 10(3), 199–217. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.esr.a036333. (1994).
[10]. Zacher. Social Market Economy, Social Policy, and the Law. Zeitschrift Für Die Gesamte Staatswissenschaft, 138(3), 367–388. (1982).
[11]. Zacher. Social Market Economy, Social Policy, and the Law. Zeitschrift Für Die Gesamte Staatswissenschaft, 138(3), 367–388. (1982).
Cite this article
Cui,B. (2023). A Comparison of Market Economy and Planned Economy: Based on German Democratic Republic and Federal Republic of Germany. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,17,233-240.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Qi Jiang , Jiujiu Yu. On the economic differences between east and west Germany after the war. Eastern Europe and Central Asia today (03),1-6. doi:CNKI:SUN:ELSY.0.1995-03-000. (1995).
[2]. East Germany. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/East_Germany. last accessed 2022/10/27.
[3]. Komlos, J., & Kriwy, P. The biological standard of living in the two Germanies. German Economic Review, 4(4), 459-473. (2003).
[4]. Admin. (2015). Difference Between Planned Economy and Market Economy https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-planned-economy-and-vs-market-economy/
[5]. GDP per capita. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b7/GDP_per_capita_East_Germany.png. last accessed 2022/10/27.
[6]. By Midofe - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=93665423 Growth of GDP per capita. last accessed 2022/10/27.( 1996)
[7]. Yan Fang.(1987). Some Problems on the Comparison between East and West Germany. Today's Soviet Union and Eastern Europe (01),39-41. doi:CNKI:SUN:ELSY.0.1987-01-010.
[8]. Boguszewski, J. Growth and Productivity in Industry and Its Principal Sectors in the FRG, Austria, Poland, and Hungary, 1960-72. Eastern European Economics, 18(2), 3-75. (1979).
[9]. SZYDLIK. Incomes in Planned and a Market Economy: The Case of the German Democratic Republic and the “Former” Federal Republic of Germany. European Sociological Review, 10(3), 199–217. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.esr.a036333. (1994).
[10]. Zacher. Social Market Economy, Social Policy, and the Law. Zeitschrift Für Die Gesamte Staatswissenschaft, 138(3), 367–388. (1982).
[11]. Zacher. Social Market Economy, Social Policy, and the Law. Zeitschrift Für Die Gesamte Staatswissenschaft, 138(3), 367–388. (1982).









