1. Introduction
Among many clothing enterprises, Bosideng, the leading enterprise in China's Down jacket industry, was founded in 1976 and its main business is the research, development, design and production of Down jacket. After years of development, Bosideng was listed in Hong Kong, China. Since 2012, Bosideng has developed its strategy of "diversification, seasonalization and internationalization". However, the company's performance has significantly declined. By 2015, Bosideng's operating revenue had declined for four consecutive years, from 9.325 billion yuan to 5.787 billion yuan, with net profit decreasing by as much as 80%, and both revenue and net profit fell to their lowest point since going public. So the company decided to transfer from diversification to specification, and the following years it has achieved better performance. Ansoff is the acknowledged scholar who first brought up the company strategies. He explained the concept and significance of the strategies and thought that environment, strategies and organizations are key to improving the efficiency of the company. Later, strategies were brought into the financial management of companies [1]. Richard thought that internal factors play a decisive role, and emphasizes that companies should adjust their products under different circumstances, and should pay close attention to Customers’ needs [2]. Blumenthal focuses on the core business and analyzes the positive effect under different policies [3]. Kotter thought that companies’ sence of crisis comes from the external environment and the fierce competition makes the company transfer [4]. Mitsuru and Tomoatsu used the case study of a multinational company and concluded that it transformed in order to gain an advantage when competing in the industry [5]. Longwen Hou studied the significance and positive effect of strategies on companies and gave some examples as references [6].
After carefully studying several papers, this paper focuses on the reasons why Bosideng had to change its strategies and how could the company transfer successfully and what other companies learn from Bosideng’s experience. What’s more, this paper uses case study analysis to put the theories into practice.
So focusing on the transformation, this research can have a thorough understanding of how Bosideng achieved a reverse performance and could be a reference for other companies.
2. Case Study
2.1. Background of the Company
Bosideng was founded in 1976 and listed on HKSE on October eleventh, 2007, and now it is the largest down garment enterprise in China, its main business activities are down coats, producing clothes for other brands and diversified clothes.
Though taking the leading position in the down coats industry, its development is not always smooth. It has experienced two tremendous revolutions in its history: one is in 2007 when the company decided to diversify its products; another is in 2018 when the company decided to specialize in the main products: down coats. In the first revolution period, Bosideng decided to diversify its products: apart from the down coats, it also produce men’s wear and fashion items. However, its revenue decreased and the inventory was overstocked as well as shutting down many stores, so the company scrutinized the policies and decided to transfer; In the second revolution period, Bosideng had diverted from diversification to specification. It focused on the main products--down coats and aimed to provide various down coats for different users. The revenue has grown at a steady speed and the number of the chain stores began to increase at the same time, with the reputation and brand image being lifted in customers. So the article aims to find the reasons why the company needed to transfer and how could transfer successfully.
2.2. The Importance of the Diversification of Bosideng’s Strategies
Apart from the down coat as the main business, the company also seeks to develop more diverse products. At that time, Bosideng was in the leading position in the down coat industry in China and was listed on Hong Kong Stock Exchange, so the company analyzed the external environment using Porter’s Fives Model and internal factors using SWOT analysis to evaluate the potential benefits that diversification could bring for Bosideng.
2.2.1. Porter’s Five Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces was brought in 1985 by Micheal Porter. This model thinks that there are five forces that could influence the industry’s competitiveness and the company’s ability to survive under the competition, and the five forces are bargaining power of suppliers、bargaining power of buyers、threats to new entrants、substitutes、rivalry [6].
Bargaining Power of Suppliers. Bosideng takes up a large portion of the down coats market, so it needs constant suppliers of the feather/fabric for the down coat, so they have high bargaining power; but because it is a green hand in other kinds of clothes, so whether the customers will accept its products remains doubtful, so their demand, sustainability is not promising. As a result, Bosideng does not have a strong bargaining power when faced with suppliers.
Bargaining Power of Buyers. Previously, customers buy down coat in order to keep warm, so their demands are very simple. What’s more, Bosideng is in the leading position in the industry, so as a consequence, the prices are steady, for the down coats just play a functional role and the brand premium is not very high. The customers do not have many choices, so their bargaining power is relatively low; however, when referring to other kinds of clothes such as leisure style, fashion styles or sports clothes, customers have much more other choices, for example, in the women clothes of fashion style, when referred to high-end brands, people can choose LV, Gucci, Dior, etc., when referred to economic clothes, consumers can choose HM, GU, UNIQLO and so on, so their bargaining power towards Bosideng is high.
Threats of New Entrants. As for the down coat industry, new entrants do not have advantages because Bosideng has its own exclusive technology and large-scale economy; while other areas are mature, and the market is divided in detail, so if Bosideng wants to join other areas, the company will face much pressure.
Substitutes. Down coats are more of a functional clothes, and Bosideng has developed for several years and earns a reputation for its good quality as durable and cold-resistant, and it also has technology that it can gain a more favourable position than its competitors; however, if they want to advance into no matter the leisure or the fashion field, they are not good at it.
Rivalry. In domestic market, Bosideng has achieved relatively superior status in the industry, regarding to the quality and the reputation among elder people, so when competing with the existing rivals, they have advantages. When the company attempted to enter the other fields such as clothes for fashion-style or commuters, it was faced with great difficulty, because the existing competition is fierce. What’s more, diverting to other fields will distract the attention and resources, so the current main business will not be as strongly funded as before thus its development would be impaired.
2.2.2. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis was brought up by KJ Andrews in 1971 in his book “Corporate Strategy Notion”. It analyzes the internal and external factors that could influence the corporate’s management strategies.
Strength. As for diversification, Bosideng has several advantages: firstly, Bosideng has abundant resources, that is, Bosideng listed on HKSE in October 2007, which made it have enough fund to explore other clothes areas such as the fabrics and the designs. Secondly, since Bosideng has developed for many years and achieved a leading role in the down coats industry, meaning that it has mature sales channel: retail network so it can promote its new products to its current customers and existing sales stores and workers, which, without doubt, could save the company a lot of costs. Thirdly, Bosideng has developed a good reputation for the products’ quality, so customers have more confidence in this brand when they encounter another brand-new products.
Weakness. However, diversification also has many shortcomings: firstly, customers’ stereotype on Bosideng: consumers tend to regard the brand particularly for down coats, so when they need to buy fashion or sports clothes, they would not give Bosideng a slight consideration, so the new products lack recognition from customers. Secondly, the fabrics needed for the fashion industry and the sports line are different from the down coats, so Bosideng has to hire new designers and seek new suppliers, and at the beginning, they could not achieve large-scale economics. So they lack competitiveness in the cost and diversification of the products. Thirdly, diversification could blur the brand positioning: different lines are mixed, which means that stores for down coats also sell men’s suits, so the competition between sub-brands is fierce, worsening the condition.
Opportunity. Diversification could bring more opportunities for Bosideng, for example, Bosideng could achieve an expanded market: previously, the company only had down coats and now it has men’s clothes and fashion style clothes, obviously, the market is expanded. What’s more,by entering new markets and having expanded markets, Bosideng might have growing revenue: in the past, the company could only sell down coats, which means that it could earn one season’s revenue, but now with more diverse products, it expands its products from two seasons into four seasons.
Threats. Diversification is also a double-edged sword: while it might bring more opportunities for Bosideng, it could bring threats at the same time. When Bosideng entered other areas, it was faced with more intense competition, that is, it had to compete with much more brands which have their loyal consumers. Moreover, the products of Bosideng had more substitutes for the clothes do not need some unique technologies so the threshold is not as high as the down coats industry.
2.3. The Strategies Bosideng Takes
2.3.1. Pricing&Product Strategy
The company has several different products line, and every line aims at different people with different incomes and different demands. For example, firstly, the fashion line is more expensive than the general one for the fashion line involves famous designers and has idles to represent the brand, which means the costs are higher; also, people who pursue fashionable items could afford the relatively high prices. Secondly, the prices of the outdoor-activity line and commuters line are also higher, for the target people of the two series’ products are relatively high-income people, for they can stand on their own feet and have spare money to support their hobbies and have some specific features such as water-proof or are defensive to extremely cold weather for mountain climbers or are more well-signed which is lighter and stylish for staff. As for the ordinary line, target customers buy it only to keep warm other than other extra demands, so the products are cheaper and more economical [7].
2.3.2. Promotion Strategy
Firstly, Bosiden has been spending lots of budgets on advertisement and promotion, that is, holding several fashion shows、cooperating with nationwide famous designers or inviting stars as an icon, such as Yangmi, Jackson Yee, Eileen Feng Gu, they stand for different products line: Yangmi represents the fashion line; Jackson Yee represents the men’s clothes, and Eileen represents the sports and the outdoors line. What’s more, except for the representatives, they also promote their products by advertising some clothes in the same style as the stars, so the fans are more willing to pay for the clothes. Now, they select younger stars to attract young consumers.
2.3.3. Place Strategy
Previously, the company had many retailers and the products displayed in the stores were out-of-date and mixed and the services were not good; after transformation, now most of the stores are regular chain stores, so headquarters could have better control over the inventory, logistics, services and could adapt its products to the local tastes; Moreover, the company also adapts a combination of physical stores and online stores, as well as cooperating with several famous anchors: they give up few price advantages to enhance their sales and popularity as well as promoting their products to a wider range of consumers.
3. Changes after the Transformation
3.1. Profitability Metrics
3.1.1. Earnings Per Share/Diluted Earnings Per Share
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is probably the most common measure of the firm profitability, and it reflects profitability at the shareholder level, and the function is as follows:
EPS= Net Income/Weighted Average Shares
Many companies have financial instruments such as stock options or convertible debt that can be converted to common shares, so this paper also uses diluted earnings per share. Diluted earnings per share is the portion of a firm’s profit allocated to each share after adjusting for possible transactions that could trigger an increase in the number of outstanding shares. The function is as follows:
Diluted EPS=Net Income/(Weighted Average Shares+Convertible Securities, Including Preferred Shares, Stocks Options, Warrants,etc.)
Table 1:The earning per share and diluted earnings per share of Bosideng.
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
Earnings Per Share | 5.82 | 9.32 | 11.27 | 15.98 | 19.14 |
Diluted Earnings Per Share | 5.80 | 9.17 | 11.06 | 15.77 | 18.78 |
Resources: from Bosideng’s annual report.
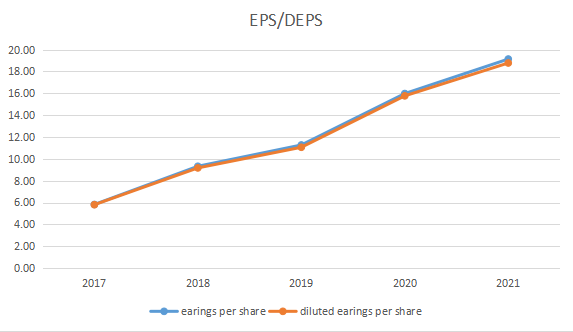
Figure 1: EPS/DEPS of Bosideng.
As is shown in Table 1 and Figure 1, it can be seen that the EPS/DEPS has gone up steadily, which means that the profitability has been increasing after the transmission.
3.1.2. Gross Margin of the Group
Gross profit could present the profitability of the company, the higher the gross profit, the better ability a company has to create profits. The calculating formula is shown below:
Gross margin =(sales revenue-sales cost)/sales revenue*100%
Table 2:The gross profit of Bosideng.
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
Gross margin | 46.40% | 53.10% | 55.00% | 58.60% | 60.10% |
Resources: From Bosideng’s annual report.
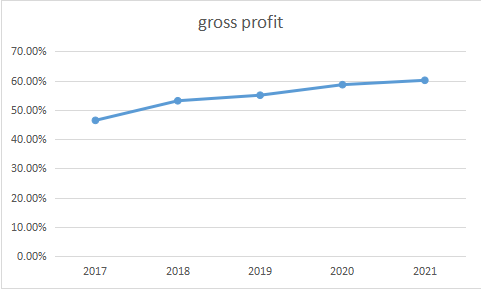
Figure 2: Gross profit of Bosideng.
As is shown in Table 2 and Figure 2, we could see that Bosideng’s gross profit increases steadily after the transformation. Even during the COVID-19 period its performance was stable.
3.2. Liquidity Metrics
3.2.1. Inventory Turnover Day
Inventory turnover day starts from the date when the inventories are procured to the date when the inventories are finally sold out. The shorter the inventory turnover day is, the shorter the inventories could be turned to cash, the better the company’s ability to manage the inventory. The calculating formula is as follows:
Inventory Turnover Day=(Average Inventory*365)/Cost of Sales
Table 3:The inventory turnover day of Bosideng.
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
Inventory Turnover Day | 111 | 127 | 155 | 175 | 150 |
Resources: From Bosideng’s annual report.
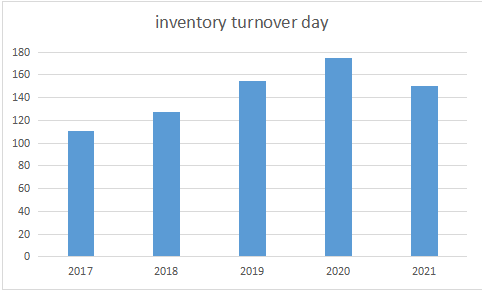
Figure 3:Inventory Turnover Day of Bosideng.
As is shown in Table 3 and Figure 3, we could see that the inventory turnover day increased before 2020, and from 2020 to 2021, the inventory turnover day decreased for the company asked the chain stores to order goods according to the sales demand, so the retailers’ first order ratio remains low level, which reduces the inventory turnover day. What’s more, Bosideng has adapted CDC systems, which enable them to have better control over the nationwide inventories and can dispatch goods to serve customers’ needs[8].
3.2.2. Current Ratio
Current Ration reflects the company’s ability to pay back its short-term liabilities(debt and payable ) with its short-term assets(cash, inventory, receivables)
The higher the current ratio is, the more capable the company is of paying its obligations. The calculating function is as follows:
Current Ratio=Current Assets/Current Liabilities
Table 4:The current ratio of Bosideng.
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
Current Ratio | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.5 |
Resources: From Bosideng’s annual report.
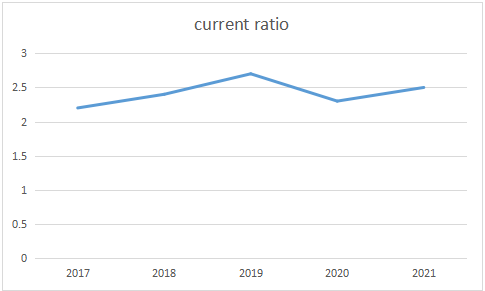
Figure 4:Current Ratio of Bosideng.
Form Table 4 and Figure 4, we can see that the current ratio was on the increasing trend before 2019, and dropped in 2020, which was under the effect of COVID 19, and it climbed slowly in 2021. the whole process, current ratio is above 1, meaning that the company’s cash flow is healthy.
3.3. Credit Metrics
Debt ratio indicates the company’s ability to repay the principles and pay the interests, the calculating formula is as follows:
Debt Ratio=Total Debt/Total Assets*100%
Table 5: The debt ratio of Bosideng.
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
Debt Ratio | 23.90% | 16.10% | 24.00% | 20.30% | 20.80% |
Resources: From Bosideng’s annual report.
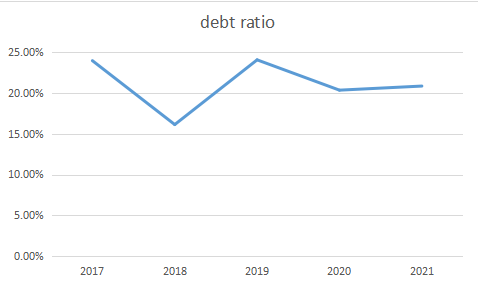
Figure 5:Debt ratio of Bosideng.
From Table 5 and Figure 5, we can see the debt ratio declined in 2018, which is the start of the transformation, and during other periods, it is relatively stable, which means the capital structure is healthy.
4. Suggestions on the Following Development of Bosideng
Bosideng should stick to the core main business. Though diversification is beneficial at most times, it is not suitable for all companies. As for Bosideng, it’s better to base it on the main business where it has unique core techniques; If the company wants to explore other areas, it should have something to do with the down coats, so it could make use of the existing advantages and gain more recognition from customers.
Traditional businesses can seek new opportunities, for example, as for the down coats, previously, people just uses them for warmth, so their demands were simple and not big, but the company could foster people’s interests and needs so as to increase the sales and revenue. For example, make the clothes suitable for more occasions or specialize each type for certain occasions: work suits that are smart and fashionable or out-door types that are water-proof and wind-proof; or add more designs into to ordinary type. Consumers buy down coats not only to keep warm but also to pursue fashion and trends. As a result, the sales will definitely increase.
Bosideng should be adapting more diverse methods to promote products. Up to now, Bosideng has invited several famous idols to represent the brand, which has significant importance in the rise of the down coats. In the future, the company could hire different people to stand for different products line so the targeted customers will have a better understanding of the products and would be more willing to pay for the products. However, the company must check in advance whether the stars are qualified and whether the idols they invite have law or moral issues problems to prevent the company’s reputation from being harmed.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, the history of Bosideng has been reviewed and the reasons why Bosideng had to transform has been studied in detail; What’s more, the strategies Bosideng took to transform successfully are scrutinized carefully. From all the analysis above, it could be concluded that the poor performance and fierce competition made Bosideng determined to change its strategies and after adopting a specification strategy with more advertising and more channels to promote the products, Bosideng has achieved sales growth significantly. So diversification is not beneficial for all companies. However, the investigations could be improved if more financial ratios could be calculated such as the quick ratio、return on equity and so on. It is without a doubt that comparing with the average industry data would make the advances of Bosideng more profound and measurable.
References
[1]. Ansoff H I. Managing strategic surprise by response to weak signals[J]. California Management Review, 1975, 18(2):21-23Richard E.Cascarino.Strategic Planning[M].Auditor’s Guide to IT auditing, Second Edition,2015(65):147-158
[2]. Blumenthal.Photonic Packet Switches:Architectures and Experimental implementations[J].Proceedings of the IEEE,1994,82(11):1650-1667
[3]. Kotter,The Balanced Scorecard:Measures That Drieve Performance[J].Harvard Business Review,2005,83(7):172
[4]. Mitsuru Kodama,Tomoatus Shibata,Strategy transformation through strategic innovation capability a case study of Fanuc[J].Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences,2017(2):373-389.
[5]. Wenliang Hou.Enterprise financial strategy research[J].Finance and accounting newsletter,1993(02):19-22
[6]. Lu Zhang. Theoretical research and reflection on Porter's Five forces model[J]. Brand(Finance and accounting newsletter), 2015(06):345.
[7]. Fanqi Liao. Research on financial performance of Bosideng under strategic transformation[D]. Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, 2022. DOI:10.27731/d.cnki.ggzcj.2022.000140.
[8]. Bingxue Liu. Research on financial strategy of Bosideng Company based on financial strategy matrix[D]. Changchun University of Technology, 2021.DOI:10.27805/d.cnki.gccgy.2021.000521.
Cite this article
Chen,Y. (2023). Analysis of Bosideng’s Strategic Transformation. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,43,70-78.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Ansoff H I. Managing strategic surprise by response to weak signals[J]. California Management Review, 1975, 18(2):21-23Richard E.Cascarino.Strategic Planning[M].Auditor’s Guide to IT auditing, Second Edition,2015(65):147-158
[2]. Blumenthal.Photonic Packet Switches:Architectures and Experimental implementations[J].Proceedings of the IEEE,1994,82(11):1650-1667
[3]. Kotter,The Balanced Scorecard:Measures That Drieve Performance[J].Harvard Business Review,2005,83(7):172
[4]. Mitsuru Kodama,Tomoatus Shibata,Strategy transformation through strategic innovation capability a case study of Fanuc[J].Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences,2017(2):373-389.
[5]. Wenliang Hou.Enterprise financial strategy research[J].Finance and accounting newsletter,1993(02):19-22
[6]. Lu Zhang. Theoretical research and reflection on Porter's Five forces model[J]. Brand(Finance and accounting newsletter), 2015(06):345.
[7]. Fanqi Liao. Research on financial performance of Bosideng under strategic transformation[D]. Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, 2022. DOI:10.27731/d.cnki.ggzcj.2022.000140.
[8]. Bingxue Liu. Research on financial strategy of Bosideng Company based on financial strategy matrix[D]. Changchun University of Technology, 2021.DOI:10.27805/d.cnki.gccgy.2021.000521.









