1. Introduction
With the economic globalization trend gradually developing, the role of international entrepreneurship in the enterprise development is becoming more prominent as a systematic activity focusing on foreign opportunities [1]. According to relevant social network research, firms with high-quality social ties or that benefit from network structure tend to receive more resources and knowledge [2,3]. Social networks play an important part in the worldwide entrepreneurship and commercial innovation processes. Chinese firms' entrepreneurial activities are growing more international, and there are more and more international entrepreneurial behaviors, yet the quality of entrepreneurship still has to be enhanced. The main factor is that businesses do not fully utilize social networks to seek additional international entrepreneurial prospects and collaboration [4].
Previous research has concentrated on the impact of network linkages at various levels and structures on many aspects of international entrepreneurship, such as the identification and development of international entrepreneurial possibilities, access to information, and green innovation. For example, entrepreneurs use social networks to gain access to information and resources that aid in the identification and development of international opportunities for entrepreneurship [5-7]. International start-ups' network of commercial partnerships can help to overcome resource limits and facilitate the growth of international entrepreneurial prospects [7,8]. However, existing studies pay little attention to the process of international entrepreneurship to improve enterprise innovation performance, as well as the impact of stakeholders in this process.
As a result, in order to thoroughly examine the internal mechanism of social network formation and the promotion of enterprise innovation performance when it comes to international entrepreneurship, this study analyzes the process of improving company innovation performance through international entrepreneurial behavior based on government networks, business networks and technological networks with an exploratory single case study of Midea Group. In the first section, this study covers the research on international entrepreneurship, social network performance, and innovation performance, investigates the correlation between the three, and proposes a conceptual measurement of each of them. The second section elaborates on the research approach, the foundation for case selection, and the data collecting and analysis method. In the third stage, a case study is conducted using the materials and data gathered. In the final section, summarize the entire article and offer conclusions and recommendations.
2. Literature Review
Morrow was the first to suggest the concept of international entrepreneurship, pointing out that as technology, knowledge, and culture advance, firms might penetrate unknown international markets for entrepreneurial activity [9]. Subsequently, McDougall and Oviatt expanded and supplemented the definition and connotation of international entrepreneurship, complementing the discovery and utilization of "cross-border" opportunities in international entrepreneurship [10]. This explanation reflects the purpose of international entrepreneurship to find and use opportunities to achieve the improvement of products and services. Social network is a specific connection between organizations or individuals that allows them to gain various social resources inherent in the relationship [11]. Scholars have since conducted research on the importance and significance of relationship networks in the process of international entrepreneurship. Through a cross-case study, Vasilchenko and Morgrish found that social relationship network facilitates the identification of opportunities in international entrepreneurship, while business relationship network facilitates the exploitation of these opportunities [7]. Hao et al. use BYD as a case study to investigate the value co-creation mechanism in the process of international entrepreneurship, pointing out that enterprises' international social entrepreneurial activities are constrained by a variety of factors, and social networks have an impact on the scope of their activities [12].
In terms of the innovation performance, Wang et al. found that network centrality and relationship strength have a promotion effect on knowledge dissemination efficiency and enterprise innovation performance [13]. According to Li and Liu , structural embeddedness has a favorable effect on the enterprise innovation effect in environmental protection, and the diversity of partners has a corrective effect on the relationship between the two mentioned above [14].
Previous studies have proved the correlation between social networks, international entrepreneurship and innovation performance, reflecting the important influence of social networks on international entrepreneurship and innovative effect of firms. This paper draws on the research results of Feng, Qu and some other scholars [12,15,16], focuses on international entrepreneurial behaviors that seek to improve the firm innovation performance in a cross-border way, including the establishment of overseas subsidiaries, joint ventures, product export, technology licensing and transnational technology cooperation, and a series of action strategies for implementing these behaviors [17]. In the case study, the social network is divided into three levels: government network, business network and technological network. Specifically, government network refers to the formal or informal relationship network of enterprises or their senior managers with officials of government and regulatory agencies [18]. Business network refers to the network of relationships established by an enterprise with suppliers, clients, partners, competitors, and industry associations [19]. Technological network refers to the relationship network with universities and research institutions, which is manifested in school-enterprise cooperation, industry-university-research cooperation and so on [20]. In terms of innovation performance, this paper mainly explores the role of international entrepreneurship in promoting innovation performance from two aspects: the improvement of technology level and the expansion of international market [21]. The main performance is the increase of the number of patents, the increase of product market share, the improvement of global competitiveness of products, and the improvement of brand value [22]. In view of this, this paper applies social network theory to enrich the research context of international entrepreneurship to improve innovation performance, provide a new research perspective for international entrepreneurship, and explore the impact mechanism of international entrepreneurship on innovation performance based on the perspective of social network.
3. Method
3.1. Case Study of the Midea Group
The exploratory single case study method is used in this paper. This study aims to address the "what is" research challenge by investigating the mechanism of international entrepreneurship to increase enterprise innovation performance from the perspective of social networks. This type of research topic is appropriate for the case study technique, which can objectively demonstrate the research situation and unearth the essence and relational logic behind the phenomena [23,24]. In addition, this paper needs to detail the process of the formation of events and social networks in different stages of the international entrepreneurial process of case companies. Compared with multi-case studies, single case studies are more conducive to paying attention to dynamic processes [25].
Following the principle of typicality [26], this paper takes the case with inspiration and abundant sample data as the premise, and selects Midea Group as the case study sample. Midea Group, founded in 1968, has become a leading brand in the field of home appliances in China today through years of deep cultivation and development in the home appliance industry, and is a typical representative of the successful implementation of Chinese home appliance enterprises' internationalization strategy.
The reasons for case selection are as follows: First, the government, the market and the technical network are sound. Midea Group has established more than 60 abroad branches in the international market after years of overseas operations, and overseas business has expanded significantly, spanning more than 200 countries and regions worldwide [27]. Simultaneously, Midea Group established R&D centers in the United States, Germany, Japan, and other developed countries to take full advantage of geographical advantages, absorb local experience, encourage talents to accelerate the development of high-tech products, and expand the scale of global research and development layout. Midea Group plans to add 17,000 worldwide sales outlets by 2020, as well as use digital ways to empower, improve company production and sales, and strengthen the global development system. As indicated in Table 1, Midea Group has successfully collaborated with a number of advantageous companies in the world over the last ten years through mergers and acquisitions, joint ventures, and other means, assisting its in-depth layout in the world and establishing a comprehensive social network.
Table 1: Major overseas mergers and acquisitions or joint ventures in the Midea Group.
2010 | 2011 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
Africa | Acquisition of Egypt Misr Refrigeration And Air Conditioning Manufacturing Co. | ||||
Latin America | Established Midea - Carrier Latin America Joint Venture with Carrier corporation | ||||
Europe | Established a joint venture with Robert Bosch GmbH of Germany | Acquisition of Clivet in Italy | |||
Asia | Established a joint venture with SIIX of Japan | Acquisition of Toshiba corporation in Japan | Acquisition of Servotronix motion control ltd. in Israel |
Data resource: Midea Group official; website: https://www.midea.com/cn/
Second, the performance in terms of innovation is exceptional. Table 2 shows the number of patents issued by Midea Group from 2012 to 2018. The increase from 200 pieces in 2012 to 13,525 pieces in 2019 is a testament of Midea Group's excellent R&D skills and outstanding innovation performance. According to Clarivate Analytics statistics in 2018, the number of invention patents of Midea Group in the home appliance industry has topped the world for three consecutive years. Third, the data is rich, and the authenticity and availability of case data sources are guaranteed. Third, the data is abundant, and the authenticity and availability of case data sources are ensured. Midea Group is a Fortune Global 500 company with an international reputation. Its internationalization process has been widely concerned by many scholars, authoritative media and research institutions. The specific data disclosed on the company's official website, China Securities Regulatory Commission, the stock exchange, and the Great Tide Information Network are subject to the supervision and restriction of relevant departments, laws, and regulations, and their authenticity and accuracy are guaranteed, as is their accessibility. This case study is useful for refining and summarizing the mechanism by which enterprises use social network to identify and utilize cross-border entrepreneurial opportunities and promote innovative performance, and it serves as a helpful reference.
Table 2: Patent applications in the Midea Group.
Year | Patent applications |
2012 | 200 |
2013 | 5447 |
2014 | 7378 |
2015 | 10523 |
2016 | 13546 |
2017 | 16934 |
2018 | 15895 |
2019 | 13525 |
Data resource: Midea Group annual report.
3.2. Data Collection
Secondary data were used to analyze the subject content of the research, to diverse data sources, and to complement and cross-confirm various data to meet the triangulation requirements [24]. The use of secondary data can effectively avoid the subjective influence of researchers in the collection process [27]. The secondary information collected in this paper mainly includes: (1) Data published on the official website of Midea Group; (2) Research reports issued by Wind research platform and Prospective Industry Research Institute; (3) Relevant research reports published in journals and literatures; (4) Relevant publicity materials and reports of domestic and foreign official media and we-media. To lay the groundwork for the subsequent collection and sorting of second-hand data, first consult the official website of Midea Group to search the basic information of the enterprise, such as development history, strategic layout, service concept, investor relations, and so on. Formal data collecting begins with a systematic comprehension of the data content related to the study topic in order to further clarify the requirement for specific data content and extract effective information. Following that, check relevant journals and books to dig into and refine the research topic's substance. Finally, the data gathered is complemented by domestic and foreign government media as well as we media.
4. Case Findings and Analysis
By classifying the development process of Midea Group's international entrepreneurship, the key events of its international entrepreneurship are extracted, and the key events of Midea Group's international entrepreneurship process and corresponding network types are classified in conjunction with the characteristics of government networks, business networks, and technological networks, as illustrated in Table 3.
Table 3: The key course of Midea Group's international entrepreneurship development.
Year | Key course | Type of network |
2007 | Established Midea Group's first overseas base in Vietnam | business networks |
2010 | Acquisition of EgyptMisr Refrigeration And Air Conditioning Manufacturing Co. | business networks |
2012 | Midea Group and Carrier corporation set up Indian joint venture | business networks |
2015 | Midea Group and SIIX announced a joint venture | business networks |
Set up research and development center in US | technological networks | |
Midea Group assisted 10,000 induction stoves in Nepal through the Chinese Ministry of Commerce | government networks | |
2016 | Signed an acquisition agreement with Clivet ;Acquired 80.1% stake in Toshiba corporation entity | business networks |
2017 | Midea Group acquired 94.55% of KUKA Schweissanlagen + Roboter GmbH; Acquired 79.37% of the shares of Servotronix motion control ltd. | business networks |
2019 | Set up research and development center in Japan | technological networks |
2021 | Set up research and development center in Germany | technological networks |
2022 | Set up research and development center in Italy | technological networks |
2023 | The municipality of Pouso Alegre in Brazil cooperated with Midea Group's investment in the new factory Midea Industria do Brasil | government networks |
Data resource: Midea Group official website: https://www.midea.com/cn/
4.1. Government Network
A good formal or informal partnership between enterprises and the government helps enterprises develop resources. Midea Group creates social value through charitable activities like donations and forms close ties with more government agencies. On the other hand, Midea Group invests in overseas factories and bases to create more jobs and improve local consumers' quality of life, gaining the local government's cooperation.
Midea Group founder He Xiangjian has long maintained solid relations with the government as a deputy to the Shunde District People's Congress in Guangdong Province and a member of the Foshan Political Consultative Conference Standing Committee. Since 2008, Midea Group has conducted charity and public welfare activities in poverty alleviation, poverty assistance, education, and other areas, extending its beneficiaries. Midea Group has built a good bond with the local government through its many charitable donations. In 2015, Midea Group's public welfare initiatives experienced further growth as it collaborated with the Chinese Ministry of Commerce to provide 10,000 induction stoves to Nepal in order to address the fuel crisis. Additionally, the Egyptian branch of Midea Group extended support to impoverished local residents during Ramadan by offering complimentary Iftar meals and traditional Ramadan gift boxes, in accordance with local customs. Figure 1 displays Midea Group's charity gift expenditure over the past decade, which has increased to 3-6 times since 2018. Figure 1 shows that Midea's government subsidies are rising overall, which indirectly indicates that Midea Group's long-standing government relations have been fully developed and that government funds and policy support can help international start-ups innovate and grow.
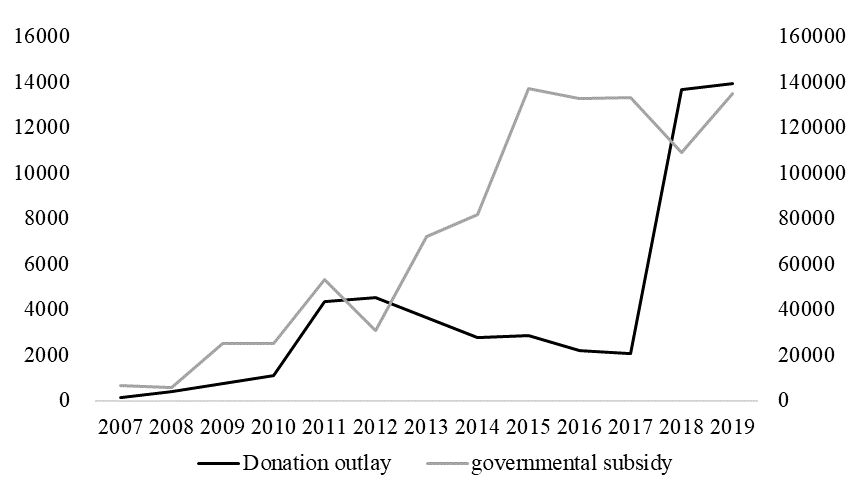
Figure 1: Donation outlay and government subsidies of Midea Group from 2007 to 2019 (ten thousand yuan).
Data resource: Midea Group annual financial report.
Investment in abroad factories and bases by Midea Group can transform resources with the host government, extending the international market and improving innovation.First, with digital production technology and creative technologies, Midea Group helps the local home appliance industry thrive, creating a new economic growth point and improving government performance. Second, Midea Group expands local consumers' smart home appliance options and improves their quality of life. High-quality usage experience helps Midea Group build a favourable brand image in international entrepreneurship, acquire local consumers' trust, and access many local customer resources. Third, the government cooperated with Midea Group's investment to accelerate local infrastructure construction and create more jobs for local people, allowing Midea Group to work with the local government to promote local social and economic development and increase its overseas market share.
4.2. Business Network
Midea Group's business network focuses on firms' relationships with customers, suppliers, partners, competitors, and industry associations. These multi-subject network relationships have a profound impact on the enterprise innovation performance.
4.2.1. Network Relationship with Clients and Suppliers
Enterprises' intimate relationships with clients and suppliers can reduce communication costs, build trust, and cut transaction costs. Midea Group created the "Supplier Blacklist Management Measures" in 2006 to strengthen supplier management and promote a fair, open, and transparent business environment. The introduction of this management method maintains and enhances the friendly relationship between Midea and its suppliers, and also attracts new suppliers to cooperate with it. Figure 2 shows the concentration of Midea Group's relationship network with clients and suppliers by the proportion of top five clients' sales and suppliers' purchases. The proportion of sales of the top five clients in total sales shows a trend of fluctuating growth, while the proportion of the purchases of the top five suppliers in the total purchase volume is also generally declining, from 16.52% in 2006 to 5.42% in 2019. This is because since Midea Group opened the supplier global cloud platform in 2013, all the purchase orders are issued from the platform to seek suitable and high-quality suppliers for the public, so the purchase orders are no longer concentrated in the hands of a few suppliers as before. Thus, Midea Group's customer relationship network tends to centralise, while its supplier relationship network tends to spread and scatter.
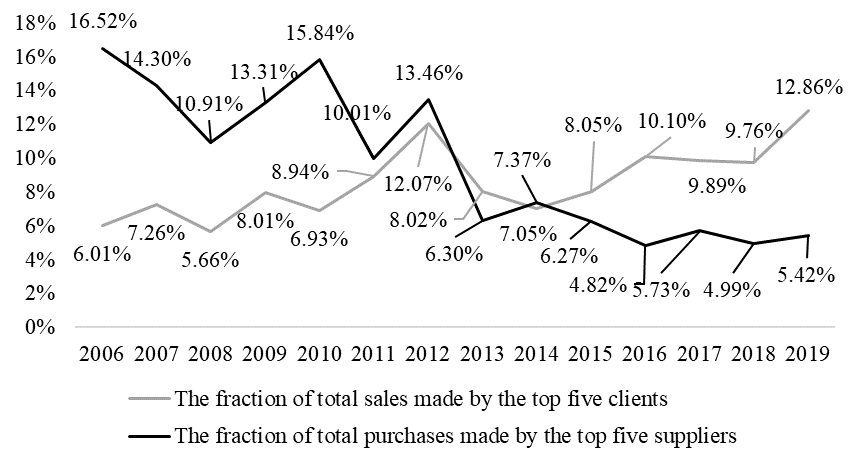
Figure 2: The fraction of total sales made by the top five clients and the fraction of total purchases made by the top five suppliers of Midea Group from 2006 to 2019.
Data resource: Midea Group annual financial report.
4.2.2. Network Relationship with Industry Associations
During his time as the founder of the Midea Group, He Xiangjian has assumed the role of president in several associations and actively engaged in numerous industry summits. The social contacts network of Midea Group is conducive to gain diverse resources and the establishment of a convenient conduit for the company. He Xiangjian has held the position of president of the Guangdong Chamber of Commerce and the Shunde Chamber of Commerce for a continuous period of five years, starting from 2004. Subsequently, the Midea Group became a core member of various industry associations, including the China Household Appliances Association, Guangdong Industrial Park Association, China Enterprise Federation, Guangdong Association for Science and Technology Intelligent Manufacturing Association, Foshan Industry and Commerce Federation, and Guangdong Council for the Promotion of International Trade. The association has facilitated the broadening of Midea's corporate collaboration and has contributed additional knowledge to the enterprise's research and innovation endeavours through its engagement with members of the science and technology association.
4.2.3. Network Relationship with Other Enterprises
Midea Group integrates market resources and has long-term solid supply and demand relationships with other businesses, both partners and competitors. Midea Group's internationalisation effort began in 1988, when it first used the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) technique to enter the international market. Midea Group received orders from 18 major retail companies and 10 global well-known brand owners at the time. Midea Group has gained valuable experience and funds as a result of the trust and support of these outstanding businesses.
Midea Group enters new markets through acquisition, joint venture, equity participation, and holding, and absorbs leading technology and experience from around the world to achieve a consistent expansion in worldwide sales.Midea Group successfully created the first overseas production base in 2007, symbolising Midea manufacturing's true penetration of overseas markets. Midea Group has formed joint partnerships with a number of companies since then. Midea Group purchased 80.1% of Toshiba Corporation in 2016, along with a 40-year global licence and over 5,000 patented technologies. Midea Group's overseas operating income has expanded right along after years of worldwide development. Midea Group's international business income climbed by 75.7% from 2010 to 2020, as shown in Figure 3, and the proportion of total revenue increased from 26.71% to 42.3% today. It can be seen that as globalisation deepens, Midea Group's emphasis on the international market grows, the scale of overseas business grows, the business network established with overseas enterprises grows, and it plays a key role in Midea Group's social network.
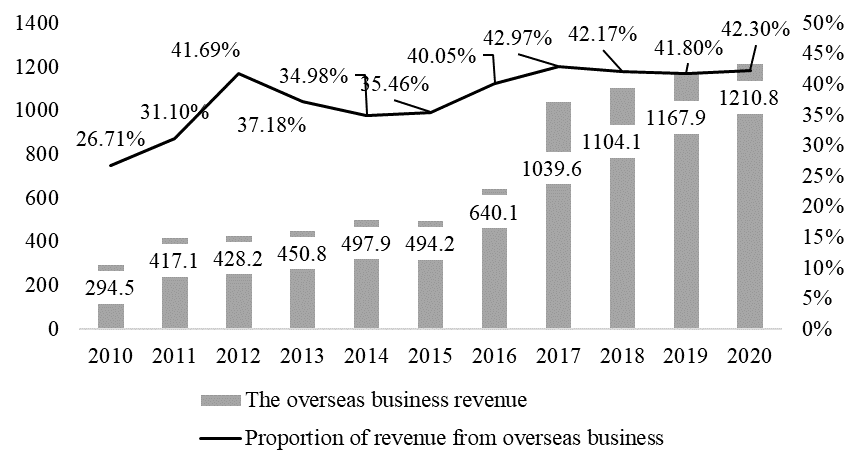
Figure 3: The overseas business revenue and proportion of Midea Group from 2010 to 2020.
Data resource: Wind data: https://www.wind.com.cn/
4.3. Technological Network
4.3.1. Domestic Technological Network
Maintaining solid relationships between businesses and universities, research institutes, and other scientific research institutions helps ensure that the latest technology development information is available the first time. Furthermore, collaboration with universities can provide employees with the possibility to improve their professional excellence. Midea Group began collaborating with Tsinghua University and South China University of Technology in 2006, frequently offering EMBA, master of engineering, and other possibilities for additional study to employees. Midea Group collaborated with Xi'an Jiaotong University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and other top Chinese universities in 2010 to conduct basic and applied research and development of new technologies and products. Outstanding college students who participate in the project collaboration may be given the option to intern and remain with Midea Group, in order to train the company's reserve talents in industrial design. Midea Group launched the "Future Life Innovation Joint Laboratory" in December 2016 after six years of collaboration with Jiangnan University, further enhancing the partnership in talent training through the cooperation model of "platform + project + talent training." Midea Group formed a strategic partnership with Academician Yuan Longping Workstation in 2017. This strategic collaboration has resulted in the creation of a closed loop of rice research from field to table, which is a novel product of the convergence of production, learning, and research. Midea and Shanghai Jiao Tong University continued their collaboration in 2019 by establishing a "Open Innovation Joint Laboratory" to jointly investigate school-enterprise cooperation in the field of home appliance innovation and entice top students to stay with the company. The Midea Group's R&D team has more than doubled, from less than 10,000 at the start of the transition to approximately 20,000 currently. The ratio of R&D personnel to corporate management personnel increased from 27% in 2012 to more than 50% in 2016. Midea, on the other hand, places a high value on research and development personnel incentives. The company has built a perfect incentive mechanism and launched the "equity incentive plan" for research and development personnel since 2014, with the incentive content consisting of stock options and restricted shares, and the total number of incentives is increasing.
4.3.2. Overseas Technological Network
Midea's investment in innovative research and development expanded from more than 3 billion yuan to more than 10 billion yuan between 2013 and 2020, with a growing trend year by year, and the total investment is over 60 billion yuan. Midea Group established four global R&D centres in the United States, Germany, Japan, and Italy, as well as 28 R&D centres in Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Chongqing, and Shanghai, which gradually formed the "2+4+N" network, a highly competitive global innovation R&D network, and the use of product scale experience to help R&D gradually form a scale. The number of international R&D centres increased from 10 to 18 between 2017 and 2020. In 2020, it accounted for 64.29% of global R&D centres (Table 4). Midea Group, by establishing a multi-level R & D global system, integrating worldwide research resources, enhancing company core competitiveness, and achieving overseas market competitors are tough to match the efficiency and cost advantages. Midea Group had approximately 60,000 patent applications as of 2021, with the number of patent granted ranking first in the home appliance market for five years in a row.
Table 4: R & D center development of Midea Group
Midea Group | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
Number of R&D centers worldwide | 20 | 20 | 28 | 28 |
Number of overseas R&D centers | 10 | 11 | 18 | 18 |
Proportion of overseas R&D centers | 50.00% | 55.00% | 64.29% | 64.29% |
Data resource: Midea Group annual report.
Based on the above description and analysis, the mechanism of international entrepreneurship to play the role of social network, thereby promoting enterprise innovation is sorted out, as shown in Figure 4.
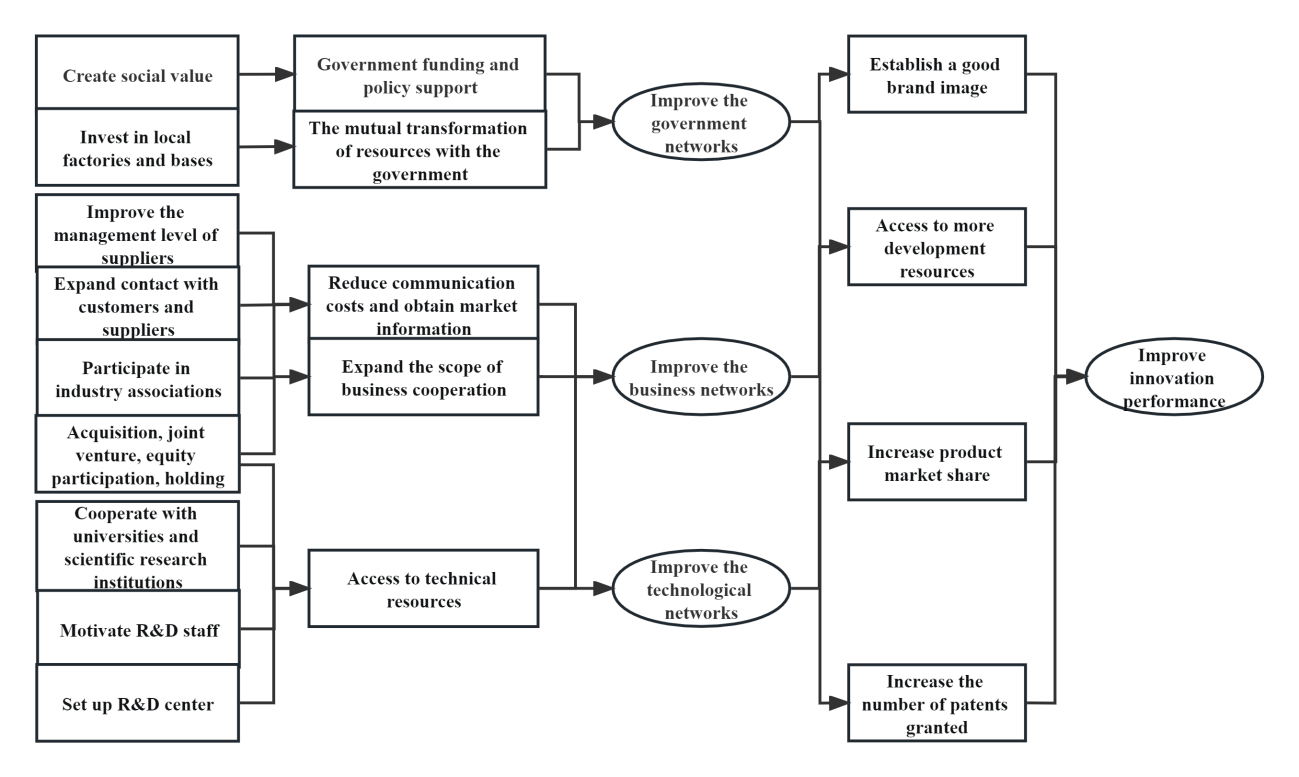
Figure 4: The mechanism of international entrepreneurship to improve innovation performance of enterprises.
5. Suggestions
With the rise of "anti-globalization" in the world, Chinese enterprises are facing great difficulties and challenges in international entrepreneurship. The research conclusion of this paper can help firms explore the international market, reduce international entrepreneurship risk, and improve innovation performance. The main practical enlightenment is in three areas:
First, enterprises should attach importance to the strategic choice of international entrepreneurship, and reasonably design the development strategy of international entrepreneurship to improve their competitiveness and innovation performance. An enterprise that is new to international entrepreneurship can prioritise expanding the distribution scope of overseas sales and subsidiaries and gradually entering the international market to reduce the negative effects of excessive resource embedding in a region. In addition, research the local market to grasp client wants and boost product competitiveness. If the company has good management and internal control, it can progressively increase its foreign market penetration. Second, international entrepreneurship should be regarded as an effective way for enterprises to obtain development resources, learn industry-leading technologies, expand the scope of business cooperation, and improve the effective allocation of innovation resources, so as to continuously improve the innovation performance of enterprises. Third, enterprises need to establish a close network relationship with stakeholders in the process of international entrepreneurship. By making full use of government, business and technological networks, communication costs can be reduced, disadvantages of newcomers and outsiders can be reduced, risks of international entrepreneurship can be reduced, and success rates of international entrepreneurship can be improved.
6. Conclusions
This paper takes Midea Group as a case study to discuss the formation of multiple networks in the process of enterprise entrepreneurship in the international community, the role of multiple network elements in the process of improving innovation performance, etc., and then concludes the mechanism of international entrepreneurship to improve innovation performance.
First, multinational businesses create social value, invest in local industries and bases, etc., to gain government subsidies and policy backing and build a complete government network. Enterprises and the government have transformed resources to improve their image and gain more development resources. Second, multinational entrepreneurs build market networks with customers, suppliers, industry groups, and other companies that collaborate and compete. Enterprises and partners have established a multi-level business network based on supply and demand matching by improving supplier management, strengthening supplier-customer contact, participating in industry associations, acquisition, joint venture, equity participation, holding, and other ways. This has expanded business cooperation, gained market information, and improved market resource integration. At the same time, by obtaining and utilizing the technical resources of the partners in the business network, the market competitiveness of the core products is enhanced. Based on the establishment of business networks, enterprises can achieve the purpose of increasing the market share of goods. Third, multinational entrepreneurship has created technological networks at both domestic and international levels. Cooperation with domestic and international scientific research institutions, encouragement of R&D talents, and the establishment of R&D centres at home and abroad have improved the company's research and development capabilities and greatly increased its patents. The three dimensions of social networks together impact the process of international entrepreneurship and improve the innovation performance of enterprises.
In this paper, Midea Group is selected to conduct a single case study. In the future, the universality of this study conclusion can be tested by multiple cases to enhance the persuasiveness of the research conclusion. Future research can examine how international entrepreneurial enterprises learn in different national systems and cultural environments to maximise technological innovation efficiency and discuss enterprise learning dynamics in the global market.
References
[1]. Mainela, T., Puhakka, V., & Sipola, S. (2018). International entrepreneurship beyond individuals and firms: On the systemic nature of international opportunities. Journal of Business Venturing, 33(4), 534-550.
[2]. Ozcan, P. (2018). Growing with the market: H ow changing conditions during market growth affect formation and evolution of interfirm ties. Strategic Management Journal, 39(2), 295-328.
[3]. Phillips, N., Tracey, P., & Karra, N. (2013). Building entrepreneurial tie portfolios through strategic homophily: The role of narrative identity work in venture creation and early growth. Journal of Business Venturing, 28(1), 134-150.
[4]. Peng Huatao, Pan Yueyi, Chen Yun. (2022). Research on Social Network Embedding, Dual Equilibrium Innovation, and International Entrepreneurship, Research Management, 43 (11): 45-54
[5]. Ozgen, E., & Baron, R. A. (2007). Social sources of information in opportunity recognition: Effects of mentors, industry networks, and professional forums. Journal of business venturing, 22(2), 174-192.
[6]. Chandra, Y., Styles, C., & Wilkinson, I. F. (2012). An opportunity-based view of rapid internationalization. Journal of International Marketing, 20(1), 74-102.
[7]. Vasilchenko, E., & Morrish, S. (2011). The role of entrepreneurial networks in the exploration and exploitation of internationalization opportunities by information and communication technology firms. Journal of International Marketing, 19(4), 88-105.
[8]. Zhou, L., Wu, W. P., & Luo, X. (2007). Internationalization and the performance of born-global SMEs: the mediating role of social networks. Journal of international business studies, 38, 673-690.
[9]. Morrow, J. F. (1988). International entrepreneurship: A new growth opportunity. New Management, 3(5), 59-61.
[10]. McDougall, P. P., & Oviatt, B. M. (2003). Some fundamental issues in international entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship Theory & Practice, 18(27), 1-27.
[11]. Vissa, B. (2011). A matching theory of entrepreneurs' tie formation intentions and initiation of economic exchange. Academy of Management Journal, 54(1), 137-158.
[12]. Hao Chen, Zhang Weiguo, Li Mengya. (2021). The Value Co creation Mechanism of International Social Entrepreneurship: A Case Study from the Perspective of Social Networks, Management Review, 33 (08): 326-340
[13]. Wang, F., Su, Q., & Zhang, Z. (2023). The influence of collaborative innovation network characteristics on firm innovation performance from the perspective of innovation ecosystem. Kybernetes.
[14]. Li X, Liu X. (2023). The impact of the collaborative innovation network embeddedness on enterprise green innovation performance. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 11: 1190697.
[15]. Zhou Yang. (2023). A study on the impact mechanism of network connectivity on innovation behavior and performance of technology-based entrepreneurial enterprises, University of Electronic Science and technology.
[16]. Feng Haihong, Qu Wan. (2019). Innovation and Entrepreneurship in Social Networks and Mass Creation Spaces: A Case Study Based on Entrepreneurship Café, Research management
[17]. Hao Chen. (2021). Research on the Mechanism of International Entrepreneurship to Enhance Enterprise Innovation Performance, Chongqing University
[18]. Jiang, X., Liu, H., Fey, C., & Jiang, F. (2018). Entrepreneurial orientation, network resource acquisition, and firm performance: A network approach. Journal of Business Research, 87, 46-57.
[19]. Zhang, J. A., O'Kane, C., & Chen, G. (2020). Business ties, political ties, and innovation performance in Chinese industrial firms: The role of entrepreneurial orientation and environmental dynamism. Journal of Business Research, 121, 254-267.
[20]. Xu, L., Li, J., & Zeng, D. (2017). How does knowledge network affect a firm’s explorative innovation? The contingent role of R&D collaborations. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 29(9), 973-987.
[21]. Meng Donghui, Li Xianjun, Mei Liang, et al.(2108). Core Technology Deconstruction and Breakthrough: A Longitudinal Case Study of "Tsinghua Green Control" AMT Technology from 2000 to 2016, Research Management, 39 (06): 75-84.
[22]. Tsai, K. H. (2009). Collaborative networks and product innovation performance: Toward a contingency perspective. Research policy, 38(5), 765-778.
[23]. Yin R. K. (2018). Case study research and applications: Design and methods. 6th ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
[24]. Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (Vol. 5). sage.
[25]. Langley, A. (1999). Strategies for theorizing from process data. Academy of Management review, 24(4), 691-710.
[26]. Eisenhardt K.M.,Graebner M.E.(2007). Theory Building from Cases: Opportunities and Challenges.Academy of Management Journal, 50( 1) : 25-32.
[27]. Liang Huanning. (2023). Research on the International Marketing Model of Midea Group, Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics
Cite this article
Cai,S. (2024). The Mechanism of International Entrepreneurship to Improve the Innovation Performance of Enterprises: Based on the Perspective of Social Network. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,59,48-59.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Mainela, T., Puhakka, V., & Sipola, S. (2018). International entrepreneurship beyond individuals and firms: On the systemic nature of international opportunities. Journal of Business Venturing, 33(4), 534-550.
[2]. Ozcan, P. (2018). Growing with the market: H ow changing conditions during market growth affect formation and evolution of interfirm ties. Strategic Management Journal, 39(2), 295-328.
[3]. Phillips, N., Tracey, P., & Karra, N. (2013). Building entrepreneurial tie portfolios through strategic homophily: The role of narrative identity work in venture creation and early growth. Journal of Business Venturing, 28(1), 134-150.
[4]. Peng Huatao, Pan Yueyi, Chen Yun. (2022). Research on Social Network Embedding, Dual Equilibrium Innovation, and International Entrepreneurship, Research Management, 43 (11): 45-54
[5]. Ozgen, E., & Baron, R. A. (2007). Social sources of information in opportunity recognition: Effects of mentors, industry networks, and professional forums. Journal of business venturing, 22(2), 174-192.
[6]. Chandra, Y., Styles, C., & Wilkinson, I. F. (2012). An opportunity-based view of rapid internationalization. Journal of International Marketing, 20(1), 74-102.
[7]. Vasilchenko, E., & Morrish, S. (2011). The role of entrepreneurial networks in the exploration and exploitation of internationalization opportunities by information and communication technology firms. Journal of International Marketing, 19(4), 88-105.
[8]. Zhou, L., Wu, W. P., & Luo, X. (2007). Internationalization and the performance of born-global SMEs: the mediating role of social networks. Journal of international business studies, 38, 673-690.
[9]. Morrow, J. F. (1988). International entrepreneurship: A new growth opportunity. New Management, 3(5), 59-61.
[10]. McDougall, P. P., & Oviatt, B. M. (2003). Some fundamental issues in international entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship Theory & Practice, 18(27), 1-27.
[11]. Vissa, B. (2011). A matching theory of entrepreneurs' tie formation intentions and initiation of economic exchange. Academy of Management Journal, 54(1), 137-158.
[12]. Hao Chen, Zhang Weiguo, Li Mengya. (2021). The Value Co creation Mechanism of International Social Entrepreneurship: A Case Study from the Perspective of Social Networks, Management Review, 33 (08): 326-340
[13]. Wang, F., Su, Q., & Zhang, Z. (2023). The influence of collaborative innovation network characteristics on firm innovation performance from the perspective of innovation ecosystem. Kybernetes.
[14]. Li X, Liu X. (2023). The impact of the collaborative innovation network embeddedness on enterprise green innovation performance. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 11: 1190697.
[15]. Zhou Yang. (2023). A study on the impact mechanism of network connectivity on innovation behavior and performance of technology-based entrepreneurial enterprises, University of Electronic Science and technology.
[16]. Feng Haihong, Qu Wan. (2019). Innovation and Entrepreneurship in Social Networks and Mass Creation Spaces: A Case Study Based on Entrepreneurship Café, Research management
[17]. Hao Chen. (2021). Research on the Mechanism of International Entrepreneurship to Enhance Enterprise Innovation Performance, Chongqing University
[18]. Jiang, X., Liu, H., Fey, C., & Jiang, F. (2018). Entrepreneurial orientation, network resource acquisition, and firm performance: A network approach. Journal of Business Research, 87, 46-57.
[19]. Zhang, J. A., O'Kane, C., & Chen, G. (2020). Business ties, political ties, and innovation performance in Chinese industrial firms: The role of entrepreneurial orientation and environmental dynamism. Journal of Business Research, 121, 254-267.
[20]. Xu, L., Li, J., & Zeng, D. (2017). How does knowledge network affect a firm’s explorative innovation? The contingent role of R&D collaborations. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 29(9), 973-987.
[21]. Meng Donghui, Li Xianjun, Mei Liang, et al.(2108). Core Technology Deconstruction and Breakthrough: A Longitudinal Case Study of "Tsinghua Green Control" AMT Technology from 2000 to 2016, Research Management, 39 (06): 75-84.
[22]. Tsai, K. H. (2009). Collaborative networks and product innovation performance: Toward a contingency perspective. Research policy, 38(5), 765-778.
[23]. Yin R. K. (2018). Case study research and applications: Design and methods. 6th ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
[24]. Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (Vol. 5). sage.
[25]. Langley, A. (1999). Strategies for theorizing from process data. Academy of Management review, 24(4), 691-710.
[26]. Eisenhardt K.M.,Graebner M.E.(2007). Theory Building from Cases: Opportunities and Challenges.Academy of Management Journal, 50( 1) : 25-32.
[27]. Liang Huanning. (2023). Research on the International Marketing Model of Midea Group, Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics









