1. Introduction
Modern marketing is often defined as a series of actions to sell products and maximize profits oriented to customer needs. Supply chain management is often defined as a set of processes from purchasing to selling products to minimize cost. Research on the combination of marketing and supply chain management began to emerge a long time ago and has been gradually maturing in practice after more than ten years of development. According to Noci, people also find the benefits of combining marketing and supply chain from such relationship management: that is, not only pay attention to the management of the relationship between upstream and downstream but also achieve the combination of cost minimization and benefit maximization, which means to achieve the best financial results and maintain a stable and good system and output [1]. However, in the well-studied field, there seems to be doubt as to whether the goal of lower-cost operation of the supply chain will lead to higher performance and profits. Golgeci and Gligor exclaimed in 2017 that it is because marketing alone to enhance the perceived value of the product in the minds of customers is not a long-term reliable way [2]. It has to be admitted that improving customers' cognition of the value of products can indeed bring higher profits for enterprises. However, if there are only gimmicks, product quality control and production and sales problems in all links, then enterprises will face greater losses. Especially in supply chain management aiming at the lowest cost, whether the low-cost operation can meet the standard and bring a reliable and sustained high profit has become a problem worth thinking about. Starting from the objective of supply chain management, this paper will study whether it can affect sales revenue in the operation process, to test whether the coordination between marketing and supply chain management is relatively reasonable. The main research methods used in this paper are literature research and correlation analysis. It will not only understand the mechanism and effect of actual operation from previous literature but also study the relationship between operation cost and sales income from actual data. Through the combined analysis of the two, the conclusion is drawn and the future research direction is provided. The research significance of this paper lies in understanding the actual relationship between marketing and supply chain management and laying the groundwork for future research.
2. Literature Review
The best existing result of combining marketing and supply chain management is the formation of demand chains. The emergence of the demand chain makes many enterprises get rid of the red sea of cost competition and turn to the production mode based on customer demand. Such strategic transformation and the transformation of production mode make enterprises free from all kinds of political, economic, natural disasters and other emergencies and make a great indelible contribution to the risk management of enterprises [3]. This demand-oriented supply chain management can be said to mainly affect the production link, but a report from Bai, Gao and Lv in 2021 suggested high quality and intelligence and data and fast information delivery processes can lead to better marketing strategies [4]. The whole production process of the supply chain can also be greatly adjusted to adapt to the market, reducing past losses and increasing the possibility of expanding profits. In general, marketing focuses externally on how to increase the perceived value of customers; On the other hand, supply chain management focuses on internally, studying how to use effective resources to make the whole system respond more quickly to the newly decided marketing strategy [5].
In a demand-oriented market, the key competitive factors are related to product availability, delivery accuracy, and product flexibility, which are closely related to the demand-oriented production path.
In addition, customer relationship management (CRM) is a very important branch of marketing, and its role in the supply chain cannot be ignored. The upstream and downstream relationship of the supply chain is composed of suppliers, enterprises and customers. Each layer influences the other. The production process of products is from suppliers to customers. As with the general marketing process, customer analysis is a very important part of the manufacturing process of the supply chain. Ryals and Humphries demonstrated that customers can continue to carry out market segmentation, determine the different needs of different customers, analyze the age, consumption mode, consumption power and consumption preference of customer groups, etc. Meanwhile, according to the importance of customers, the production conditions of the supply chain can be adjusted, and special customized services such as preferential orders and urgent orders can be provided [6]. If the supplier becomes flexible, it can adjust the speed of production and focus on production and other parts. And such requirements often have higher coordination and production capacity requirements for enterprises.
According to Parente and the other two scholars’ reports in 2008, supply chain management itself can be divided into three main links: procurement, operation and logistics [7]. Lamberti and Pero ascertain the claim that the reason why marketing can be applied and achieve good results successfully is that marketing knowledge can be spread to all links of the supply chain, and it can ensure that the marketing knowledge penetrates each staff, forming psychological cognition, to better combine the marketing channels and establish the entire supply chain based on marketing analysis process [8]. Operation link is an important part of the supply chain, its efficiency determines the overall efficiency of the supply chain, which has to mention the operation cost of the supply chain. As we all know, the higher the cost, the higher the price, while the operation cost belongs to the expense of product production. High operation cost means more steps in the supply chain, fast response, strong flexibility, and excellent overall labour capacity, to form a production process that can quickly respond to marketing strategies. Low operation cost means a simple supply chain. It doesn't offer much flexibility, which means the vulnerability of the entire supply chain. Therefore, it is an urgent problem to identify which factors should be used to make the whole supply chain structure efficient and low-cost.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
This article uses data from Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from Statista from 2008 to 2022. This report assumes an ideal condition, that is, this company is used as a case study. It mainly includes the sales revenue, operating cost and logistics cost from 2008 to 2022. The correlation of these related factors will be drawn and calculated, to show the relationship between them. It can be used to analyze the problems of the thesis and draw conclusions. The report also assumes that operating costs and logistics costs have a positive impact on sales revenue and a strong correlation.
3.2. Verification
According to the regression analysis of the literature, it is not difficult to find that operating cost can be used as an indicator to test the flexibility of the supply chain, while sales revenue can be used as an indicator to measure the effect of the supply chain. This paper selects the data of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022, denoting operating cost as O and sales revenue as R [9].
Since logistics is also a very important part of the supply chain, the index that can measure the level of logistics is the cost of commissions and transportation [10]. Sales revenue is denoted R, logistics cost is denoted L. Based on the data, it can be drawn in the following Figure1 and Figure2:
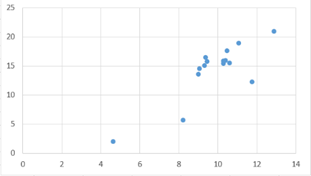
Figure 1: Sales Revenue and Operating Cost of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022.
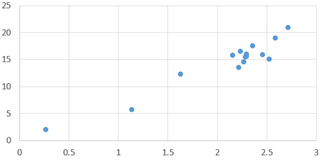
Figure 2: Sales Revenue and Logistics Cost of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022.
3.3. Analysis
According to the table in Figure 1, it can be obtained
\( y=2.1738x-7.0247 \) (1)
Therefore, it can be found that the relationship between sales revenue and operating costs is positively correlated, with correlation coefficient R² = 0.698, indicating moderate correlation, which can be expressed as a relatively correlated state. This shows that operating costs are indeed closely related to sales revenue, and the higher the operating cost, the higher the sales revenue, that is to say, the more mature and flexible the supply chain system, the higher the revenue. Moreover, there is a strong linear correlation between operating cost and sales income, which means that in actual operation, the more money invested in the supply chain, the more efficient and stable operation of the supply chain can be guaranteed. The linear correlation here further proves this point. The higher the efficiency of operation, the closer the cooperation and connection between each link, and the more harmonious the cooperation. Therefore, the linear correlation here provides good proof and future research direction.
According to the table in Figure 2, it can be obtained:
\( y=7.2226x-0.8651 \) (2)
Moreover, the correlation coefficient R² = 0.9191 is highly correlated. The relationship between sales revenue and logistics cost is positive and highly correlated. The higher the logistics cost, the higher the sales revenue. High logistics costs can indicate faster logistics speed and higher logistics support, which represents better supply chain management and better sales revenue. At the same time, the strong correlation between logistics cost and sales revenue is very intuitive and firmly proves the relationship between the operational efficiency of the supply chain and sales performance. Logistics is a part of supply chains and operations that is responsible for the transportation of goods from factories to distribution centres and from retailers to customers. The operational efficiency of this process can be intuitively felt by customers, and enterprises tend to invest a large amount of funds in this link, which is the difference between Figure 1 and Figure 2. Both of them are linearly correlated, while logistics cost is more closely correlated with sales income. That is to say, the link that allows customers to contact directly and give feedback directly will often become the link of large capital investments of enterprises.
The combination of marketing and supply chain management has been the most commonly used situation at present and can minimize costs and maximize profits. However, the factors restricting the development of this process are the response-ability and flexibility of the supply chain, and whether the production direction and logistics transportation of the supply chain can be timely adjusted according to the marketing strategy [11]. Among the many methods that can improve the efficiency of the whole supply chain, cost control seems to be a natural method, but the actual situation shows that the flexibility and timeliness of the supply chain are difficult to improve in a short time.
4. Conclusion
According to the results, the operating cost and logistics cost in the supply chain are highly correlated with the sales revenue, and are positively correlated. This indicates that the input of higher operating costs and logistics costs will enhance the flexibility of the supply chain, which can generate higher sales revenue. In a word, improving the flexibility of the supply chain can bring benefits to enterprises. Enterprises can enhance management in terms of increasing supply chain costs and achieving better coordination and operation ability. In practice, however, this approach does not work well for all companies and all conditions. Generally related to financial matters, tend to become more cautious and not easy to adjust, because it will involve a wide range of personnel and scope, even said, and the environment of the enterprise, and the business scope of the enterprise are related. This puts forward the method of case-by-case analysis. According to the environment of different supply chains and the size of enterprises, what methods should be used to improve the flexibility of supply chains should be decided. Future research is whether there are other ways to improve the operational capacity in addition to increasing the cost of supply chain management, and what kind of supply chain management method can maximize the benefits of enterprises with limited capacity, resources and funds is also worth studying.
Acknowledgement
I would like to thank all the teachers and professors who helped me to create this paper and have always helped me, taught me professional knowledge and completed this paper. Without you, I could not have written this paper. I also want to thank my parents who have always supported me and always supported me behind what I want to do.
References
[1]. Noci, G. (2019). The evolving nature of the marketing–supply chain management interface in contemporary markets. Business Process Management Journal. Vol.25(2). pp. 379-383.
[2]. Golgeci, I. & Gligor, D. M. (2017). The interplay between key marketing and supply chain management capabilities: the role of integrative mechanisms. The Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing. Vol. 32(3). pp.472-483.
[3]. Jüttner, U., Christopher, M., Baker, S. (2007) Demand chain management-integrating marketing and supply chain management. Industrial Marketing Management. Vol.36(3). Pp. 377-392.
[4]. Bai, B., Gao, J., Lv, Y. (2021). Linking marketing and supply chain management in the strategy of demand chains via a review of the literature. Management Research Review. Vol.44 (9). ISSN: 2040-8269.
[5]. Mostaghel, R., Oghazi, P., Patel, P.C., Parida, V., Hultman M. (2019). Marketing and supply chain coordination and intelligence quality: A product innovation performance perspective. Journal of Business Research. Vol.101. pp. 597-606
[6]. Ryals, L. J. & Humphries, A. S. (2007) Managing Key Business-to-Business Relationships: What Marketing Can Learn from Supply Chain Management. Journal of Service Research Vol. 9(4). Pp.312-326.
[7]. Parente, D. H., Lee, P.D., Ishman, M.D., Roth, A.V. (2008) Marketing and supply chain management: a collaborative research agenda. The Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing. Vol. 23(8). pp.520-528.
[8]. Lamberti, L. & Pero, M. (2019). Special issue editorial: Managing the supply chain management–marketing interface. Business Process Management Journal. Vol.25(2). pp. 246-249.
[9]. Statista. (2022) Revenue of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022. Travel, Tourism & Hospitality Leisure Travel. https://www-statista-com.ezproxy.lancs.ac.uk/statistics/266272/revenue-of-cruise-operator-carnival-corporation-und-plc/
[10]. Statista. (2022) Cruise operating costs of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022, by segment. Travel, Tourism & Hospitality› Leisure Travel.
[11]. Kozlenkova, I.V., Hult, G.T.M., Lund, D.J., Mena, J.A., Kekec, P. (2015). The Role of Marketing Channels in Supply Chain Management. Journal of Retailing. Vol.91(4). pp. 586-609.
Cite this article
Jiangyi,T. (2023). From Marketing to Supply Chain Management: A More Flexible Supply Chain System Through Increased Costs. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,38,64-69.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Noci, G. (2019). The evolving nature of the marketing–supply chain management interface in contemporary markets. Business Process Management Journal. Vol.25(2). pp. 379-383.
[2]. Golgeci, I. & Gligor, D. M. (2017). The interplay between key marketing and supply chain management capabilities: the role of integrative mechanisms. The Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing. Vol. 32(3). pp.472-483.
[3]. Jüttner, U., Christopher, M., Baker, S. (2007) Demand chain management-integrating marketing and supply chain management. Industrial Marketing Management. Vol.36(3). Pp. 377-392.
[4]. Bai, B., Gao, J., Lv, Y. (2021). Linking marketing and supply chain management in the strategy of demand chains via a review of the literature. Management Research Review. Vol.44 (9). ISSN: 2040-8269.
[5]. Mostaghel, R., Oghazi, P., Patel, P.C., Parida, V., Hultman M. (2019). Marketing and supply chain coordination and intelligence quality: A product innovation performance perspective. Journal of Business Research. Vol.101. pp. 597-606
[6]. Ryals, L. J. & Humphries, A. S. (2007) Managing Key Business-to-Business Relationships: What Marketing Can Learn from Supply Chain Management. Journal of Service Research Vol. 9(4). Pp.312-326.
[7]. Parente, D. H., Lee, P.D., Ishman, M.D., Roth, A.V. (2008) Marketing and supply chain management: a collaborative research agenda. The Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing. Vol. 23(8). pp.520-528.
[8]. Lamberti, L. & Pero, M. (2019). Special issue editorial: Managing the supply chain management–marketing interface. Business Process Management Journal. Vol.25(2). pp. 246-249.
[9]. Statista. (2022) Revenue of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022. Travel, Tourism & Hospitality Leisure Travel. https://www-statista-com.ezproxy.lancs.ac.uk/statistics/266272/revenue-of-cruise-operator-carnival-corporation-und-plc/
[10]. Statista. (2022) Cruise operating costs of Carnival Corporation & plc worldwide from 2008 to 2022, by segment. Travel, Tourism & Hospitality› Leisure Travel.
[11]. Kozlenkova, I.V., Hult, G.T.M., Lund, D.J., Mena, J.A., Kekec, P. (2015). The Role of Marketing Channels in Supply Chain Management. Journal of Retailing. Vol.91(4). pp. 586-609.









