1 Introduction
The development of new energy vehicles has become a critical strategy for several countries seeking to achieve green industry, energy conservation, and pollution reduction. In this regard, China has also implemented a few supporting policies for new energy vehicles. Purchases of new energy cars may be eligible for government financial subsidies, and there are favored policies for the purchase of new energy vehicles in many places where such purchases are prohibited [1]. China's oil consumption ranks second in the world, even though oil is primarily reliant on exports. Developing new energy vehicles aggressively and decreasing fuel vehicle production and sales will help China's energy consumption structure change from a heavy reliance on oil to an increased reliance on electricity consumption.
SWOT analysis mainly integrates the internal and external environment of a company to study its competitive situation [2]. It analyzes the company's strengths and weaknesses, as well as what opportunities and threats it faces [3]. The 4PS of Marketing is a management decision-based approach to marketing products and services. It includes the product (how the product meets the customer's needs), price (how much the product is worth), location (where customers look for the product) and promotion (how to differentiate the product from competitors).
This article applies SWOT analysis to examine why the Tesla brand chose to construct manufacture in China, the benefits, and the marketing strategies employed. It offers a range of ideas and experiences for other new energy vehicle firms interested in entering the Chinese market.
2 SWOT Analysis of Tesla's Operations in China
2.1 Strengths
To begin with, Tesla Motors has a brand advantage in the sector of alternative energy cars. Tesla Motors' entrepreneurial team first leveraged IT principles to construct automobiles rather than traditional car manufacturers as an emerging brand. It has a huge number of devoted users. Elon Musk claimed $3.11 billion in sales in China during the third quarter, with the Model 3 and Y ranking in the top three in China's new energy vehicle passenger car market. [4] Also, it is clearly a leader in the new energy vehicle sector due to its superb technology and creative design. [5] Second, when compared to existing competition. Tesla vehicles offer cutting-edge product technology. Its products are well-known for their technology and performance, and it holds a commanding position in the fields of software and hardware design, platform layout, information systems, and power systems. A Tesla is a piece of hardware that is controlled by software. It will first provide the car with an advanced hardware basis. Later, the car’s system will be updated via OTA upgrade to improve the driver's experience. In addition, it is the first to combine dual-motor all-wheel drive and efficient battery management technology in the power system, giving Tesla automobiles a long battery life and great performance when compared to competitors. Furthermore, Tesla is concerned with customer experience and has several offline experience locations across the world, allowing customers to properly grasp Tesla's goods and culture. [6] In China, for example, there are 40 Tesla experience stores, mostly in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and other cities. Traditional auto companies use 4S storefronts as physical maintenance centers. On the other hand, Tesla has established a customer-centric intelligent service process, which "replicates" links such as car viewing, test driving, ordering, and after-sales on the Internet. This provides consumers with an innovative and humanized service system.
2.2 Weakness
Tesla's product line is restricted. Tesla now sells four models: Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y. With fewer product designs available, buyers have limited options, constraining Tesla's sales, and growth. Another concern is the battery life. First-tier cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, and others have created a huge number of new energy vehicle charging stations, but supply remains limited. The supply-demand imbalance in cities with less developed economies will only worsen. As a result, the charging infrastructure is not flawless, which prompts some buyers to avoid purchasing Tesla goods. In 2021, Tesla suffered repeated brake failure accidents, leading buyers to believe there was a safety risk. On May 3, 2022, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States announced the recall of almost 130,000 Tesla vehicles owing to overheating issues with certain of the vehicles' central information displays. The report sparked debate about Tesla's history of recalls, with at least a quarter of the cars it formerly sold being recalled. The numerous recalls have also impacted the Tesla brand's reputation. [7] Concurrently, customer trust in the brand has declined.
2.3 Opportunities
The development of new energy vehicles is critical for addressing urban environmental issues and reducing human reliance on nonrenewable energy. State and local governments have introduced over 600 initiatives to assist the development of the new energy vehicle sector to boost new energy vehicle market consumption. These rules address technology innovation, promotion, and implementation, as well as safety oversight and other issues. Subsidies for the purchase of new energy cars, unrestricted travel, unlimited purchases, and the use of special licence plates, for example, have all assisted in the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry. [8]
Furthermore, China has built a national manufacturing innovation center for power batteries and intelligent networked cars, as well as a new energy vehicle industry technological innovation project. The Power Battery Innovation Center, for example, is China's first national-level industrial innovation center. It assists upstream and downstream firms in increasing R&D expenditure, innovating business models, and forming a powerful endogenous driving force for industrial growth. Another positive scenario for new energy cars is rising customer environmental consciousness. When shopping, the public will pay greater attention to energy saving and emission reduction and will prefer more ecologically friendly items. On the one hand, when it comes to purchasing items, Chinese shoppers have begun to choose those that are helpful to their health. According to Figure 1, consumers in China have increased their spending on health and lifestyle products, and sales of organic food have surged by 125% since 2015, reaching 80.5 billion RMB in 2020. Consumers, on the other hand, have come to prioritize the long-term interests of individuals and society. They always choose ecologically friendly items that are low in carbon, low in emissions, or even zero in emissions. Customers, for example, will bring their own shopping bags.In other words, items with environmental protection ideals are exactly what the Chinese market wants because of current Chinese fashion trends. Pure electric car goods fueled by renewable energy also satisfy consumers' demands. [10]
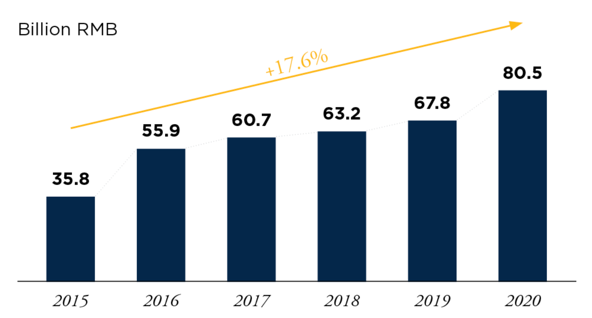
Fig. 1. State Administration for Market Regulation. [9]
2.4 Threats
With the Chinese government's adoption of pro-new energy vehicle regulations, the new energy vehicle industry is continuously expanding, and competition among various manufacturers is intense. According to the development research of Tesla's wholly owned plant in Shanghai, BYD's quote is between 129,900 and 329,900, while BAIC's EC series quotation is between 121,900 and 166,800. MODEL S prices range from 782,900 to 1,091,000, while MODEL X prices range from 861,800 to 1,189,300. [11] It's clear that Tesla is aiming for the high-end consumer market, and the lack of a pricing advantage has turned off a lot of potential purchasers. Affected by Tesla's construction in China, competitors such as Volkswagen, Jianghuai, and Seat have united against it. They have established their own R&D centers, and technological competition has become increasingly fierce. As a result, Tesla faces both the pricing threat of rival products and the threat of the opponent's technology constantly improving.
3 The Four Ps of Marketing
3.1 Product
Tesla sells five models in China: Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y, and Cybertruck, with sedans and SUVs being the most widespread. It caters to a diverse clientele, and items are constantly updated to meet the needs of customers with varying economic levels. Tesla has developed luxury sedans, premium sports vehicles, and SUVs with a major target market of high-end income groups, focused on the industry’s idea of green environmental protection. The launch of mid-to-low-end automobile items enlarged the target consumer base to the middle-class group, resulting in increased product sales and brand exposure. For example, entry-level luxury automobiles meet customers' brand quest and respect for environmental protection ideals, but the significant and affordable costs improve the spending power of young consumers. Tesla has witnessed a jump in sales and income since it began mass manufacturing in China after constructing its Gigafactory in Shanghai. Tesla follows the trend of technology growth in China by offering a simple method of direct sales on the Internet to better serve clients in many regions. At the same time, Tesla has achieved product marketing, which is to use the "word of mouth" of customers to attract new consumers. Consumers may have a more intuitive purchase experience and generate new consumer markets when combined with the unique marketing strategy of physical experience stores, therefore encouraging the platform's development. (Expanding the consumer market and encouraging platform growth) [8]
3.2 Place
Tesla's sales approach in China differs from that of typical local automobile manufacturers. There is no middleman in the direct sales model, which has reduced the gap between the brand and consumers and made customer communication simpler. In the Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Social Sciences and Economic Development, Jinpeng Liu and Shiyun Zhou stated that, up to 102 car stores and showrooms would have been created in China by 2020. To create a high-end automotive brand, most brick-and-mortar store structures are mostly situated around the city center and packed retail districts. [7] Tesla's buying approach involves the buyer first making a deposit, then contacting the designer to create the personalized automobile look and configuration, and then building it to the customer's specifications. Customers may monitor the production process on the internet at any time. Customers who have chosen their favorite items offline can also purchase them online, and the products will be delivered door-to-door. Unlike the dealer model, experiential shops and online direct sales ensure that customers receive high-quality goods and services. Tesla's revolutionary service approach further increases the openness and transparency of product information. Simultaneously, the direct selling technique saves superfluous marketing efforts, improves cash flow and inventory management, and lowers the cost of purchase, usage, and time for customers.
3.3 Price
Tesla's flexible pricing strategy allows its product prices to fluctuate based on government strategies, market changes, and internal company decisions. According to Xuming Huang's research on Tesla Motors' marketing strategy in China, Tesla's product prices have experienced several fluctuations, rapid changes, and significant ups and downs from 2019 to date [12]. Its high transportation and R&D costs, as the first company to produce electric vehicle technology in China, have resulted in higher starting prices than other competitors in the same category. The non-advantageous price does not help it to capture the market in a short period of time and does not attract enough consumers to be competitive and profitable. Therefore, Tesla's first step in the Chinese market is to adopt a high price strategy to give the impression of a premium brand to the middle- and high-income consumer groups. The perception of a classic luxury electric car is shaped in the Chinese market, making the brand's cars the first choice for many high-end people to display status symbols. Also, the high-end product image provides the groundwork for a positive company image in the following stage of the approach.
The second step in Tesla's strategy is penetration pricing. The first is to expand the customer base as a target-oriented approach, so that the product can quickly take over the market and improve the competitiveness in the later stage. Tesla's different levels of products correspond to different consumer groups. For example, the Model 3 and Model Y are more affordable and cost-effective choices than the Roadster, Model S, and Model X. In 2020, Tesla reduced the price of the Model 3 by about $100,000. Also, in 2021, the two Model Y models were reduced by $165,100 and $148,100 [13]. This shows that the strategy of gradually reducing the price is to further capture market share. According to the spending power of the low- and middle-income groups, low-price marketing can stimulate purchases and open the market to sales. To sum up, Tesla's pricing strategy mainly adopts the skimming pricing method. First set a high price to stimulate the curiosity of consumers and get a high revenue return. Then, to meet the needs of different consumer groups, Tesla introduces more cost-effective products to capture the market and maximize brand profit.
3.4 Promotion
Tesla's promotion strategy is different from traditional car companies, relying mainly on emerging media methods, such as Twitter forums, to expand the scope and strength of advertising. To promote the impact and development of the product technology, the company's CEO has personally published blog posts about it. Tesla also updates car information and news in real time on its official website and launches limited models and customized models to attract consumers' attention. The offline experience stores and car centers showcase the products, allowing customers to have a more direct experience without the dealership's promotion. Another promotion strategy of Tesla is to make use of the Netflix effect to promote its products to more consumers. The first way it uses the Netflix effect to market its products is by using the names of celebrities. Unlike other brands that use the names of their founders, Tesla uses the name of a famous physicist who has made a huge impact on the world. By associating the product with high technology through such a name, it also shows Tesla's ambitious goal to build a high-end brand image to promote to the world.
In addition to this, Tesla Motors defines itself as a luxury brand that enjoys a higher reputation in the market and a more high-end customer orientation than the average car company. Among its customers are many business celebrities, such as Lei Jun, Larry Page, Sergey, Schwarzenegger, and so on [14]. These celebrities with high social status have chosen Tesla, which also affirms the quality and technology of its products. The celebrity effect has a positive impact on increasing brand recognition and spreading word of mouth. These celebrities also bring their own popularity, and their huge fan base will imitate them out of love for their idols, thus increasing the loyalty of more customers to the brand.
4 Conclusion
The following findings may be taken from this paper's analysis of the marketing environment and marketing tactics of Tesla enterprises in China. Tesla has a strong brand, cutting-edge product technology, and an easy-to-use service system. However, it has a limited product offering, charging limits, and safety concerns that must be addressed. National policies, industry innovation, and consumer environmental awareness are all positive external environment trends for marketing. The competition is also fiercer. Tesla's marketing strategy aims to provide high-end and low-end products to fulfill the demands of various consumers with the theme of green and environmental protection. Additionally, it employs direct sales as well as online and offline synchronization to cut purchase and time expenses. At the same time, it is price flexible enough to capture the market and uses emerging media to promote and spread awareness.
While Tesla's success in China is instructive, the hurdles it faces should be considered by manufacturers hoping to enter the new energy vehicle market. As a result, this article seeks to elicit some lessons from Tesla's marketing strategy for automakers to apply to achieve a competitive edge in the future Chinese new energy vehicle market.
However, due to the limited data of Tesla at present, and different cities have different policies for new energy vehicles, this research is based on the national market. It is expected that future studies can expand the amount of data to take different policy factors into account.
References
[1]. Dai, Xinran and Zhang, Haoyang. The Opportunities and Challenges of Tesla’s Entry into Chinese Market. ATLANTIS PRESS. 2022: 824
[2]. Zhang, Jihua and Wang, Rong. Research on the Marketing Strategy of New Energy Vehicles in SL Company. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, Vol.9 No.2. Scientific Research. 2019: 306
[3]. Wang, Maoheng. Research on the Brand Marketing of Tesla Electric Vehicle. SIAM UNIVERSITY. 2018: 3-4
[4]. Cheng, Evelyn. Tesla’s China sales have grown to nearly half the size of the company’s U.S. sales. CNBC. 2021
[5]. Yao, Zhenyu. Marketing Strategy Research of Tesla Motors. University of Guodongcaijing. WANFANG. 2016: 23
[6]. Du, Xiaofei and Li, Bingcan. Analysis of Tesla’s Marketing Strategy in China. ATLANTIS PRESS. 2021: 1685
[7]. Liu, Jinpeng and Zhou, Shiyun. Analysis of China's New Energy Vehicle Market Competitive Strategy: Taking Tesla and NIO as Examples. ATLANTIS PRESS. 2022: 360
[8]. Qi,Fangming. Research on the marketing strategy of Tesla Motors brand in China. Yingxiaoxinji. WANFANG. 2020: 115
[9]. Lennefalk, Johan and Liu, Windy. Health on the rise – Opportunities in China within healthy food, beverages, and supplements. BUSINESS SWEDEN. 2022
[10]. Li, Shan. Analysis of the comparative advantages of the macro environment of Tesla and domestic electric vehicles in China. Xiaofeikandao. WANFANG. 2016: 32
[11]. Qi, Renyue. Study on the development of Tesla's wholly-owned factory in Shanghai based on SWOT. WANFANG. 143
[12]. Fuming, Huang. Research on the Marketing Strategy of Tesla Motors in China. WANFANG. 2016
[13]. Mao, Qingsong. Factors, Challenges and Implications for the Rise of Tesla Motors Brand. Shangyanyanjiu. ZHIWANG. 5
[14]. Chen, Zhengqi. From the Tesla car phenomenon to see the way of brand marketing. Jingyingguanli. ZHIWANG. 2013: 201
Cite this article
Li,J. (2023). Research on the Marketing Strategy of Tesla Vehicle in China. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,4,402-407.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development (ICEMGD 2022), Part Ⅱ
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Dai, Xinran and Zhang, Haoyang. The Opportunities and Challenges of Tesla’s Entry into Chinese Market. ATLANTIS PRESS. 2022: 824
[2]. Zhang, Jihua and Wang, Rong. Research on the Marketing Strategy of New Energy Vehicles in SL Company. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, Vol.9 No.2. Scientific Research. 2019: 306
[3]. Wang, Maoheng. Research on the Brand Marketing of Tesla Electric Vehicle. SIAM UNIVERSITY. 2018: 3-4
[4]. Cheng, Evelyn. Tesla’s China sales have grown to nearly half the size of the company’s U.S. sales. CNBC. 2021
[5]. Yao, Zhenyu. Marketing Strategy Research of Tesla Motors. University of Guodongcaijing. WANFANG. 2016: 23
[6]. Du, Xiaofei and Li, Bingcan. Analysis of Tesla’s Marketing Strategy in China. ATLANTIS PRESS. 2021: 1685
[7]. Liu, Jinpeng and Zhou, Shiyun. Analysis of China's New Energy Vehicle Market Competitive Strategy: Taking Tesla and NIO as Examples. ATLANTIS PRESS. 2022: 360
[8]. Qi,Fangming. Research on the marketing strategy of Tesla Motors brand in China. Yingxiaoxinji. WANFANG. 2020: 115
[9]. Lennefalk, Johan and Liu, Windy. Health on the rise – Opportunities in China within healthy food, beverages, and supplements. BUSINESS SWEDEN. 2022
[10]. Li, Shan. Analysis of the comparative advantages of the macro environment of Tesla and domestic electric vehicles in China. Xiaofeikandao. WANFANG. 2016: 32
[11]. Qi, Renyue. Study on the development of Tesla's wholly-owned factory in Shanghai based on SWOT. WANFANG. 143
[12]. Fuming, Huang. Research on the Marketing Strategy of Tesla Motors in China. WANFANG. 2016
[13]. Mao, Qingsong. Factors, Challenges and Implications for the Rise of Tesla Motors Brand. Shangyanyanjiu. ZHIWANG. 5
[14]. Chen, Zhengqi. From the Tesla car phenomenon to see the way of brand marketing. Jingyingguanli. ZHIWANG. 2013: 201









