1. Introduction
Richard and Morris established the "Dick and Mac McDonald's" restaurant in 1940, which served as the prototype for McDonald's. McDonald's, the world's largest fast food chain, was founded in 1955. McDonald's officially entered the Chinese market in 1990, when it opened its first restaurant in Shenzhen, officially entering the socialist country. McDonald's now has over 32000 fast food restaurants in 121 countries and regions around the world [1]. The success of McDonald’s is not an accident. Effective and reasonable strategies play a significant role in the company’s operation, which advance McDonald’s to nowadays position step by step. There are many research methods that can be used to analyze McDonald’s strategies, such as the Ansoff Matrix, Porter’s Generic Strategy, swot analysis, and marketing mix. McDonald’s would apply these methods to manage business activities and assess risk.
Chen and Hu [2] also claims that as the COVID-19 outbreak, the catering industry took a hit in several years, how McDonald’s manage risk and maintain operation to respond to such public health crisis is also a good experience for other company to learn from. This paper mainly analyzes McDonald’s franchise agreement and structure and tries to discover its successful business model and marketing and management strategies to improve sustainability.
2. Marketing Strategy Analysis
2.1. SWOT
SWOT analysis, which stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, is a useful tool for developing an overall marketing strategy or planning individual campaigns.
2.1.1. Strengths
McDonald's has high brand awareness, influence and credibility. McDonald's operates globally and has more than 38,000 stores in more than 100 countries. It has opened up sales channels around the world and is recognized by the public. It has a great advantage in the highly competitive catering industry [3].
New technical support. The development of McDonald's has been following the progress of the times, not only providing consumers with self-ordering and skip-the-line functions to realize the concept of future restaurants, but also quickly calculating the calories of McDonald's food for customer reference through technology. At the same time, as many countries want to achieve the goal of carbon neutrality, McDonald's also has technical support and progress in energy conservation and emission reduction. For example, the use of electric vehicles in transportation, the use of solar power instead of gas power in restaurants, etc.
Financial Status. McDonald's revenue in 2019 was $21.98 billion, and its market share has been growing slowly but steadily, which gives McDonald's an absolute advantage in future development.
2.1.2. Weakness
The chain business model. The chain operation mode of McDonald's makes the management of the company very complicated. McDonald's cannot guarantee the uniform quality and service of each company. If one McDonald's has problems, the reputation and trust of the whole McDonald's will be affected.
The food is not nutritionally balanced. McDonald's food is mostly junk food, such as fried food and carbonated drinks, which is very bad for some people who pursue a nutritious diet.
Lack of employee satisfaction. Because McDonald's has been pursuing high profits and low wages, employees have serious dissatisfaction with their work treatment and salary. McDonald's has faced frequent employee protests and strikes.
2.1.3. Opportunities
Expansion of the menu. More and more consumers are concerned about their health, but McDonald's currently offers a very limited number of healthy diets meals, and McDonald's can add more choices for consumers to attract more health-conscious consumers.
Global store expansion. McDonald's can continue to expand its stores around the world to broaden the global market and give it a more leadership in the fast-food market.
Green development. As the world pays more and more attention to sustainable development, McDonald's should follow the world's mainstream energy conservation and emission reduction and pay attention to its own green development. At a time when other competitors have not yet transitioned to green development, McDonald's has opened up the market first to lay the foundation for its future development.
2.1.4. Threats
Although McDonald's is now the leader in the fast food industry, it also has many competitors, such as Burger King, chick-fil-a and KFC, which should not be ignored. Moreover, now more and more fast food brands are established, they will make up for the defects that McDonald's does not bring to consumers. McDonald's will have to work hard to be a leader in the future.
Economic uncertainty. In the first quarter of 2020, McDonald's missed quarterly profit expectations due to economic uncertainty. That led to a 4% drop in the value of its shares, which could be steeper if the economic uncertainty continues for longer [4].
Emerging consumer preferences. Consumer trends and consumer preferences are changing with The Times. At present, fast food is still popular among consumers, but in the future, with the concept of healthy and green development, if people choose healthier diet and better quality of life, McDonald's will face great changes.
Strict state regulations. Some countries restrict the development of many fast food companies due to health problems, and many countries shut down McDonald's due to political problems, such as Russia closed all the local McDonald's.
2.2. Marketing Mix
2.2.1. Product Strategy
McDonald’s products mainly include hamburgers, sandwiches, salads, snacks, sides, beverages, desserts and shakes. According to Shastri [5], McDonald’s regularly change its menu to adapt to changing needs, trends and tastes. Before adding new products to the menu, it has undergone a thorough market test, so franchisees have a fair understanding of its potential. Meyer also claims that the McDonald’s business gradually expands its product mix, making its products diversified [6]. This action not only satisfies market demand and improves its revenues but also reduces the risk of over-dependence on one or several food service segments.
2.2.2. Place Strategy
The company’s revenue mainly relies on McDonald’s restaurants. It has more than 38000 standardized restaurants, distributed in over 100 countries. In addition, in order to meet the digital trend of the catering industry, McDonald’s allows customers to order food online via their website and cooperates with some leading online food delivery services companies [5]. McDonald’s also manages kiosks to sell some specific categories of products, such as some desserts, which provide extra revenue [6].
2.2.3. Pricing Strategy
McDonald’s pricing strategy include bundle pricing strategy and psychological pricing strategy. Bundle pricing strategy is to encourage customers to purchase product portfolio instead of a single product. For example, if customers go to McDonald’s ordering system, they will discover that the price of a set male is much cheaper than the sum of each component’s price. Psychological pricing strategy is another common pricing strategy existing in many companies. They will price their product at a price that could give customers mental suggestions. For instance, they will price their product at 99$ instead of 100$ to let customers feel cheaper.
2.2.4. Promotion Strategy
McDonald’s promotion strategies include advertisement, sales promotion, public relations and direct marketing [6]. The company publicizes its products through TV, the internet and other carriers. McDonald’s also discounts some of their products to attract customers. For public relations, McDonald’s releases their CSR report actively and promotes the company’s sustainability. Direct marketing is for some big events or activities held by local governments or communities. In addition, McDonald’s has personalized marketing strategies for different regions, which considered factors about religion, custom, culture, and tradition.
2.3. Generic Strategy
In 1980, Michael Porter introduced Porter’s Generic Strategy, which are standard basic strategies that an enterprise can follow. It’s comprised of three basic strategies, namely the “Cost Leadership Strategy”, “Differentiation Strategy” and “Focus Strategy” [7]. By choosing the right strategies, the enterprise can pursue a higher competitive advantage. The strategies proposed depend on the company’s competitive advantage and the scope of the market targeted.
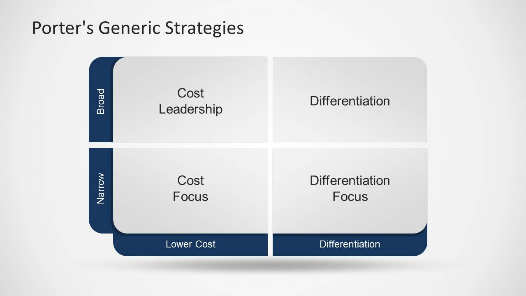
Figure 1: Porter’s Generic Strategy.
McDonald's has made cost leadership its main generic strategy. It involves minimizing costs in order to offer products at lower prices. The objective of McDonald’s by using this strategy is to attain market leadership position by establishing efficient value chain management. In addition, Gregory considered that the company’s standardized processes make it possible to maximize efficiency, minimize costs, and ensure profitability despite the use of competitive selling prices. He also explained that the huge business organization promotes economies of scale, which lower the cost of raw materials [8].
2.4. Intensive Growth Strategies
The Ansoff Matrix was developed in 1957 by Igor Ansoff, the father of strategic management. It refers to two broad areas of concern for a firm: Product and Market. This model helps enterprises identify opportunities to increase business income by developing new products and services or exploring new markets. The matrix contains 4 options: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification. Each option has a different level of risk.
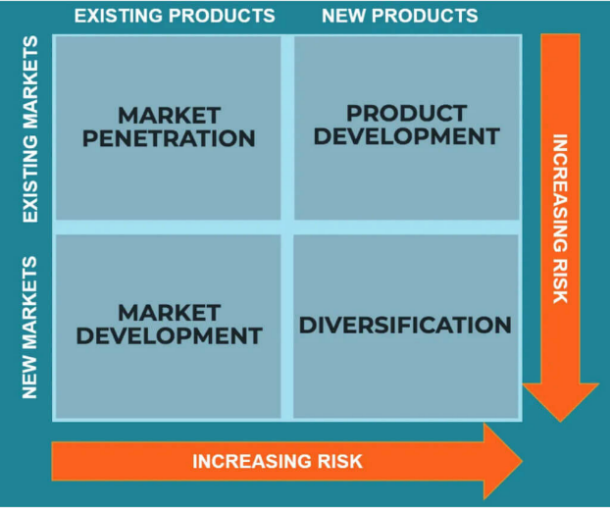
Figure 2: The Ansoff Matrix.
2.4.1. Market Penetration
Intensive growth refers to the growth of a company by expanding its product line or market scope [9]. McDonald’s aims to improve profitability and increase market share by using these strategies, and the primary strategy is market penetration, which is a measure of how much a product or service is being used by customers compared to the total estimated market for that product or service [10]. One of the concrete methods is related to cost leadership strategy because lower cost leads to lower prices, increasing market penetration. The promotion strategy, which was mentioned in the marketing mix is another way for McDonald’s to achieve this goal as promotions and discounts are good ways to increase sales. In addition, McDonald’s competitive advantages will be strengthened by doing SWOT analysis for increasing growing sales and market reach [8].
2.4.2. Product Development
McDonald’s develops new products or modifies its product lines for their current customers in the existing market. The company has enlarged its product line and owned its competitors’ products to improve its ability to against risk. Accompanied by product development, McDonald's has increased investment in research and development. Considering that McDonald's mainly relies on market penetration, this intensive growth strategy has a supportive effect on business growth. Because of the increased risk, the frequency of developing new products or changing menu is quite low. In addition, Gregory considered this strategy is related to the cost leadership strategy in his report, as the company can use lower introductory prices to attract customers [8].
2.4.3. Market Development
McDonald’s mainly use this strategy to develop new market in global business expansion. New market development based on low prices products, effective promotion strategy, and strong brand awareness. The company applies this strategy by developing new products or considering new geographic areas to expand its value chain. What’s more, while accessing in different markets, personalized marketing for different regions is also important, which fully considers the religion, customs, values, and cultures of its operation areas.
2.4.4. Diversification
According to Ansoff Matrix, diversification refers to developing new products and entering new market. Diversification provides the greatest growth potential, but also the greatest risk of failure. For McDonald’s, diversification strategy has been only applied to a minimum extent [8]. The company mainly utilizes related diversification in food preparation and production such as developing new products in the global drink industry. However, some lateral diversification has developed nowadays as the changes in the development situation. For example, in response to the growing criticism about environmental impact, the company has invested in green business practices to set up a good enterprise image.
3. Sustainability Strategy
3.1. Climate Action
McDonald’s is focusing on reducing emissions in their restaurant operations and engaging suppliers to reduce emissions in supply chains. The company has joined the United Nations Race to Zero campaign, committing to put McDonald’s on the path to net zero emissions by 2050 [11].
3.1.1. Restaurant Energy
The company has invested in areas such as renewable energy, LED lighting, energy-management systems and energy-efficient kitchen equipment. McDonald’s is getting LEED recognition---Tibet (convenient traffic reducing traffic pollution), Hainan Island (convenient traffic, environmental protection fitment and decoration) & Nanjing (power saving system), the UK’s first “net zero carbon restaurant”. The company expects to have 1800 LEED-certified restaurants by the end of 2022. Moreover, McDonald's provides electric vehicle (EV) charging points in restaurants located in multiple markets around the world.
3.1.2. Supply Chain Management
For farm management, McDonald’s support farmers to continuously improve farm management practices, systems and technologies to reduce emissions and increase production efficiency. They also support regenerative agriculture initiatives to promote soil regeneration and improve soil health [12]. The company is also committed to reducing deforestation in supply chain to reduce emissions. In addition, McDonald’s is reducing energy usage at supplier facilities, sourcing renewable energy, transportation efficiency and reducing waste.
3.2. Food Safety
McDonald's attaches importance to customer feedback and operates multiple global social media accounts and toll-free phone numbers for customers’ suggestions. They use these feedback to improve the quality and safety of products and services. The company also work with experts, it has established McDonald’s Global Food Safety Advisory Council which include leaders of food safety industry from all over the world [11]. The council provides suggestions on production safety standards and restaurant food safety practices so that McDonald's can continuously improve their standards. In addition, McDonald’s also conducts annual food safety audits of their suppliers to check if the food meets the standard. In addition, McDonald’s also conducts annual food safety audits of their suppliers to check if the food meets the standard. The food sources should go through strict inspection procedures. For example, beef patties have to go through multiple control indicators and tests. Even if 1.5 mm metal is mixed, it will be immediately detected and removed by the metal detector [12].
3.3. Safe & Respectful Working Environment and Empowerment
McDonald's works hard to create a safe working environment for the crew and provide customers with a safe experience. It strives to provide a good restaurant atmosphere by strengthening staff training. Meanwhile, McDonald's will conduct safety inspections for all restaurants every year and take measures against unqualified restaurants. The company also provides learning and development opportunities for its employees and focuses on attracting and retaining the best employees. McDonald's has established Hamburger University around the world to provide talent [13]. What’s more, they take serious responsibility to respect human rights throughout the value chain, preventing forced labor and other human rights violations.
3.4. Community Impact
McDonald's can create a lasting positive impact through community service. By supporting the development of communities, the company have established impactful relationships with community-based organizations [11]. One of the significant examples is Ronald McDonald House Charities (RMHC). The Ronald McDonald’s House provides free temporary housing for families of sick children who seek medical care away from home and donate necessary foods and suppliers. Consumers enjoy the humanistic care of McDonald's and the company builds a reputation.
4. Risk Strategy
4.1. Establish a Standardized Management System
The standardized management system plays an important role in the face of existing major risk. After the COVID-19 outbreak, McDonald’s acquire its employees wear mask uniformly. Employee also strictly obey the Six-step washing hands rule [2]. The company also strengthened the disinfection of the ventilation system in the store and the facilities frequently contacted by customers [2]. These actions minimize the risk of epidemic spread and ensure the health of employees and customers, Keeping most stores open during the epidemic.
4.2. Buy Back Shares
McDonald's has bought back millions of shares in a stock buyback program. From 2010 to 2020, McDonald's cut the total number of outstanding shares by more than 30% [14]. Basically, that is because of McDonald’s pursuit of low cost. Low price lead to low-profit margins, which is a common phenomenon in fast food industry. Another key reason is the decrease in sales. For these reasons, the company bought back shares to increase the share dividends. McDonald’s increased the portion of sales from franchisees to increase free cash flow, and they use these extra money to buy back shares [14]. These measures eventually lead to higher buybacks and dividends. From 2009 to 2020, the dividends per share increased by 125% while the cost of dividends rose by only 56.4%.
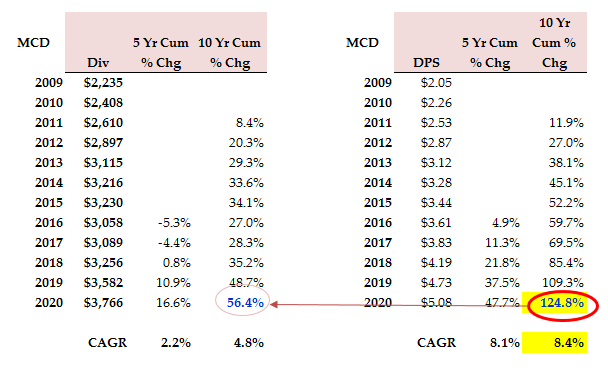
Figure 3: Hake calculations [14].
4.3. Invest in Real Estate
McDonald’s earned most of its income from real estate investment, which is related to franchising. The company operate three different types of it: developmental license, which is the franchisee invests their own capital in setting up the restaurant. Conventional franchising, which is the franchisee paying rent and royalty for using the restaurants. Affiliates, which is receiving investment and accounts for equity investments from the company [15]. According to McDonald's business report in the third quarter of 2020, about 7% of McDonald's stores are owned and operated by the company, and the remaining 93% of stores pay some form of rent and royalty to the corporate office. In addition, the report also shows that the revenue generated from food sales at company-operated restaurants was $2.2864 billion, while $3.0448 billion from franchised restaurants. So McDonald’s mainly gain income from rent and royalty of franchised restaurants.
5. Conclusion
To sum up, in terms of marketing strategies, swot analysis shows that McDonald's has high brand awareness, influence and credibility. It also has strong new technique support and good financial status. There are also lots of opportunities such as the expansion of the menu, global store expansion and green development. However, McDonald’s has its own weaknesses. The overstrict chain model impedes effective management, the not nutritionally balanced food, and lack of employee satisfaction. McDonald’s is also facing the rat race, economic uncertainty, emerging consumer preferences, strict state regulations and other kinds of threats. In order to improve profitability, McDonald’s has adopted different approach of its 4p marketing mix in their global outlets, which greatly depends on their globalization approach and localization approach. In the aspect of sustainability performance, the ESG report claims that according to The Upright Project, McDonald's has a net impact ratio of -43.3%, indicating an overall negative sustainability impact [16]. McDonald's seems to create positive value in the categories of Jobs, Taxes, and Meaning & Joy by using resources or causing negative impacts in the categories of Physical diseases, GHG emissions, and Scarce human capital. Under this situation, McDonald’s also adopt some strategies in the aspect of the environment, labour and human rights, supporting local communities and so on.
In terms of risk assessment, McDonald's bought back millions of shares, reducing the number of shares outstanding to reduce debt level. The unprecedented growth is mainly because its successfully usage of franchisee entrepreneurs to promote the McDonald's product, which reduce risk to a large extent.
This study has some limitations. Not every problem is fully covered, the operation situation may change over time. However, this paper is also a useful source to research the business strategies of McDonald’s and enlighten others.
References
[1]. Han, J.: The business strategy of Mcdonald's. International Journal of Business and Management, 3(11), 72-74 (2008).
[2]. Chen & Hu.: McDonald's risk management in the context of the COVID-19 Modern Commerce and Trade Industry (18), 33-34 (2020). doi: 10.19311/j.cnki.1672-3198.2020.18.017.
[3]. Li, Y.: Strategic Appraisal of McDonald's (2020). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340601256_Strategic_Appraisal_of_McDonald's.
[4]. Schramade, Willem, McDonald's: A Sustainable Finance Case Study (September 24, 2019). Erasmus Platform for Sustainable Value Creation, September 2019, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3459108.
[5]. Shastri, A.: Marketing Strategy of Mcdonald's - A Case Study | IIDE. Iide (2022). https://iide.co/case-studies/mcdonalds-marketing-strategy/.
[6]. Meyer, P.: McDonald's Marketing Mix (4Ps) Analysis. Panmore Institute (2022). https://panmore.com/mcdonalds-marketing-mix-4ps-analysis.
[7]. Eldring, J.: Porter's (1980) Generic Strategies, Performance and Risk. Diplomica Verlag (2009).
[8]. Gregory, L.: McDonald's Generic Strategy & Intensive Growth Strategies. Panmore Institute (2015, October 4). https://panmore.com/mcdonalds-generic-strategy-intensive-growth-strategies.
[9]. Bhasin, H.: Intensive growth. Marketing91 (2015, June 10). https://www.marketing91.com/intensive-growth/#:~:text=Intensive%20growth%20is%20when%20a%20firm%20grows%20by.
[10]. Kenton, W.: Market Penetration. Investopedia (2020, September 26). https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/market-penetration.asp.
[11]. McDonald's. (n.d.). Governance & Stakeholder Engagement. Corporate.mcdonalds.com. https://corporate.mcdonalds.com/corpmcd/our-purpose-and-impact/impact-strategy-and-reporting/governance-and-stakeholder-engagement.html.
[12]. None. Supply chain and logistics construction of western fast food chain enterprises Logistics Technology and Application, (08), 102-104 (2013).
[13]. Ma. The reference of McDonald's staff training model to the staff training of Chinese chain catering enterprises - staff training and development research China Business Review (03), 253-254 (2019). doi: 10.19699/j.cnki.issn2096-0298.2019.03.253.
[14]. Hake.: McDonald's Stock Clearly Benefits From Its Large Buybacks: Here Is Why. Seeking, Alpha (2020). https://seekingalpha.com/article/4330606-mcdonalds-stock-clearly-benefits-from-large-buybacks-is-why.
[15]. Pereira, D.: McDonald's Business Model (2022, March 23). https://businessmodelanalyst.com/mcdonalds-business-model/#Developmental_License.
[16]. MarketBeat.: McDonald's ESG Score and Rating (MCD) (2022, December 11). https://www.marketbeat.com/stocks/NYSE/MCD/sustainability/.
Cite this article
Yu,H. (2023). Strategies in Corporate Finance and Risks Assessment to Improve Profitability--Taking McDonald’s as an Example. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,20,72-80.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Han, J.: The business strategy of Mcdonald's. International Journal of Business and Management, 3(11), 72-74 (2008).
[2]. Chen & Hu.: McDonald's risk management in the context of the COVID-19 Modern Commerce and Trade Industry (18), 33-34 (2020). doi: 10.19311/j.cnki.1672-3198.2020.18.017.
[3]. Li, Y.: Strategic Appraisal of McDonald's (2020). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340601256_Strategic_Appraisal_of_McDonald's.
[4]. Schramade, Willem, McDonald's: A Sustainable Finance Case Study (September 24, 2019). Erasmus Platform for Sustainable Value Creation, September 2019, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3459108.
[5]. Shastri, A.: Marketing Strategy of Mcdonald's - A Case Study | IIDE. Iide (2022). https://iide.co/case-studies/mcdonalds-marketing-strategy/.
[6]. Meyer, P.: McDonald's Marketing Mix (4Ps) Analysis. Panmore Institute (2022). https://panmore.com/mcdonalds-marketing-mix-4ps-analysis.
[7]. Eldring, J.: Porter's (1980) Generic Strategies, Performance and Risk. Diplomica Verlag (2009).
[8]. Gregory, L.: McDonald's Generic Strategy & Intensive Growth Strategies. Panmore Institute (2015, October 4). https://panmore.com/mcdonalds-generic-strategy-intensive-growth-strategies.
[9]. Bhasin, H.: Intensive growth. Marketing91 (2015, June 10). https://www.marketing91.com/intensive-growth/#:~:text=Intensive%20growth%20is%20when%20a%20firm%20grows%20by.
[10]. Kenton, W.: Market Penetration. Investopedia (2020, September 26). https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/market-penetration.asp.
[11]. McDonald's. (n.d.). Governance & Stakeholder Engagement. Corporate.mcdonalds.com. https://corporate.mcdonalds.com/corpmcd/our-purpose-and-impact/impact-strategy-and-reporting/governance-and-stakeholder-engagement.html.
[12]. None. Supply chain and logistics construction of western fast food chain enterprises Logistics Technology and Application, (08), 102-104 (2013).
[13]. Ma. The reference of McDonald's staff training model to the staff training of Chinese chain catering enterprises - staff training and development research China Business Review (03), 253-254 (2019). doi: 10.19699/j.cnki.issn2096-0298.2019.03.253.
[14]. Hake.: McDonald's Stock Clearly Benefits From Its Large Buybacks: Here Is Why. Seeking, Alpha (2020). https://seekingalpha.com/article/4330606-mcdonalds-stock-clearly-benefits-from-large-buybacks-is-why.
[15]. Pereira, D.: McDonald's Business Model (2022, March 23). https://businessmodelanalyst.com/mcdonalds-business-model/#Developmental_License.
[16]. MarketBeat.: McDonald's ESG Score and Rating (MCD) (2022, December 11). https://www.marketbeat.com/stocks/NYSE/MCD/sustainability/.









