1. Introduction
Gasoline is a petroleum product and an important secondary energy source in China. It is of great significance in transportation and industry in modern society. Gasoline is the most commonly used fuel for automobiles. It is not only an essential energy source for transportation but is also used for the operation of many mechanical devices. It can be said that gasoline laid the foundation for the transportation and industrial development of China. The stability and security of gasoline supply are important guarantees for national economic development, so it is necessary to stabilize gasoline prices.
However, in the past four years, Chinese gasoline price fluctuations have shown very unusual trends. Gasoline prices have seen a trough and a peak in just a few years, going from one extreme to the other due to the COVID and the Russia-Ukraine conflict one after another. This article is to study, during the COVID period, what factors have affected the fluctuation of gasoline prices in China, and how to solve the problems of these factors. The purpose of this study is to propose possible countermeasures to stabilize gasoline prices, prevent huge price fluctuations that may occur in the future, and thus promote stable economic development.
2. Characteristics of Chinese Gasoline Price Trend
In China, gasoline No. 92 and No. 95 are the gasoline most people use. In the following price analysis, NO. 92 gasoline in Beijing is used as an example. The price trend of No. 95 gasoline is basically the same as that of No. 92 gasoline, but the average price is 0.5 CNY/L higher. according to figure 1.
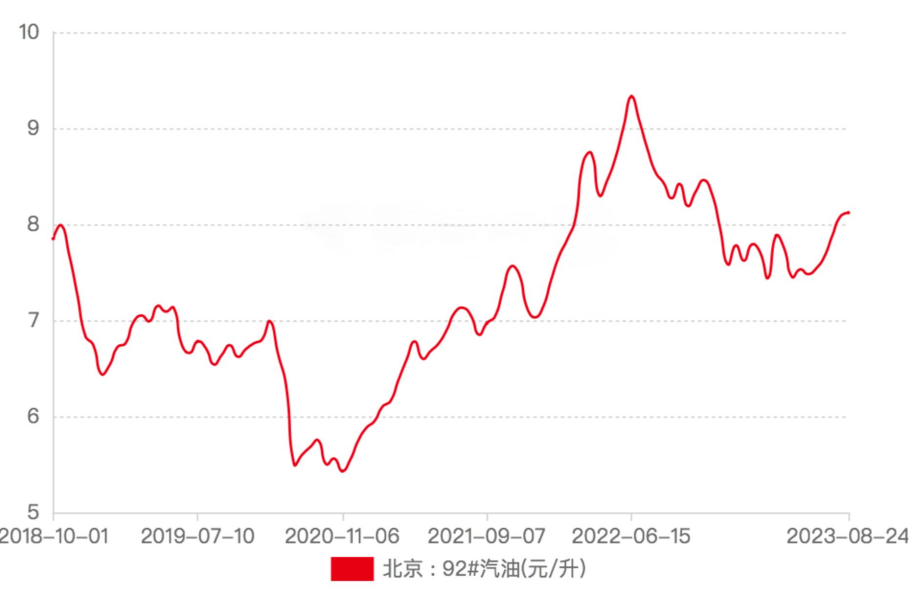
Figure 1: No.92 gasoline price trend in China from 2019 to 2023.
In 2019, the price of gasoline in China has been fluctuating slightly in the range of 6.44 CNY/L to 7.13 CNY/L. The beginning of 2019 was the lowest point in the whole year of gasoline prices. It showed an upward trend from January to May, then fell after June, and finally began to rise in November. At the beginning of the following year, gasoline prices recovered to 6.99 CNY/L before falling to 5.5 CNY/L in just three months. From March to November 2020, the price of gasoline in China ushered in the lowest price in many years. It fell to 5.43 CNY/L in early November, and then began to gradually recover. Until the end of 2020, the price of gasoline was still 5.95 CNY/L. It is very unusual for the price of gasoline to be below 6.0 CNY/L for most of the year. In 2021, gasoline prices continued to rise, reaching 7.56 CNY/L at the end of October after three consecutive increases. This was the first time that Chinese gasoline prices have exceeded 7.5 CNY/L since 2018. After this brief peak, gasoline prices fell back to 7.14 CNY/L at the end of the year. Immediately afterwards, in 2022, gasoline prices experienced an unprecedented rise, climbing all the way to 8.74 CNY/L in early April, and reaching 9.33 CNY/L in mid-June. Although the price dropped in the second half of the year, the gasoline price basically fluctuated between 8.0 CNY/L and 9.0 CNY/L throughout the year, and even broke through 9.0 CNY/L in the second quarter. In 2023, gasoline prices still fluctuated stably between 7.5 CNY/L and 8.0 CNY/L, and there is currently no downward trend [1].
Under normal circumstances, gasoline prices will fluctuate slightly within a price gap of 1.0 CNY every year, but it is clear that gasoline prices have not fluctuated in accordance with the general law since COVID broke out. During these five years, gasoline prices in China have experienced a sharp drop and then a sharp rise, which is very rare in the history of gasoline prices. It has been less than a year and a half since the price of gasoline rose from 5.43 CNY/L in 2020 to 9.33 CNY/L in 2022. There are many factors that lead to this unusual price fluctuation.
3. Factors Influencing Gasoline Price Fluctuations
Since 2020, gasoline prices in China have suddenly plummeted and then risen. The price fluctuation range exceeded 2.5 CNY/L, which is an abnormal fluctuation. The outbreak of COVID and the sharp drop in the price of crude oil are the reasons gasoline prices fell in 2020, while the Russia-Ukraine conflict and national environmental protection policies were the factors that caused gasoline prices to surge in 2022.
3.1. COVID
In December 2019, the coronavirus epidemic broke out in Wuhan, China. With the arrival of the Spring Festival, population mobility has increased dramatically, leading to the rapid spread of the epidemic across the country. In the face of the increasingly serious epidemic, China has implemented blockade measures, and people are restricted from hanging out, so the demand for gasoline has dropped sharply [2]. With the shrinking demand, the supply price of refined oil has also fallen all the way, ushering in the lowest point in many years from April to September 2020.
In the first quarter of 2020, domestic gasoline sales in China were dismal due to the blockade policy, so domestic companies increased exports to ease the increased supply pressure in the domestic market. China’s gasoline exports are mainly to Southeast Asia. Due to the increase in domestic gasoline inventories compared with previous years, the export volume also increased significantly in the early stages of the epidemic, reaching its peak in April, 2020 [3]. As the COVID epidemic spreads around the world, the export demand for gasoline has also decreased, falling by 60% in May. The shrunk of global demand for gasoline has exacerbated the pressure of a domestic gasoline glut.
3.2. Price of Crude Oil
The price of gasoline depends largely on the price of crude oil. The COVID epidemic was not only a huge blow to China, but also to all countries in the world. With the continuous spread of the epidemic, airlines in various countries around the world have begun to reduce their flights, resulting in a significant reduction in the demand for transportation oil. The sharp drop in global demand for crude oil and excess crude oil reserves in oil-producing countries have led to a dramatic decline in global oil prices [4]. Therefore, the cost of refining gasoline also became lower, and the price of gasoline fell again.
3.3. The Political Situation
As one of the most important energy sources in the world, oil supply and price are deeply affected by the international situation. In February 2022, the conflict between Russia and Ukraine continued to intensify, culminating in a war. The initial stage of the outbreak of the war caused panic in the energy market, and international oil prices began to rise, so gasoline prices also rose. As an oil-producing country, Russia’s oil exports have been affected by ongoing wars and international sanctions [5]. The global supply of oil has decreased, so the price of gasoline has soared since the beginning of the war, and reached its peak in June 2022.
3.4. Environmental Protection Policies
In recent years, China has continuously promoted environmental protection policies, advocating energy conservation and emission reduction, and using green new energy. For traditional energy, which currently occupies a large share of the market, the government imposed high taxes on companies that produce gasoline, which led to higher production costs, so gasoline prices rose accordingly [6]. This is the reason that even though the Russia-Ukraine conflict has ended, the Chinese gasoline price remains at 7.5 CNY/L and continues to fluctuate without falling nowadays. As the Chinese government pays more attention to the development and application of new energy sources, gasoline prices will only rise.
4. Suggestions on Stabilizing Gasoline Prices
4.1. Strengthen Environmental Policies
When there is a high demand for gasoline, the price of gasoline will rise accordingly. But once people find alternatives to gasoline and reduce the demand, the price of gasoline will fall and become manageable. To achieve this goal, the government can formulate policies to support the development of renewable energy, such as providing tax incentives, subsidies, and loan guarantees to companies that develop new energy. This will help promote the technical research and market application of renewable energy sources such as solar energy, wind energy, and water energy [6]. Moreover, the government can invest in the construction of green infrastructure, such as renewable energy power generation facilities, increasing the proportion of renewable energy in the energy supply and reducing dependence on traditional energy.
In order to reduce people’s dependence on gasoline and reduce the carbon emissions of transportation, the promotion of electric vehicles is a good solution. The government can provide support, such as car purchase subsidies and charging facility construction, to encourage consumers and businesses to adopt electric transportation vehicles. In addition, they can establish partnerships with new energy vehicle manufacturers to jointly promote the development and popularization of electric vehicles. When electric vehicles become popular, gasoline will no longer be the dominant energy source in the transportation market, so the price will therefore go down.
4.2. Strengthen International Cooperation
Since rising gasoline prices are a serious global problem, countries can cooperate internationally to control rising prices. Countries can promote import and export trade to ensure that each country’s demand for oil is met to the greatest extent, which can solve the problem of a certain area’s oil being in short supply and a certain area’s oil reserves being too large at the same time. This approach ensures that each country imports enough oil to meet demand, thereby preventing the price of oil storage from skyrocketing due to shortages. Moreover, countries can establish a shared strategic oil reserve to deal with market tensions when prices fluctuate sharply. Keeping oil prices under control ensures that there will be no sudden spikes in gasoline prices.
Conflicts and wars between countries will lead to sudden increases in oil prices, as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine last year was a good example. In order to avoid the recurrence of this situation as much as possible, countries can promote diplomacy, consultation and cooperation, and actively negotiate when they have different opinions on international events, so as to avoid further escalation of conflicts. This can minimize the sharp rise of oil prices caused by political events and keep the prices as stable as possible, which has a great effect on stabilizing gasoline prices within a certain fluctuation range.
5. Conclusion
This article studies the factors causing the volatility of gasoline prices in China. After the above research, it is concluded that the COVID epidemic was the biggest reason for the decline in gasoline prices in 2020. Not only was the domestic demand tightening, but the global spread of the epidemic has led to a decline in global demand. The global oil supply far exceeded demand, so the cost of gasoline refining has dropped, and the price has also fallen to the lowest point in many years. The Russia-Ukraine conflict in 2022 was the biggest factor leading to the rise of gasoline prices. The war brought panic to the energy market, and Russia was subject to international sanctions as an oil exporter, which led to a reduction in exports. The shortage of supply led to an increase in oil prices, so gasoline prices increased as well. In addition, China’s policy of continuously promoting the development and application of green new energy and imposing higher taxes on gasoline companies has kept gasoline prices at a relatively high level and will not fall back. These are the factors that led to the bottom and peak of gasoline prices in the past four years.
In order to stabilize gasoline price fluctuations, this article proposes two feasible solutions. One is to strengthen environmental protection policies by promoting new energy technologies and subsidizing new energy vehicle companies, thereby reducing the demand for gasoline. The second is to strengthen international cooperation by encouraging oil imports and exports, stabilizing international relations to avoid conflicts, and reducing sudden increases in oil prices. Both of these proposals would lead to more stable gasoline prices, and stable gasoline prices would reduce economic panic and promote national economic development.
This article has some deficiencies in the source of data, because the gasoline price data released by the Chinese government in recent years has not been found, so the data can only be extracted from unofficial websites. And because there are slight differences in gasoline prices in each region of China, it is impossible to make all the statistics on the gasoline prices of the 31 inland provinces, so the price of No. 92 gasoline in Beijing is selected as an example. Although the price fluctuation trends of No. 92 gasoline, No. 89 gasoline, and No. 95 gasoline are exactly the same, there is still a difference of about 0.5 CNY/L between the prices. If the data on the three gasolines can be summarized and discussed together, it will make this article more convincing.
The volatility in gasoline prices that characterizes these extraordinary times of COVID is not universal. At present, the world has come out of the epidemic period, and the future trend of gasoline prices is the most worthy of attention and research.
References
[1]. National Oil Price Data - Data Center , Oriental Fortune.com, data.eastmoney.com/cjsj/oil_city.html. Accessed 4 Sept. 2023.
[2]. Norouzi, Nima, et al. “When pandemics impact economies and climate change: Exploring the impacts of covid-19 on oil and electricity demand in China.” Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 68, 2020, p. 101654, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2020.101654.
[3]. Albulescu, Claudiu. “Coronavirus and oil price crash.” SSRN Electronic Journal, 2020, https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3553452.
[4]. Wu Lei China (2020) “Analysis of the Oil Crisis and Its Impact Under COVID”, 10.19422/j.cnki.ddsj.2020.06.003
[5]. Zhang, Qi, et al. “Unveiling the impact of geopolitical conflict on oil prices: A case study of the russia-ukraine war and its channels.” Energy Economics, vol. 126, 2023, p. 106956, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106956.
[6]. Yuan, Xueliang, et al. “The development of New Energy Vehicles for a sustainable future: A Review.” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 42, 2015, pp. 298–305, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.016.
Cite this article
Zhang,C. (2023). Research on the Influencing Factors of Chinese Gasoline Price Fluctuation During the COVID-19 Epidemic. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,56,119-123.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. National Oil Price Data - Data Center , Oriental Fortune.com, data.eastmoney.com/cjsj/oil_city.html. Accessed 4 Sept. 2023.
[2]. Norouzi, Nima, et al. “When pandemics impact economies and climate change: Exploring the impacts of covid-19 on oil and electricity demand in China.” Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 68, 2020, p. 101654, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2020.101654.
[3]. Albulescu, Claudiu. “Coronavirus and oil price crash.” SSRN Electronic Journal, 2020, https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3553452.
[4]. Wu Lei China (2020) “Analysis of the Oil Crisis and Its Impact Under COVID”, 10.19422/j.cnki.ddsj.2020.06.003
[5]. Zhang, Qi, et al. “Unveiling the impact of geopolitical conflict on oil prices: A case study of the russia-ukraine war and its channels.” Energy Economics, vol. 126, 2023, p. 106956, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106956.
[6]. Yuan, Xueliang, et al. “The development of New Energy Vehicles for a sustainable future: A Review.” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 42, 2015, pp. 298–305, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.016.









